The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Biologic Drug Tapering and Relapse Monitoring: Findings from a One-Year Prospective Study in a Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Sustained Clinical Remission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
3. Results
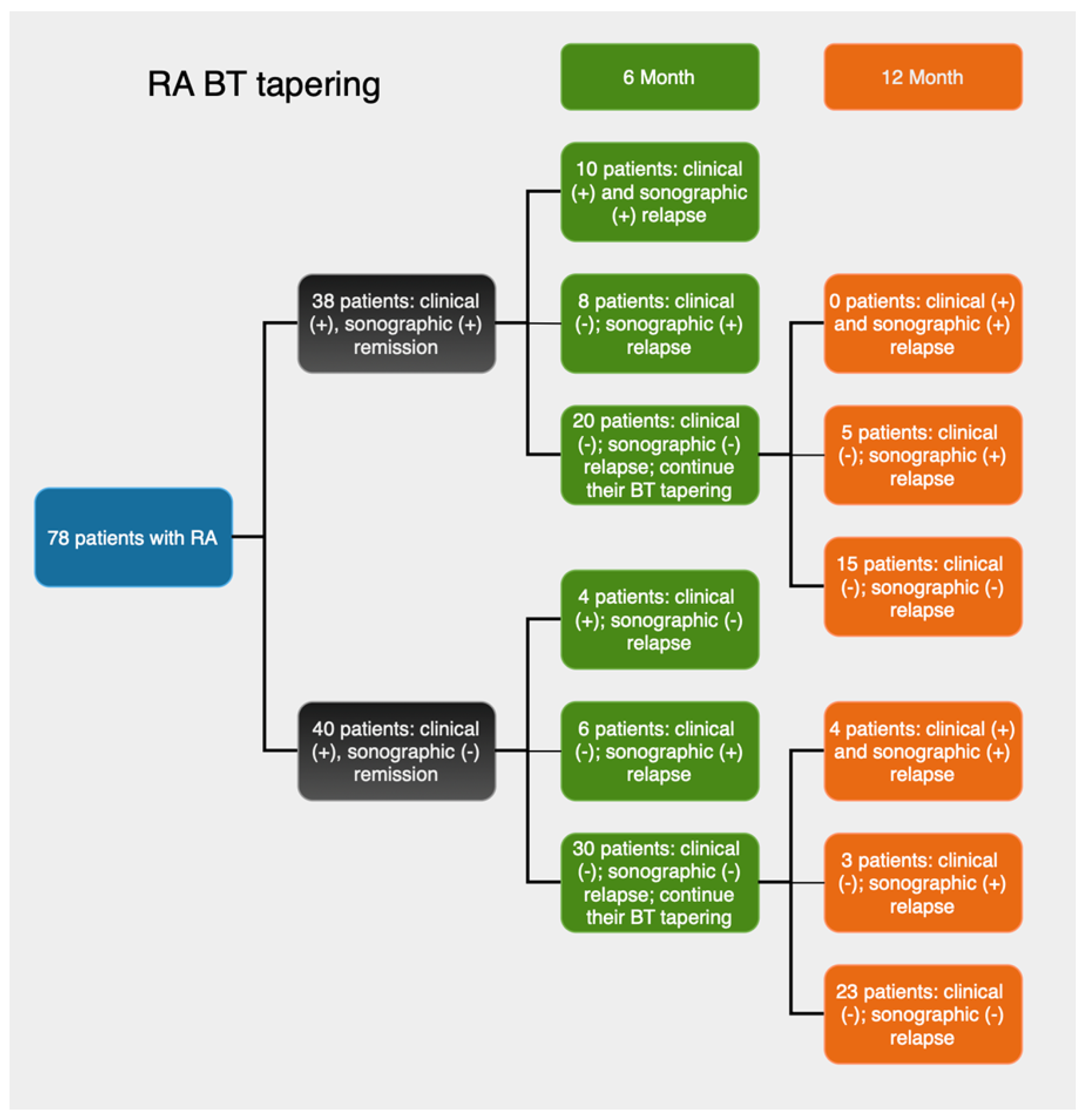
3.1. Background Information About the Patients
3.2. Clinical and Sonographic Findings at the 6th Month
3.3. Clinical and Sonographic Findings at the 12th Month
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colebatch, A.N.; Edwards, C.J.; Østergaard, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Balint, P.V.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Forslind, K.; Grassi, W.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Haugeberg, G.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging of the joints in the clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felson, D.T.; Smolen, J.S.; Wells, G.; Zhang, B.; van Tuyl, L.H.; Funovits, J.; Aletaha, D.; Allaart, C.F.; Bathon, J.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, E.T.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Dinant, H.J.; Bezemer, P.D.; Boers, M.; Dijkmans, B.A. Progression of radiologic damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical remission. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmjou, A.A.; Brook, J.; Elashoff, D.; Kaeley, G.; Choi, S.; Kermani, T.; Ranganath, V.K. Ultrasound and multi-biomarker disease activity score for assessing and predicting clinical response to tofacitinib treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapundzhieva, T.; Karalilova, R.; Batalov, A. Musculoskeletal ultrasound as a biomarker of remission—Results from a one-year prospective study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Ultrason. 2018, 20, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapundzhieva, T.; Sapundzhiev, L.; Batalov, A. Practical Use of Ultrasound in Modern Rheumatology—From A to Z. Life 2024, 14, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saku, A.; Furuta, S.; Kato, M.; Furuya, H.; Suzuki, K.; Fukuta, M.; Suehiro, K.; Makita, S.; Tamachi, T.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Experience of musculoskeletal ultrasound scanning improves physicians’ physical examination skills in assessment of synovitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase-Minegishi, K.; Horita, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshimi, R.; Kirino, Y.; Ohno, S.; Kaneko, T.; Nakajima, H.; Wakefield, R.J.; Emery, P. Diagnostic test accuracy of ultrasound for synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouterde, G.; Lukas, C.; Filippi, N.; Marin, G.; Molinari, N.; Combe, B.; Morel, J. Persistence of power Doppler ultrasonography-detected synovitis over 1 year of follow-up predicts poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis in clinical remission: The SONORE prospective longitudinal study. RMD Open 2024, 10, e004269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Gandjbakhch, F.; Constantin, A.; Foltz, V.; Cantagrel, A. Prevalence of ultrasound-detected residual synovitis and risk of relapse and structural progression in rheumatoid arthritis patients in clinical remission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naredo, E.; Valor, L.; De la Torre, I.; Montoro, M.; Bello, N.; Martínez-Barrio, J.; Martínez-Estupiñán, L.; Nieto, J.C.; Ovalles-Bonilla, J.G.; Hernández-Flórez, D.; et al. Predictive value of Doppler ultrasound-detected synovitis in relation to failed tapering of biologic therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivernini, S.; Peluso, G.; Fedele, A.; Tolusso, B.; Gremese, E.; Ferraccioli, G. Tapering and discontinuation of TNF-α blockers without disease relapse using ultrasonography as a tool to identify patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical and histological remission. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Ikeda, K.; Hosokawa, J.; Yamagata, M.; Tanaka, S.; Norimoto, A.; Sanayama, Y.; Nakagomi, D.; Takahashi, K.; Hirose, K.; et al. Prediction of relapse after discontinuation of biologic agents by ultrasonographic assessment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical remission. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.; Holroyd, C.; Dimitrov, B.; Armstrong, R.D.; Calogeras, A.; Cooper, C.; Davidson, B.K.; Dennison, E.M.; Harvey, N.C.; Edwards, C.J. Does combined clinical and ultrasound assessment allow selection of individuals with rheumatoid arthritis for sustained reduction of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy? Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers-Karnebeek, F.; Luime, J.; Ten Cate, D.; Teerenstra, S.; Swen, N.W.A.A.; Gerards, A.H.; Hendrikx, J.; van Rooyen, E.M.; Voorneman, R.; Haagsma, C.; et al. Limited value for ultrasonography in predicting flare in rheumatoid arthritis patients with low disease activity stopping TNF inhibitors. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavardsholm, E.; Aga, A.; Olsen, I.; Lillegraven, S.; Hammer, H.B.; Uhlig, T.; Fremstad, H.; Madland, T.M.; Lexberg, Å.S.; Haukeland, H.; et al. Ultrasound in management of rheumatoid arthritis: ARCTIC randomised controlled strategy trial. BMJ 2016, 354, i4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, G.; Michelutti, A.; Bosello, S.; Gremese, E.; Tolusso, B.; Ferraccioli, G. Clinical and ultrasonographic remission determines different chances of relapse in early and long standing rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, B.; Brown, A.; Keen, H.; Nizam, S.; Freeston, J.; Karim, Z.; Quinn, M.; Wakefield, R.; Hensor, E.; Conaghan, P.G.; et al. Disease remission state in patients treated with the combination of tumor necrosis factor blockade and methotrexate or with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A clinical and imaging comparative study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ven, M.; Kuijper, T.; Gerards, A.; Tchetverikov, I.; Weel, A.E.; van Zeben, J.; Hazes, J.M.; Luime, J.J. No clear association between ultrasound remission and health status in rheumatoid arthritis patients in clinical remission. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchianti Diamanti, A.; Cattaruzza, M.; Salemi, S.; Rosa, R.D.; Sesti, G.; Lorenzo, C.D.; Felice, G.M.; Frediani, B.; Baldi, C.; Chimenti, M.S.; et al. Clinical and Ultrasonographic Remission in Bio-naïve and Bio-failure Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis at 24 Weeks of Upadacitinib Treatment: The UPARAREMUS Real-Life Study. Rheumatol. Ther. 2024, 11, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heutz, J.; de Jong, P.; Verstappen, M.; Mil, A.H.M.v.H.; Mulligen, E.v. Sustained DMARD-free remission in subgroups of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: An analysis of two prospective cohorts with early arthritis. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e252–e260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, M.; Terslev, L.; Aegerter, P.; Backhaus, M.; Balint, P.; Bruyn, G.A.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W.; Iagnocco, A.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; et al. Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: A EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 1: Definition and development of a standardised, consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terslev, L.; Naredo, E.; Aegerter, P.; Backhaus, M.; Balint, P.; Bruyn, G.A.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W.; Iagnocco, A.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; et al. Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: A EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 2: Reliability and application to multiple joints of a standardised consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsa, A.; de Miguel, E.; Castillo, C.; Peiteado, D.; Martín-Mola, E. Superiority of SDAI over DAS-28 in assessment of remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients using power Doppler ultrasonography as a gold standard. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Sung, Y.; Kavanaugh, A.; Bae, S.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Kishimoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Tohma, S.; Solomon, D.H. Biologic discontinuation studies: A systematic review of methods. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Sánchez-Piedra, C.; Freire, M.; Colazo, M.; Busquets, N.; Meriño-Ibarra, E.; Rodríguez-Lozano, C.; Manrique, S.; Campos, C.; Sánchez-Alonso, F.; et al. Factors associated with discontinuation of biologics in patients with inflammatory arthritis in remission: Data from the BIOBADASER registry. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapundzhieva, T.; Karalilova, R.; Batalov, A. Musculoskeletal ultrasound for predicting remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a 1-year prospective study. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, K.; Miladi, S.; Makhlouf, Y.; Fazaa, A.; Sallemi, M.; Souebni, L.; Ouenniche, K.; Kassab, S.; Chekili, S.; Salem, K.B.; et al. Validity of remission criteria in rheumatoid arthritis compared to ultrasound-defined remission. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2022, 22, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, L.; van den Bemt, B.; van der Maas, A.; Vriezekolk, J.; Hulscher, M.; van den Hoogen, F.; Jacobs, W.; van Herwaarden, N.; den Broeder, A. Down-titration and discontinuation strategies of tumour necrosis factor–blocking agents for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with low disease activity. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD010455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Herwaarden, N.; van der Maas, A.; Minten, M.; Hoogen, F.H.J.v.; Kievit, W.; Vollenhoven, R.F.v.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; den Bemt, B.J.F.v.; Broeder, A.A.d. Disease activity guided dose reduction and withdrawal of adalimumab or etanercept compared with usual care in rheumatoid arthritis: Open label, randomised controlled, non-inferiority trial. BMJ 2015, 350, h1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvagni, E.; Zandonella Callegher, S.; Mauric, E.; Chiricolo, S.; Schreiber, N.; Tullio, A.; Zabotti, A.; Scirè, C.A.; Dejaco, C.; Sakellariou, G. Musculoskeletal ultrasound for treating rheumatoid arthritis to target—A systematic literature review. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4590–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, M.; Mueller, F.; Nigg, A.; Reindl, C.; Leipe, J.; Proft, F.; Stein, N.; Hammitzsch, A.; Mayer, S.; Dechant, C.; et al. Relevance of grade 1 gray-scale ultrasound findings in wrists and small joints to the assessment of subclinical synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.; Kvien, T.; Terslev, L. Ultrasound of the hand is sufficient to detect subclinical inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis remission: A post hoc longitudinal study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Total (n = 78) | GROUP | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (n = 38) | Group 2 (n = 40) | |||
| Age | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 59.15 (13.35) | 58.80 (14.52) | 59.85 (13.05) | 0.723 U |
| Min–Max | 39–73 | 43–73 | 39–72 | |
| Gender n (%) | ||||
| Female | 62 (79.50%) | 30 (78.90%) | 32 (80.00%) | 1.000 f |
| Male | 16 (20.50%) | 8 (21.10%) | 8 (20.00%) | |
| Disease duration | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 12.50 (10.00) | 11.50 (12.25) | 13 (8.00) | 0.920 U |
| Min–Max | 3–26 | 3–26 | 3–23 | |
| ACPA positive n (%) | 63 (80.80%) | 31 (81.60%) | 32 (80.00%) | 1.000 f |
| IgM-RF positive n (%) | 51 (65.40%) | 26 (68.40%) | 25 (62.50%) | 0.639 f |
| ACPA and IgM-RF negative n (%) | 3 (3.80%) | 1 (2.60%) | 2 (5.00%) | 0.811 f |
| DAS28 | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 2.30 (0.40) | 2.30 (0.30) | 2.20 (0.40) | 0.238 U |
| Min–Max | 1.50–2.50 | 1.50–2.50 | 1.60–2.50 | |
| Remission duration (months) | ||||
| Median (IQR) | 26 (24.25) | 26.50 (23.50) | 24.50 (27.00) | 0.795 U |
| Min–Max | 7–50 | 7–48 | 7–50 | |
| Diagnosis | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 38) | (n = 40) | ||
| Clinical and sonographic remission | 20 (52.60%) | 30 (75.00%) | 0.090 |
| Clinical and sonographic relapse | 10 (26.30%) | 4 (10.00%) | 0.865 |
| Sonographic relapse | 8 (21.10%) | 6 (15.00%) | 0.949 |
| Weighted Kappa | 0.568 | 0.500 | |
| 95% CI | 0.328 to 0.807 | 0.180 to 0.819 | |
| AUC | 0.778 | 0.700 | |
| SE | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.937 |
| 95% CI | 0.614 to 0.896 | 0.535 to 0.834 |
| Diagnosis | Group 1 (n = 38) | Group 2 (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical and sonographic remission | 15 (39.40%) | 23 (57.50%) | 0.909 |
| Clinical and sonographic relapse | 10 (26.30%) | 8 (20.00%) | 0.954 |
| Sonographic relapse | 13 (34.20%) | 9 (22.50%) | 0.922 |
| Weighted Kappa | 0.377 | 0.505 | |
| 95% CI | 0.163 to 0.592 | 0.258 to 1.000 | |
| AUC | 0.717 | 0.735 | 0.981 |
| SE | 0.05 | 0.06 | |
| 95% CI | 0.548 to 0.851 | 0.572 to 0.862 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batalov, Z.; Sapundzhieva, T.; Batalov, K.; Karalilova, R.; Batalov, A. The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Biologic Drug Tapering and Relapse Monitoring: Findings from a One-Year Prospective Study in a Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Sustained Clinical Remission. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141753
Batalov Z, Sapundzhieva T, Batalov K, Karalilova R, Batalov A. The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Biologic Drug Tapering and Relapse Monitoring: Findings from a One-Year Prospective Study in a Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Sustained Clinical Remission. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141753
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatalov, Zguro, Tanya Sapundzhieva, Konstantin Batalov, Rositsa Karalilova, and Anastas Batalov. 2025. "The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Biologic Drug Tapering and Relapse Monitoring: Findings from a One-Year Prospective Study in a Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Sustained Clinical Remission" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141753
APA StyleBatalov, Z., Sapundzhieva, T., Batalov, K., Karalilova, R., & Batalov, A. (2025). The Role of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in Biologic Drug Tapering and Relapse Monitoring: Findings from a One-Year Prospective Study in a Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Sustained Clinical Remission. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141753






