Genetic Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Gastrointestinal Disease
1.2. Explainable Artificial Intelligence
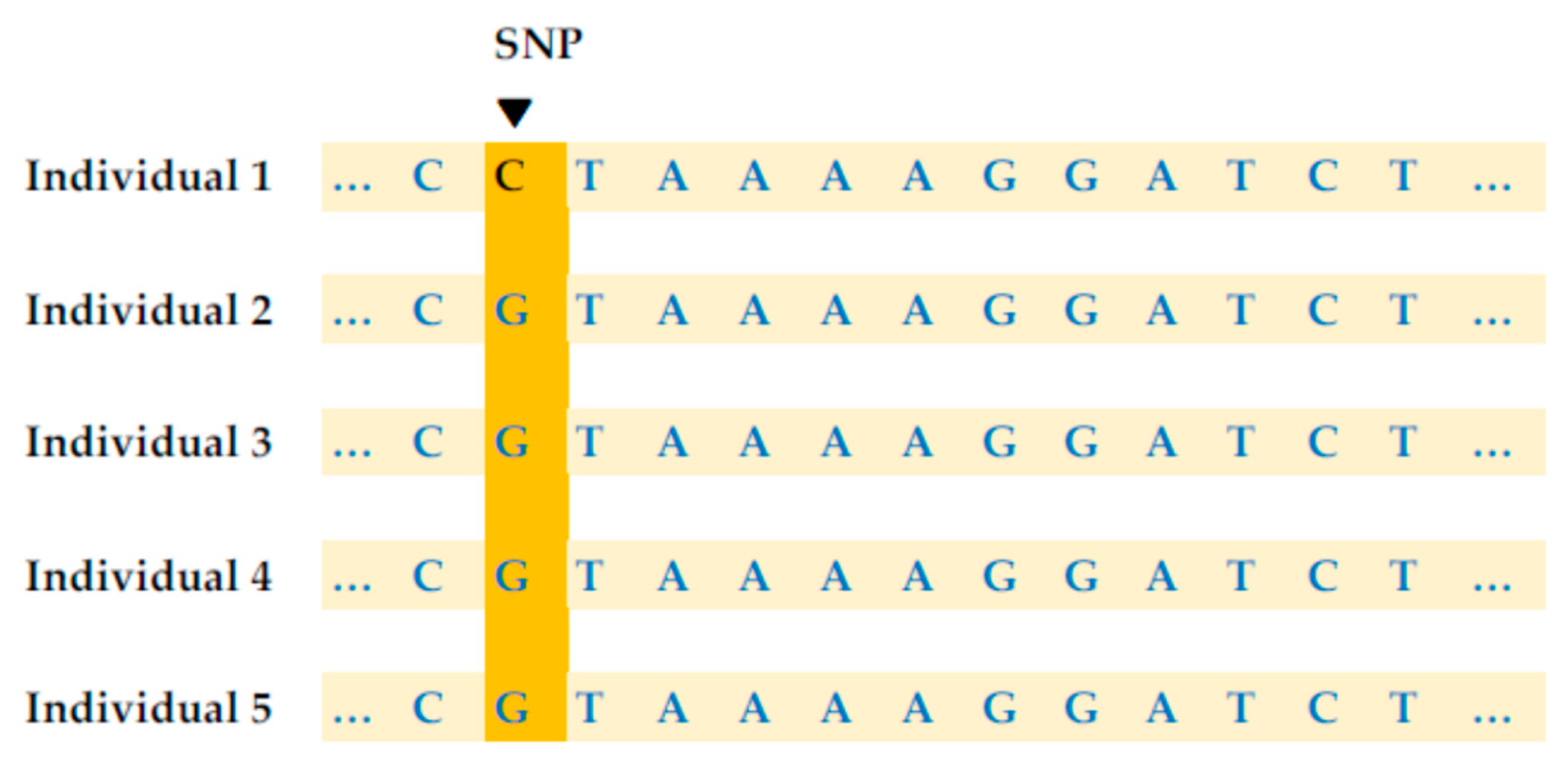
1.3. Genetic Artificial Intelligence
2. Methods
2.1. Data and Search Terms
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Summary Measures
3. Results
3.1. Summary
3.2. Genetic Artificial Intelligence for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
3.3. Genetic Artificial Intelligence for Gastrointestinal Cancer
3.4. Genetic Artificial Intelligence for Other Gastrointestinal Diseases
4. Discussion
4.1. Contributions of This Study
4.2. Limitations of Existing Literature
4.3. Suggestions for Future Research
4.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cleveland Clinic. Health: Gastrointestinal Diseases. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7040-gastrointestinal-diseases (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Milivojevic, V.; Milosavljevic, T. Burden of Gastroduodenal Diseases from the Global Perspective. Curr. Treat. Opt. Gastroenterol. 2020, 18, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; Jensen, E.T.; Kim, H.P.; Egberg, M.D.; Lund, J.L.; Moon, A.M.; Pate, V.; Barnes, E.L.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2021. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 621–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-E.; Park, H.; Jo, M.-W.; Oh, I.-H.; Go, D.-S.; Jung, J.; Yoon, S.-J. Trends and Patterns of Burden of Disease and Injuries in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34 (Suppl. S1), e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-K.; Jang, B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.; Park, S.Y.; Nam, M.-H.; Choi, M.-G. Health Care Costs of Digestive Diseases in Korea. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 58, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Digestive Diseases. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases (accessed on 1 June 2025).[Green Version]
- Lee, K.-S.; Ahn, K.H. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Early Diagnosis of Spontaneous Preterm Labor and Birth. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayana, G.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.W.; Choe, S.W. A novel multistage transfer learning for ultrasound breast cancer image classification. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Lund, J. Applications of explainable artificial intelligence in diagnosis and surgery. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.S.; Yang, S.W.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, K.H. Sex-based differences in prenatal and perinatal predictors of autism spectrum disorder using machine learning with national health data. Autism Res. 2025, 18, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.S.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.J. A machine learning-based decision support system for the prognostication of neurological outcomes in successfully resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saux, P.; Bauvin, P.; Raverdy, V.; Teigny, J.; Verkindt, H.; Soumphonphakdy, T.; Debert, M.; Jacobs, A.; Jacobs, D.; Monpellier, V.; et al. Development and validation of an interpretable machine learning-based calculator for predicting 5-year weight trajectories after bariatric surgery: A multinational retrospective cohort SOPHIA study. Lancet Digit. Health 2023, 5, e692–e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.W.; Choi, Y.; Lim, H.J.; Kwak, K.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, Y.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, K.H. Impact of platelet transfusion and bleeding risk stratification in patients with immune thrombocytopenia before procedures. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Ham, B.J. Graph machine learning with systematic hyper-parameter selection on hidden networks and mental health conditions in the middle-aged and old. Psychiatry Investig. 2024, 21, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, K.S. Predictive and explainable artificial intelligence for neuroimaging applications. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, K.S.; Heo, J.S.; Ahn, K.H. Clinical and dental predictors of preterm birth using machine learning methods: The MOHEPI study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24664–24675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Lee, K.S.; Pyun, S.B. Explainable artificial intelligence on safe balance and its major determinants in stroke patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23735–23748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.W.; Lee, K.S.; Heo, J.S.; Choi, E.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Ahn, K.H. Machine learning analysis with population data for prepregnancy and perinatal risk factors for the neurodevelopmental delay of offspring. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13993–14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xie, Y. Machine learning techniques for independent gait recovery prediction in acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Package Randomforest. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/randomForest/randomForest.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Python Package Sklearn. Ensemble. Random Forest Classifier. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier.html (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Lundberg, S.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Package Shap. Available online: https://github.com/slundberg/shap (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Mokhtari, K.E.; Higdon, B.P.; Basar, A. Interpreting financial time series with SHAP values. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Markham, ON, Canada, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalathu, S.; Hwang, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-S. Failure mode and effects analysis of RC members based on machine-learning-based SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) approach. Eng. Struct. 2020, 219, 110927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, A.B.; Movahedi, A.; Taghipour, H.; Derrible, S.; Mohammadian, A. (Kouros) toward safer highways, application of XGBoost and SHAP for real-time accident detection and feature analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 136, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kha, Q.-H.; Le, V.-H.; Hung, T.N.K.; Le, N.Q.K. Development and Validation of an Efficient MRI Radiomics Signature for Improving the Predictive Performance of 1p/19q Co-Deletion in Lower-Grade Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikis, G.; Ioannidis, G.; Siakallis, L.; Nikiforaki, K.; Iv, M.; Vozlic, D.; Surlan-Popovic, K.; Wintermark, M.; Bisdas, S.; Marias, K. Multicenter DSC–MRI-Based Radiomics Predict IDH Mutation in Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laios, A.; Kalampokis, E.; Johnson, R.; Munot, S.; Thangavelu, A.; Hutson, R.; Broadhead, T.; Theophilou, G.; Leach, C.; Nugent, D.; et al. Factors predicting surgical effort using explainable artificial intelligence in advanced stage epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buergel, T.; Steinfeldt, J.; Ruyoga, G.; Pietzner, M.; Bizzarri, D.; Vojinovic, D.; zu Belzen, J.U.; Loock, L.; Kittner, P.; Christmann, L.; et al. Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.I.; Hong, H.T.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.B. A machine learning approach for predicting suicidal ideation in post stroke patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Goździejewska, A.M.; Artiemjew, P. Predicting the effects of winter water warming in artificial lakes on zooplankton and its environment using combined machine learning models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Islam, T.; Shajalal, M.; Beyan, O.; Lange, C.; Cochez, M.; Rebholz-Schuhmann, D.; Decker, S. Explainable AI for bioinformatics: Methods, tools and applications. Brief Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhekar, R.S.; Rawekar, A. Artificial Intelligence in Genetics. Cureus 2024, 16, e52035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, J.M.; Cedric Notredame, C. Bioinformatics for Dummies, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner, J. Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. GenBank. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/about/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Weizmann Institute of Science. GeneCards. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory-European Bioinformatics Institute. UniProt. Available online: https://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Genetic Education Inc. What Is Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)? Available online: https://geneticeducation.co.in/what-is-single-nucleotide-polymorphism-snp/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- National Human Genome Research Institute. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs). Available online: https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Single-Nucleotide-Polymorphisms-SNPs (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Media Wiki and National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.snpedia.com/index.php/SNPedia (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Gaudillo, J.; Rodriguez, J.J.R.; Nazareno, A.; Baltazar, L.R.; Vilela, J.; Bulalacao, R.; Domingo, M.; Albia, J. Machine learning approach to single nucleotide polymorphism-based asthma prediction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, B.; Torrent-Fontbona, F.; Viñas, R.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism relevance learning with Random Forests for Type 2 diabetes risk prediction. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 85, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muflikhah, L.; Fatyanosa, T.N.; Widodo, N.; Perdana, R.S.; Solimun; Ratnawati, H. Feature selection for hypertension risk prediction using XGBoost on single nucleotide polymorphism data. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2025, 31, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, K.Y.; Dhaliwal, J.; Wong, K. Risk score prediction model based on single nucleotide polymorphism for predicting malaria: A machine learning approach. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameli, A.; Peña-Castillo, L.; Usefi, H. Assessing the reproducibility of machine-learning-based biomarker discovery in Parkinson’s disease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 174, 108407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Pulido, V.; Seoane, J.A.; Rabuñal, J.R.; Dorado, J.; Pazos, A.; Munteanu, C.R. Machine learning techniques for single nucleotide polymorphism-disease classification models in schizophrenia. Molecules 2010, 15, 4875–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.P.; Gaudillo, J.D.; Vilela, J.A.; Roxas-Villanueva, R.M.L.; Tiangco, B.J.; Domingo, M.R.; Albia, J.R. A machine learning-based SNP-set analysis approach for identifying disease-associated susceptibility loci. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Rostami, M.; Guzzi, P.H. AI-enabled pipeline for virus detection, validation, and SNP discovery from next-generation sequencing data. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1492752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Ter-Minassian, M.; Wu, I.C.; Wang, Z.; Su, L.; Asomaning, K.; Chen, F.; Kulke, M.H.; et al. Interactions between environmental factors and polymorphisms in angiogenesis pathway genes in esophageal adenocarcinoma risk: A case-only study. Cancer 2012, 118, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.A.; Jang, J.; Choi, C.H.; Kang, S.B.; Bang, K.B.; Kim, T.O.; Seo, G.S.; Cha, J.M.; Chun, J.; Jung, Y.; et al. Development of a Clinical and Genetic Prediction Model for Early Intestinal Resection in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: Results from the IMPACT Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Hu, S.; He, Z.; Feng, C.; Dong, G.; An, S.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Chen, Y.; Ying, X. Towards Strain-Level Complexity: Sequencing Depth Required for Comprehensive Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Analysis of the Human Gut Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Hernandez, D.; Estrada, K.; Trevino, V. Multivariate genome-wide association study models to improve prediction of Crohn’s disease risk and identification of potential novel variants. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhuang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wu, W.; Ding, K. Different Characteristics in Gut Microbiome between Advanced Adenoma Patients and Colorectal Cancer Patients by Metagenomic Analysis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0159322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.A.; Savegnago, R.P.; Alves, A.A.C.; Stafuzza, N.B.; Pedrosa, V.B.; Rocha, R.A.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Paz, C.C.P. Genome-enabled prediction of indicator traits of resistance to gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep using parametric models and artificial neural networks. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 166, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.W.; Wu, Z.G.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.B.; Yao, Z.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Yu, Y.B. Intestinal flora and inflammatory bowel disease: Causal relationships and predictive models. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Lan, F.; Wen, C.; Wu, G.; Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Yang, N.; et al. Calcium deposition in chicken eggshells: Role of host genetics and gut microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schophaus, S.; Creasy, K.T.; Koop, P.; Clusmann, J.; Jaeger, J.; Punnuru, V.; Koch, A.; Trautwein, C.; Loomba, R.; Luedde, T.; et al. Machine learning uncovers manganese as a key nutrient associated with reduced risk of steatotic liver disease. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 2807–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ma, S.; Yang, Z.; Niu, R.; Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y. Revolutionizing ESCC prognosis: The efficiency of tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIIC) signature score. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Siddiqui, H.I.; Qureshi, G.S.; Bernhardt, G.V. A Review of Literature on the Pharmacogenomics of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms. Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J. 2022, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.V.R.; Farías, A.F.-S.; Álvarez, R.d.C.C.; de Oca, E.P.M. Predicted regulatory SNPs reveal potential drug targets and novel companion diagnostics in psoriasis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. Why should I trust you? Explaining the predictions of any classifier. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.04938. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, A.; Hartmann, S.; Vollmer, M.; Shavlokhova, V.; Brands, R.C.; Kübler, A.; Wollborn, J.; Hassel, F.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Lang, G.; et al. Multimodal artificial intelligence-based pathogenomics improves survival prediction in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhancing the Quality and Transparency of Health Research Network. Reporting Guidelines. 2024. Available online: https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/ten-simple-rules-for-neuroimaging-meta-analysis/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Müller, V.I.; Cieslik, E.C.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.T.; Radua, J.; Mataix-Cols, D.; Tench, C.R.; Yarkoni, T.; Nichols, T.E.; Turkeltaub, P.E.; et al. Ten simple rules for neuroimaging meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid Ghasemi, M.; Dariush Ebrahimi, D. Introduction to reinforcement learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.07712. [Google Scholar]
- Hambly, B.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Recent advances in reinforcement learning in finance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2112.04553. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Nemati, S. Reinforcement learning in healthcare: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1908.08796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronato, A.; Naeem, M.; De Pietro, G.; Paragliola, G. Reinforcement learning for intelligent healthcare applications: A survey. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; See, K.C.; Ngiam, K.Y.; Celi, L.A.; Sun, X.; Feng, M. Reinforcement learning for clinical decision support in critical care: Comprehensive review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puiutta, E. Veith EMSP. Explainable reinforcement learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.06247. [Google Scholar]

| Amino Acid | RNA Codons | DNA Codons |
|---|---|---|
| Ala A | GCU, GCC, GCA, GCG | GCT, GCC, GCA, GCG |
| Arg R | CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG; AGA, AGG | CGT, CGC, CGA, CGG; AGA, AGG |
| Asn N | AAU, AAC | AAT, AAC |
| Asp D | GAU, GAC | GAT, GAC |
| Asn/Asp B | AAU, AAC; GAU, GAC | AAT, AAC; GAT, GAC |
| Cys C | UGU, UGC | TGT, TGC |
| Gln Q | CAA, CAG | CAA, CAG |
| Glu E | GAA, GAG | GAA, GAG |
| Gln/Glu Z | CAA, CAG; GAA, GAG | CAA, CAG; GAA, GAG |
| Gly G | GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG | GGT, GGC, GGA, GGG |
| His H | CAU, CAC | CAT, CAC |
| Ile I | AUU, AUC, AUA | ATT, ATC, ATA |
| Leu L | CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG; UUA, UUG | CTT, CTC, CTA, CTG; TTA, TTG |
| Lys K | AAA, AAG | AAA, AAG |
| Met M | AUG | ATG |
| Phe F | UUU, UUC | TTT, TTC |
| Pro P | CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG | CCT, CCC, CCA, CCG |
| Ser S | UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG; AGU, AGC | TCT, TCC, TCA, TCG; AGT, AGC |
| Thr T | ACU, ACC, ACA, ACG | ACT, ACC, ACA, ACG |
| Trp W | UGG | TGG |
| Tyr Y | UAU, UAC | TAT, TAC |
| Val V | GUU, GUC, GUA, GUG | GTT, GTC, GTA, GTG |
| Start | AUG, CUG, UUG | ATG, TTG, GTG, CTG |
| Stop | UAA, UGA, UAG | TAA, TGA, TAG |
| Study | Sample Size | Method—Baseline | Method—Innovation | Dependent Variable | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | 335 | RF GERD Included | RF Smoking Included | Esophageal Adenocarcinoma | Classification |
| [52] | 463 | Boosting SNP Excluded | Boosting SNP Included | Crohn’s Disease EIR | Classification |
| [53] | 3 | LR | RF | Gut Microbiome SNP SN | Regression |
| [54] | 8421 | LASSO | LD | Crohn’s Disease | Classification |
| [55] | 26 | RF Microbiome Baseline | RF Microbiome SNP | Colorectal Cancer | Classification |
| [56] | 1664 | ANN | LASSO | GI Nematode Resistance | Classification |
| [57] | 757,042 | ANN | RF | Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Classification |
| [58] | 570 | Wilcoxon Rank Sum | RF | Calcium Metabolism | Classification |
| [59] | 199,732 | Cox | Steatotic Liver Disease | Classification | |
| [60] | 439 | RF 1-Year Survival | RF 2-Year Survival | ESCC | Classification |
| Study | Performance—Baseline | Performance—Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Area Under the Curve | Accuracy | Area Under the Curve | |
| [51] | 70 | 80 | ||
| [52] | 81 | 84 | ||
| [53] | 80 | 99 | ||
| [54] | 52 | 63 | ||
| [55] | 87 | 92 | ||
| [56] | 65 | 79 | ||
| [57] | 91 | 98 | ||
| [58] | 25 | 100 | ||
| [59] | 99 | |||
| [60] | 65 | 80 | ||
| Min | 25 | 52 | 79 | 63 |
| Max | 87 | 91 | 100 | 99 |
| R-Square | ||||
| 100 × (1 − p value) | ||||
| Study | Predictor Demographic | Predictor Health | Predictor SNP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | GERD Smoking BMI | rs2295778 | rs13337626 | rs2296188 | rs2114039 | |
| rs11941492 | rs17708574 | rs7324547 | rs17619601 | |||
| rs17625898 | ||||||
| [52] | Age | Disease Behavior | rs28785174 | rs60532570 | rs13056955 | rs7660164 |
| [53] | SNP Density/Number | |||||
| [54] | MARCKS Protein | rs4945943 | ||||
| [55] | Microbiome Intestinal | IB175794 | BA459738 | EM8439 | ||
| [56] | SNPs 41676 | |||||
| [57] | Microbiome Intestinal | SNPs 13 | EXOC3: 6 | SLC25A26: 1 | YIF1B: 6 | |
| [58] | Microbiome Intestinal | rs316115020 | rs316420452 | |||
| [59] | rs738409_G | rs2642438_A | rs58542926_T | rs72613567_TA | ||
| [60] | Immune Cell Types | rs148710154 | rs75146099 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-S.; Kim, E.S. Genetic Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Disease: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172227
Lee K-S, Kim ES. Genetic Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Disease: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172227
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kwang-Sig, and Eun Sun Kim. 2025. "Genetic Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Disease: A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172227
APA StyleLee, K.-S., & Kim, E. S. (2025). Genetic Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Disease: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172227







