Differentiating Main-Duct IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid: A Pilot Study †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Pre-Procedural Workup
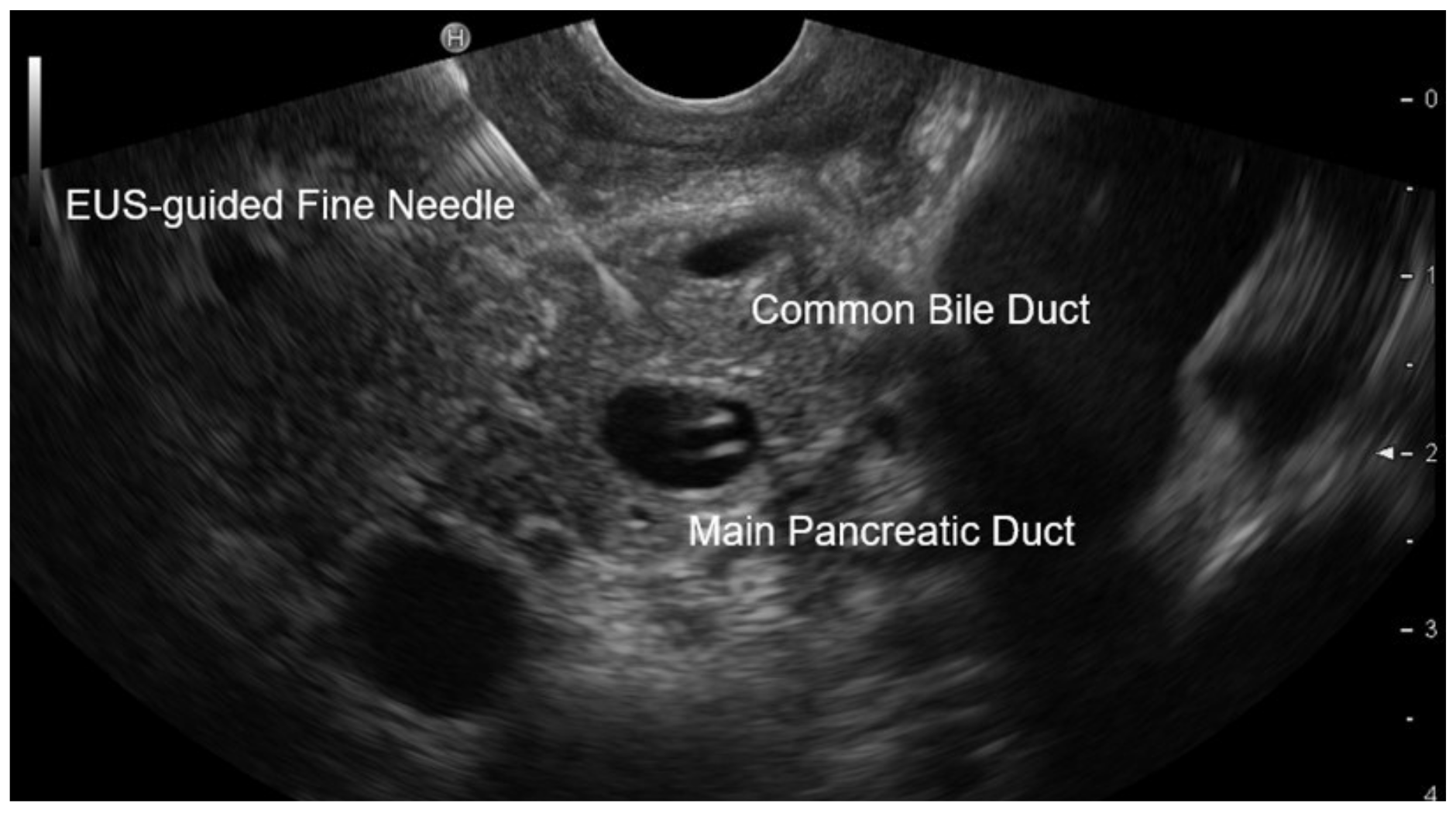
2.4. EUS Procedure
2.5. Analysis of Aspirated Pancreatic Duct Fluid
2.6. Analysis of Paraffin-Embedded Pancreatic Tissue Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Enrolment
3.2. Patient Characteristics
3.3. Analysis of Aspirated Pancreatic Duct Fluid
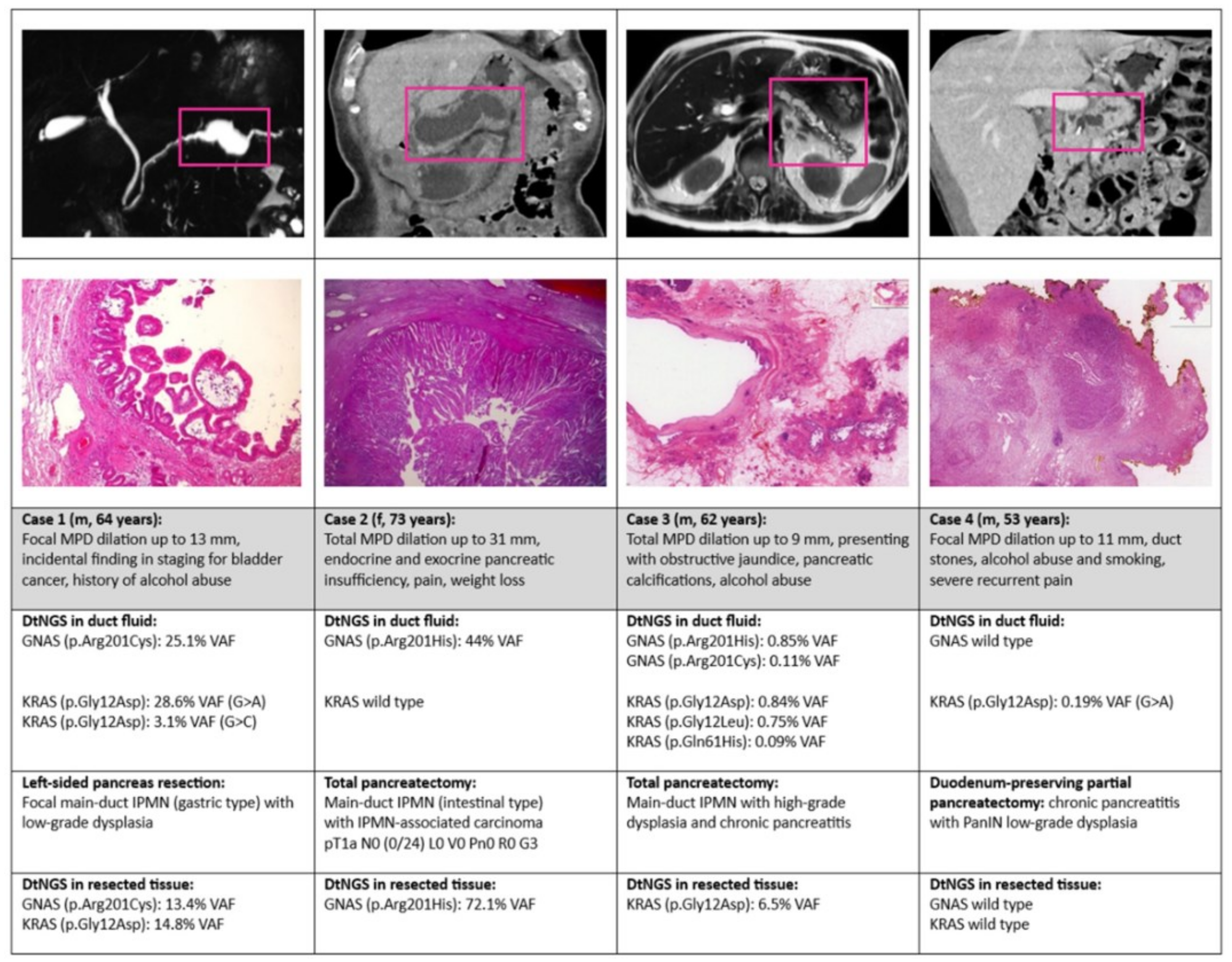
3.4. Presentation of Representative Cases Including Tissue DNA Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cfDNA | cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid |
| CP | chronic pancreatitis |
| dtNGS | deep targeted next-generation sequencing |
| ERCP | endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
| EUS | endoscopic ultrasound |
| HGD | high-grade dysplasia |
| LGD | low-grade dysplasia |
| MD-IPMN | main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| MPD | main pancreatic duct |
| PERT | pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy |
| PCL | pancreatic cyst lesion |
| VAF | variant allele frequency |
References
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Study Group on Cystic Tumours of the Pancreas. European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Gut 2018, 67, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vege, S.S.; Ziring, B.; Jain, R.; Moayyedi, P.; Clinical Guidelines Committee; American Gastroenterology Association. American gastroenterological association institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Isayama, H.; Gunji, T.; Sato, H.; Matsuhashi, N. Prevalence Rate and Predictive Factors of Pancreatic Diseases in Cases with Pancreatic Duct Dilation: A Cross-sectional Study of a Large, Healthy Japanese Population. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapiach, M.; Yadav, D.; Smyrk, T.C.; Fletcher, J.G.; Pearson, R.K.; Clain, J.E.; Farnell, M.B.; Chari, S.T. Calcifying obstructive pancreatitis: A study of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm associated with pancreatic calcification. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Raijman, I.; Machicado, J.D.; Edmundowicz, S.A.; Shah, R.J. Per Oral Pancreatoscopy Identification of Main-duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms and Concomitant Pancreatic Duct Stones: Not Mutually Exclusive. Pancreas 2019, 48, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Johnston, R.; Narin, O.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Ingkakul, T.; Warshaw, A.; Castillo, C.F.-D.; Sahani, V. Frequency and significance of calcification in IPMN. Pancreatology 2013, 13, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, R.; Malleo, G.; Marchegiani, G.; Pennacchio, S.; Paiella, S.; Paini, M.; Pea, A.; Butturini, G.; Pederzoli, P.; Bassi, C. Pancreatic resections for cystic neoplasms: From the surgeon’s presumption to the pathologist’s reality. Surgery 2012, 152 (Suppl. S1), S135–S142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Wang, Y.; Dal Molin, M.; Masica, D.L.; Jiao, Y.; Kinde, I.; Blackford, A.; Raman, S.P.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Tomita, T.; et al. A combination of molecular markers and clinical features improve the classification of pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; McGrath, K.; Brand, R.E.; Khalid, A.; Zeh, H.J.; Chennat, J.S.; Fasanella, K.E.; Papachristou, G.I.; Slivka, A.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. Preoperative next-generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid is highly accurate in cyst classification and detection of advanced neoplasia. Gut 2018, 67, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.; Kazdal, D.; Allgäuer, M.; Trunk, M.; Vornhusen, S.; Nahm, A.-M.; Doll, M.; Weingärtner, S.; Endris, V.; Penzel, R.; et al. KRAS/GNAS-testing by highly sensitive deep targeted next generation sequencing improves the endoscopic ultrasound-guided workup of suspected mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2021, 60, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugge, W.R.; Lewandrowski, K.; Lee-Lewandrowski, E.; Centeno, B.A.; Szydlo, T.; Regan, S.; del Castillo, C.F.; Warshaw, A.L. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, M.B.; Centeno, B.A.; Reid, M.D.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Layfield, L.J.; Perez-Machado, M.; Weynand, B.; Stelow, E.B.; Lozano, M.D.; Fukushima, N.; et al. The World Health Organization Reporting System for Pancreaticobiliary Cytopathology. Acta Cytol. 2023, 67, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volckmar, A.L.; Endris, V.; Gaida, M.M.; Leichsenring, J.; Stögbauer, F.; Allgäuer, M.; von Winterfeld, M.; Penzel, R.; Kirchner, M.; Brandt, R.; et al. Next generation sequencing of the cellular and liquid fraction of pancreatic cyst fluid supports discrimination of IPMN from pseudocysts and reveals cases with multiple mutated driver clones: First findings from the prospective ZYSTEUS biomarker study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Ni, C.Y.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; Li, L.; Lin, Y.; Xia, Z.S.; Wu, W.R.; Chen, Q.K.; Zhong, W. Acute pancreatitis in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: A single-center retrospective cohort study with systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Ideno, N.; Kono, H.; Nagayoshi, Y.; Mori, Y.; Ohuchida, K.; Ueda, J.; Takahata, S.; Morimatsu, K.; et al. Diagnostic significance of a dilated orifice of the duodenal papilla in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Sadler, T.J.; Whitley, S.; Brais, R.; Godfrey, E. The CT fish mouth ampulla sign: A highly specific finding in main duct and mixed intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levink, I.J.M.; Jaarsma, S.C.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Van Riet, P.A.; Overbeek, K.A.; Meziani, J.; Sprij, M.L.J.A.; Casadei, R.; Ingaldi, C.; Polkowski, M.; et al. The additive value of CA19.9 monitoring in a pancreatic cyst surveillance program. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2023, 11, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesak, B.; Harlozinska-Szmyrka, A.; Knast, W.; Sedlaczek, P.; van Dalen, A.; Einarsson, R. Tissue polypeptide specific antigen (TPS), a marker for differentiation between pancreatic carcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. A comparative study with CA 19-9. Cancer 2000, 89, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Stanley, M.W.; Bardales, R.; Linzie, B.; Mallery, S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct aspiration: Diagnostic yield and safety. Endoscopy 2002, 34, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thosani, N.; Thosani, S.; Qiao, W.; Fleming, J.B.; Bhutani, M.S.; Guha, S. Role of EUS-FNA-based cytology in the diagnosis of mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, G.D.; McPhail, M.J.; Nayagam, S.; Hewitt, M.J.; Vlavianos, P.; Monahan, K.J. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2013, 13, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faias, S.; Cravo, M.; Chaves, P.; Pereira, L. Comparative analysis of glucose and carcinoembryonic antigen in the diagnosis of pancreatic mucinous cysts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Fukasawa, M.; Maekawa, S.; Kadokura, M.; Miura, M.; Shindo, H.; Takahashi, E.; Sato, T.; Enomoto, N.; Hoheisel, J.D. Deep sequencing of cancer-related genes revealed GNAS mutations to be associated with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and its main pancreatic duct dilation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Matthaei, H.; Maitra, A.; Dal Molin, M.; Wood, L.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Goggins, M.; Canto, M.I.; Schulick, R.D.; Edil, B.H. Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 92ra66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhi, A.D.; Wood, L.D. Early detection of pancreatic cancer using DNA-based molecular approaches. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, M.; Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. K-Ras mutations and benign pancreatic disease. Int. J. Pancreatol. 2000, 27, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.G.; Wood, L.D. From somatic mutation to early detection: Insights from molecular characterization of pancreatic cancer precursor lesions. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleo, A.; Forte, G.; Fasano, C.; Signorile, M.L.; Sanese, P.; De Marco, K.; Di Nicola, E.; Latrofa, M.; Grossi, V.; Disciglio, V.; et al. Understanding the Genetic Landscape of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma to Support Personalized Medicine: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflüger, M.J.; Jamouss, K.T.; Afghani, E.; Lim, S.J.; Franco, S.R.; Mayo, H.; Spann, M.; Wang, H.; Singhi, A.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Predictive ability of pancreatic cyst fluid biomarkers: A systematic review and meta- analysis. Pancreatology 2023, 23, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.W.; Pratt, E.D.; Kang, J.M.; Zhao, J.; Wilhelm, J.J.; Abdulla, M.; Qiao, E.M.; Brennan, L.P.; Ulintz, P.J.; Bellin, M.D.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer-Related Mutational Burden Is Not Increased in a Patient Cohort with Clinically Severe Chronic Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2017, 29, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.E.; Flick, K.F.; Gromski, M.A.; Al-Haddad, M.A.M.; Easler, J.J.; Sherman, S.; Fogel, E.L.M.; Schmidt, C.M.M.; DeWitt, J.M. Utility of DNA Profiling From Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid by Endoscopic Ultra- sound and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography to Screen for Malignant Potential. Pancreas 2020, 49, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D. Autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer: Epidemiological aspects and immunological considerations. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.; Prax, S.; Kliment, M.; Kazdal, D.; Allgäuer, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Stenzinger, A.; Ritz, J.P.; Volckmar, A.L. Differentiation of MD-IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis by cfDNA Next Generation Sequencing from Ductal Fluid Using EUS-Guided FNA: A Prospective Controlled Study. Endoscopy 2025, 57 (Suppl. S2), S44–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All n = 22 | Main-Duct IPMN n = 12 | Chronic Pancreatitis n = 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age in years: mean (range) | 70.5 (52–82) | 74.3 (62–83) | 65.9 (52–80) |
| Sex (m/f/d) | 13/9/0 | 6/6/0 | 7/3/0 |
| Medical history | |||
| 6 | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Symptoms | |||
| 15 | 7 | 8 |
| 11 | 9 | 2 |
| 10 | 6 | 4 |
| 7 | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Main pancreatic duct dilation | |||
| 15 | 10 | 5 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 |
| MPD diameter in mm: mean (range) | 12.4 (7–31) | 13.5 (8–31) | 11.1 (7–30) |
| Pancreas with calcification or duct stone (s) 2 | 12 | 5 | 7 |
| Fish-mouth papilla | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Worrisome features 3 | |||
| 9 | 3 | 6 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 1 |
| 4 | 4 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| High-risk stigmata 4 | |||
| 13 | 9 | 4 |
| 6 | 5 | 1 |
| 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Main-duct IPMN | |||
| 7 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 | ||
| Chronic pancreatitis | |||
| 4 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 1 | ||
| Final diagnosis made by | |||
| 9 | 7 | 2 |
| 8 | 1 | 7 |
| 5 | 4 | 1 |
| All n = 22 | Main-Duct IPMN n = 12 | Chronic Pancreatitis n = 10 | |
| Cytology in duct fluid consistent with mucinous neoplasia: n (%) 1 | 2/19 (10.5%) | 2/11 (18.2%) | 0/8 (0.0%) |
| CEA in duct fluid in ng/mL: mean (range) 2 | 957 (2–9370) | 1412 (2–9370) | 275 (2–1399) |
| CEA in duct fluid ≥ 192 ng/mL: n (%) | 6/14 (42.9%) | 4/8 (50.0%) | 2/6 (33.3%) |
| cfDNA-NGS of variant GNAS/KRAS gene in duct fluid: n (%) | |||
| 11 (50.0%) | 11 (91.6%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 8 (36.4%) | 8 (66.6%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 3 (13.6%) | 3 (25.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 11 (50.0%) | 9 (75.0%) | 2 (20.0%) |
| 4 (18.2%) | 3 (25.0%) | 1 (10.0%) |
| 7 (31.8%) | 6 (50.0%) | 1 (10.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmitz, D.; Prax, S.; Kliment, M.; Gocke, F.; Kazdal, D.; Allgäuer, M.; Penzel, R.; Kirchner, M.; Neumann, O.; Sültmann, H.; et al. Differentiating Main-Duct IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151964
Schmitz D, Prax S, Kliment M, Gocke F, Kazdal D, Allgäuer M, Penzel R, Kirchner M, Neumann O, Sültmann H, et al. Differentiating Main-Duct IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151964
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmitz, Daniel, Stefan Prax, Martin Kliment, Felix Gocke, Daniel Kazdal, Michael Allgäuer, Roland Penzel, Martina Kirchner, Olaf Neumann, Holger Sültmann, and et al. 2025. "Differentiating Main-Duct IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid: A Pilot Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151964
APA StyleSchmitz, D., Prax, S., Kliment, M., Gocke, F., Kazdal, D., Allgäuer, M., Penzel, R., Kirchner, M., Neumann, O., Sültmann, H., Budczies, J., Schirmacher, P., Bergmann, F., Ritz, J.-P., Hinze, R., Grassmann, F., Rudi, J., Stenzinger, A., & Volckmar, A.-L. (2025). Differentiating Main-Duct IPMN from Chronic Pancreatitis Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Main Pancreatic Duct Fluid: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151964








