Genogroup-Specific Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Norovirus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primer Design for NoV RT-LAMP Assay
2.2. RNA and Plasmid Preparation
2.3. RT-LAMP Assay
2.4. Optimization of the NoV RT-LAMP Reaction
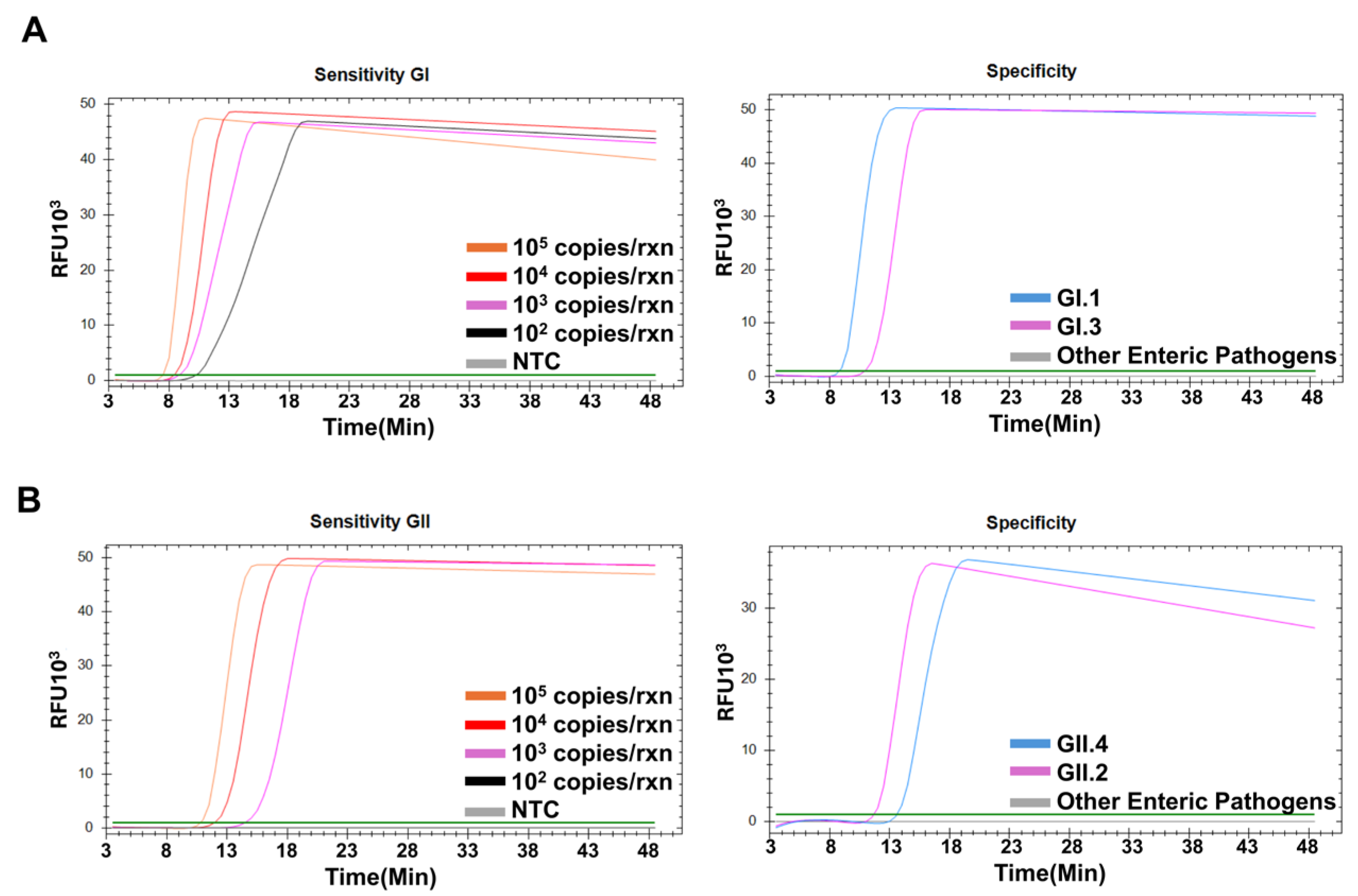
2.5. Sensitivity and Specificity of the NoV RT-LAMP Assays
2.6. Application to Point-of-Care Platform
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of NoV RT-LAMP Conditions
3.2. Sensitivity and Specificity of NoV RT-LAMP Assays
3.3. Application of RT-LAMP Assay Under POCT Platform
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deb, S.; Mondal, R.; Lahiri, D.; Shome, G.; Roy, A.G.; Sarkar, V.; Sarkar, S.; Benito-León, J. Norovirus-associated neurological manifestations: Summarizing the evidence. J. Neurovirol. 2023, 29, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.J.; Wikswo, M.E.; Pringle, K.; Gould, L.H.; Parashar, U.D. Vital Signs: Foodborne norovirus outbreaks—United States, 2009–2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, K.B.; Dilley, A.; O’Grady, T.; Johnson, J.A.; Lopman, B.; Viscidi, E. A narrative review of Norovirus epidemiology, biology, and challenges to vaccine development. Npj Vaccines 2024, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, N.; Lopman, B.A.; Parashar, U.D.; Hall, A.J. Progress toward Norovirus vaccines: Considerations for further development and implementation in potential target populations. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M. Norovirus vaccines: Current clinical development and challenges. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, L.; Park, G.W.; Vega, E.; Hall, A.; Parashar, U.; Vinjé, J.; Lopman, B. Infection control for Norovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; de Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.W.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of Norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-N.; Chang, Y.C.; Chao, H.C.; Hsu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, S.Y. Emerging Norovirus GII.12 infection in 2010 in Northern Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2025, 124, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marpaung, D.S.S.; Yap Sinaga, A.O.Y.; Damayanti, D. Norovirus detection technologies: From conventional methods to innovative biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2025, 698, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butot, S.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Krol, J.; Putallaz, T.; Amoroso, R.; Sánchez, G. Evaluation of various real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection and quantitation of human Norovirus. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 167, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Das, S.; Ahmed, R.; Mori, Y.; Notomi, T.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Thakor, A.S. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, sensitive, specific, and cost-effective point-of-care test for coronaviruses in the context of COVID-19 pandemic. Biology 2020, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. Advancements and applications of loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology: A comprehensive overview. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1406632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thippornchai, N.; Pengpanich, S.; Jaroenram, W.; Kosoltanapiwat, N.; Sukphopetch, P.; Kiatpathomchai, W.; Leaungwutiwong, P. A colorimetric reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification method targeting the L452R mutation to detect the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S.; Seo, M.R.; Chung, Y.J. Development of reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for point-of-care testing of human influenza virus subtypes H1N1 and H3N2. Genom. Inform. 2022, 20, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atceken, N.; Munzer Alseed, M.; Dabbagh, S.R.; Yetisen, A.K.; Tasoglu, S. Point-of-care diagnostic platforms for loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Takao, S.; Kuwayama, M.; Shimazu, Y.; Miyazaki, K. Rapid detection of Norovirus from fecal specimens by real-time reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.B.; Seo, D.J.; Oh, H.; Kingsley, D.H.; Choi, C. Development of one-step reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for Norovirus detection in oysters. Food Control 2017, 73, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiken Chemical Co., LTD. LAMP Primers Designing Software Primer Explorer Version 5. Available online: https://primerexplorer.eiken.co.jp/lampv5e/index.html (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Zhang, S.; Shin, J.; Shin, S.; Chung, Y.J. Development of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for point-of-care testing of avian influenza virus subtype H5 and H9. Genom. Inform. 2020, 18, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliot, G.; Lopman, B.A.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Pothier, P. The burden of Norovirus gastroenteritis: An important foodborne and healthcare-related infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, T.; Kojima, S.; Shinohara, M.; Uchida, K.; Fukushi, S.; Hoshino, F.B.; Takeda, N.; Katayama, K. Broadly reactive and highly sensitive assay for Norwalk-like viruses based on real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamalee, A.; Changsen, C.; Jaroenram, W.; Buates, S. Enhancement of loop mediated isothermal amplification’s sensitivity and speed by multiple inner primers for more efficient identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Sakon, N.; Kanki, M.; Aoyama, I.; Tsukamoto, T. Evaluation and application of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of noroviruses. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Shin, J.; Kang, S.; Shin, S.; Chung, Y.J. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella species targeting the hilA gene using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Genom. Inform. 2021, 19, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xu, Z.; Nie, K.; Ding, X.; Guan, L.; Wang, J.; Xian, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, X. Visual detection of Norovirus genogroup II by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification with hydroxynaphthol blue dye. Food Environ. Virol. 2014, 6, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.; Doré, B.; Keaveney, S.; Rupnik, A.; Butler, F. A quantitative exposure assessment model for Norovirus in oysters harvested from a classified production area. Microb. Risk Anal. 2023, 23, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Freedman, S.B.; Williamson-Urquhart, S.; Farion, K.J.; Gouin, S.; Poonai, N.; Schuh, S.; Finkelstein, Y.; Xie, J.; Lee, B.E.; et al. Significantly longer shedding of Norovirus compared to Rotavirus and adenovirus in children with acute gastroenteritis. Viruses 2023, 15, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Tan, M.; Daud, A.; Huang, P.; Jiang, J.X. Quantitative Norovirus viral load is not affected by home storage of stool. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2022, 24, e13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Kuwayama, M.; Miyazaki, K. Simultaneous detection and genogroup-screening test for norovirus genogroups I and II from fecal specimens in single tube by reverse transcription- loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Qin, C.; Han, Y.; Xu, X. Rapid detection of norovirus genogroup II in clinical and environmental samples using recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 605, 113834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, C.; Lan, H.; Pan, D.; Wu, Y. Comparison of four isothermal amplification techniques: LAMP, SEA, CPA and RPA for the identification of chicken adulteration. Food Control. 2024, 159, 110302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primer | Length (bp) | 5′Oligo Seq-3′ |
|---|---|---|
| GI | ||
| GI3017F3 | 18 | GNTGGCAGGCCATGTTCC |
| GI3017B3-1 | 20 | ACAGGATCCATTGCAAGAGG |
| GI3017B3-2 | 20 | ACAGGTTCCATTGATATAGG |
| GI3017FIP-1 | 40 | ACGAATTCGGGCAGRAGATYGC- |
| CTGGATGCGMTTCCATGA | ||
| GI3017FIP-2 | 40 | ACATAATCGGGCAGGAGATCGC- |
| CTGGATGCGMTTCCATGA | ||
| GI3017BIP-1 | 40 | TGATGATGGCGTCTAAGGACGC- |
| TCCGGTACCAACTGACCA | ||
| GI3017BIP-2 | 40 | TGATGATGGCGTCTAAGGACGC- |
| TCTGGAACCAGCTGACCG | ||
| GI3017LF-1 | 21 | ATCTCCTGTCCACAATCCGAG |
| GI3017LF-2 | 21 | GTCCCCTGTCCACAAACTTAG |
| GI3017LB-1 | 17 | GCGTGGATGGCGCYAGT |
| GI3017LB-2 | 17 | ACATGGATGGCACCAGT |
| GII | ||
| GII3017F3 | 20 | GGTGGGATGGACTTTTACGT |
| GII3017B3-1 | 20 | GCTCCAAAGCCATAACCTCA |
| GII3017B3-2 | 20 | GTTCAAGAGCCATGACCTCA |
| GII3017FIP | 39 | GATTGCGATCGCCCTCCCAC- |
| CAAGGCAGGAACCCATGTT | ||
| GII3017BIP-1 | 41 | GAAGATGGCGTCGARTGACGC- |
| TGTTGACCTCTGGTACGAGG | ||
| GII3017BIP-2 | 41 | GAAGATGGCGTCGARTGACGC- |
| TGTTACTTTCTGGCACGAGG | ||
| GII3017LF | 22 | GTCAGARAACCTCATCCACCTG |
| GII3017LB-1 | 20 | CAACCCATCTGATGGGTCCG |
| GII3017LB-2 | 20 | CGCTCCATCTACTGATGGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ansari, W.K.; Seo, M.-R.; Chung, Y.-J. Genogroup-Specific Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Norovirus. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151868
Ansari WK, Seo M-R, Chung Y-J. Genogroup-Specific Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Norovirus. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151868
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnsari, Wahedul Karim, Mi-Ran Seo, and Yeun-Jun Chung. 2025. "Genogroup-Specific Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Norovirus" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151868
APA StyleAnsari, W. K., Seo, M.-R., & Chung, Y.-J. (2025). Genogroup-Specific Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Point-of-Care Detection of Norovirus. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151868









