Applying Intraoperative Portal Venography in Liver Transplantation Vascular Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
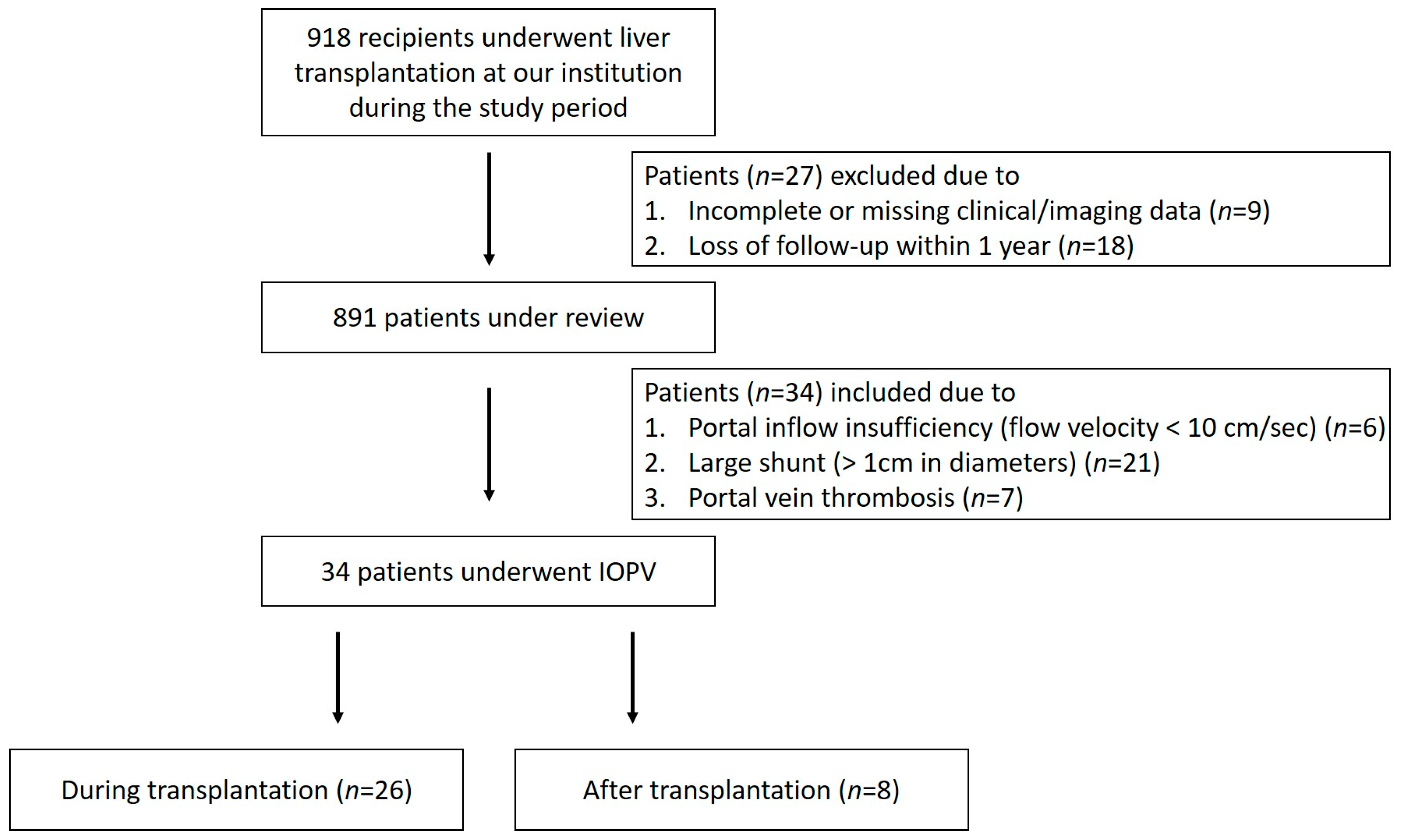
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. IOPV Procedure
2.2.1. Indication
2.2.2. Approach and Intervention Management
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Impact of IOPV on Surgical Decision-Making and Portal Flow
3.3. Graft Regeneration and Patient Survival
3.4. Subgroup Analysis: Intraoperative vs. Postoperative IOPV
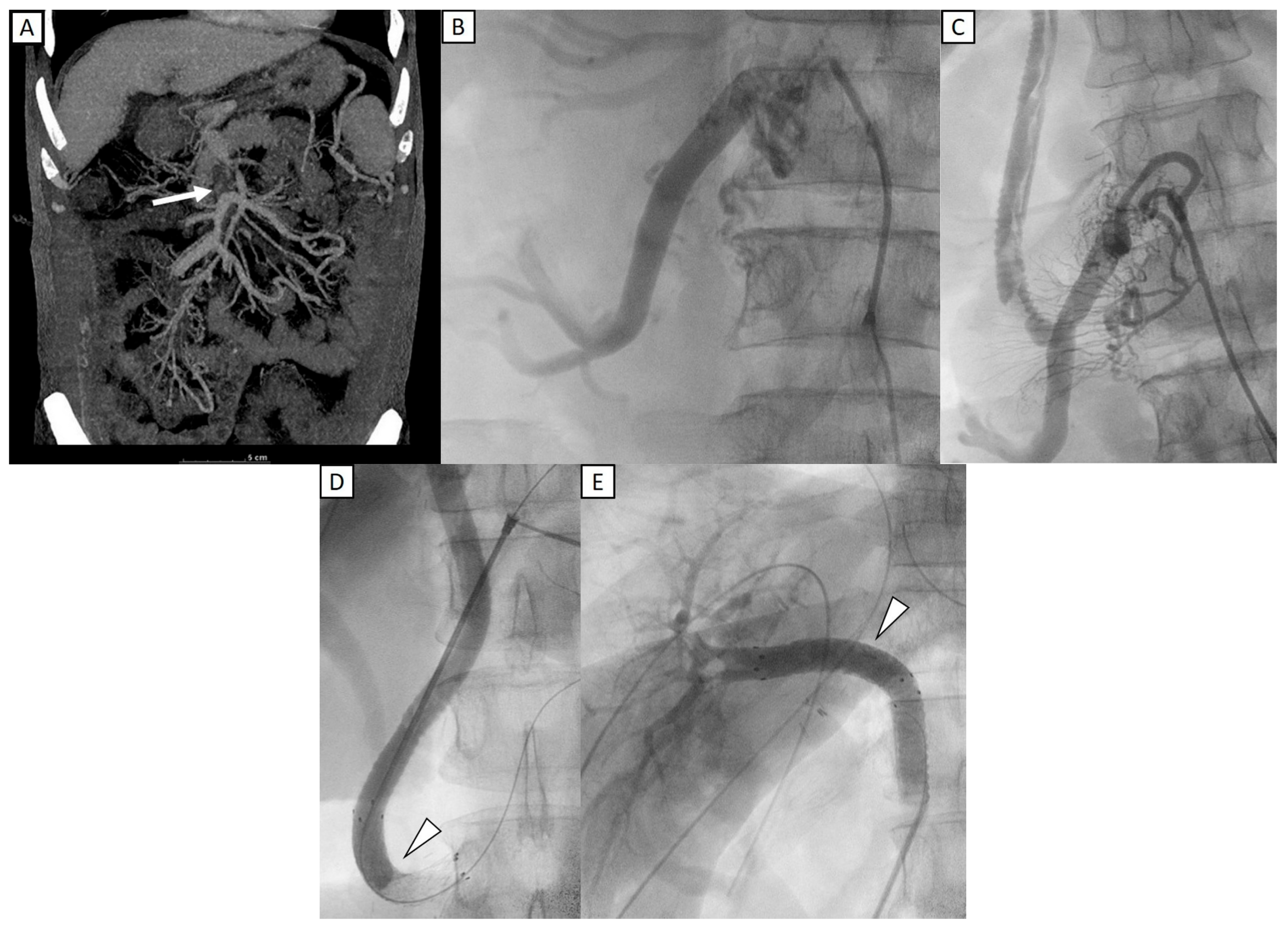
3.5. Representative Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, T.J.; Dahiya, D.; Lee, C.-S.; Lee, C.-F.; Chou, H.-S.; Chan, K.-M.; Lee, W.-C. Impact of portal venous hemodynamics on indices of liver function and graft regeneration after right lobe living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambio, A.; Tuñon, J.M.C.; Gómez, L.M.M.; Martínez, J.M.A.; Bellido, C.B.; Artacho, G.S.; Franco, C.C.; Pulido, L.B.; Ruiz, F.J.P.; Bravo, M.A.G. Intraoperative Portal Vein Flow > 123 mL/min Per 100 g Predicts a Better Survival of Patients After Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, A.; Hjortrup, A.; Kirkegaard, P. Intraoperative measurement of graft blood flow–A necessity in liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 1997, 10, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.B.; Lee, S.-G.; Ahn, C.; Hwang, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Ha, T.; Song, G.; Ryu, J.; Sung, K.; Ko, G. Application of intraoperative cine-portogram to detect spontaneous portosystemic collaterals missed by intraoperative doppler exam in adult living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2007, 13, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Shimizu, S.; Takeda, M.; Yanagi, Y.; Fukuda, A.; Abdelwahed, M.S.; Miyazaki, O.; Nosaka, S.; Kasahara, M. Efficacy of intraoperative cine-portogram for complicated portal vein reconstruction in pediatric living donor liver transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2021, 25, e13835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Ou, H.-Y.; Tsang, L.L.-C.; Yu, C.-Y.; Huang, T.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Concejero, A.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, S.-H.; Lin, T.-S.; et al. Vascular stents in the management of portal venous complications in living donor liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwonko, M.E.; Pekolj, J.; Mattera, J.; Peralta, O.A.; García-Mónaco, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; de Santibañes, M. Intraoperative stent placement for the treatment of acute portal vein complications in pediatric living donor liver transplantation. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2019, 404, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Ko, G.-Y.; Yoon, H.-K.; Shin, J.-H.; Ko, H.-K.; Sung, K.-B. Intraoperative stent placement in the portal vein during or after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2007, 13, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, T.; Shirabe, K.; Nakagawara, H.; Yoshizumi, T.; Toshima, T.; Soejima, Y.; Uchiyama, H.; Yamashita, Y.-I.; Harimoto, N.; Maehara, Y. Obstructing spontaneous major shunt vessels is mandatory to keep adequate portal inflow in living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 95, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, H.; Odaman, H.; Altay, C.; Ünek, T.; Özbilgin, M.; Egeli, T.; Ağalar, C.; Astarcıoğlu, İ.K.; Barlık, F. Manual and semi-automated computed tomography volumetry significantly overestimates the right liver lobe graft weight: A single-center study with adult living liver donors. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.S.; Rela, M. Portosystemic collaterals in living donor liver transplantation: What is all the fuss about? Liver Transplant. 2017, 23, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, Y.; Hori, T.; El Moghazy, W.M.; Yoshizawa, A.; Oike, F.; Mori, A.; Kaido, T.; Takada, Y.; Uemoto, S. Portal pressure <15 mm Hg is a key for successful adult living donor liver transplantation utilizing smaller grafts than before. Liver Transplant. 2010, 16, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Ogura, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kaido, T.; Segawa, H.; Okajima, H.; Kogure, T.; Uemoto, S. How transplant surgeons can overcome the inevitable insufficiency of allograft size during adult living-donor liver transplantation: Strategy for donor safety with a smaller-size graft and excellent recipient results. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, E324–E334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denys, A.; Chevallier, P.; Doenz, F.; Qanadli, S.D.; Sommacale, D.; Gillet, M.; Schnyder, P.; Bessoud, B. Interventional radiology in the management of complications after liver transplantation. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, M.-Q.; Yan, L.-N.; Lu, W.-S.; Li, X.; Shi, Z.-R.; Li, B.; Wen, T.-F.; Wang, W.-T.; Yang, J.-Y. Management of venous stenosis in living donor liver transplant recipients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4969–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajko, A.B.; Sheng, R.; Bron, K.; Reyes, J.; Nour, B.; Tzakis, A. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of venous anastomotic stenoses complicating liver transplantation: Intermediate-term results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1994, 5, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauthey, J.N.; Abdalla, E.K.; Doherty, D.A.; Gertsch, P.; Fenstermacher, M.J.; Loyer, E.M.; Lerut, J.; Materne, R.; Wang, X.; Encarnacion, A.; et al. Body surface area and body weight predict total liver volume in Western adults. Liver Transplant. 2002, 8, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosteller, R.D. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-F.; Wu, T.-J.; Yu, M.-C.; Chan, K.-M.; Lee, W.-C. Clinical analysis and strategy for liver transplantation in patients with pre-existing portal vein thrombosis. Chang Gung Med. J. 2011, 34, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Ko, G.-Y.; Sung, K.-B.; Yoon, H.-K.; Kim, K.R.; Moon, D.-B.; Lee, S.-G. Transvenous variceal embolization during or after living-donor liver transplantation to improve portal venous flow. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.B.; Lee, S.-G.; Ahn, C.-S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Ha, T.-Y.; Song, G.-W.; Jung, D.-H.; Park, G.-C.; Namkoong, J.-M.; et al. Section 6. Management of extensive nontumorous portal vein thrombosis in adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation 2014, 97 (Suppl. S8), S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Yoshimaru, K.; Yanagi, Y.; Esumi, G.; Hayashida, M.; Taguchi, T. Insufficient Portal Vein Inflow in Children without Major Shunt Vessels During Living Donor Liver Transplantation. Ann. Transplant. 2016, 21, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case | Age/Gender | MELD | Etiology | Type of Transplantation/Graft Used | Additional Procedure | Portal Vein Flow Velocity (cm/s) (Before Intervention) | Portal Vein Flow Velocity (cm/s) (Intraoperative Ultrasound) | Portal Vein Flow Velocity (cm/s) (After Intervention) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48/M | 15 | Alcoholic cirrhosis, HCV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of distal portion of iliocolic vein | 6.5 | 24.6 | 32.1 |
| 2 | 23/M | 11 | Cryptogenic liver cirrhosis | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein, splenorenal shunt and splenectomy | 0 | - | 31.4 |
| 3 | 53/M | 17 | Alcoholic cirrhosis, HBV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 0 | 28.6 | 36.5 |
| 4 | 55/M | 18 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of mesenteric vein | 10.8 | 26.5 | 27.4 |
| 5 | 59/M | 11 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 7.8 | 35 | 48.1 |
| 6 | 58/M | 14 | HBV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| 7 | 57/F | 11 | HCV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 9.4 | 21.9 | 45.7 |
| 8 | 58/F | 14 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of SMV-IVC shunt | 10.1 | 35.2 | 57.4 |
| 9 | 19/M | 20 | Biliary atresia | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of SMV-IVC shunt and coronary vein | 8 | 18.4 | 30 |
| 10 | 19/M | 24 | Biliary atresia | LDLT/left lobe | Embolization of coronary vein | 0 | - | 34.6 |
| 11 | 51/M | 27 | HBV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 21.4 b | 24.2 | 30.6 |
| 12 | 60/F | 11 | HCV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 0 | 18.4 | 47.8 |
| 13 | 65/F | 15 | HCV, HCC | DDLT/split right lobe | Ligation of SMV-IVC shunt and coronary vein | 5 | 9 | 30 |
| 14 | 68/F | 10 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation splenorenal shunt and splenoectomy | 6.7 | 0 | 7.5 |
| 15 | 62/F | 21 | Autoimmune hepatitis, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation engorged IMV | 11.6 | - | 37.3 |
| 16 | 53/F | 15 | Primary biliary cirrhosis | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 12.7 | 10.2 | 38.2 |
| 17 | 64/M | 13 | HCV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and mesorenal shunt | 5.2 | 24 | 33 |
| 18 | 61/F | 17 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and splenorenal shunt | 7.7 | 15.9 | 30.9 |
| 19 | 62/M | 10 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 7.1 | 34 | 27.6 |
| 20 | 55/F | 12 | HCV | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 0 | 15.4 | 21.3 |
| 21 | 56/M | 11 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 0 | - | 0 |
| 22 | 50/F | 17 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 0 | 23.4 | 35.4 |
| 23 | 62/M | 15 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 8.6 | 5.5 | 26 |
| 24 | 51/M | 8 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and splenic artery | 13.1 | 37.8 | 39.5 |
| 25 | 46/M | 26 | HBV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and short gastric vein | 8.8 | 35.5 | 63.4 |
| 26 | 55/M | 10 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| 27 | 60/M | 18 | Alcoholic cirrhosis | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and splenic artery | 8.6 | 26 | 35.4 |
| 28 | 54/F | 25 | HCV | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of splenorenal shunt | 0 | 13 | 26 |
| 29 | 54/M | 14 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/right lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and splenorenal shunt | 0 | 17.3 | 21 |
| 30 | 64/M | 16 | Alcoholic cirrhosis, HCC | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and splenorenal shunt | 10.5 b | 16.3 | 22.2 |
| 31 | 49/M | 14 | HBV | LDLT/right lobe | RAPV thrombosis for thrombolysis | 6 | 0 | 30 |
| 32 | 1/F | 7 a | Biliary atresia | LDLT/left lobe | SMV thrombosis for thrombolysis | 0 | - | 22 |
| 33 | 57/F | 17 | HCV, HCC | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein | 5.4 | 31.6 | 33 |
| 34 | 60/F | 10 | HCV | LDLT/left lobe | Ligation of coronary vein and portal vein stenting | 0 | 7.6 | 21.2 |
| During LT (n = 26) | After LT (n = 8) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56 (IQR, 49.8–60) | 55.5 (IQR, 53.3–64.3) | 0.537 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 17 (65.4%) | 3 (37.5%) | 0.228 |
| Female | 9 (34.6%) | 5 (62.5%) | |
| MELD | 14.5 (IQR, 11–18) | 15 (IQR, 10–15) | 0.450 |
| Pre-treatment portal vein flow velocity (cm/s) | 6.8 (IQR, 0–9.6) | 2.5 (IQR, 0–8.1) | 0.368 |
| Post-treatment portal vein flow velocity (cm/s) | 32.6 (IQR, 27.6–37.9) | 24 (IQR, 8.4–29) | 0.010 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-K.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Lim, W.-X.; Chen, C.-L.; Tsang, L.-C.; Yu, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-W.; Huang, P.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Ou, H.-Y. Applying Intraoperative Portal Venography in Liver Transplantation Vascular Surgery. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182321
Wang S-K, Cheng Y-F, Lim W-X, Chen C-L, Tsang L-C, Yu C-Y, Hsu H-W, Huang P-H, Chiu C-H, Ou H-Y. Applying Intraoperative Portal Venography in Liver Transplantation Vascular Surgery. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182321
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Szu-Kai, Yu-Fan Cheng, Wei-Xiong Lim, Chao-Long Chen, Leung-Chit Tsang, Chun-Yen Yu, Hsien-Wen Hsu, Po-Hsun Huang, Chun-Hua Chiu, and Hsin-You Ou. 2025. "Applying Intraoperative Portal Venography in Liver Transplantation Vascular Surgery" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182321
APA StyleWang, S.-K., Cheng, Y.-F., Lim, W.-X., Chen, C.-L., Tsang, L.-C., Yu, C.-Y., Hsu, H.-W., Huang, P.-H., Chiu, C.-H., & Ou, H.-Y. (2025). Applying Intraoperative Portal Venography in Liver Transplantation Vascular Surgery. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182321





