A Questionnaire-Derived Prediction Nomogram for Affected Semicircular Canal and Laterality of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Questionnaire Information
2.3. Diagnostic Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Predictive Factors
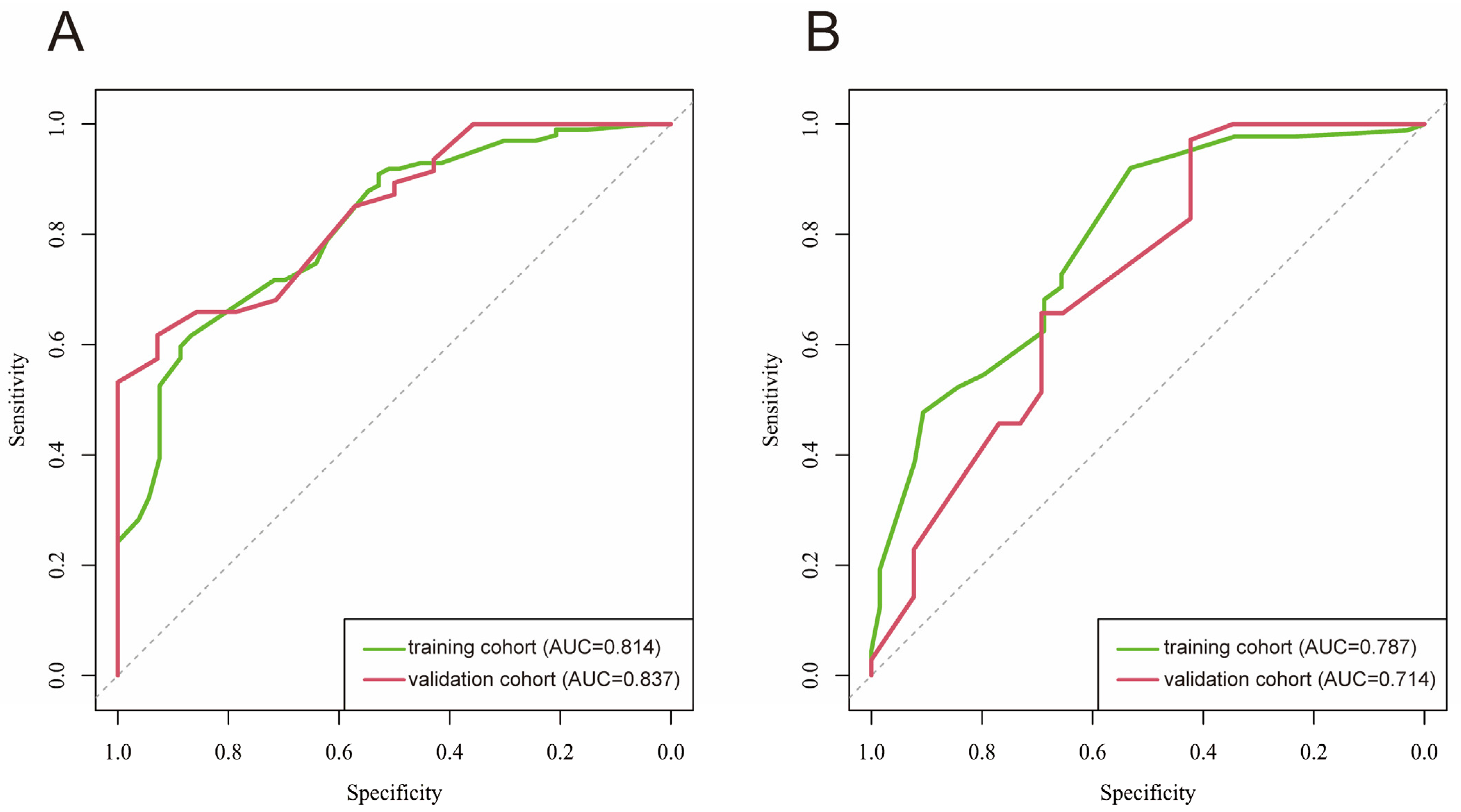
3.3. Prediction Model Construction and Assessment
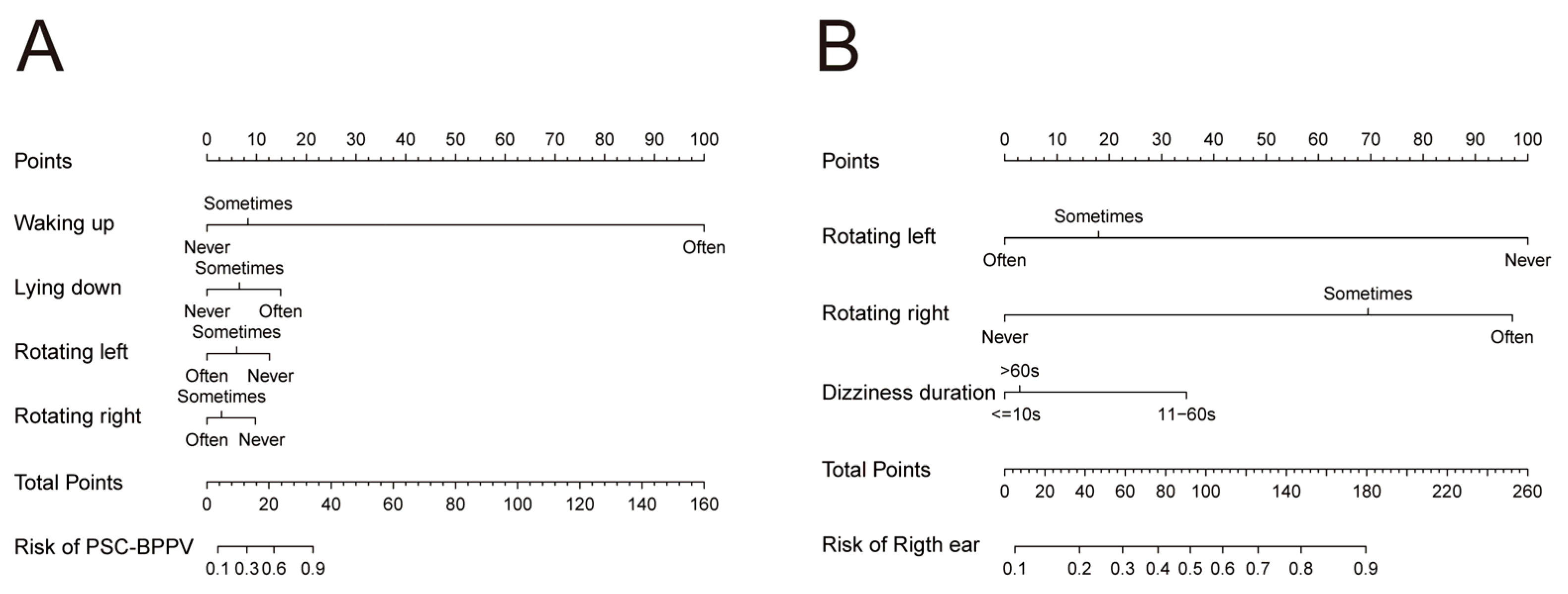
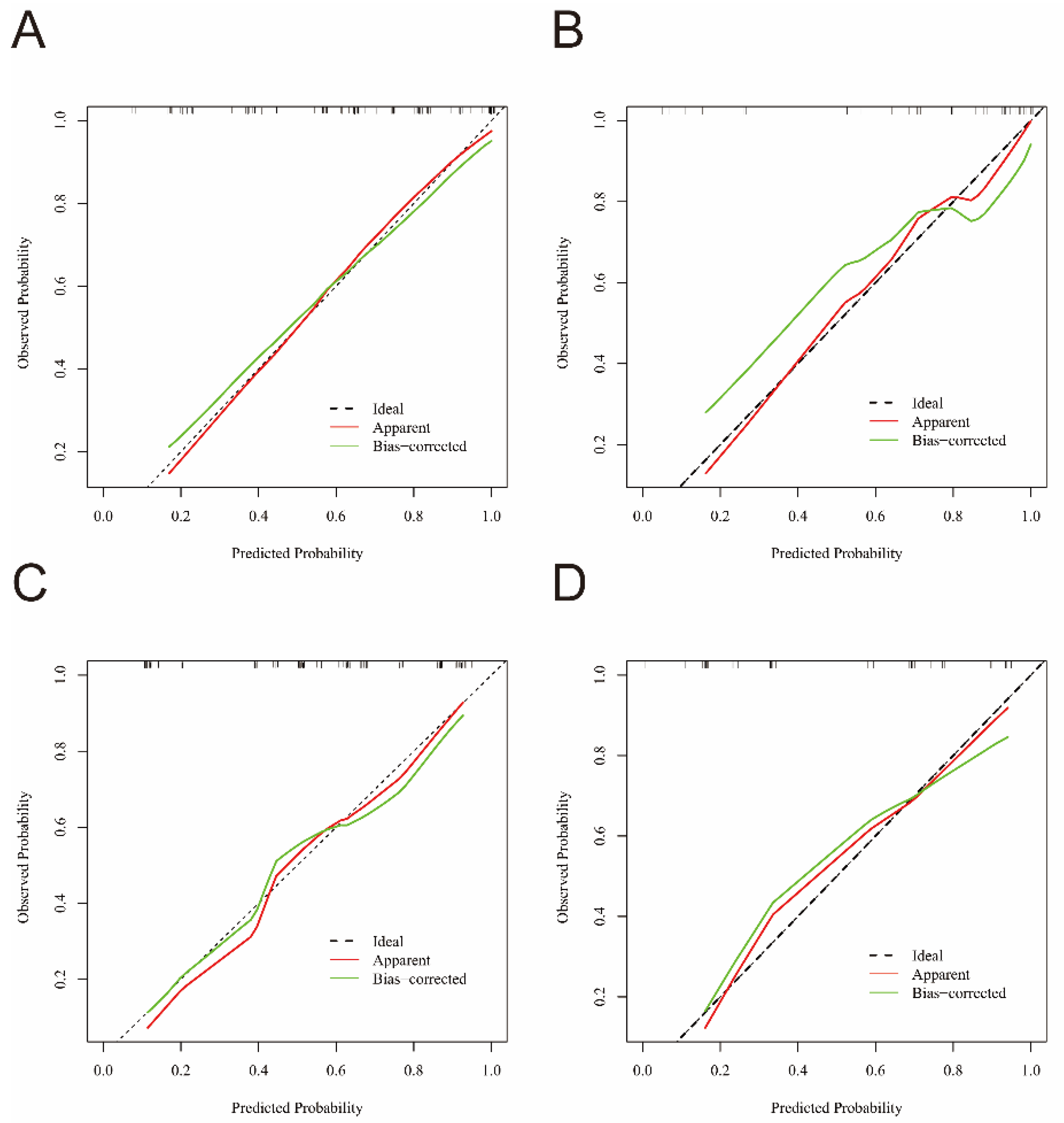
3.4. Nomogram and Calibration Curve Preparation
3.5. Web-Based Nomogram
4. Discussion
4.1. Two Clinical Prediction Models of BPPV
4.2. The Independent Predictors for Affected Semicircular of BPPV
4.3. The Independent Predictors for Affected Side of BPPV
4.4. The Independent Predictor of Pathological Type of BPPV
4.5. Strengthens and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPPV | Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| DSP | Dizziness Symptom Profile |
| PSC-BPPV | Posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| HSC-BPPV | Horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| HSC-BPPV-geo | Geotropic horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| HSC-BPPV-apo | Apogeotropic horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| ASC-BPPV | Anterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |
| HSC-BPPV-can | horizontal semicircular canal canalolithiasis |
| HSC-BPPV-cup | horizontal semicircular canal cupulolithiasis |
| CI | confidence interval |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| VNG | video nystagmography |
References
- von Brevern, M.; Bertholon, P.; Brandt, T.; Fife, T.; Imai, T.; Nuti, D.; Newman-Toker, D. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2015, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Koukoutsis, G.; Ganelis, P.; Economou, N.C.; Moukos, A.; Aspris, A.; Katotomichelakis, M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to vestibular neuritis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.; Jeon, E.J.; Kim, M.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Nam, S.I.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Clinical features of secondary BPPV: A nation-wide multicenter study. J. Vestib. Res. 2025, 35, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.H.; Ban, J.H.; Lee, K.C.; Kim, S.M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo secondary to inner ear disease. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fife, T.D.; Iverson, D.J.; Lempert, T.; Furman, J.M.; Baloh, R.W.; Tusa, R.J.; Hain, T.C.; Herdman, S.; Morrow, M.J.; Gronseth, G.S. Practice parameter: Therapies for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (an evidence-based review): Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008, 70, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Takeda, N.; Ikezono, T.; Shigeno, K.; Asai, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzuki, M. Classification, diagnostic criteria and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Zaag-Loonen, H.J.; van Leeuwen, R.B.; Bruintjes, T.D.; van Munster, B.C. Prevalence of unrecognized benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in older patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghalai, J.S.; Manolidis, S.; Barth, J.L.; Stewart, M.G.; Jenkins, H.A. Unrecognized benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in elderly patients. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 122, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.G.; Piccirillo, J.F.; Spitznagel, E.L., Jr.; Kallogjeri, D.; Goebel, J.A. Predictive capability of historical data for diagnosis of dizziness. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, L.T.; Kallogjeri, D.; Sinks, B.C.; Rauch, S.D.; Shepard, N.T.; White, J.A.; Goebel, J.A. Utility of an Abbreviated Dizziness Questionnaire to Differentiate Between Causes of Vertigo and Guide Appropriate Referral: A Multicenter Prospective Blinded Study. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, G.P.; Piker, E.G.; Hatton, K.; Watford, K.E.; Trone, T.; McCaslin, D.L.; Bennett, M.L.; Rivas, A.; Haynes, D.S.; Roberts, R.A. Development and Preliminary Findings of the Dizziness Symptom Profile. Ear Hear. 2019, 40, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedland, D.R.; Tarima, S.; Erbe, C.; Miles, A. Development of a Statistical Model for the Prediction of Common Vestibular Diagnoses. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, S.L.; Marchetti, G.F.; Morris, L.O. Usefulness of the dizziness handicap inventory in the screening for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.G.; Wang, Z.W.; Qi, X.K. Formulation and evaluation of diagnostic questionnaire for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017, 97, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, J.P.; Zhou, Q. Rapid screening questionnaire based on clinical symptoms of patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2019, 33, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Higashi-Shingai, K.; Takimoto, Y.; Masumura, C.; Hattori, K.; Inohara, H. New scoring system of an interview for the diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016, 136, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, V.S.; Maas, B.; Schermer, T.R.; van Benthem, P.G.; Bruintjes, T.D. Two Symptoms Strongly Suggest Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in a Dizzy Patient. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 625776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, E.; Finizia, C.; Johansson, M.; Karlsson, T.; Nilson, J.; Magnusson, M. Asking about dizziness when turning in bed predicts examination findings for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Vestib. Res. 2018, 28, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Inohara, H. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2022, 49, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, C.J.; Ward, B.K.; Owusu, Y.; Friedland, D.; Russell, J.O.; Weinreich, H.M. Assessment of a Statistical Algorithm for the Prediction of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.B.; Ko, K.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.S.; Song, M.H. Can the affected semicircular canal be predicted by the initial provoking position in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, J.M.; Zhong, L.; Yang, X.; Kim, J.S. Questionnaire-based diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2020, 94, e942–e949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H. Nomogram for predicting the prognostic role in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 44, 103736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleon, M.D.C.; Torres-Garcia, L.; Batuecas-Caletrio, A.; Castillo-Ledesma, N.; Gonzalez-Aguado, R.; Magnoni, L.; Rossi, M.; Di Berardino, F.; Perez-Guillen, V.; Trinidad-Ruiz, G.; et al. A Predictive Model of Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Meniere Disease Using Clinical Data. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.D.; Ensor, J.; Snell, K.I.E.; Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Martin, G.P.; Reitsma, J.B.; Moons, K.G.M.; Collins, G.; van Smeden, M. Calculating the sample size required for developing a clinical prediction model. BMJ 2020, 368, m441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmagyi, G.M. Diagnosis and management of vertigo. Clin. Med. 2005, 5, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.R.; Honaker, J.A. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Effective diagnosis and treatment. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2022, 89, 653–662. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, E.; Strupp, M.; Müller, M.; Jahn, K. Health services utilization of patients with vertigo in primary care: A retrospective cohort study. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, D.; Song, N.; Su, K.; Yin, S. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo associated with current practice. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnes, L.S.; Agrawal, S.K.; Atlas, J. Diagnosis and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2003, 169, 681–693. [Google Scholar]
- Ichijo, H.; Ichijo, H. A new roll test to diagnose posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Feng, Y.; Mei, L.; He, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H. The analysis of nystagmus in patients with posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigoin positioning test. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2015, 29, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Ito, M.; Takeda, N.; Uno, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Sekine, K.; Kubo, T. Natural course of the remission of vertigo in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2005, 64, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuknecht, H.F. Cupulolithiasis. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1969, 90, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.E.; Morgan, B.; Fletcher, J.C., Jr.; Krueger, W.W. Anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: An underappreciated entity. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balatsouras, D.G. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with multiple canal involvement. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2012, 33, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; He, X.; Hu, M.; Mao, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Chang, L. Objective findings in patients with multi-canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024, 103, NP508–NP513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostou, E.; Kouzi, I.; Spengos, K. Diagnosis and Treatment of Anterior-Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, B.O.; Ercan, I.; Cakir, Z.A.; Civelek, S.; Sayin, I.; Turgut, S. What is the true incidence of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 134, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Zee, D.S. Clinical practice. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugaiczyk, J.; Siebert, S.; Hecker, D.J.; Brase, C.; Schick, B. Involvement of the anterior semicircular canal in posttraumatic benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2011, 32, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Questions |
|---|
| Q1: Do you feel vertigo when you wake up? |
| Q2: Do you feel vertigo when you lie down? |
| Q3: Do you feel vertigo when you lean or look upward? |
| Q4: Do you feel vertigo when you bend or look downward? |
| Q5: Do you feel vertigo when rotating the head toward the left in the supine position? |
| Q6: Do you feel vertigo when rotating the head toward the right in the supine position? Q7: How long does the vertigo last? |
| Variables | Training Cohort (n = 154) | Validation Cohort (n = 66) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 51.84 ± 13.99 | 52.33 ± 12.06 | 0.805 |
| Disease course, medium (Q1, Q3) | 16.50 (7.00, 30.00) | 14.00 (8.00, 33.75) | 0.960 |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.268 | ||
| Female | 103 (66.88) | 39 (59.09) | |
| Male | 51 (33.12) | 27 (40.91) | |
| Waking up, n (%) | 0.401 | ||
| Never | 29 (18.83) | 15 (22.73) | |
| Sometimes | 103 (66.88) | 38 (57.58) | |
| Often | 22 (14.29) | 13 (19.70) | |
| Lying down, n (%) | 0.501 | ||
| Never | 31 (20.13) | 14 (21.21) | |
| Sometimes | 100 (64.94) | 46 (69.70) | |
| Often | 23 (14.94) | 6 (9.09) | |
| Leaning or looking upward, n (%) | 0.618 | ||
| Never | 82 (53.25) | 37 (56.92) | |
| Sometimes | 72 (46.75) | 28 (43.08) | |
| Bending or looking downward, n (%) | 0.426 | ||
| Never | 81 (52.60) | 38 (58.46) | |
| Sometimes | 73 (47.40) | 27 (41.54) | |
| Rotating the head toward the left in the supine position, n (%) | 0.182 | ||
| Never | 57 (37.01) | 16 (24.24) | |
| Sometimes | 77 (50.00) | 40 (60.61) | |
| Often | 20 (12.99) | 10 (15.15) | |
| Rotating the head toward the right in the supine position, n (%) | 0.146 | ||
| Never | 41 (26.62) | 18 (27.27) | |
| Sometimes | 80 (51.95) | 41 (62.12) | |
| Often | 33 (21.43) | 7 (10.61) | |
| Vertigo duration, n (%) | 0.955 | ||
| <10 s | 100 (64.94) | 43 (65.15) | |
| 10 s~60 s | 43 (27.92) | 19 (28.79) | |
| >60 s | 11 (7.14) | 4 (6.06) |
| Variables | Univariate Logistic Regression | Multivariate Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| Age | 0.99 (0.97~1.01) | 0.429 | ||
| Disease course | 1.00 (0.99~1.01) | 0.477 | ||
| Gender | 0.58 (0.32~1.05) | 0.074 | 0.61 (0.30~1.26) | 0.18 |
| Waking up | 4.42 (2.16~9.03) | <0.001 | 3.27 (1.39~7.70) | 0.007 |
| Lying down | 3.20 (1.61~6.38) | <0.001 | 2.47 (0.99~6.16) | 0.053 |
| Leaning or looking upward | 0.89 (0.50~1.58) | 0.679 | ||
| Bending or looking downward | 0.63 (0.35~1.12) | 0.113 | ||
| Rotating the head toward the left in the supine position | 0.14 (0.05~0.36) | <0.001 | 0.15 (0.05~0.45) | <0.001 |
| Rotating the head toward the right in the supine position | 0.23 (0.09~0.56) | 0.001 | 0.22 (0.07~0.66) | 0.007 |
| Vertigo duration | 0.60 (0.20~1.80) | 0.365 | ||
| Variables | Univariate Logistic Regression | Multivariate Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.00 (0.98~1.02) | 0.828 | ||
| Disease course | 1.00 (0.99~1.00) | 0.359 | ||
| Gender | 0.61 (0.35~1.06) | 0.082 | 0.58 (0.30~1.13) | 0.108 |
| Waking up | 1.69 (0.68~4.18) | 0.255 | ||
| Lying down | 1.52 (0.58~3.99) | 0.395 | ||
| Leaning or looking upward | 1.17 (0.68~2.02) | 0.563 | ||
| Bending or looking downward | 1.27 (0.74~2.18) | 0.394 | ||
| Rotating the head toward the left in the supine position | 0.11 (0.04~0.29) | <0.001 | 0.07 (0.02~0.21) | <0.001 |
| Rotating the head toward the right in the supine position | 2.94 (1.54~5.61) | 0.001 | 5.13 (2.27~11.57) | <0.001 |
| Vertigo duration | 2.21 (1.15~4.22) | 0.017 | 2.15 (1.03~4.49) | 0.041 |
| Variables | Univariate Logistic Regression | Multivariate Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| Age | 0.99 (0.98~0.99) | 0.01 | 0.99 (0.98~0.99) | 0.017 |
| Disease course | 0.35 (0.15~0.82) | 0.016 | 0.33 (0.13~0.87) | 0.025 |
| Gender | 1.08 (0.40~2.91) | 0.881 | ||
| Waking up | 1.08 (0.40~2.91) | 0.881 | ||
| Lying down | 3.31 (1.36~8.04) | 0.008 | 4.44 (1.65~11.94) | 0.003 |
| Leaning or looking upward | 1.10 (0.46~2.64) | 0.824 | ||
| Bending or looking downward | 1.10 (0.46~2.64) | 0.824 | ||
| Rotating left | 1.36 (0.53~3.45) | 0.524 | ||
| Rotating right | 0.60 (0.19~1.94) | 0.397 | ||
| Vertigo duration | 0.20 (0.06~0.67) | 0.009 | 0.14 (0.03~0.58) | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Xia, K.; Leng, Y.; Zhou, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Xiao, H.; Liu, B. A Questionnaire-Derived Prediction Nomogram for Affected Semicircular Canal and Laterality of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192435
Wang L, Xia K, Leng Y, Zhou R, Liu J, Wang H, Xiao H, Liu B. A Questionnaire-Derived Prediction Nomogram for Affected Semicircular Canal and Laterality of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192435
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Linlin, Kaijun Xia, Yangming Leng, Renhong Zhou, Jingjing Liu, Hongchang Wang, Hongjun Xiao, and Bo Liu. 2025. "A Questionnaire-Derived Prediction Nomogram for Affected Semicircular Canal and Laterality of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192435
APA StyleWang, L., Xia, K., Leng, Y., Zhou, R., Liu, J., Wang, H., Xiao, H., & Liu, B. (2025). A Questionnaire-Derived Prediction Nomogram for Affected Semicircular Canal and Laterality of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192435






