Electroencephalography Signatures Associated with Developmental Dyslexia Identified Using Principal Component Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. EEG Data Acquisition
2.3. Behavioural Measures
2.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
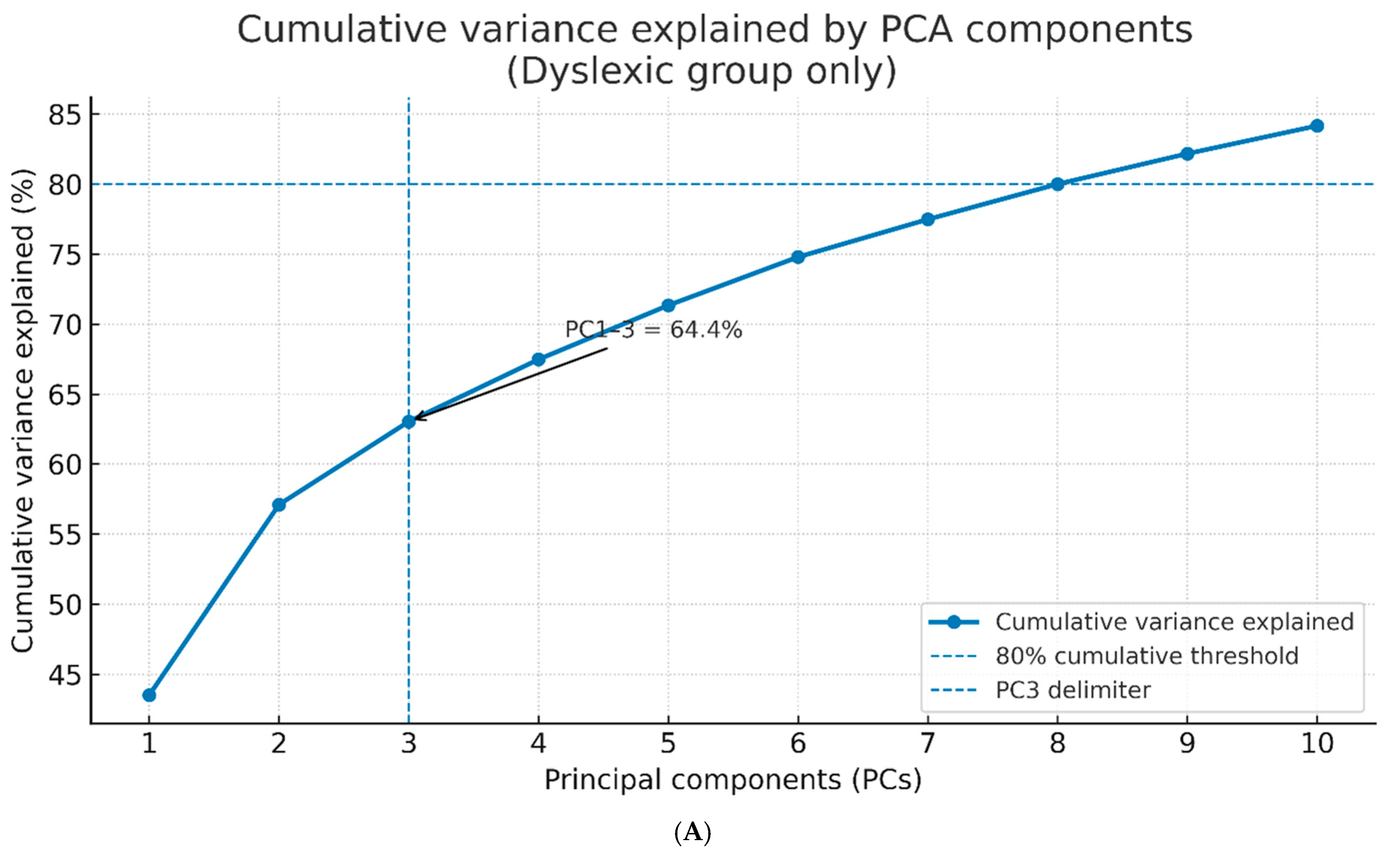
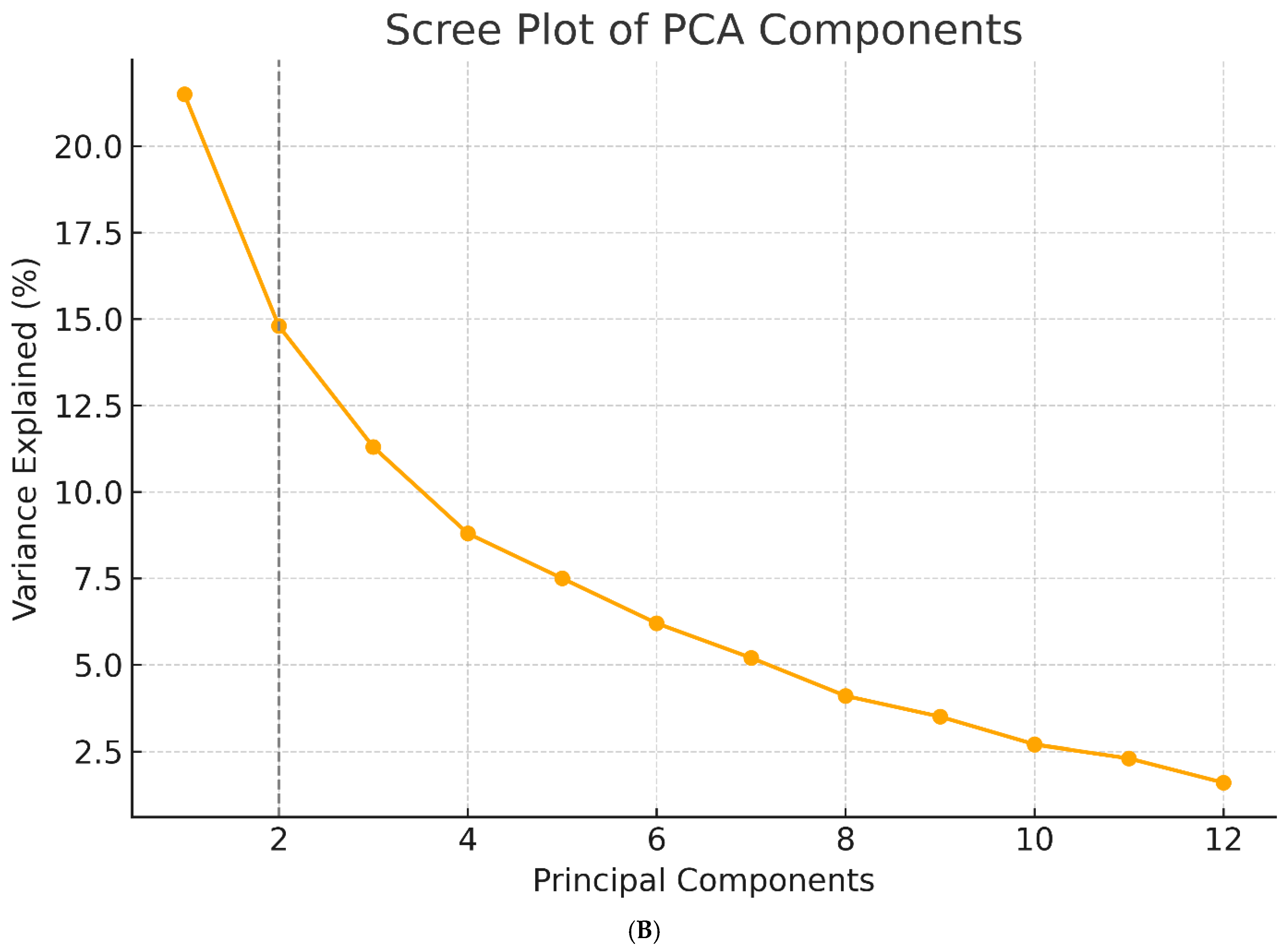
3.1. Principal Component Extraction and Variance Explanation
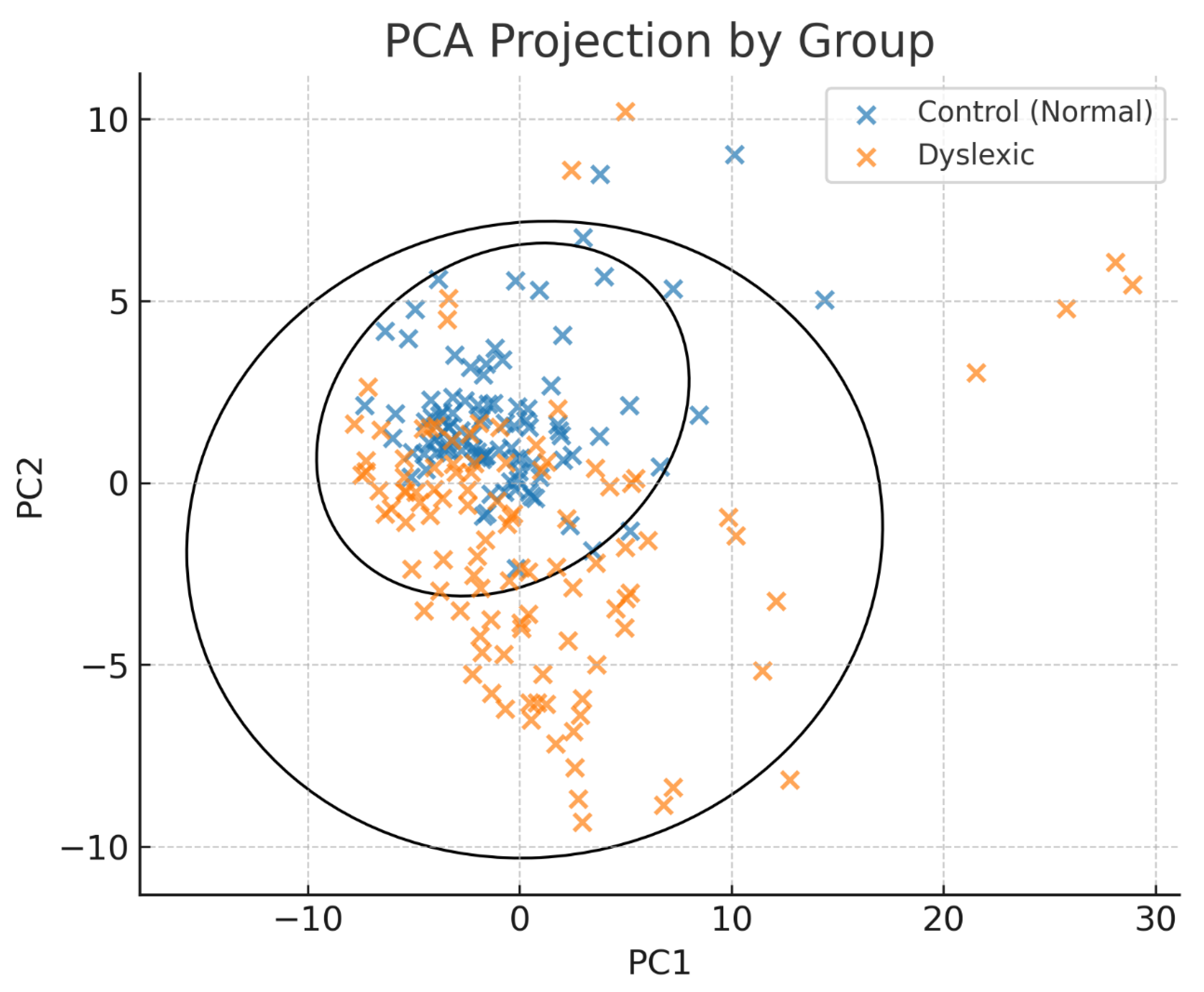
3.2. Cluster Separation and Group Classification
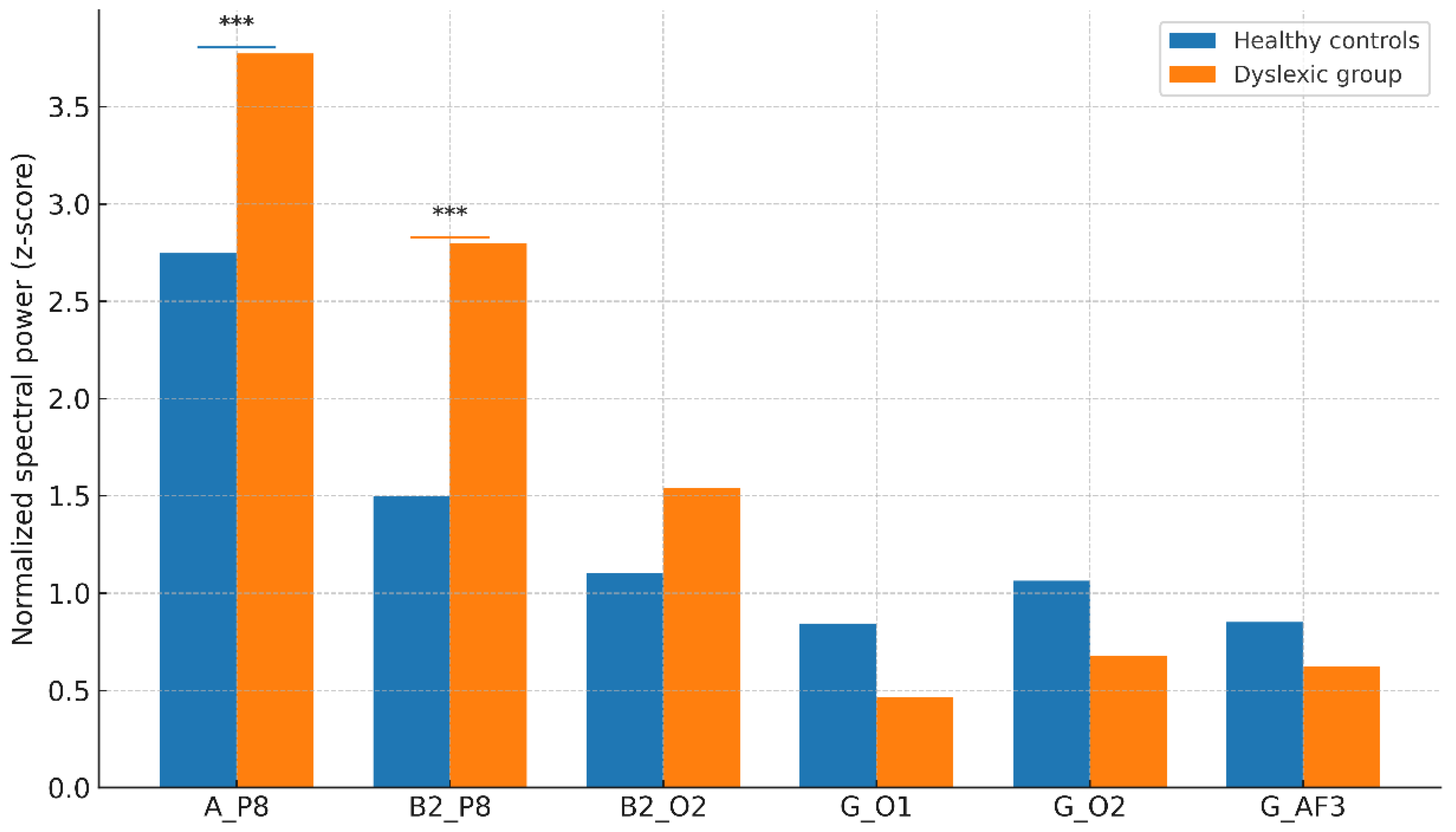
3.3. Hemisphere-Specific Activity Patterns
- Alpha at P8: Dyslexic Mean = 3.77 ± 0.61 vs. Control Mean = 2.74 ± 0.56, t(198) = 11.23, p < 0.001, Cohen’s d = 1.38.
- Beta-2 at P8: Dyslexic Mean = 2.79 ± 0.73 vs. Control Mean = 1.49 ± 0.62, p < 0.001.
3.4. Component Loadings and Biomarker Interpretation
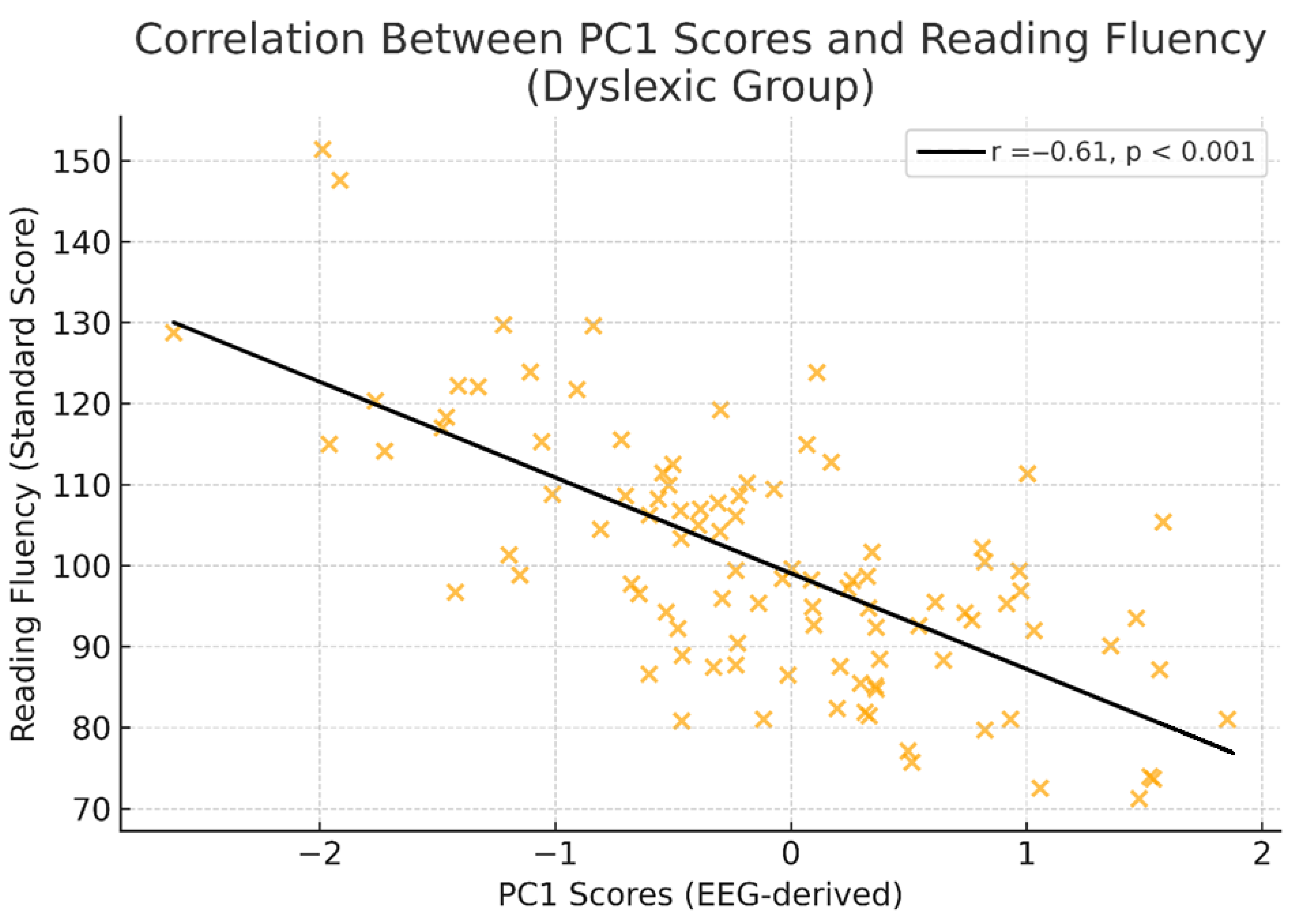
3.5. Behavioural Data Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemispheric Imbalance and Neural Interpretation
4.2. PCA as a Biomarker Discovery Tool
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaywitz, B.A.; Shaywitz, S.E. The American experience: Towards a 21st-century definition of dyslexia. Oxf. Rev. Educ. 2020, 46, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowling, M.J.; Hulme, C.; Nation, K. Defining and understanding dyslexia: Past, present and future. Oxf. Rev. Educ. 2020, 46, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, U.; Neef, N.E.; Kraft, I.; Schaadt, G.; Dörr, L.; Brauer, J.; Czeppezauer, I.; Müller, B.; Wilcke, A.; Kirsten, H. The emergence of dyslexia in the developing brain. NeuroImage 2020, 211, 116633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Yi, C.; Li, C.; Tao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Si, Y.; Yao, D.; Yin, G. A survey of brain network analysis by electroencephalographic signals. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2022, 16, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, J.M.; Holden, C.; Kirby, P.; Thompson, P.A.; Snowling, M.J.; Dyslexia Delphi Panel. Toward a consensus on dyslexia: Findings from a Delphi study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2025, 66, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliaee, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Shirani, S.; Rostami, R. Extraction of discriminative features from EEG signals of dyslexic children before and after the treatment. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 16, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, G.; Noccetti, S. A Linguistic Approach to the Study of Dyslexia; Channel View Publications: Bristol, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cainelli, E.; Vedovelli, L.; Carretti, B.; Bisiacchi, P. EEG correlates of developmental dyslexia: A systematic review. Ann. Dyslexia 2023, 73, 184–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huo, S.; Wang, J.; Maurer, U. Spectral and topological abnormalities of resting and task state EEG in Chinese children with developmental dyslexia. Brain Topogr. 2025, 38, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wong, W.-F. EEG classification with spiking neural networks: Smaller, better, and more energy efficient. Smart Health 2022, 24, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahad, R.; Yeasin, M.; Bidelman, G.M. Decoding of single-trial EEG reveals unique states of functional brain connectivity that drive rapid speech categorisation decisions. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarrán-Cárdenas, L.; Silva-Pereyra, J.; Martínez-Briones, B.J.; Bosch-Bayard, J.; Fernández, T. Neurofeedback effects on EEG connectivity among children with reading disorders: I. Coherence. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Barnes, D.; Gallego-Molina, N.J.; Formoso, M.A.; Ortiz, A.; Figueiredo, P.; Luque, J.L. Probabilistic and explainable modelling of phase–phase cross-frequency coupling patterns in EEG: Application to dyslexia diagnosis. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 44, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, G.; Aydın, S.; Çetin, M.; Balcışoy, S. Improving cognitive functions of dyslexics using multi-sensory learning and EEG neurofeedback. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Izmir, Turkey, 2–5 May 2018; p. 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, G.; Gürkan, M.; Teber, S.; Ertürk, K.; Kırmızı, M.; Ekici, B.; Arman, F.; Balcışoy, S.; Özgüz, V.; Çetin, M. Changes in EEG complexity with neurofeedback and multi-sensory learning in children with dyslexia: A multiscale entropy analysis. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2022, 11, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, A.-L.; Ramus, F. Neurogenetics and auditory processing in developmental dyslexia. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnica-Agudelo, D.; van de Velden, D.; Stier, C.; Brockmann, K.; Schroeder, S.; Neef, N.E.; Focke, N.K. Source reconstruction of clinical resting-state EEG reveals differences in power and functional connectivity in children with developmental dyslexia. NeuroImage 2023, 248, 118761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glica, A.; Wasilewska, K.; Jurkowska, J.; Żygierewicz, J.; Kossowski, B.; Jednoróg, K. Reevaluating the neural noise in dyslexia using biomarkers from electroencephalography and high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy. eLife 2025, 13, RP99920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunsell, M. Dyslexia in a global context: A cross-linguistic, cross-cultural perspective. Lat. Am. J. Content Lang. Integr. Learn. 2020, 13, 217–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Paunwala, C. Early detection of dyslexia based on EEG with novel predictor extraction and selection. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2023, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, P.; Harshani, H.; Shiratuddin, M.F.; Wong, K.W.; Fullarton, K. EEG signal analysis of writing and typing between adults with dyslexia and normal controls. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2018, 10, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.B.; Oliveira, D.G.; Cardoso, A.D.; Laurence, P.G.; Boggio, P.S.; Macedo, E.C. Event-related potential and lexical decision task in dyslexic adults: Lexical and lateralisation effects. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 852219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Acharya, U.R. Automated EEG signal classification using chaotic local binary patterns. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 182, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turri, C.; Di Dona, G.; Santoni, A.; Zamfira, D.A.; Franchin, L.; Melcher, D.; Ronconi, L. Periodic and aperiodic EEG features as potential markers of developmental dyslexia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridou, D.; Tsiantis, C.-O.; Vlaikou, A.-M.; Chondrou, V.; Zakopoulou, V.; Christodoulides, P.; Oikonomou, E.D.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Kostoulas, C.; Tzallas, A.T. Developmental dyslexia: Insights from EEG-based findings and molecular signatures—A pilot study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, O.L.; Muniyandi, R.C.; Omar, K.; Mohamad, M. Advanced machine learning methods for dyslexia biomarker detection: A review of implementation details and challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36879–36897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Features | Healthy Controls | Dyslexic Group |
|---|---|---|
| G_O1 | 0.8438 | 0.4634 |
| B2_P8 | 1.4965 | 2.7974 |
| B2_P7 | 0.7195 | 0.4567 |
| G_AF3 | 0.8513 | 0.6238 |
| A_P8 | 2.7465 | 3.7737 |
| B2_O2 | 1.1039 | 1.5401 |
| B2_F3 | 0.9134 | 0.8903 |
| G_O2 | 1.0631 | 0.6768 |
| B2_FC5 | 0.9891 | 0.8656 |
| G_P7 | 0.707 | 0.2881 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eroğlu, G.; Abou Harb, M.R. Electroencephalography Signatures Associated with Developmental Dyslexia Identified Using Principal Component Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172168
Eroğlu G, Abou Harb MR. Electroencephalography Signatures Associated with Developmental Dyslexia Identified Using Principal Component Analysis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172168
Chicago/Turabian StyleEroğlu, Günet, and Mhd Raja Abou Harb. 2025. "Electroencephalography Signatures Associated with Developmental Dyslexia Identified Using Principal Component Analysis" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172168
APA StyleEroğlu, G., & Abou Harb, M. R. (2025). Electroencephalography Signatures Associated with Developmental Dyslexia Identified Using Principal Component Analysis. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2168. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172168







