Prognostic Significance of High-Sensitivity Troponin-T and Hematological Biomarkers in Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage Patients Undergoing Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Patient Population
2.2. Evaluation of Laboratory Data
2.3. Measurement of Hematoma Volume
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| sICH | Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage |
| NLR | neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PLR | platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| MLR | lympho-cyte-to-monocyte ratio |
| LMR | lympho-cyte-to-monocyte ratio |
| SII | systemic immune-inflammation index |
| GLR | glucose-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| Hs-cTn-I | high-sensitivity troponin-I |
References
- Wu, S.; Wu, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Anderson, C.S.; Sandercock, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; et al. Stroke in China: Advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Ikeda, T.; Feigin, V.L. Global, regional and country-specific burden of ischaemic stroke, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage: A systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.; Alvarez-Sabín, J.; Abilleira, S.; Santamarina, E.; Purroy, F.; Arenillas, J.F.; Molina, C.A.; Fernández-Cadenas, I.; Rosell, A.; Montaner, J. Plasma d-dimer predicts poor outcome after acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2006, 67, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadeh, S.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Eshghyar, F.; Rezaei, K.; Clark, A. The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in poststroke infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1983455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, E.M.; Golea, A.; Vesa, S.C.; Givan, I.; Perju-Dumbrava, L. Admission emergency department point-of-care biomarkers for prediction of early mortality in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, M.E.; Kalagara, R.; Moody, S.; Drake, J.; Margolis, S.A.; Cizginer, S.; Mahta, A.; Rao, S.S.; Stretz, C.; Wendell, L.C.; et al. Common biomarkers of physiologic stress and associations with delirium in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Crit. Care 2021, 64, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifan, G.; Testai, F.D. Systemic immune-inflammation (SII) index predicts poor outcome after spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, J. Prognostic significance of admission systemic inflammation response index in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A propensity score matching analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 718032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, B.M.; Zeller, T.; Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M.; Blankenberg, S. High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I and B-type natriuretic peptide as predictors of vascular events in primary prevention: Impact of statin therapy. Circulation 2015, 131, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thålin, C.; Rudberg, A.S.; Johansson, F.; Jonsson, F.; Laska, A.C.; Nygren, A.T.; von Arbin, M.; Wallén, H.; Aspberg, S. Elevated troponin levels in acute stroke patients predict long-term mortality. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batal, O.; Jentzer, J.; Balaney, B.; Kolia, N.; Hickey, G.; Dardari, Z.; Reddy, V.; Jovin, T.; Hammer, M.; Gorcsan, J.; et al. The prognostic significance of troponin I elevation in acute ischemic stroke. J. Crit. Care 2016, 31, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, H.; Kruska, M.; Marx, A.; Haucke, L.; Ebert, A.; Becker, L.; Szabo, K.; Akin, I.; Alonso, A.; Fastner, C. The phenomenon of dynamic change of cardiac troponin levels in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage increases in-hospital mortality independent of macrovascular coronary artery disease. J. Neurol Sci. 2025, 476, 123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, V.; Mackensen, G.B.; Gibbons, E.F.; Vavilala, M.S. Cardiac Dysfunction After Neurologic Injury: What Do We Know and Where Are We Going? Chest 2016, 149, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.W.; Ding, H.; Wang, W. Prognostic value of elevated cardiac troponin I in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulger, H.; Icme, F.; Parlatan, C.; Avci, B.S.; Aksay, E.; Avci, A. Prognostic relationship between high sensitivity troponin I level, hematoma volume and glasgow coma score in patients diagnosed with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerner, S.T.; Auerbeck, K.; Sprügel, M.I.; Sembill, J.A.; Madžar, D.; Gölitz, P.; Hoelter, P.; Kuramatsu, J.B.; Schwab, S.; Huttner, H.B. Peak troponin I levels are associated with functional outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 46, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, F.; McGinnis, J.; Baki, E.; Wiltgen, T.; Müller, A.; Maegerlein, C.; Kirschke, J.; Zimmer, C.; Hemmer, B.; Wunderlich, S.; et al. Predictors and Implications of Myocardial Injury in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2025, 35, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzi, S.; Elia, A.; Del Maestro, M.; Morotti, A.; Elbabaa, S.K.; Cavallini, A.; Galzio, R. Indication, Timing, and Surgical Treatment of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Systematic Review and Proposal of a Management Algorithm. World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, e769–e778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agewall, S.; Giannitsis, E.; Jernberg, T.; Katus, H. Troponin elevation in coronary vs. non-coronary disease. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lin, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Hao, Z.; Lei, C. Cardiac troponin and cerebral herniation in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broersen, L.H.A.; Stengl, H.; Nolte, C.H.; Westermann, D.; Endres, M.; Siegerink, B.; Scheitz, J.F. Association between high-sensitivity cardiac troponin and risk of stroke in 96 702 individuals: A meta-analysis. Stroke 2020, 51, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Cervellin, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Predicting mortality with cardiac troponins: Recent insights from meta-analyses. Diagnosis 2021, 8, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazerin, S.M.; Chi, G.; Marandi, R.; Najafi, H.; Shojaei, F.; Lee, J.J.; Marszalek, J.; Seifi, A. Evaluation of cardiac troponin and adverse outcomes after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 36, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, M.; Qiu, J.; Cao, X.; Xu, B.; Sui, Y. Prognostic value of serum cardiac troponin in acute ischemic stroke: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitliya, A.; AlEdani, E.M.; Bhangu, J.K.; Javed, K.; Manshahia, P.K.; Nahar, S.; Kanda, S.; Chatha, U.; Odoma, V.; Mohammed, L. The impact of elevated troponin levels on clinical outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2023, 26, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guette, P.; Launey, Y.; Arnouat, M.; Bleichner, J.P.; Masseret, E.; Rousseau, C.; Frasca, D.; Seguin, P. Prognostic value of high-sensitivity troponin T in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective observational study. Brain Inj. 2019, 33, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureșan, E.M.; Golea, A.; Vesa, Ș.C.; Lenghel, M.; Csutak, C.; Perju-Dumbravă, L. Emergency department point-of-care biomarkers and day 90 functional outcome in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A single-center pilot study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Q.W.; Wang, J. Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, P.M.; de Souza, M.A.; Mello-Carpes, P.B. Green tea and red tea from Camellia sinensis partially prevented the motor deficits and striatal oxidative damage induced by hemorrhagic stroke in rats. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 5158724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, K.; Goyal, N.; Chang, J.J.; Broce, M.; Pandhi, A.; Kerro, A.; Shahripour, R.B.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Tsivgoulis, G. Differential leukocyte counts on admission predict outcomes in patients with acute ischaemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Ding, Y.; Ju, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, Q.; Wu, X. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and 30-day mortality in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, R.A.; Terecoasă, E.O.; Tiu, C.; Ghiță, C.; Nicula, A.I.; Marinescu, A.N.; Popescu, B.O. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Medicina 2021, 57, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saand, A.R.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Chou, S.H. Systemic inflammation in hemorrhagic strokes—A novel neurological sign and therapeutic target? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 959–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
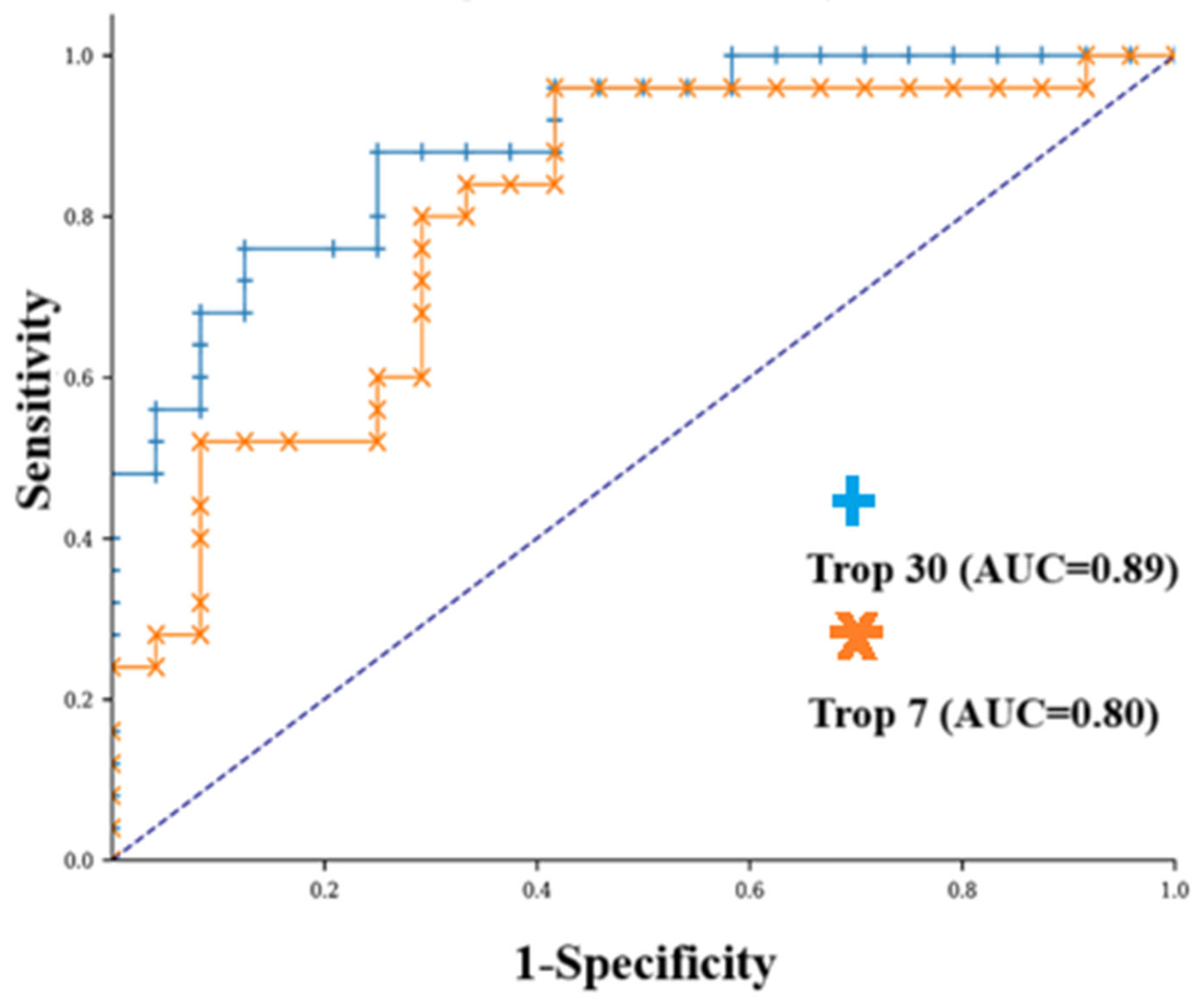
| Overall (n = 49) | Alive at Discharge (n = 25) | Mortality (n = 24) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.588 | |||
| male, n (%) | 35 (71.4%) | 17 (68%) | 18 (75%) | |
| female, n (%) | 14 (28.6%) | 8 (32%) | 6 (25%) | |
| Age, (years) mean ± SD | 56.37 ± 11.99 | 54.2 ± 9.14 | 58.63 ± 14.23 | 0.200 |
| GCS, mean ± SD | 8.59 ± 3.51 | 8.64 ± 4.02 | 8.54 ± 2.96 | 0.923 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 36 (73.5%) | 16 (64%) | 20 (83.3%) | 0.125 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 28 (57.2%) | 12 (48%) | 16 (66.7%) | 0.187 |
| Smoker, n (%) | 33 (67.3%) | 18 (72%) | 15 (62.5%) | 0.478 |
| Heart disease, n (%) | 9 (18.4%) | 4 (16%) | 5 (20.8%) | 0.662 |
| Previous Stroke History | ||||
| İschemic, n (%) | 7 (14.3%) | 4 (16%) | 3 (12.5%) | 0.726 |
| Hemorrhagic, n (%) | 1 (2.04%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4.17%) | 0.977 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 13 (26.5%) | 5 (25%) | 8 (33.3%) | 0.291 |
| Prothrombin time, mean ± SD | 15.35 ± 7.79 | 13.43 ± 3.16 | 15.69 ± 5.87 | 0.098 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time, mean ± SD | 28.72 ± 8.87 | 27.19 ± 5.25 | 30.31 ± 11.41 | 0.222 |
| International normalized ratio, mean ± SD | 1.25 ± 0.65 | 1.09 ± 0.13 | 1.27 ± 0.55 | 0.109 |
| WBC, (103/μL) | 15.46 ± 4.98 | 15.2 ± 4.21 | 15.75 ± 5.76 | 0.709 |
| NEU, (103/μL) | 12.12 ± 4.37 | 11,77 ± 3.65 | 12.48 ± 5.08 | 0.578 |
| LYM, (103/μL) | 2.16 ± 1.94 | 2.37 ± 2.24 | 1.95 ± 1.58 | 0.466 |
| MON, (103/μL) | 0.62 ± 0.32 | 0.57 ± 0.28 | 0.68 ± 0.36 | 0.220 |
| PLT, (103/μL) | 224.2 ± 75.83 | 220 ± 90 | 228.5 ± 59.26 | 0.698 |
| Hematoma volume, cm3 | 69.35 ± 37.69 | 62.62 ± 25.03 | 76.37 ± 47.01 | 0.235 |
| Hematoma location | 0.921 | |||
| Supratentorial labor | 33 (67.3%) | 17 (68%) | 16 (66.7%) | |
| Supratentorial deep | 16 (32.7%) | 8 (32%) | 8 (33.3%) |
| Overall (n = 49) | Alive at Discharge (n = 25) | Mortality (n = 24) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC, (103/μL) | 15.46 ± 4.98 | 15.2 ± 4.21 | 15.75 ± 5.76 | 0.709 |
| NEU, (103/μL) | 12.12 ± 4.37 | 11.77 ± 3.65 | 12.48 ± 5.08 | 0.578 |
| LYM, (103/μL) | 2.16 ± 1.94 | 2.37 ± 2.24 | 1.95 ± 1.58 | 0.466 |
| MON, (103/μL) | 0.62 ± 0.32 | 0.57 ± 0.28 | 0.68 ± 0.36 | 0.220 |
| PLT, (103/μL) | 224.2 ± 75.83 | 220 ± 90 | 228.5 ± 59.26 | 0.698 |
| SII | 2.19 ± 1.74 | 2.07 ± 1.83 | 2.31 ± 1.67 | 0.639 |
| SIRI | 5.85 ± 5.91 | 4.89 ± 5.33 | 6.85 ± 6.42 | 0.250 |
| NLR | 9.95 ± 7.54 | 9.73 ± 8.53 | 10.18 ± 6.51 | 0.838 |
| LMR | 3.92 ± 3.63 | 4.68 ± 4.54 | 3.14 ± 2.15 | 0.140 |
| GLR | 8.12 ± 6.65 | 6.48 ± 4.98 | 9.82 ± 7.77 | 0.78 |
| hs-cTn-I 1st day (ng/mL) | 18.4 ± 28.82 | 17.9 ± 38.18 | 18.88 ± 19.15 | 0.897 |
| hs-cTn-I 3rd day (ng/mL) | 56.21 ± 112.75 | 50.69 ± 151.39 | 61.95 ± 50.44 | 0.728 |
| hs-cTn-I 7th day (ng/mL) | 117.72 ± 193 | 49.88 ± 128.33 | 188.39 ± 224.35 | 0.010 |
| hs-cTn-I 30th day (ng/mL) | 84.22 ± 84.52 | 36.36 ± 31.62 | 134.08 ± 93.71 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öztürk, A.; Dilbaz, S.; Çakaroğlu, K.; Tekin, A.; Can, E.; Sönmez, E.; Ayhan, L.; Özlük, E.; Baş, N.S.; Çevik, S. Prognostic Significance of High-Sensitivity Troponin-T and Hematological Biomarkers in Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage Patients Undergoing Surgery. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172274
Öztürk A, Dilbaz S, Çakaroğlu K, Tekin A, Can E, Sönmez E, Ayhan L, Özlük E, Baş NS, Çevik S. Prognostic Significance of High-Sensitivity Troponin-T and Hematological Biomarkers in Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage Patients Undergoing Surgery. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172274
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖztürk, Akın, Suna Dilbaz, Kadir Çakaroğlu, Abdurrahim Tekin, Engin Can, Evren Sönmez, Lokman Ayhan, Enes Özlük, Nuri Serdar Baş, and Serdar Çevik. 2025. "Prognostic Significance of High-Sensitivity Troponin-T and Hematological Biomarkers in Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage Patients Undergoing Surgery" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172274
APA StyleÖztürk, A., Dilbaz, S., Çakaroğlu, K., Tekin, A., Can, E., Sönmez, E., Ayhan, L., Özlük, E., Baş, N. S., & Çevik, S. (2025). Prognostic Significance of High-Sensitivity Troponin-T and Hematological Biomarkers in Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage Patients Undergoing Surgery. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2274. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172274






