Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population: Clinical Characteristics and Ethnic Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Selection and Determination of the TCF7L2 Genotype (rs7903146)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Control and Diabetic Groups
3.2. Association Between TCF7L2 Genotypes and T2DM
3.3. Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of All Subjects, the Diabetes and Control Groups, Stratified by TCF7L2 Genotype
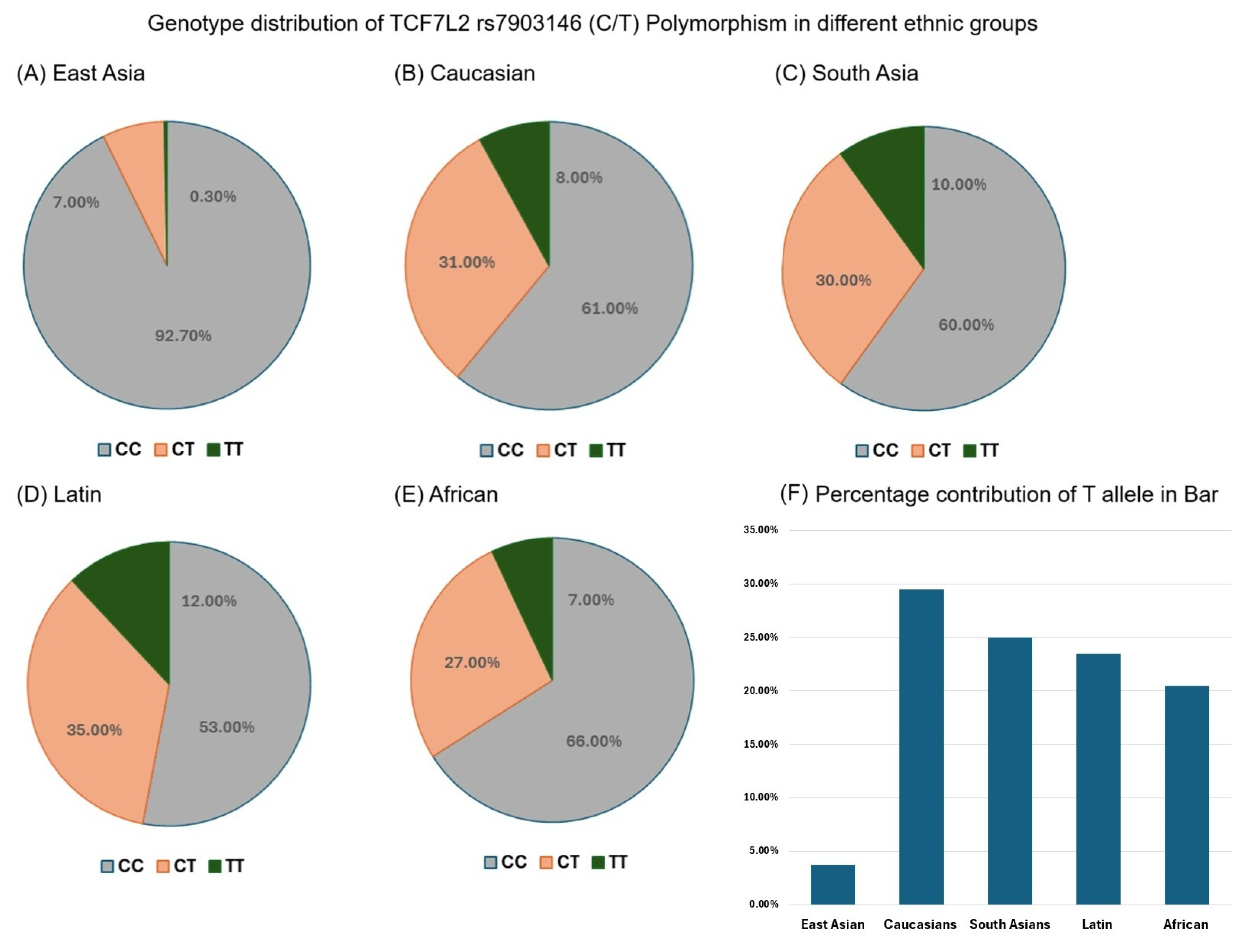
3.4. Genotype Distribution of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism in Different Ethnic Groups
3.5. TCF7L2 rs7903146 T Allele Frequency in Different Ethnic Groups
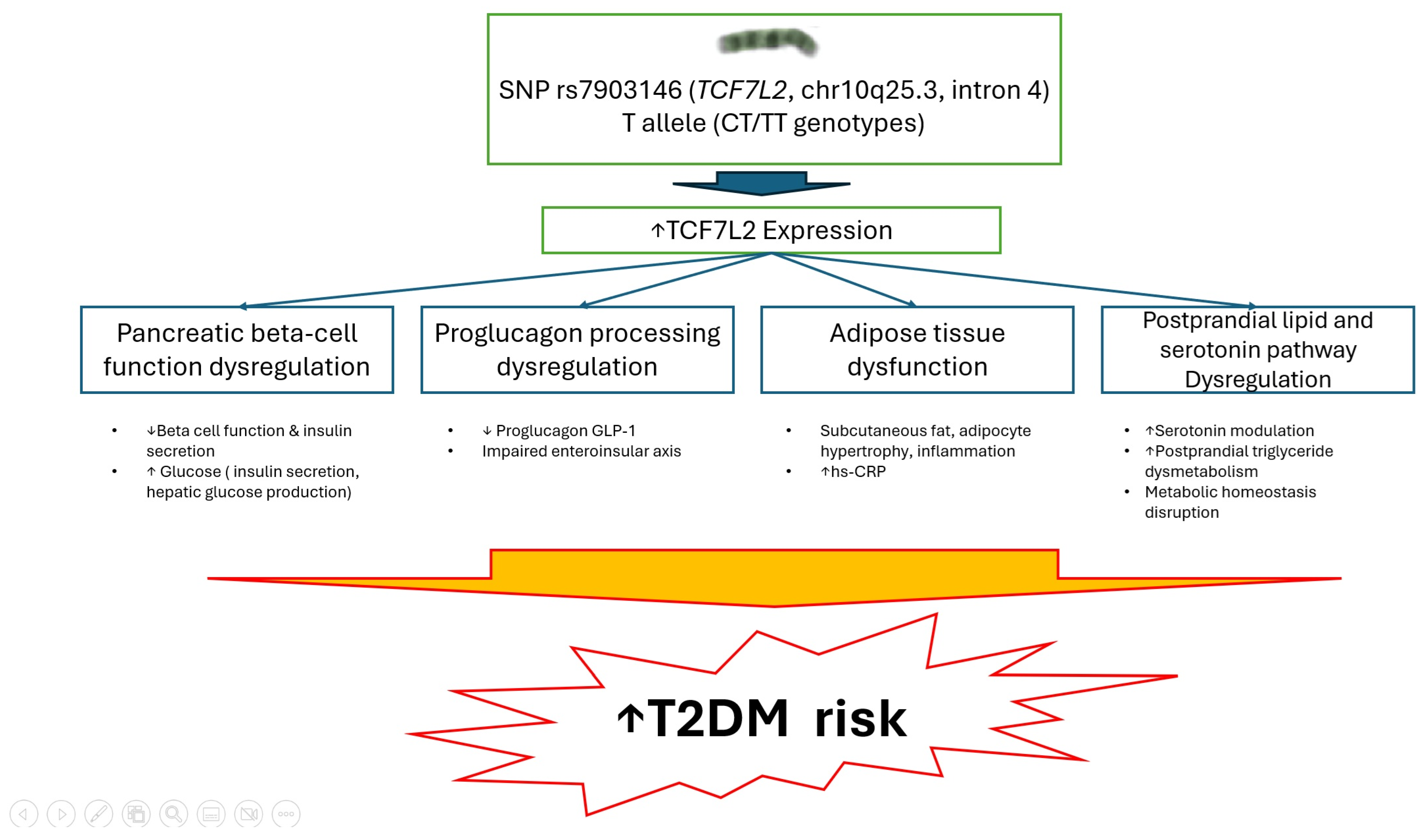
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCF7L2 | Transcription factor 7-like 2 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| WHR | Waist-to-hip ratio |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| Hs-CRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| AOR | Adjusted odds ratio |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HMG | High-mobility group |
References
- Cerf, M.E. Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.J.; Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.R. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.C.; Wang, Z. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus of Chinese populations in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 73, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.; Hamet, P. Environmental and genetic contributions to diabetes. Metabolism 2019, 100, 153952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witka, B.Z.; Oktaviani, D.J.; Marcellino, M.; Barliana, M.I.; Abdulah, R. Type 2 Diabetes-Associated Genetic Polymorphisms as Potential Disease Predictors. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2689–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Genetic associations between Transcription Factor 7 Like 2 rs7903146 polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of 115,809 subjects. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanasegaran, K.; Ng, J.Y.E.; Chua, E.W.; Nawi, A.M.; Ng, P.Y.; Abdul Manaf, M.R. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes among Asians: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciat, G.; Florian, A.R.; Chaikh-Sulaiman, M.S.; Staicu, A.; Caracostea, G.V.; Procopciuc, L.M.; Stamatian, F.; Muresan, D. TCF7L2 Polymorphism rs7903146 (C/T) and Gestational Diabetes Influence on Obstetric Outcome: A Romanian Case-Control Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyssenko, V.; Lupi, R.; Marchetti, P.; Del Guerra, S.; Orho-Melander, M.; Almgren, P.; Sjögren, M.; Ling, C.; Eriksson, K.F.; Lethagen, A.L.; et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T. Current understanding on role of the Wnt signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 in glucose homeostasis. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 254–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu, S.; Thida, A.; Maung, K.K.; Chit, T.T. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at rs7903146 of Transcription Factor 7-like 2 gene Among Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Myanmar. J. ASEAN Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 38, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2012, 35 (Suppl. S1), 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Hung, W.C.; Wang, C.P.; Wu, C.C.; Hsuan, C.F.; Yu, T.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Cheng, Y.A.; Chung, F.M.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. The Lower Limit of Reference of Urinary Albumin/Creatinine Ratio and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 858267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jin, S. Meta-analysis of association between TCF7L2 polymorphism rs7903146 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendup, T.; Feng, X.; Clingan, S.; Astell-Burt, T. Environmental Risk Factors for Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beulens, J.W.J.; Pinho, M.G.M.; Abreu, T.C.; den Braver, N.R.; Lam, T.M.; Huss, A.; Vlaanderen, J.; Sonnenschein, T.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Environmental risk factors of type 2 diabetes-an exposome approach. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, M.; Fernandes Silva, L. Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes: Past, Present, and Future. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyssenko, V.; Jonsson, A.; Almgren, P.; Pulizzi, N.; Isomaa, B.; Tuomi, T.; Berglund, G.; Altshuler, D.; Nilsson, P.; Groop, L. Clinical risk factors, DNA variants, and the development of type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Huang, T. Gene-environment interactions and type 2 diabetes. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 29, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Kriti, M.; Anamika, K.S.; Sarma, D.K.; Verma, V.; Nagpal, R.; Mohania, D.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M. Deciphering the complex interplay of risk factors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A comprehensive review. Metabol. Open 2024, 22, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraczynska, M.; Swatowski, A.; Markowska-Gosik, D.; Kuczmaszewska, A.; Ksiazek, A. Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphism and complication/comorbidity profile in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.F.; Thorleifsson, G.; Reynisdottir, I.; Benediktsson, R.; Manolescu, A.; Sainz, J.; Helgason, A.; Stefansson, H.; Emilsson, V.; Helgadottir, A.; et al. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prakash, P.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, N. Genetic Association of Transcription Factor 7-Like-2 rs7903146 Polymorphism With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2024, 16, e52709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danquah, I.; Othmer, T.; Frank, L.K.; Bedu-Addo, G.; Schulze, M.B.; Mockenhaupt, F.P. The TCF7L2 rs7903146 (T) allele is associated with type 2 diabetes in urban Ghana: A hospital-based case-control study. BMC Med. Genet. 2013, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Huang, R.Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Sun, H.L. Lack of association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in TCF7L2 and T2DM in the Chinese Yao population: A case-control study. Medicine 2021, 100, e25326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, L.; Khan, S.; Mishra, S.; Das, D.; Bora, K.; Shubham, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, R.R.; Tiwari, A.; et al. Genetic variants and type 2 diabetes in India: A systematic review and meta-analysis of associated polymorphisms in case-control studies. Lancet Reg. Health Southeast Asia 2024, 32, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B. Association between TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus: A large human genome epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta- analysis. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 19, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zeggini, E.; McCarthy, M.I. TCF7L2: The biggest story in diabetes genetics since HLA? Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchi, S.; Froguel, P. TCF7L2 genetic defect and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2008, 8, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, J.C.; Jablonski, K.A.; Bayley, N.; Pollin, T.I.; de Bakker, P.I.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Knowler, W.C.; Nathan, D.M.; Altshuler, D.; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. TCF7L2 polymorphisms and progression to diabetes in the diabetes prevention program. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ayala, I.; Shannon, C.; Fourcaudot, M.; Acharya, N.K.; Jenkinson, C.P.; Heikkinen, S.; Norton, L. The diabetes gene and WNT pathway effector TCF7L2 regulates adipocyte development and function. Diabetes 2018, 67, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Morin, P.J.; Clevers, H. The yin-yang of TCF/beta-catenin signaling. Adv. Cancer Res. 2000, 77, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nusse, R.; Varmus, H.E. WNT genes. Cell 1992, 69, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Zhao, Y.; Harris, D.C.; Zheng, G. E-cadherin/b-catenin complex and the epithelial barrier. BioMed Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 567305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Su, J.; Bailey, K.; Ottosson-Laakso, E.; Shcherbina, L.; Oskolkov, N.; Zhang, E.; Thevenin, T.; Fadista, J.; et al. TCF7L2 is a master regulator of insulin production and processing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6419–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Wang, D.; Chiang, Y.T.; Ip, W.; Zhu, L.; Xu, F.; Columbus, J.; Belsham, D.D.; Irwin, D.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. The WNT signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 controls gut and brain proglucagon gene expression and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes 2013, 62, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Brubaker, P.L.; Jin, T. TCF-4 mediates cell type-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression by beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; van Es, J.H.; Huch, M.; Li, V.S.; José, A.; Hatzis, P.; Mokry, M.; Haegebarth, A.; van den Born, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. Diabetes risk gene and WNT effector Tcf7l2/TCF4 controls hepatic response to perinatal and adult metabolic demand. Cell 2012, 151, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropano, C.; Santoro, N.; Groop, L.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Galderisi, A.; Kursawe, R.; Pierpont, B.; Goffredo, M.; Caprio, S. The rs7903146 Variant in the TCF7L2 Gene Increases the Risk of Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes in Obese Adolescents by Impairing β-Cell Function and Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiherer, A.; Muendlein, A.; Saely, C.H.; Fraunberger, P.; Drexel, H. Serotonin is elevated in risk-genotype carriers of TCF7L2-rs7903146. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, S.V.; Mishra, B.K.; Mannar, V.; Aslam, M.; Banerjee, B.; Agrawal, V. TCF7L2 gene associated postprandial triglyceride dysmetabolism- a novel mechanism for diabetes risk among Asian Indians. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 973718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Ling, Q.; Ye, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shu, J.; Chen, G.; Fei, Y.; Li, C. TCF7L2 involvement in estradiol-and progesterone-modulated islet and hepatic glucose homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jainandunsing, S.; Koole, H.R.; van Miert, J.N.I.; Rietveld, T.; Wattimena, J.L.D.; Sijbrands, E.J.G.; de Rooij, F.W.M. Transcription factor 7-like 2 gene links increased in vivo insulin synthesis to type 2 diabetes. EBioMedicine 2018, 30, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkov, P.; Olsson, A.H.; Gillberg, L.; Jørgensen, S.W.; Brøns, C.; Vaag, C. Epigenetic and genetic factors influencing TCF7L2 expression in human adipose tissue. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Dayeh, T.; Volkov, P.; Salö, S.; Hall, E.; Nilsson, E.; Olsson, A.H.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Wollheim, C.B.; Eliasson, L.C. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of human pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic donors identifies candidate genes that influence insulin secretion. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Type 2 Diabetes | Non-Diabetic Controls | p-Value | Effect Sizes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 600 | 511 | ||
| Sex (% men) | 49.2 | 50.5 | 0.660 | 0.95 |
| Age (year) | 73.3 ± 6.5 (72.7–73.8) | 46.9 ± 12 (25.9–47.9) | <0.0001 | |
| Duration of disease (year) | 15.8 ± 8.1 (15.1–16.4) | - | - | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 3.7 (25.6–26.2) | 24.0 ± 4.0 (23.7–24.4) | <0.0001 | |
| Age at diagnosis (year) | 54.6 ± 9.5 (53.8–55.3) | - | - | |
| WHR Men | 0.95 ± 0.07 (0.94–0.96) | 0.89 ± 0.06 (0.88–0.90) | <0.0001 | |
| Women | 0.89 ± 0.06 (0.88–0.90) | 0.79 ± 0.06 (0.78–0.80) | <0.0001 | |
| Systolic BP (mm Hg) | 134 ± 18 (132–135) | 125 ± 18 (123–126) | <0.0001 | |
| Diastolic BP (mm Hg) | 78 ± 11 (77–29) | 77 ± 12 (76–78) | 0.213 | |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 192.8 ± 40.0 (189.6–196.1) | 208.2 ± 39.2 (204.7–211.6) | <0.0001 | |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 122.0 (85.3–168.0) | 92.0 (63.0–138.0) | <0.0001 * | |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 50.9 ± 13.3 (49.8–52.0) | 61.1 ± 19.0 (59.5–62.8) | <0.0001 | |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 108.7 ± 35.1 (105.9–111.6) | 131.1 ± 36.1 (127.9–134.3) | <0.0001 | |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 151.5 ± 56.5 (147.0–156.1) | 91.0 ± 8.4 (90.2–91.7) | <0.0001 | |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.3 ± 2.0 (8.2–8.5) | 5.5 ± 0.4 (5.4–5.5) | <0.0001 | |
| Treatment (%) | ||||
| Oral drugs | 87.4 | - | - | |
| Insulin | 5.4 | - | - | |
| Oral drugs + insulin | 7.2 | - | - | |
| Antihypertensive therapy (%) | 28.0 | - | - | |
| Statin therapy (%) | 57.5 | - | - | |
| Current smoker (%) | 27.8 | 17.2 | <0.0001 | 1.85 |
| Genotype | Controls (n, %) | T2DM (n, %) | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WFH (n, %) | WOFH a (n, %) | ADO ≥ 60 (n, %) | ADO < 60 (n, %) | BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 (n, %) | BMI < 27 kg/m2 (n, %) | Male (n, %) | Female (n, %) | |||
| N (%) | 511 | 600 | 224 (62.2) | 136 (37.8) | 180 (30.0) | 420 (70.0) | 203 (33.8) | 397 (66.2) | 295 (49.2) | 305 (50.8) |
| CC | 496 (97.1) | 568 (94.7) | 208 (92.9) | 128 (94.1) | 173 (96.1) | 395 (94.1) | 194 (95.6) | 374 (94.2) | 280 (94.9) | 288 (94.4) |
| CT | 15 (2.9) | 31 (5.2) | 15 (6.7) | 8 (5.9) | 7 (3.9) | 24 (5.7) | 9 (4.4) | 22 (5.5) | 15 (5.1) | 16 (5.3) |
| TT | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.3) |
| CT + TT | 15 (2.9) | 32 (5.3) * | 16 (7.1) | 8 (5.9) | 7 (3.9) | 25 (6.0) | 9 (4.4) | 23 (5.8) | 15 (5.1) | 17 (5.6) |
| Crude OR b | - | 1.86 | 1.23 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 1.56 | 0.75 | 1.33 | 0.91 | 1.10 |
| (95% CI) | - | (1.02–3.58) | (0.53–3.11) | (0.32–1.90) | (0.25–1.43) | (0.70–3.98) | (0.33–1.61) | (0.62–3.08) | (0.44–1.86) | (0.54–2.28) |
| p-value | - | 0.045 | 0.639 | 0.639 | 0.289 | 0.289 | 0.477 | 0.477 | 0.790 | 0.790 |
| Parameter | Controls (n = 511) | T2DM (n = 600) | AOR a | p-Value a | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCF7L2 genotypes | |||||
| Dominant model | |||||
| CC genotype b | 496 (97.1) | 568 (94.7) | 1.00 | - | - |
| CT/TT genotype | 15 (2.9) | 32 (5.3) | 2.24 | 0.025 | 1.10–4.80 |
| Alleles | |||||
| C allele (%) | 1007 (98.5) | 1167 (97.3) | 0.20 | 0.016 | 0.05–0.75 |
| T allele (%) | 15 (1.5) | 33 (2.8) | 2.22 | 0.016 | 1.16–4.46 |
| All Subjects | Type 2 Diabetes | Controls | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | CC | CT + TT | p-Value | CC | CT + TT | p-Value | CC | CT + TT | p-Value |
| N | 1064 | 47 | 568 | 32 | 496 | 15 | |||
| Age | 61.0 ± 16.2 (60.0–61.9) | 65.5 ± 15.3 (61.0–70.0) | 0.062 | 73.3 ± 6.5 (72.8–73.8) | 74.0 ± 6.8 (71.5–76.5) | 0.549 | 46.9 ± 12.0 (45.8–48.0) | 47.4 ± 12.2 (40.6–54.2) | 0.777 |
| Sex (male/female) | 531/533 | 22/25 | 0.678 | 280/288 | 15/17 | 0.857 | 251/245 | 7/8 | 0.799 |
| BMI (male) (kg/m2) | 25.6 ± 3.7 (25.4–25.9) | 25.4 ± 3.5 (24.4–26.4) | 0.732 | 26.0 ± 3.7 (25.7–26.3) | 24.8 ± 3.5 (23.5–26.0) | 0.384 | 25.3 ± 3.6 (25.0–25.6) | 26.5 ± 3.3 (24.7–28.3) | 0.251 |
| BMI (female) (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 4.2 (24.2–24.8) | 23.7 ± 4.7 (22.3–25.0) | 0.329 | 24.0 ± 4.0 (23.8–24.3) | 26.1 ± 3.7 (24.7–27.4) | 0.024 | 22.7 ± 3.9 (22.4–23.0) | 23.1 ± 6.3 (19.6–26.6) | 0.716 |
| WHR (male) (cm) | 0.92 ± 0.07 (0.92–0.93) | 0.92 ± 0.07 (0.90–0.94) | 0.991 | 0.95 ± 0.06 (0.94–0.96) | 0.93 ± 0.08 (0.90–0.96) | 0.667 | 0.89 ± 0.07 (0.88–0.90) | 0.90 ± 0.05 (0.87–0.92) | 0.620 |
| WHR (female) (cm) | 0.85 ± 0.08 (0.84–0.85) | 0.85 ± 0.06 (0.83–0.87) | 0.655 | 0.89 ± 0.06 (0.88–0.90) | 0.87 ± 0.04 (0.86–0.88) | 0.132 | 0.79 ± 0.06 (0.78–0.80) | 0.82 ± 0.08 (0.77–0.86) | 0.470 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 130 ± 19 (128–131) | 132 ± 16 (127–137) | 0.413 | 134 ± 19 (132–136) | 132 ± 15 (126–137) | 0.618 | 124 ± 18 (122–126) | 131 ± 19 (120–142) | 0.238 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 77 ± 11 (76–78) | 79 ± 13 (75–83) | 0.351 | 78 ± 11 (77–79) | 79 ± 12 (74–83) | 0.633 | 77 ± 12 (75–78) | 79 ± 15 (71–87) | 0.370 |
| TCHOL (mg/dL) | 200.1 ± 40.7 (197.7–202.5) | 194.1 ± 33.1 (184.4–203.8) | 0.317 | 192.7 ± 40.4 (189.4–196.0) | 195.0 ± 33.2 (183.0–206.9) | 0.754 | 208.6 ± 39.3 (205.1–212.1) | 192.2 ± 33.9 (173.4–210.9) | 0.073 |
| TG (mg/dl) * | 107.0 (72.0–156.0) | 114.0 (75.0–174.0) | 0.206 | 122.5 (86.0–167.8) | 118.5 (83.3–199.8) | 0.220 | 92.0 (63.0–137.0) | 100.0 (52.0–143.0) | 0.958 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 55.7 ± 17.0 (54.7–56.7) | 54.0 ± 15.2 (49.5–58.5) | 0.501 | 50.8 ± 13.2 (49.7–51.9) | 51.8 ± 15.0 (46.3–57.2) | 0.680 | 61.2 ± 19.1 (59.5–62.9) | 58.5 ± 15.2 (50.1–66.9) | 0.670 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 119.4 ± 37.5 (119.8–125.9) | 110.7 ± 29.5 (102.0–119.4) | 0.115 | 108.8 ± 35.3 (105.9–111.7) | 107.3 ± 29.9 (96.5–118.0) | 0.808 | 131.5 ± 36.2 (128.3–134.7) | 117.9 ± 28.2 (102.2–133.5) | 0.109 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 122.9 ± 51.4 (119.8–125.9) | 140.5 ± 54.8 (124.4–156.6) | 0.023 | 150.9 ± 56.6 (146.2–155.6) | 162.5 ± 54.2 (142.9–182.0) | 0.111 | 90.8 ± 8.3 (90.0–91.5) | 95.3 ± 10.3 (89.6–101.0) | 0.043 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.0 ± 2.1 (6.8–7.1) | 7.4 ± 2.2 (6.8–8.0) | 0.216 | 8.3 ± 2.0 (8.1–8.5) | 8.3 ± 2.0 (7.6–9.0) | 0.727 | 5.5 ± 0.4 (5.4–5.5) | 5.5 ± 0.3 (5.3–5.6) | 0.508 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.9 ± 0.3 (0.8–0.9) | 0.9 ± 0.4 (0.8–1.0) | 0.784 | 1.0 ± 0.4 (0.9–1.0) | 1.0 ± 0.4 (0.9–1.1) | 0.588 | 0.8 ± 0.2 (0.7–0.8) | 0.8 ± 0.2 (0.7–0.9) | 0.527 |
| Hs-CRP (mg/L) * | 1.2 (0.5–3.5) | 1.3 (0.5–5.6) | 0.043 | 2.6 (0.8–7.0) | 3.6 (0.7–10.6) | 0.045 | 0.7 (0.4–1.9) | 0.8 (0.4–3.3) | 0.779 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.-C.; Yu, T.-H.; Hsuan, C.-F.; Hsu, C.-C.; Hung, W.-C.; Wang, C.-P.; Tang, W.-H.; Cheng, M.-C.; Chung, F.-M.; Lee, Y.-J.; et al. Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population: Clinical Characteristics and Ethnic Context. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162110
Lu Y-C, Yu T-H, Hsuan C-F, Hsu C-C, Hung W-C, Wang C-P, Tang W-H, Cheng M-C, Chung F-M, Lee Y-J, et al. Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population: Clinical Characteristics and Ethnic Context. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yung-Chuan, Teng-Hung Yu, Chin-Feng Hsuan, Chia-Chang Hsu, Wei-Chin Hung, Chao-Ping Wang, Wei-Hua Tang, Min-Chih Cheng, Fu-Mei Chung, Yau-Jiunn Lee, and et al. 2025. "Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population: Clinical Characteristics and Ethnic Context" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162110
APA StyleLu, Y.-C., Yu, T.-H., Hsuan, C.-F., Hsu, C.-C., Hung, W.-C., Wang, C.-P., Tang, W.-H., Cheng, M.-C., Chung, F.-M., Lee, Y.-J., & Lee, T.-L. (2025). Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) Polymorphism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population: Clinical Characteristics and Ethnic Context. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162110






