Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Following Esophageal Variceal Ligation and Its Impact on Clinical Outcomes: Real-World Data from the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
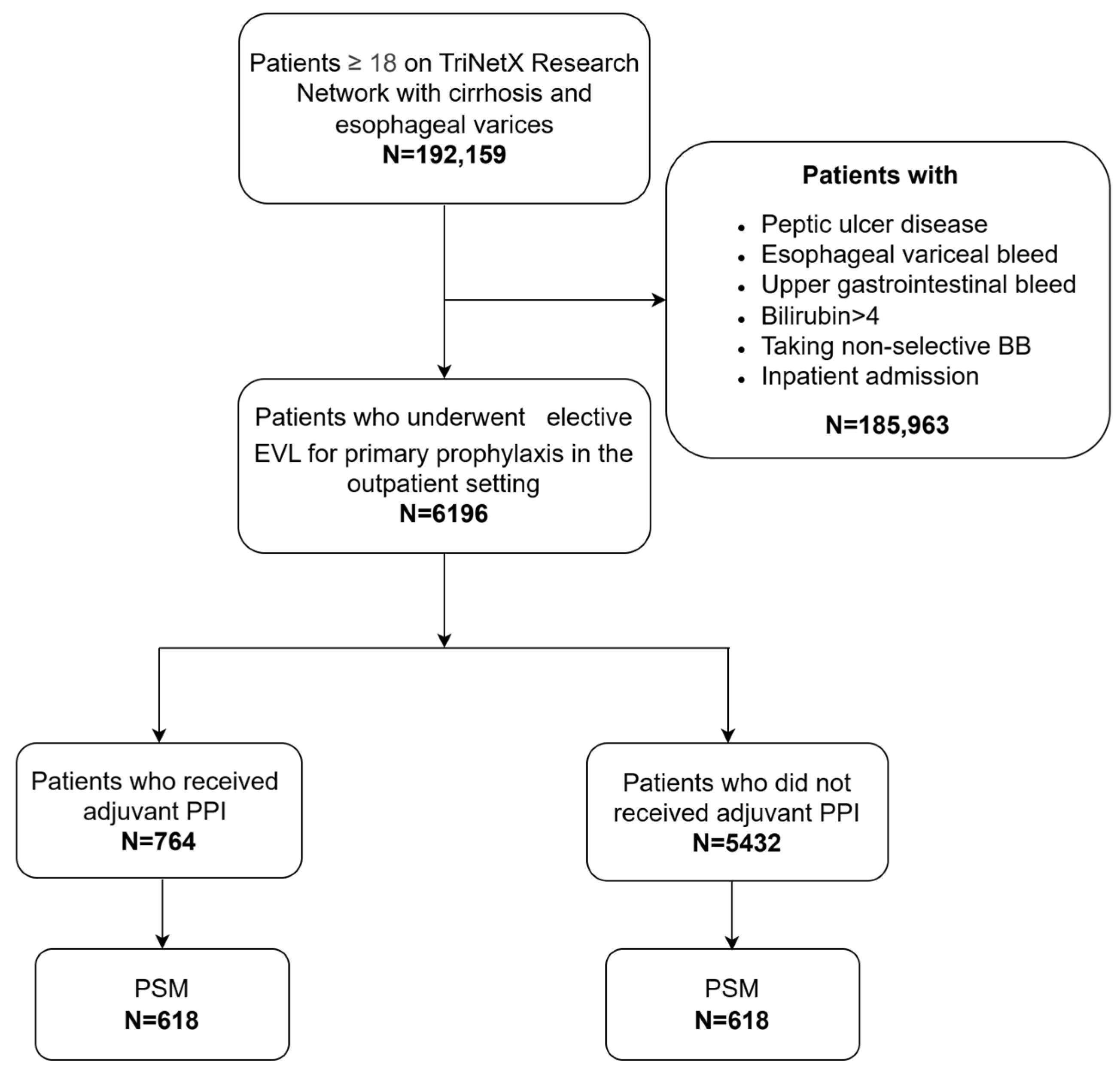
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
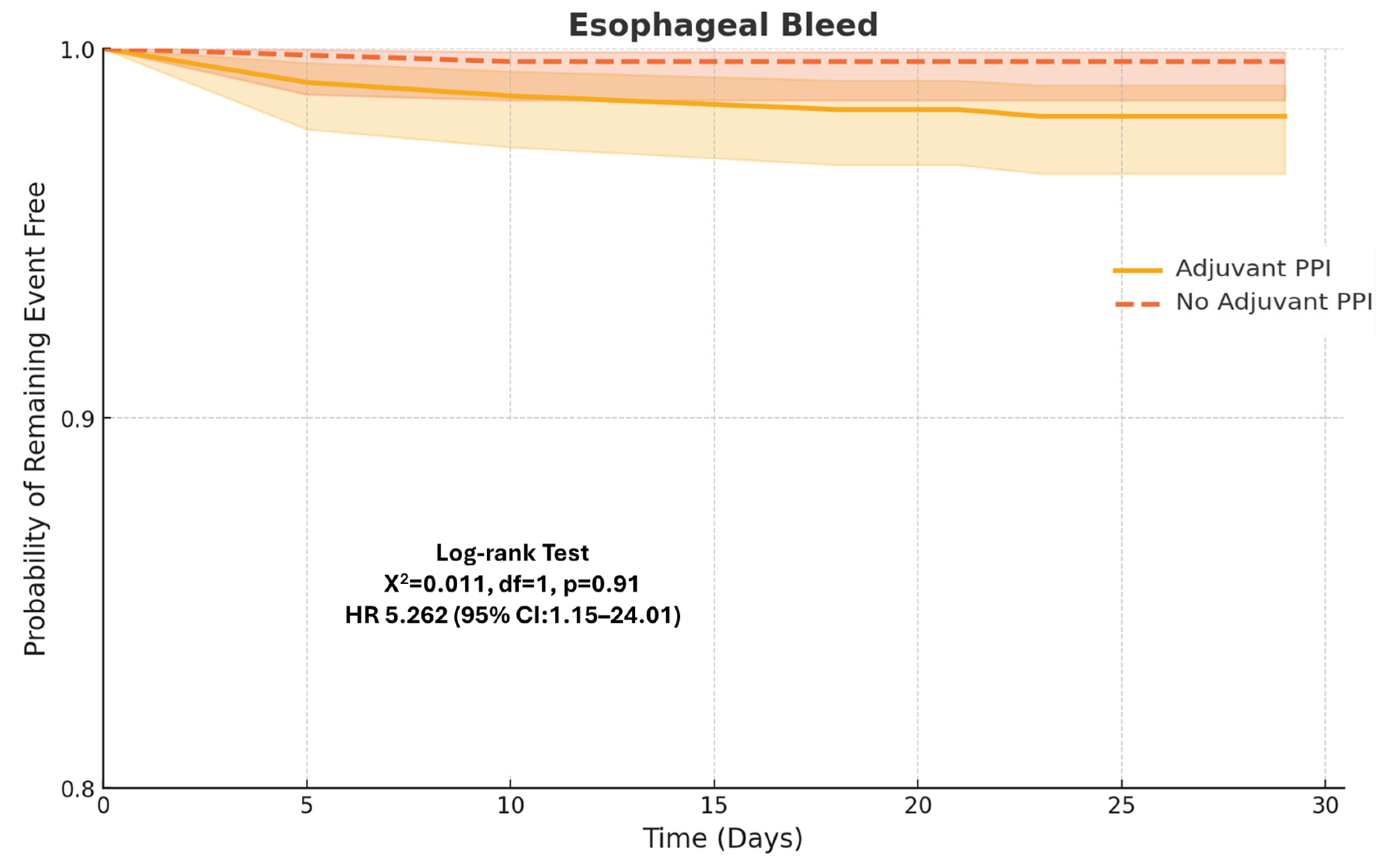
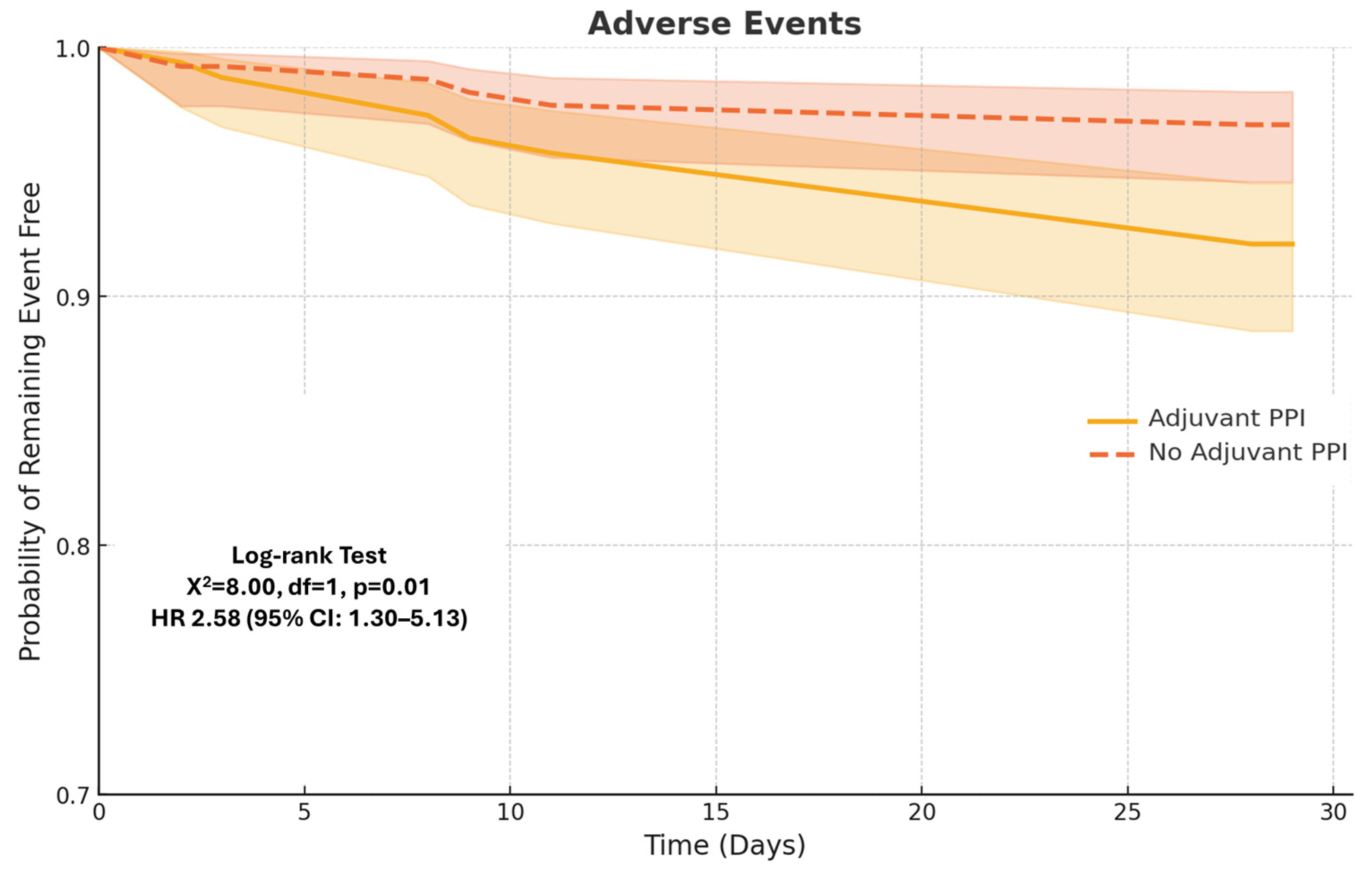
3.1. Primary Outcomes
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Sanyal, A.J.; Grace, N.D.; Carey, W.; Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 922–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Franchis, R.; Primignani, M. Natural history of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2001, 5, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G. Current management of the complications of cirrhosis and portal hypertension: Variceal hemorrhage, ascites, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 726–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North Italian Endoscopic Club for the Study and Treatment of Esophageal Varices. Prediction of the first variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and esophageal varices. A prospective multicenter study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Abraldes, J.G.; Keough, A.; Bastiampillai, R.; Jayakumar, S.; Carbonneau, M.; Wong, E.; Kao, D.; Bain, V.G.; Ma, M. Risk of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Cirrhosis and Acute Variceal Hemorrhage, Based on Child-Pugh Class, and Effects of Antibiotics. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1189–1196.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C. Prevention of variceal rebleeding. Lancet 2003, 361, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C.; Abraldes, J.G.; Albillos, A.; Baiges, A.; Bajaj, J.; Bañares, R.; et al. Baveno VII—Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.E.; Ripoll, C.; Thiele, M.; Fortune, B.E.; Simonetto, D.A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J. AASLD Practice Guidance on risk stratification and management of portal hypertension and varices in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1180–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, C.; Albillos, A.; Genescà, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Calleja, J.L.; Aracil, C.; Bañares, R.; Morillas, R.M.; Poca, M.; Peñas, B.; et al. β blockers to prevent decompensation of cirrhosis in patients with clinically significant portal hypertension (PREDESCI): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinagra, E.; Perricone, G.; D’AMico, M.; Tinè, F.; D’AMico, G. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The haemodynamic effects of carvedilol compared with propranolol for portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Tsao, G.; Abraldes, J.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2017, 65, 310–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepke, M.; Kleber, G.; Nürnberg, D.; Willert, J.; Koch, L.; Veltzke-Schlieker, W.; Hellerbrand, C.; Kuth, J.; Schanz, S.; Kahl, S.; et al. Ligation versus propranolol for the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004, 40, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Bosch, J. Endoscopic band ligation in the treatment of portal hypertension. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; Hou, M.C.; Lin, H.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Symptomatic esophageal stricture after endoscopic variceal ligation—Success of endoscopic balloon dilation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2000, 63, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoloff, M.A.; Riley, T.R., 3rd; Schreibman, I.R. Complete esophageal obstruction following endoscopic variceal ligation. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 557–559. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, N.; Ayoub, M.; Tomanguillo, J.; Chela, H.; Tahan, V.; Daglilar, E. Outcomes of Outpatient Elective Esophageal Varices Band Ligation in Cirrhosis Patients with Significant Thrombocytopenia. Diseases 2025, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbiervliet, G.; Giudicelli-Bornard, S.; Piche, T.; Berthier, F.; Gelsi, E.; Filippi, J.; Anty, R.; Arab, K.; Huet, P.M.; Hebuterne, X.; et al. Predictive factors of bleeding related to post-banding ulcer following endoscopic variceal ligation in cirrhotic patients: A case-control study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Yim, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Suh, S.J.; Hyun, J.J.; Jung, S.W.; Jung, Y.K.; Koo, J.S.; Lee, S.W. Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy Is Associated with Reduction of Early Bleeding Risk After Prophylactic Endoscopic Variceal Band Ligation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Wang, G.; Kokubu, S.; Minamino, T.; Takada, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Okuwaki, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, S.; et al. Long-term administration of PPI reduces treatment failures after esophageal variceal band ligation: A randomized, controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, I.; Babar, M.; Awan, S.A.; Shaikh, A.J.; Abbasi, A.A. Effectiveness of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in the Prevention of Bleeding After Prophylactic Endoscopic Variceal Band Ligation. Cureus 2023, 15, e33932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.S.; Shin, H.P.; Lee, J.I.; Joo, K.R.; Cha, J.M.; Jeon, J.W.; Lim, J.U. Proton pump inhibitor administration delays rebleeding after endoscopic gastric variceal obturation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17127–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Stuart, E.; Schmitz, S.M.; Mitchell, K.L.; Fried, M.W.; Zacks, S.; Russo, M.W.; Galanko, J.; Shrestha, R. Pantoprazole reduces the size of postbanding ulcers after variceal band ligation: A randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 2005, 41, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodato, F.; Azzaroli, F.; Di Girolamo, M.; Feletti, V.; Cecinato, P.; Lisotti, A.; Festi, D.; Roda, E.; Mazzella, G. Proton pump inhibitors in cirrhosis: Tradition or evidence based practice? World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 2980–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Saenz-de-Sicilia, M.; Sanchez-Avila, F.; Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; Lopez-Arce, G.; Garcia-Osogobio, S.; Ruiz-Cordero, R.; Tellez-Avila, F.I. PPIs are not associated with a lower incidence of portal-hypertension-related bleeding in cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5869–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Jun, C.H.; Cho, S.B.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.K.; Rew, J.S. Endoscopic variceal ligation-induced ulcer bleeding: What are the risk factors and treatment strategies? Medicine 2017, 96, e7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Farcomeni, A.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Proton Pump Inhibitors Are Associated with Minimal and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy and Increased Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-F.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, Y.-P.; Chu, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Hou, M.-C.; Lee, F.-Y.; Su, T.-P.; Lu, C.-L. Proton Pump Inhibitors Increase Risk for Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis in A Population Study. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedberg, D.E.; Kim, L.S.; Yang, Y.X. The Risks and Benefits of Long-term Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review and Best Practice Advice from the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almario, C.V.; Chey, W.D.; Spiegel, B.M.R. Increased Risk of COVID-19 Among Users of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.G.; Milligan, J.; Frenette, C.; Lee, T.C. Continuous Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy and the Associated Risk of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TrinetX. Available online: https://trinetx.com/ (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Song, Z.; Gong, X. Research Progress on the Potential Mechanisms of Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Induced by Proton Pump Inhibitors. Integr. Med. Nephrol. Androl. 2023, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.-L.; Parkin, L.; Paul, C.; Herbison, P. A nationwide nested case-control study indicates an increased risk of acute interstitial nephritis with proton pump inhibitor use. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, F.; Suarez, M.; Rey, M.; Vela, M.F. Systematic review: Proton pump inhibitor-associated acute interstitial nephritis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, G.; Vilstrup, H.; Watson, H.; Jepsen, P. Proton pump inhibitors as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis with ascites. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantai, X.-X.; Yang, L.-B.; Wei, Z.-C.; Xiao, C.-L.; Chen, L.-R.; Wang, J.-H.; Liu, N. Association of proton pump inhibitors with risk of hepatic encephalopathy in advanced liver disease: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2683–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N.; Serper, M.; Taddei, T.H.; Kaplan, D.E. The Association Between Proton Pump Inhibitor Exposure and Key Liver-Related Outcomes in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Veterans Affairs Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 257–269.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret-Ouda, J.; Panula, J.; Santoni, G.; Xie, S.; Lagergren, J. Proton pump inhibitor use and risk of pneumonia: A self-controlled case series study. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, A.; Stanciu, C.; Girleanu, I.; Stoica, O.C.; Singeap, A.M.; Maxim, R.; Chiriac, S.A.; Ciobica, A.; Boiculese, L. Proton pump inhibitors therapy and risk of Clostridium difficile infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6500–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jump, R.L.; Pultz, M.J.; Donskey, C.J. Vegetative Clostridium difficile survives in room air on moist surfaces and in gastric contents with reduced acidity: A potential mechanism to explain the association between proton pump inhibitors and C. difficile-associated diarrhea? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vila, A.V.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Koh, S.; Kim, W.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Im, J.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Mortality associated with proton pump inhibitors in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, I.; Tarasawa, K.; Saito, H.; Hirasawa, D.; Fujimori, K.; Fushimi, K.; Matsuda, T. Is proton-pump inhibitor effective in preventing postoperative bleeding after esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection? Dis. Esophagus 2024, 37, doad060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaoka, H.; Iwatsubo, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Kojima, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Hakoda, A.; Nishida, S.; Kawaguchi, S.; Ota, K.; Shiba, M.; et al. Is a proton-pump inhibitor necessary after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal neoplasms? A propensity score analysis. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820974908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Before Propensity Score Matching a | After Propensity Score Matching a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPI (n = 766) | No-PPI (n = 6196) | p-Value | PPI (n = 618) | No-PPI (n = 618) | p-Value | |
| Demographics | ||||||
| Age at Index, Mean years ± SD | 60.6 ± 11.7 | 59.6 ± 12.0 | 0.04 | 60.6 ± 11.7 | 60.3 ± 11.7 | 0.66 |
| Female | 238 (38.1) | 2068 (39.6) | 0.01 | 237 (38.3) | 245 (39.6) | 0.64 |
| Male | 383 (61.3) | 3028 (58.0) | 0.12 | 377 (61.0) | 370 (59.9) | 0.68 |
| Race | ||||||
| White | 420 (67.2) | 3946 (75.6) | 0.01 | 418 (67.6) | 434 (70.2) | 0.33 |
| Black or African American | 39 (6.2) | 210 (4.0) | 0.01 | 38 (6.1) | 41 (6.6) | 0.73 |
| Ethnicity | ||||||
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 453 (72.5) | 3341 (64.0) | 0.01 | 366 (59.2) | 375 (60.7) | 0.60 |
| Hispanic or Latino | 92 (14.7) | 916 (17.6) | 0.08 | 91 (14.7) | 81 (13.1) | 0.41 |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertensive disease | 371 (59.4) | 2262 (43.3) | 0.01 | 366 (59.2) | 375 (60.7) | 0.60 |
| Heart failure | 72 (11.5) | 356 (6.8) | 0.01 | 68 (11.0) | 74 (12.0) | 0.59 |
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | 148 (23.7) | 704 (13.5) | 0.01 | 145 (23.5) | 135 (21.8) | 0.50 |
| COPD | 71 (11.4) | 343 (6.6) | 0.01 | 71 (11.5) | 78 (12.6) | 0.54 |
| CKD | 128 (20.5) | 451 (8.6) | 0.01 | 126 (20.4) | 115 (18.6) | 0.43 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 283 (45.3) | 1708 (32.7) | 0.01 | 279 (45.1) | 277(44.8) | 0.90 |
| Neoplasms | 327 (52.3) | 1831 (35.1) | 0.01 | 321 (51.9) | 316 (51.1) | 0.78 |
| Portal vein thrombosis | 76(12.2) | 361 (6.9) | 0.01 | 75 (12.1) | 79 (12.8) | 0.730 |
| Gastritis | 66 (10.6) | 273 (5.2) | 0.01 | 62 (10.0) | 59 (9.5) | 0.77 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 281(45.0) | 1236 (23.7) | 0.01 | 274 (44.3) | 283 (45.8) | 0.61 |
| Ascites | 351 (56.2) | 1994 (38.2) | 0.01 | 345 (55.8) | 343 (55.5) | 0.91 |
| Tobacco use | 51 (8.2) | 213 (4.1) | 0.01 | 51 (8.3) | 60 (9.7) | 0.37 |
| Alcohol abuse | 105 (16.8) | 601 (11.5) | 0.01 | 102 (16.5) | 107 (17.3) | 0.70 |
| Chronic viral hepatitis | 151 (24.2) | 1009 (19.3) | 0.01 | 148 (23.9) | 133 (21.5) | 0.0.31 |
| NASH | 143 (22.9) | 812 (15.6) | 0.01 | 140 (22.7) | 145 (23.5) | 0.74 |
| NAFLD | 173 (27.7) | 1092 (20.9) | 0.01 | 170 (27.5) | 186 (30.1) | 0.32 |
| BMI | 29.1 ± 6.8 | 29.9 ± 6.8 | 0.01 | 29.0 ± 6.7 | 29.9 ± 7.4 | 0.06 |
| Hemodialysis | 13 (2.1) | 28 (0.5) | 0.01 | 12 (1.9) | 11 (1.9) | 0.83 |
| Medication | ||||||
| Long-term (current) use of anticoagulants and antithrombotic/antiplatelets | 84 (13.4) | 311 (6.0) | 0.01 | 81 (13.1) | 87 (14.1) | 0.62 |
| Lab Results | ||||||
| Bilirubin | 1.7 ± 1.7 | 1.6 ± 1.7 | 0.14 | 1.7 ± 1.7 | 1.6 ± 1.4 | 0.38 |
| Sodium | 137.1 ± 4.1 | 137.9 ± 3.6 | 0.01 | 137.1 ± 4.1 | 137.3 ± 3.7 | 0.50 |
| Creatinine | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.9 ± 0.7 | 0.01 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.32 |
| Albumin | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.6 | 0.01 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 0.12 |
| INR | 1.31 ± 0.33 | 1.26 ± 0.30 | 0.01 | 1.31 ± 0.33 | 1.29 ± 0.34 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, N.; Chela, H.; Mubarak, M.F.; Ayoub, M.; Daglilar, E. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Following Esophageal Variceal Ligation and Its Impact on Clinical Outcomes: Real-World Data from the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131653
Amin N, Chela H, Mubarak MF, Ayoub M, Daglilar E. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Following Esophageal Variceal Ligation and Its Impact on Clinical Outcomes: Real-World Data from the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131653
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Nisar, Harleen Chela, Muhammad Faisal Mubarak, Mark Ayoub, and Ebubekir Daglilar. 2025. "Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Following Esophageal Variceal Ligation and Its Impact on Clinical Outcomes: Real-World Data from the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131653
APA StyleAmin, N., Chela, H., Mubarak, M. F., Ayoub, M., & Daglilar, E. (2025). Proton Pump Inhibitor Use Following Esophageal Variceal Ligation and Its Impact on Clinical Outcomes: Real-World Data from the TriNetX Global Collaborative Network. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131653






