Performance of a Vision-Language Model in Detecting Common Dental Conditions on Panoramic Radiographs Using Different Tooth Numbering Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Prompt Development and Response Generation
- FDI numbering system prompt:
- “This is an anonymized dental panoramic radiograph from a research study. You are assisting in identifying observable dental anomalies as listed below, and specify the FDI tooth number of identified items. Focus only on visual patterns, not diagnoses.
- Developmental anomalies:
- Hypodontia (missing teeth) or anodontia.
- Dental anomalies:
- Caries (radiolucent lesions in enamel/dentin).
- Periapical lesions (e.g., radiolucency at root apex indicating infection or granuloma).
- Tooth fractures, cracks, or retained roots.
- Impacted teeth (e.g., third molars, canines).
- Bony anomalies:
- Periodontal bone loss (horizontal/vertical reduction in alveolar bone height).
- Osteolytic lesions (e.g., cysts, tumors like ameloblastoma or odontogenic keratocyst).
- Osteosclerosis (abnormal bone density, e.g., condensing osteitis).
- Iatrogenic/treatment-related findings:
- Endodontically treated teeth or teeth with restorations (Fillings, Crowns or bridges).
- Dental implants (screw-shaped radiopaque structures).”
- Universal numbering system prompt:
- The second prompt was identical in structure and content, except that it instructed ChatGPT to specify the Universal tooth number for identified findings.
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- GPT-4o generally demonstrated low accuracy in identifying many of the investigated radiolucent conditions, with relatively higher accuracy only for easily recognizable radiopaque features such as dental implants, endodontically treated teeth, and teeth with restorations, indicating that it was unable to reliably detect subtle but clinically important radiolucent conditions at both the patient and tooth levels.
- GPT-4o achieved higher diagnostic performance at the patient level than at the tooth level for dental implants, endodontically treated teeth, and missing teeth, suggesting that while the model could detect the presence of these conditions in the image, it might not accurately localize them.
- GPT-4o demonstrated similar diagnostic performance when using either the FDI or Universal numbering systems in identifying most dental conditions.
- Future studies should use larger and more diverse datasets, evaluate the performance of multiple language models across a wider range of dental conditions and image qualities, and include comparisons with dental students and practitioners of varying qualifications to more comprehensively understand the potential and limitations of LLMs in dental diagnostics.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| LLM | Large language model |
| ChatGPT | Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer |
References
- Wei, H.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, K.; Li, K.Y.; Hung, K.F.; Hu, E.M.; Lee, A.H.C.; Chang, J.W.W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Ai-powered problem- and case-based learning in medical and dental education: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Dent. J. 2025, 75, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr, S.; Rokhshad, R.; Daghighi, Y.; Golkar, M.; Kheybari, F.T.; Gorjinejad, F.; Kojori, A.M.; Rahimirad, P.; Shobeiri, P.; Mahdian, M.; et al. Deep learning for tooth identification and numbering on dental radiography: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2024, 53, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wong, L.M.; Shan, Z.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Shi, X.; Tsoi, J.K.H.; Hung, K.F. A semi-supervised transformer-based deep learning framework for automated tooth segmentation and identification on panoramic radiographs. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.K.; Zhu, M.; AlHadidi, A.; Wang, C.; Hung, K.; Wohlgemuth, P.; Lam, W.Y.H.; Liu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, H. A novel ai model for detecting periapical lesion on cbct: Cbct-sam. J. Dent. 2025, 153, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khubrani, Y.H.; Thomas, D.; Slator, P.J.; White, R.D.; Farnell, D.J.J. Detection of periodontal bone loss and periodontitis from 2d dental radiographs via machine learning and deep learning: Systematic review employing appraise-ai and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2025, 54, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Nalley, A.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Lam, W.Y.H.; Shan, Z.; Leung, Y.Y.; AlHadidi, A.; Bornstein, M.M.; et al. Characteristics, licensing, and ethical considerations of openly accessible oral-maxillofacial imaging datasets: A systematic review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Khan, S.M.; Xu, A.J.; Ibrahim, H.; Smith, L.; Caballero, J.; Zepeda, L.; de Blas Perez, C.; Denniston, A.K.; Liu, X.; et al. Characteristics of publicly available skin cancer image datasets: A systematic review. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e64–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.M.; Liu, X.; Nath, S.; Korot, E.; Faes, L.; Wagner, S.K.; Keane, P.A.; Sebire, N.J.; Burton, M.J.; Denniston, A.K. A global review of publicly available datasets for ophthalmological imaging: Barriers to access, usability, and generalisability. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e51–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, K.; Rajendran, R.; Ramesh, A.; Rao, S.; Agaian, S. Tufts dental database: A multimodal panoramic x-ray dataset for benchmarking diagnostic systems. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Chen, L.; Xu, F.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Children’s dental panoramic radiographs dataset for caries segmentation and dental disease detection. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lu, X.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, M.; Fan, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Yin, W.; Liu, X. A dual-labeled dataset and fusion model for automatic teeth segmentation, numbering, and state assessment on panoramic radiographs. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, N.; Sarode, S.C.; Sarode, G.S.; Ghone, U. Scarcity of publicly available oral cancer image datasets for machine learning research. Oral Oncol. 2022, 126, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-de-Assis, M.C.F.; Soares, J.P.; de Lima, L.M.; de Barros, L.A.P.; Grão-Velloso, T.R.; Krohling, R.A.; Camisasca, D.R. Ndb-ufes: An oral cancer and leukoplakia dataset composed of histopathological images and patient data. Data Brief 2023, 48, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.B.; Martins, A.S.; Tosta, T.A.A.; Loyola, A.M.; Cardoso, S.V.; Neves, L.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Nascimento, M.Z.D. Oralepitheliumdb: A dataset for oral epithelial dysplasia image segmentation and classification. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1691–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Tan, T.F.; Lu, W.; Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.W.; Liu, N. Large language models in health care: Development, applications, and challenges. Health Care Sci. 2023, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, S.; Liu, Y.; Orr-Ewing, L.; Dash, D.; Koyejo, S.; Callahan, A.; Fries, J.A.; Wornow, M.; Swaminathan, A.; Lehmann, L.S.; et al. Testing and evaluation of health care applications of large language models: A systematic review. JAMA 2025, 333, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Sheng, Y. Cloud-based intelligent self-diagnosis and department recommendation service using chinese medical bert. J. Cloud Comput. Adv. Syst. Appl. 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.C.; Lin, L.E.; Lin, L.H.; Chen, Y.C. Assessing question characteristic influences on chatgpt’s performance and response-explanation consistency: Insights from taiwan’s nursing licensing exam. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2024, 153, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guellec, B.; Lefèvre, A.; Geay, C.; Shorten, L.; Bruge, C.; Hacein-Bey, L.; Amouyel, P.; Pruvo, J.-P.; Kuchcinski, G.; Hamroun, A. Performance of an open-source large language model in extracting information from free-text radiology reports. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, e230364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosawa, T.; Harada, Y.; Yokose, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Kawamura, R.; Shimizu, T. Diagnostic accuracy of differential-diagnosis lists generated by generative pretrained transformer 3 chatbot for clinical vignettes with common chief complaints: A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenAI. Gpt-4o System Card. 2024. Available online: https://openai.com/index/gpt-4o-system-card/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Masaki, M.; Hikaru, F.; Kosuke, M.; Taiji, N.; Masanari, H.; Izumi, Y.; Kentaro, O.; Shuji, A. Evaluating gpt-4v’s performance in the japanese national dental examination: A challenge explored evaluating gpt-4v’s performance in the japanese national dental examination: A challenge explored. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Aşar, E.M.; İpek, İ.; Lge, K.B. Customized gpt-4v(ision) for radiographic diagnosis: Can large language model detect supernumerary teeth? BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, J.M.; Auer, M.K.; Strüven, A.; Massberg, S.; Stremmel, C. Chatgpt with gpt-4 outperforms emergency department physicians in diagnostic accuracy: Retrospective analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e56110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, M.N.; Rushton, V.E. A study to determine the added value of 740 screening panoramic radiographs compared to intraoral radiography in the management of adult (>18 years) dentate patients in a primary care setting. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sams, C.M.; Dietsche, E.W.; Swenson, D.W.; DuPont, G.J.; Ayyala, R.S. Pediatric panoramic radiography: Techniques, artifacts, and interpretation. Radiographics 2021, 41, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maaytah, M.; Jerjes, W.; Swinson, B.; Upile, T.; Thompson, G.; Gittelmon, S.; Baldwin, D.; Hadi, H.; Vourvachis, M.; Abizadeh, N.; et al. Inferior alveolar nerve injury and surgical difficulty prediction in third molar surgery: The role of dental panoramic tomography. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 45, e10–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ding, X.; Pu, J.J.; Chung, S.M.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Hung, K.F.; Shan, Z. Unlocking the potentials of large language models in orthodontics: A scoping review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Wong, L.M.; Zhang, R.; So, T.Y.; Shan, Z.; Hung, K.F.; Ai, Q.Y.H. Radiomics analysis in characterization of salivary gland tumors on mri: A systematic review. Cancers 2023, 15, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manek, M.; Maita, I.; Silva, D.F.B.; de Melo, D.P.; Major, P.W.; Jaremko, J.L.; Almeida, F.T. Temporomandibular joint assessment in mri images using artificial intelligence tools: Where are we now? A systematic review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2025, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, G.C.; Ribeiro, C.S.D.C.; Verner, F.S.; Lemos, C.A.A. Performance of artificial intelligence in evaluating maxillary sinus mucosal alterations in imaging examinations: Systematic review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2025, 54, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querrer, R.; Vieira, L.S.; Teodoro, A.B.; Melo, N.S.; Mesquita, C.R.M.; Silva, M.A.G.; Figueiredo, P.T.S.; Leite, A.F. Deep learning for osteoporosis screening in dental practice: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2025, twaf052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Thu, K.M.; Hung, K.F.; Yu, O.Y.; Hsung, R.T.; Lam, W.Y. Artificial intelligence in detecting periodontal disease from intraoral photographs: A systematic review. Int. Dent. J. 2025, 75, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Nalley, A.; Hao, J.; QY, H.A.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Hung, K.F. The performance of large language models in dentomaxillofacial radiology: A systematic review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2025, twaf060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mago, J.; Sharma, M. The potential usefulness of chatgpt in oral and maxillofacial radiology. Curēus 2023, 15, e42133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Morgado, M.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Accuracy of panoramic radiograph for diagnosing periodontitis comparing to clinical examination. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbiaee, N.; Pahlavanzadeh, P. Evaluation of panoramic radiography diagnostic accuracy in the assessment of interdental alveolar bone loss using cbct. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2024, 10, e70042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, B.; Çelik, M.E. Automated detection of dental restorations using deep learning on panoramic radiographs. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2022, 51, 20220244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, S.N.; Lee, J.H. Artificial intelligence in fractured dental implant detection and classification: Evaluation using dataset from two dental hospitals. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balel, Y.; Sağtaş, K.; Teke, F.; Kurt, M.A. Artificial intelligence-based detection and numbering of dental implants on panoramic radiographs. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2025, 27, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadrożny, Ł.; Regulski, P.; Brus-Sawczuk, K.; Czajkowska, M.; Parkanyi, L.; Ganz, S.; Mijiritsky, E. Artificial intelligence application in assessment of panoramic radiographs. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, K.; Zhang, F.; Yu, F.; Shi, K.; Sun, Z.; et al. Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of dental diseases on panoramic radiographs: A preliminary study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, J. Interpreting an orthopantomogram. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 49, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, A.; Matzen, L.H.; Spin-Neto, R.; Schropp, L. Effect of computer-assisted-learning and simulation clinics on dental students’ cognitive and performance skills: Panoramic image errors related to patient’s head position. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2020, 49, 20200154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.K.; Lages, F.S.; Maciel, C.A.B.; Glória, J.C.R.; Douglas-de-Oliveira, D.W. Prevalence of mandibular third molars according to the pell & gregory and winter classifications. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2022, 21, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güller, M.T.; Kumbasar, N.; Miloğlu, Ö. Evaluation of the effectiveness of panoramic radiography in impacted mandibular third molars on deep learning models developed with findings obtained with cone beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol. 2025, 41, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, A.; Arena, S.; Calzada, A.H.; Varón, A.I.C.; García, V.D.-F.; Freire, Y. Decoding wisdom: Evaluating chatgpt’s accuracy and reproducibility in analyzing orthopantomographic images for third molar assessment. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2025, 28, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmanpour, F.; Akpınar, M. Performance of chat generative pretrained transformer-4.0 in determining labiolingual localization of maxillary impacted canine and presence of resorption in incisors through panoramic radiographs: A retrospective study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2025, 168, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.P.; Andrade-Bortoletto, M.F.S.; Ocampo, T.S.C.; Alencar-Palha, C.; Bornstein, M.M.; Oliveira-Santos, C.; Oliveira, M.L. Performance of a commercially available generative pre-trained transformer (gpt) in describing radiolucent lesions in panoramic radiographs and establishing differential diagnoses. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Adjei, M.; Hayfron-Acquah, J.B.; Frimpong, T.; Abdul-Salaam, G. Imbalanced class distribution and performance evaluation metrics: A systematic review of prediction accuracy for determining model performance in healthcare systems. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
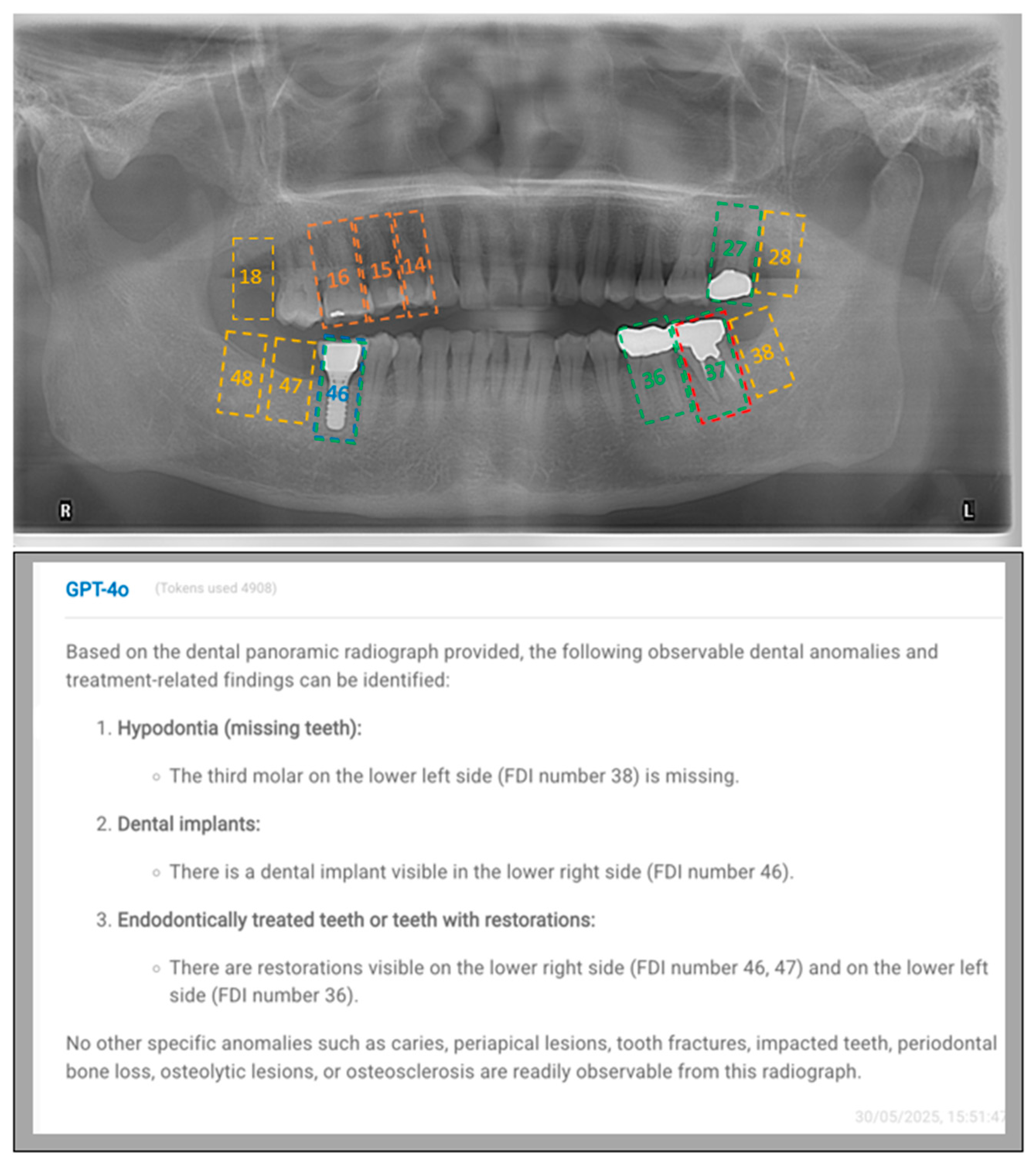
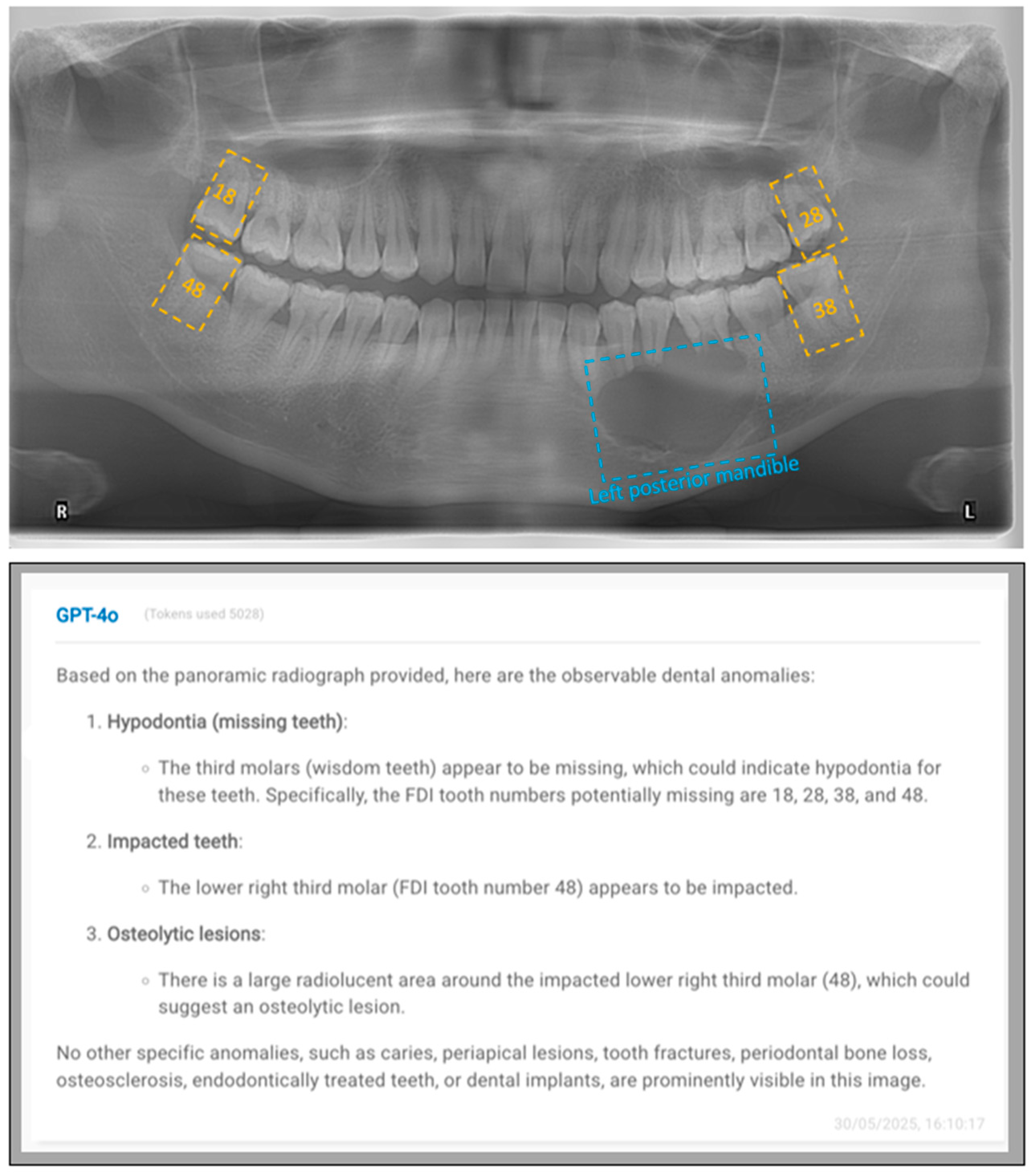
| Condition | Level | Positive Count (Reference Standard) | Negative Count (Reference Standard) | FDI Numbering System | Universal Numbering System | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Count (GPT-4o) | Negative Count (GPT-4o) | Positive Count (GPT-4o) | Negative Count (GPT-4o) | ||||
| Missing teeth | Patient | 35 | 15 | 41 | 9 | 42 | 8 |
| Tooth | 195 | 1405 | 132 | 1468 | 141 | 1459 | |
| Impacted teeth | Patient | 23 | 27 | 33 | 17 | 31 | 19 |
| Tooth | 54 | 346 | 51 | 349 | 55 | 345 | |
| Caries | Patient | 7 | 43 | 2 | 48 | 1 | 49 |
| Tooth | 21 | 1579 | 3 | 1597 | 2 | 1598 | |
| Endodontically treated teeth or teeth with restorations (Fillings, Crowns or bridges) | Patient | 38 | 12 | 36 | 14 | 35 | 15 |
| Tooth | 202 | 1398 | 103 | 1497 | 110 | 1490 | |
| Periapical lesions | Patient | 10 | 40 | 3 | 47 | 0 | 50 |
| Tooth | 17 | 1583 | 2 | 1598 | 0 | 1600 | |
| Periodontal bone loss | Patient | 23 | 27 | 8 | 42 | 5 | 45 |
| Tooth | 305 | 1295 | 41 | 1559 | 28 | 1572 | |
| Tooth fractures, cracks, or retained roots | Patient | 10 | 40 | 2 | 48 | 3 | 47 |
| Tooth | 16 | 1584 | 7 | 1593 | 8 | 1592 | |
| Dental implants | Patient | 7 | 43 | 8 | 42 | 6 | 44 |
| Tooth | 13 | 1587 | 15 | 1585 | 12 | 1588 | |
| Osteolytic lesions or Osteosclerosis | Patient | 13 | 37 | 2 | 48 | 2 | 48 |
| Region | 14 | 295 | 2 | 307 | 2 | 309 | |
| Condition | Level | F1-Score (%) | Balanced Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDI | Univ. | FDI | Univ. | FDI | Univ. | FDI | Univ. | ||
| Missing teeth | Patient | 73.68 | 77.92 | 46.67 | 52.86 | 80 | 85.71 | 13.33 | 20 |
| Tooth | 34.25 | 38.69 | 61.65 | 63.96 | 28.72 | 33.33 | 94.59 | 94.59 | |
| Impacted teeth | Patient | 64.29 | 66.67 | 60 | 65.06 | 78.26 | 78.26 | 44.44 | 51.85 |
| Tooth | 49.52 | 45.87 | 61.35 | 68.81 | 48.15 | 46.30 | 92.77 | 91.33 | |
| Caries | Patient | 0 | 0 | 47.67 | 48.84 | 0 | 0 | 95.35 | 97.67 |
| Tooth | 0 | 0 | 49.91 | 49.94 | 0 | 0 | 99.81 | 99.87 | |
| Endodontically treated teeth or teeth with restorations | Patient | 89.19 | 87.67 | 80.92 | 79.61 | 86.84 | 84.21 | 75 | 75 |
| Tooth | 32.13 | 28.21 | 60.2 | 58.53 | 24.26 | 21.78 | 96.14 | 95.28 | |
| Periapical lesions | Patient | 0 | 0 | 46.25 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 92.5 | 100 |
| Tooth | 0 | 0 | 49.94 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 99.87 | 100 | |
| Periodontal bone loss | Patient | 25.81 | 21.43 | 51.29 | 52.82 | 17.39 | 13.04 | 85.19 | 92.59 |
| Tooth | 8.67 | 9.76 | 51.46 | 52.23 | 4.92 | 5.32 | 97.99 | 99.15 | |
| Tooth fractures, cracks, or retained roots | Patient | 0 | 15.38 | 47.5 | 52.5 | 0 | 10 | 95 | 95 |
| Tooth | 0 | 0 | 49.77 | 49.75 | 0 | 0 | 99.56 | 99.49 | |
| Dental implants | Patient | 99.33 | 92.31 | 98.83 | 92.86 | 100 | 85.71 | 97.67 | 100 |
| Tooth | 28.57 | 48 | 65.04 | 77.89 | 30.77 | 46.15 | 99.31 | 99.62 | |
| Osteolytic lesions or Osteosclerosis | Patient | 13.33 | 13.33 | 52.49 | 52.49 | 7.69 | 7.69 | 97.30 | 97.30 |
| Region | 0 | 11.76 | 49.66 | 53.16 | 0 | 6.67 | 99.32 | 99.66 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Tanaka, R.; Nalley, A.; Hung, K.F. Performance of a Vision-Language Model in Detecting Common Dental Conditions on Panoramic Radiographs Using Different Tooth Numbering Systems. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182315
Liu Z, Ai QYH, Yeung AWK, Tanaka R, Nalley A, Hung KF. Performance of a Vision-Language Model in Detecting Common Dental Conditions on Panoramic Radiographs Using Different Tooth Numbering Systems. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zekai, Qi Yong H. Ai, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Ray Tanaka, Andrew Nalley, and Kuo Feng Hung. 2025. "Performance of a Vision-Language Model in Detecting Common Dental Conditions on Panoramic Radiographs Using Different Tooth Numbering Systems" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182315
APA StyleLiu, Z., Ai, Q. Y. H., Yeung, A. W. K., Tanaka, R., Nalley, A., & Hung, K. F. (2025). Performance of a Vision-Language Model in Detecting Common Dental Conditions on Panoramic Radiographs Using Different Tooth Numbering Systems. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182315







