Disturbances in Resting State Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: A Study of Hippocampal Subregions, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and Functional Brain Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Dataset
2.2. MRI Data Acquisition
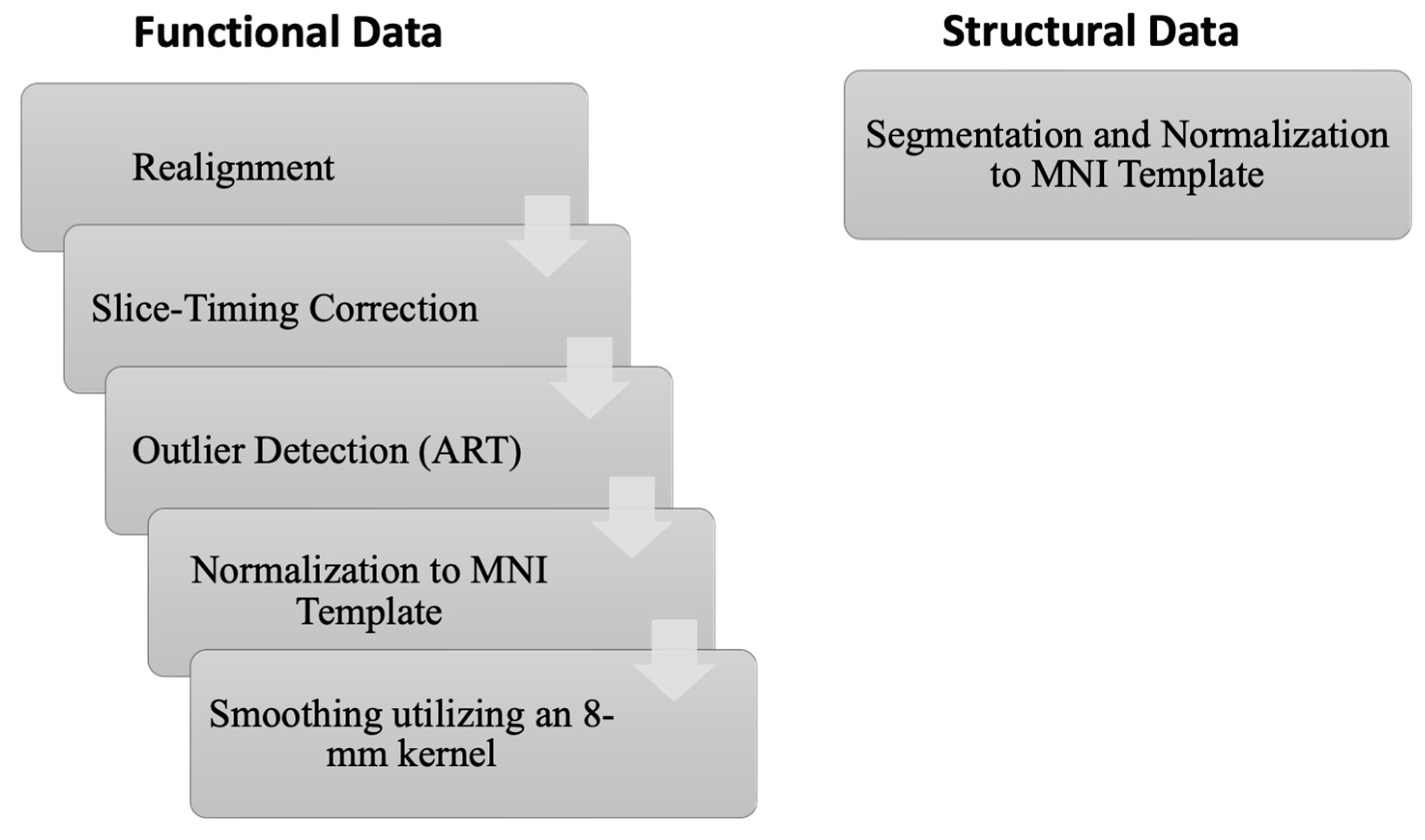
2.3. MRI Data Preprocessing
2.4. Selection of the Regions of Interest
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
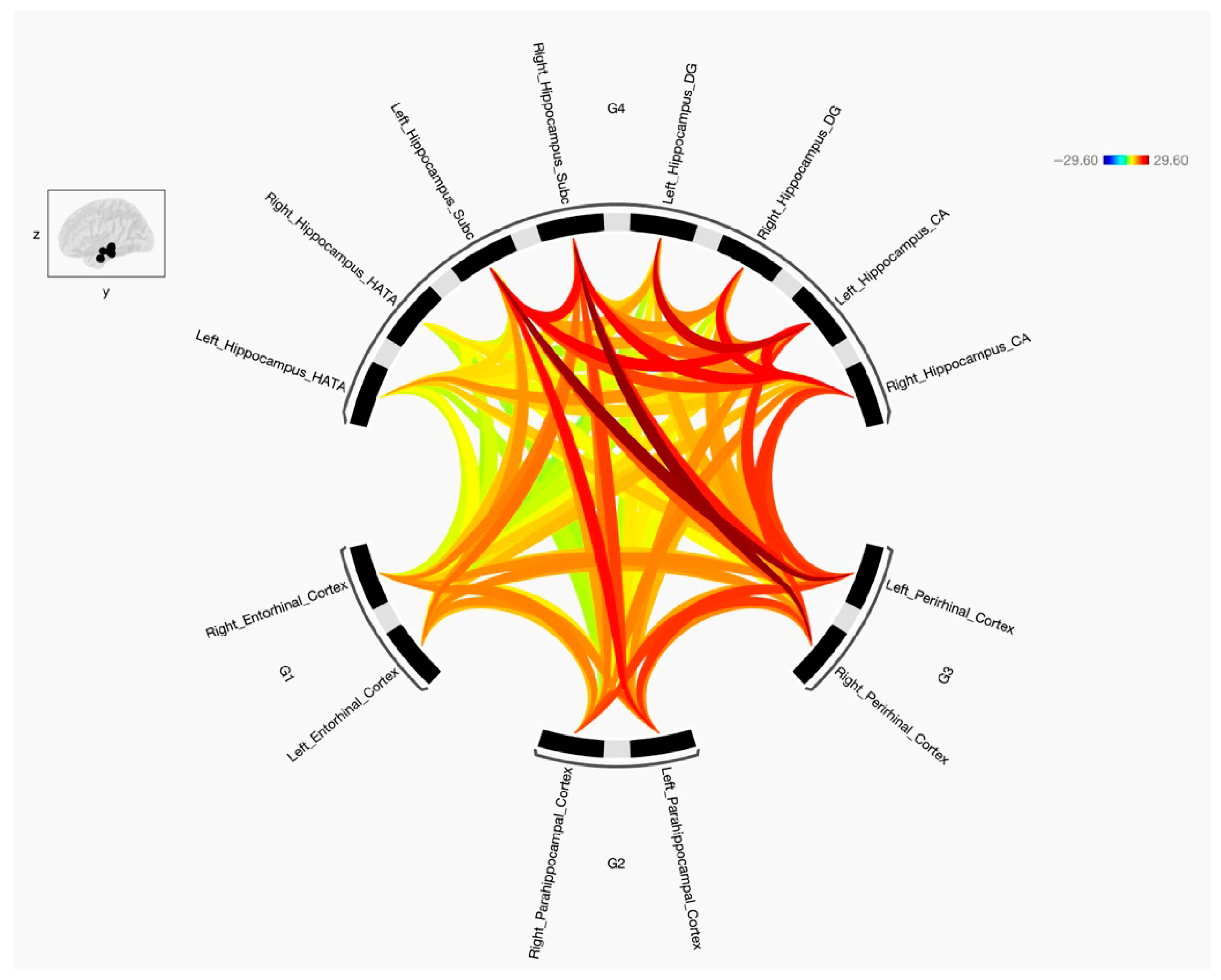
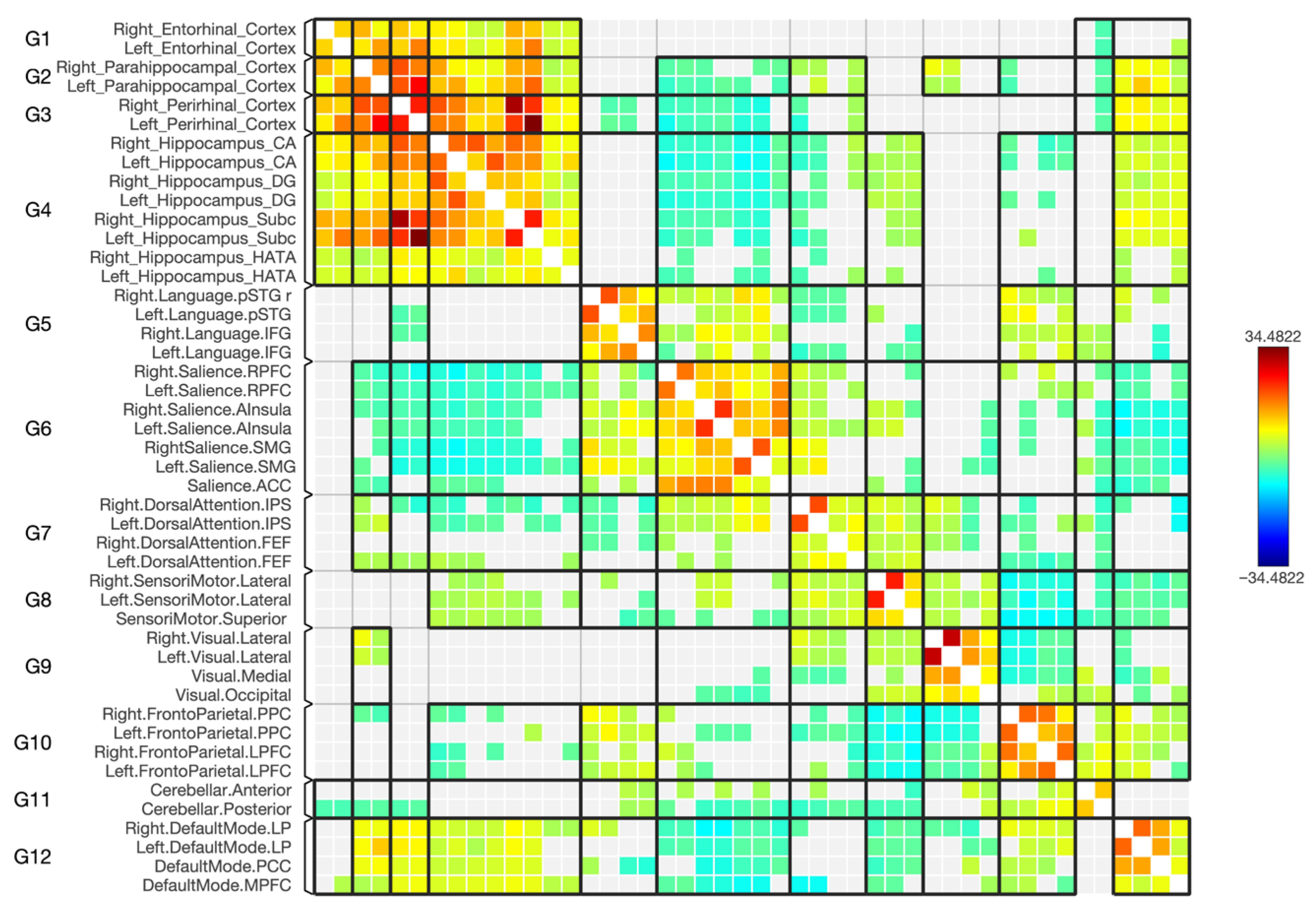
3.1. Changes in Functional Connectivity in the Parahippocampal Gyrus Cortices
3.2. Resting State Functional Connectivity Between ERC, PRC, PHC and Hippocampal Subregions
3.3. Functional Connectivity with the Default Mode Network (DMN)
3.4. Functional Connectivity with the Frontoparietal Network
3.5. Functional Connectivity with the Sensorimotor Network
3.6. Functional Connectivity with the Dorsal Attention Network
3.7. Functional Connectivity with the Salience Network
3.8. Functional Connectivity with the Visual Network
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Connectivity Between Parahippocampal Cortices and Hippocampal Subregions
4.2. Changes in the Hippocampal Subregion’s Connectivity with Functional Brain Networks
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gogtay, N.; Vyas, N.S.; Testa, R.; Wood, S.J.; Pantelis, C. Age of onset of schizophrenia: Perspectives from structural neuroimaging studies. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Cherian, J.; Gohil, K.; Atkinson, D. Schizophrenia: Overview and Treatment Options. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 638–645. [Google Scholar]
- Raslau, F.D.; Mark, I.T.; Klein, A.P.; Ulmer, J.L.; Mathews, V.; Mark, L.P. Memory Part 2: The Role of the Medial Temporal Lobe. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantonis, J.A.; Carruthers, S.P.; Rossell, S.L.; Pantelis, C.; Hughes, M.; Wannan, C.; Cropley, V.; Van Rheenen, T.E. A Systematic Review of Cognition-Brain Morphology Relationships on the Schizophrenia-Bipolar Disorder Spectrum. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 1557–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, R.; Matsumoto, J.; Ito, S.; Nemoto, K.; Fukunaga, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Kodaka, F.; Takano, H.; Hasegawa, N.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. Longitudinal reduction in brain volume in patients with schizophrenia and its association with cognitive function. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2024, 44, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, H.; Steffenach, H.A.; Van Strien, N.M.; Veltman, D.J.; Witter, M.P.; Håberg, A.K. A specific role of the human hippocampus in recall of temporal sequences. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, I.; Davachi, L.; Wagner, A.D. Functional-Neuroanatomic Correlates of Recollection: Implications for Models of Recognition Memory. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, C.; Yonelinas, A.P.; Cohen, M.X.; Dy, C.J.; Tom, S.M.; D’Esposito, M. Dissociable correlates of recollection and familiarity within the medial temporal lobes. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.R.; Graham, K.S.; Xuereb, J.H.; Williams, G.B.; Hodges, J.R. The human perirhinal cortex and semantic memory. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2441–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.H.; Buckley, M.J.; Gaffan, D.; Emery, T.; Hodges, J.R.; Graham, K.S. Differentiating the roles of the hippocampus and perirhinal cortex in processes beyond long-term declarative memory: A double dissociation in dementia. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5198–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, A.; Hijman, R.; De Haan, E.H.F.; Kahn, R.S. Memory Impairment in Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, R.W.; Zakzanis, K.K. Neurocognitive Deficit in Schizophrenia: A Quantitative Review of the Evidence. Neuropsychology 1998, 12, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saykin, A.J.; Gur, R.C.; Gur, R.E.; Mozley, P.D.; Mozley, L.H.; Resnick, S.M.; Kester, D.B.; Stafiniak, P. Neuropsychological Function in Schizophrenia Selective Impairment in Memory and Learning. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1991, 48, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Kedo, O.; Kindler, M.; Pieperhoff, P.; Mohlberg, H.; Shah, N.J.; Habel, U.; Schneider, F.; Zilles, K. Cytoarchitectonic mapping of the human amygdala, hippocampal region and entorhinal cortex: Intersubject variability and probability maps. Anat. Embryol. 2005, 210, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilles, K.; Amunts, K. Centenary of Brodmann’s map conception and fate. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Stephan, K.E.; Mohlberg, H.; Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, M.; Wei, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wu, F.; et al. Shared and Distinct Functional Connectivity of Hippocampal Subregions in Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 993356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Ye, Y.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Liang, S.; Xia, R.; Chen, Y. Deviations in Hippocampal Subregion in Older Adults With Cognitive Frailty. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 12, 615852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Allen, E.A.; Sui, J.; Arbabshirani, M.R.; Pearlson, G.; Calhoun, V.D. Brain connectivity networks in schizophrenia underlying resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, C.; Yan, Y. Impaired large-scale cortico–hippocampal network connectivity, including the anterior temporal and posterior medial systems, and its associations with cognition in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1167942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugré, J.R.; Dumais, A.; Tikasz, A.; Mendrek, A.; Potvin, S. Functional connectivity abnormalities of the long-axis hippocampal subregions in schizophrenia during episodic memory. NPJ Schizophr. 2021, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgolewski, K.J.; Durnez, J.; Poldrack, R.A. Preprocessed Consortium for Neuropsychiatric Phenomics dataset. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Congdon, E.; Triplett, W.; Gorgolewski, K.J.; Karlsgodt, K.H.; Mumford, J.A.; Sabb, F.W.; Freimer, N.B.; London, E.D.; Cannon, T.D.; et al. A Phenome-Wide Examination of Neural and Cognitive Function. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A Functional Connectivity Toolbox for Correlated and Anticorrelated Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N.; Goldstein, J.M.; Kennedy, D.; Hodge, S.M.; Caviness, V.S.; Faraone, S.V.; Tsuang, M.T.; Papadimitriou, G.N.; Pandya, D.N.; Shenton, M.E.; et al. Decreased volume of left and total anterior insular lobule in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 83, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, J.A.; Chiu, S.; Breeze, J.L.; Makris, N.; Lange, N.; Kennedy, D.N.; Herbert, M.R.; Bent, E.K.; Koneru, V.K.; Dieterich, M.E.; et al. Article Structural Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Limbic and Thalamic Volumes in Pediatric Bipolar Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2005, 162, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.M.; Seidman, L.J.; Makris, N.; Ahern, T.; O’Brien, L.M.; Caviness, V.S.; Kennedy, D.N.; Faraone, S.V.; Tsuang, M.T.; Hodge, S.M.; et al. Hypothalamic Abnormalities in Schizophrenia: Sex Effects and Genetic Vulnerability. Biol Psychiatry. 2007, 61, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, M.J.; Pearlson, G.D.; Stevens, M.; Calhoun, V.D. A method for functional network connectivity among spatially independent resting-state components in schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1666–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 5, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumbley, J.; Worsley, K.; Flandin, G.; Friston, K. Topological FDR for neuroimaging. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, D.R.; Berman, K.F.; Suddath, R.; Fuller Torrey, E. Evidence of Dysfunction of a Prefrontal-Limbic Network in Schizophrenia: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Regional Cerebral Blood Flow Study of Discordant Monozygotic Twins. Am. J. Psychiatry 1992, 149, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, D.R. Cell Biology of the Hippocampal Formation in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckers, S.; Konradi, C. Hippocampal neurons in schizophrenia. J. Neural Transm. 2002, 109, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Fukunaga, M.; Yamashita, F.; Koshiyama, D.; Yamamori, H.; Ohi, K.; Yasuda, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Hashimoto, R.; et al. Abnormal asymmetries in subcortical brain volume in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, V.M.; Goldberg, T.E. Episodic memory in schizophrenia. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2009, 19, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraguljac, N.V.; Srivastava, A.; Lahti, A.C. Memory deficits in Schizophrenia: A selective review of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies. Behav. Sci. 2013, 3, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, S.; Matsumoto, M.; van Erp, T.G.M. Hippocampal subregion abnormalities in schizophrenia: A systematic review of structural and physiological imaging studies. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2018, 38, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, B.A.; Witter, M.P.; Lein, E.S.; Moser, E.I. Functional organization of the hippocampal longitudinal axis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassa, M.A.; Stark, C.E.L. Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.F.; Iglesias, J.E.; Sum, M.Y.; Kuswanto, C.N.; Sitoh, Y.Y.; De Souza, J.; Lai, R.W.T.; Lee, W.L.; Lee, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Progression from selective to general involvement of hippocampal subfields in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.F.; Holt, D.J.; Cheung, M.; Iglesias, J.E.; Goh, A.; Wang, M.; Lee, W.L.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Lee, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Progressive Decline in Hippocampal CA1 Volume in Individuals at Ultra-High-Risk for Psychosis Who Do Not Remit: Findings from the Longitudinal Youth at Risk Study. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierhut, K.C.; Graßmann, R.; Kaufmann, J.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Schiltz, K. Hippocampal CA1 deformity is related to symptom severity and antipsychotic dosage in schizophrenia. Brain 2013, 136, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, N.; MacIntosh, B.J.; Hough, M.G.; Goodwin, G.M.; Frisoni, G.B.; Smith, S.M.; Matthews, P.M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Mackay, C.E. Distinct Patterns of Brain Activity in Young Carriers of the APOE-ε4 Allele. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7209–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talelli, P.; Waddingham, W.; Ewas, A.; Rothwell, J.C.; Ward, N.S. The effect of age on task-related modulation of interhemispheric balance. Exp. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.; Bakker, A.; Yassa, M.A.; Stark, C.E.L. Bridging Neurocognitive Aging and Disease Modification: Targeting Functional Mechanisms of Impairment. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassa, M.A.; Stark, S.M.; Bakker, A.; Albert, M.S.; Gallagher, M.; Stark, C.E.L. High-resolution structural and functional MRI of hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus in patients with amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesli, N.; van der Meer, D.; Rokicki, J.; Storvestre, G.; Røsæg, C.; Jensen, A.; Bjerkan, P.S.; Løvstad, M.; Ueland, T.; Andreassen, O.A.; et al. Hippocampal subfield and amygdala nuclei volumes in schizophrenia patients with a history of violence. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 270, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Han, H.; Jin, L.; Xu, C.; Dong, D.; Lu, J.; Wan, G.; Peng, Z. An Effect of Chronic Stress on Prospective Memory via Alteration of Resting-State Hippocampal Subregion Functional Connectivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Kitanishi, T.; Mizuseki, K. The subiculum: Unique hippocampal hub and more. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 143, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.W.; Cheong, C. Functional dissociation of hippocampal subregions corresponding to memory types and stages. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2020, 39, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminoff, E.M.; Kveraga, K.; Bar, M. The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2013, 17, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.S.; Lee, I. Disconnection of the hippocampal-perirhinal cortical circuits severely disrupts object-place paired associative memory. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9850–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.; DeWitt, I.; Ditman, T.; Zalesak, M.; Greenhouse, I.; Goff, D.; Heckers, S. Hippocampal and parahippocampal volumes in schizophrenia: A structural MRI study. Schizophr. Bull. 2006, 32, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talamini, L.M.; Meeter, M.; Elvevåg, B.; Murre, J.M.J.; Goldberg, T.E. Reduced Parahippocampal Connectivity Produces Schizophrenia-like Memory Deficits in Simulated Neural Circuits with Reduced Parahippocampal Connectivity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knierim, J.J.; Neunuebel, J.P.; Deshmukh, S.S. Functional correlates of the lateral and medial entorhinal cortex: Objects, path integration and local–global reference frames. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maass, A.; Berron, D.; Libby, L.A.; Ranganath, C.; Düzel, E. Functional subregions of the human entorhinal cortex. Elife 2015, 4, e06426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.M.; Patel, A.R.; Muddasani, S.; Sweeney, J.; Keshavan, M.S. Article the Entorhinal Cortex in First-Episode Psychotic Disorders: A Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Basavanagowda, D.M.; Rathod, B.; Mishra, N.; Fuad, S.; Nosher, S.; Nagaraju, H.; Sridhar, S.; Sulaiman, F.N.; Ranjan, R.; et al. Structural and Functional Alterations of the Temporal lobe in Schizophrenia: A Literature Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniades, M.; Schoeler, T.; Radua, J.; Valli, I.; Allen, P.; Kempton, M.J.; McGuire, D.; McGuire, P.; Shergill, S.S.; Costafreda, L.G.; et al. Verbal learning and hippocampal dysfunction in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 86, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; He, C.; Ou, J.; Wang, R.; Xiao, J.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Qi, S.; Wang, T.; et al. Reduced Hippocampal Volume and Its Relationship with Verbal Memory and Negative Symptoms in Treatment-Naive First-Episode Adolescent-Onset Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Corbetta, M.; Van Essen, D.C.; Raichle, M.E. The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 5, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Fox, M.D. Towards a consensus regarding global signal regression for resting state functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2017, 154, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenbacher, A.; Kasess, C.; Gerstl, F.; Lanzenberger, R.; Moser, E.; Windischberger, C. Correlations and anticorrelations in resting-state functional connectivity MRI: A quantitative comparison of preprocessing strategies. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichle, M.E.; MacLeod, A.M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Powers, W.J.; Gusnard, D.A.; Shulman, G.L. A Default Mode of Brain Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, M.D.; Krasnow, B.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V.; Raichle, M.E. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusnard, D.A.; Raichle, M.E. Searching for a baseline: Functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusnard, D.A.; Akbudak, E.; Shulman, G.L.; Raichle, M.E. Medial prefrontal cortex and self-referential mental activity: Relation to a default mode of brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4259–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Liu, F.; Xiao, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Increased short-range and long-range functional connectivity in first-episode, medication-naive schizophrenia at rest. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 166, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, F.; Xiao, C.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Increased causal connectivity related to anatomical alterations as potential Endophenotypes for schizophrenia. Medicine 2015, 94, e1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guo, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, G.; Lyu, H.; Wu, R.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Tan, C.; et al. Patients with first-episode, drug-naive schizophrenia and subjects at ultra-high risk of psychosis shared increased cerebellar-default mode network connectivity at rest. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotarska-Jagiela, A.; van de Ven, V.; Oertel-Knöchel, V.; Uhlhaas, P.J.; Vogeley, K.; Linden, D.E.J. Resting-state functional network correlates of psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 117, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Jung, W.H.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, C.H.; Kang, D.H.; Shin, N.Y.; Hong, K.S.; Kwon, J.S.; Namkoong, K.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Reduced prefrontal functional connectivity in the default mode network is related to greater psychopathology in subjects with high genetic loading for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 127, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camchong, J.; MacDonald, A.W.; Bell, C.; Mueller, B.A.; Lim, K.O. Altered functional and anatomical connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öngür, D.; Lundy, M.; Greenhouse, I.; Shinn, A.K.; Menon, V.; Cohen, B.M.; Renshaw, P.F.; Lafer, B.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Dougherty, D.D.; et al. Default mode network abnormalities in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2010, 183, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingoia, G.; Wagner, G.; Langbein, K.; Maitra, R.; Smesny, S.; Dietzek, M.; Burmeister, H.P.; Reichenbach, J.R.; Schlösser, R.G.; Gaser, C.; et al. Default mode network activity in schizophrenia studied at resting state using probabilistic ICA. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 138, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, A.A.S.; Alotaibi, N.O.; Hakami, N.Y.; Almutairi, R.S.; Darwesh, A.M.F.; Abdeen, R.; Alanazi, T.M.; Alyami, M.A.; Alqahtani, M.A.; Alharbi, A.F.; et al. Gender and cytoarchitecture differences: Functional connectivity of the hippocampal sub-regions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Thermenos, H.W.; Milanovic, S.; Tsuang, M.T.; Faraone, S.V.; McCarley, R.W.; Shenton, M.E.; Green, A.I.; Nieto-Castanon, A.; LaViolette, P.; et al. Hyperactivity and hyperconnectivity of the default network in schizophrenia and in first-degree relatives of persons with schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraguljac, N.V.; White, D.M.; Hadley, N.; Hadley, J.A.; ver Hoef, L.; Davis, E.; Lahti, A.C. Aberrant hippocampal connectivity in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia and effects of antipsychotic medication: A longitudinal resting state functional MRI study. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, N.; Zhang, W.; Tao, B.; Dai, J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; et al. Dysconnectivity of multiple brain networks in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Yin, Z.; Cui, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Tan, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Association between NRGN gene polymorphism and resting-state hippocampal functional connectivity in schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, E.M.; Murty, V.P.; Zeng, B.; Wang, J.; Davachi, L.; Goff, D.C. Anterior Hippocampal-Cortical Functional Connectivity Distinguishes Antipsychotic Naïve First-Episode Psychosis Patients from Controls and May Predict Response to Second-Generation Antipsychotic Treatment. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudra, N.; Ivleva, E.I.; Hubbard, N.A.; Rypma, B.; Sweeney, J.A.; Clementz, B.A.; Pearlson, G.D.; Keedy, S.K.; Tamminga, C.A.; Calhoun, V.D.; et al. Alterations in hippocampal connectivity across the psychosis dimension. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2015, 233, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniyappan, L.; Liddle, P.F. Does the salience network play a cardinal role in psychosis? An emerging hypothesis of insular dysfunction. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012, 37, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, V.; Rotarska-Jagiela, A.; van de Ven, V.G.; Haenschel, C.; Maurer, K.; Linden, D.E.J. Visual hallucinations in schizophrenia investigated with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2007, 156, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makhdoum, R.M.; Alahmadi, A.A.S. Disturbances in Resting State Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: A Study of Hippocampal Subregions, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and Functional Brain Networks. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151955
Makhdoum RM, Alahmadi AAS. Disturbances in Resting State Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: A Study of Hippocampal Subregions, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and Functional Brain Networks. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151955
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakhdoum, Raghad M., and Adnan A. S. Alahmadi. 2025. "Disturbances in Resting State Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: A Study of Hippocampal Subregions, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and Functional Brain Networks" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151955
APA StyleMakhdoum, R. M., & Alahmadi, A. A. S. (2025). Disturbances in Resting State Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia: A Study of Hippocampal Subregions, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and Functional Brain Networks. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151955





