Differences in Imaging and Histology Between Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma with and Without Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
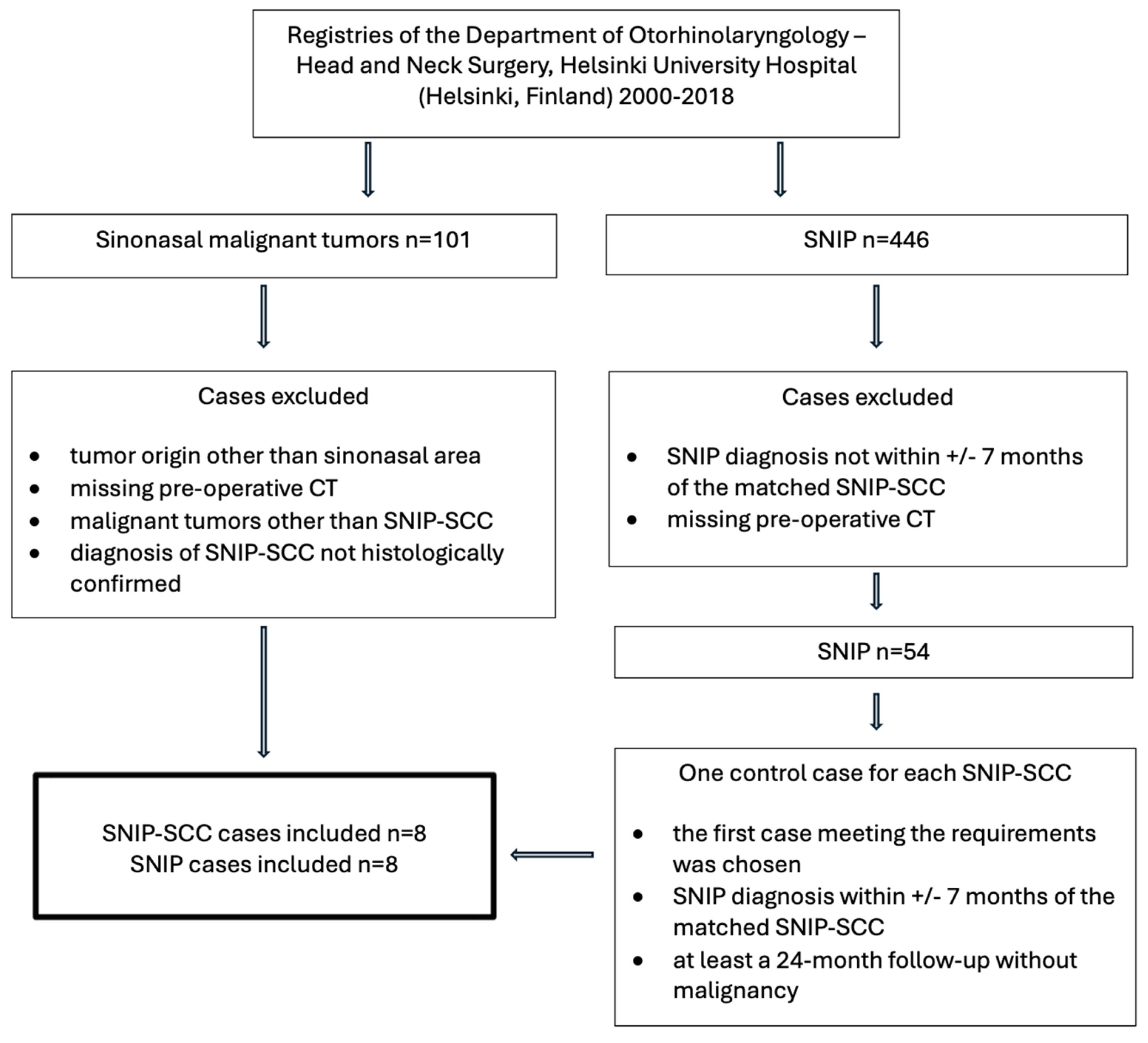
2. Materials and Methods
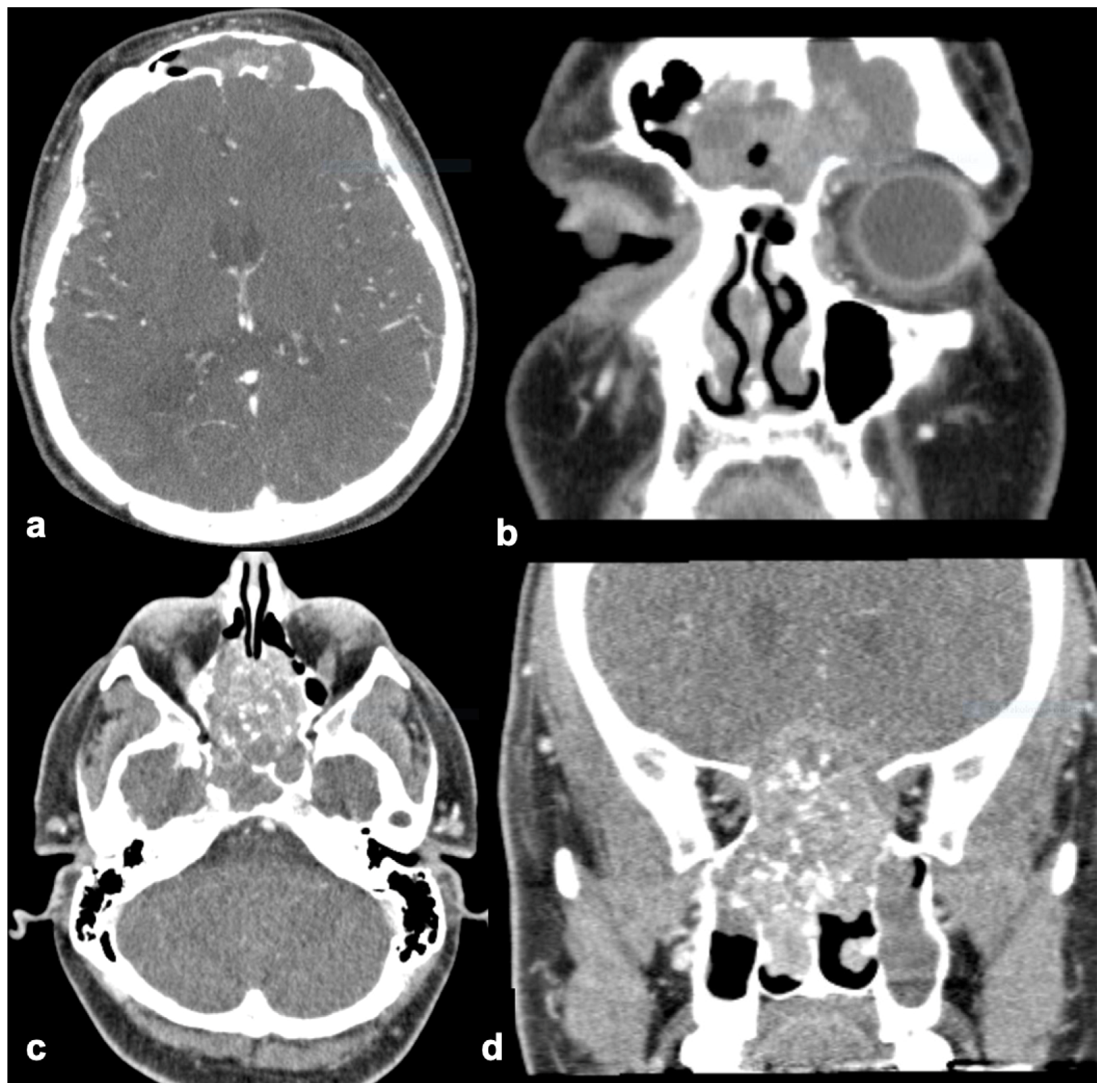
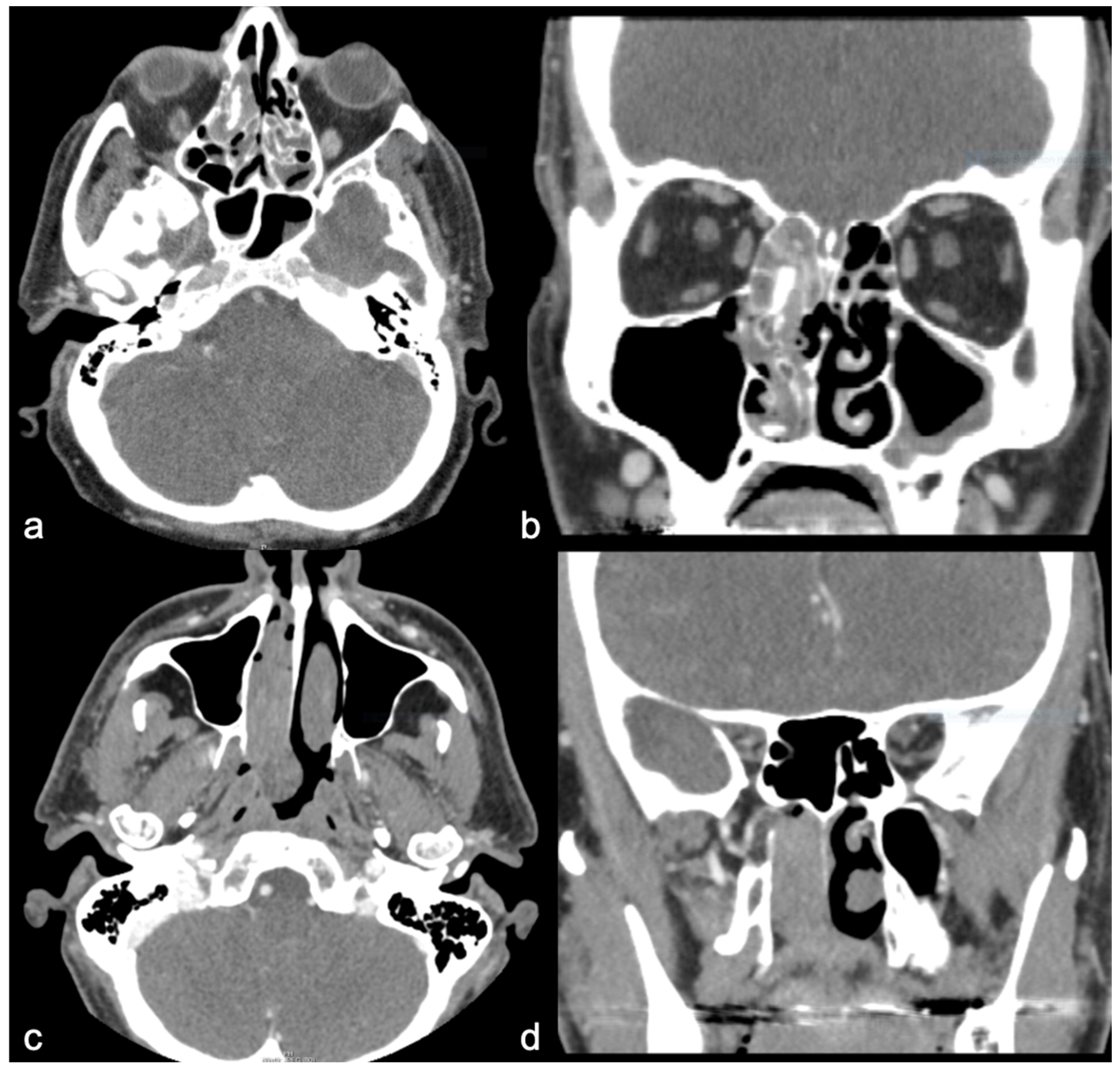
3. Results
Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| CCP | convoluted cerebriform pattern |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DCE | dynamic contrast-enhanced |
| FDG | fluorodeoxyglucose |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| SAR | specific absorption rate |
| SCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
| SNIP | sinonasal inverted papilloma |
| TIC | time intensity curve |
References
- Barnes, L.; Eveson, J.; Reichart, P.; Sidransky, D. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. In Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Outzen, K.E.; Grøntveld, A.; Jørgensen, K.; Clausen, P.P.; Ladefoged, C. Inverted papilloma: Incidence and late results of surgical treatment. Rhinology 1996, 34, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lund, V.J.; Stammberger, H.; Nicolai, P.; Castelnuovo, P.; Beal, T.; Beham, A.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Braun, H.; Cappabianca, P.; Carrau, R.; et al. European position paper on endoscopic management of tumours of the nose, paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinol. Suppl. 2010, 22, 1–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lawson, W.; Benger, J.L.; Som, P.; Bernard, P.J.; Biller, H.F. Inverted Papilloma: An Analysis of 87 Cases. Laryngoscope 1989, 99, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, E.; Sciarretta, V.; Farneti, G.; Modugno, G.C.; Ceroni, A.R. Inverted papilloma: Report of 89 cases. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2004, 25, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabec, D.P. The inverted schneiderian papilloma: A 25-year study. Laryngoscope 1994, 104, 582–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyams, V.J. Papillomas of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: A Clinicopathological Study of 315 Cases. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1971, 80, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.; Bradley, P.J.; Acharya, A.; Stacey, M.; Jones, N.S. Sinonasal inverted papillomas: Recurrence, and synchronous and metachronous malignancy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ozaki, S.; Yokota, M.; Nakayama, M.; Hattori, H.; Inagaki, H.; Murakami, S. Sinonasal inverted papilloma associated with small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: A case report and literature review of rare malignancies associated with inverted papilloma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisan, Q.; Laccourreye, O.; Bonfils, P. Sinonasal inverted papilloma: From diagnosis to treatment. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2016, 133, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Haku, Y.; Yoshizawa, A.; Iwanaga, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Mizuta, M.; Yoshida, A.; Satou, S.; Tamaki, H. Clinical features of nasal and sinonasal inverted papilloma associated with malignancy. Auris Nasus Larynx 2018, 45, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkos, P.D.; Fyrmpas, G.; Carrie, S.C.; Swift, A.C. Endoscopic versus open surgical interventions for inverted nasal papilloma: A systematic review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2006, 31, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, M.S.; Xu, X.Q.; Sung, Y.S.; Chung, S.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Baek, J.H. MRI Predictors of Malignant Transformation in Patients with Inverted Papilloma: A Decision Tree Analysis Using Conventional Imaging Features and Histogram Analysis of Apparent Diffusion Coefficients. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.H.; Tong, C.C.L.; Penta, M.; Patel, V.S.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D.; Nayak, J.V.; Hwang, P.H.; Patel, Z.M. Imaging predictors for malignant transformation of inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Aran, S. A Review of Magnetic Resonance (MR) Safety: The Essentials to Patient Safety. Cureus 2023, 15, e47345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Cho, W.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Yu, M.S. Preoperative Prediction of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma-associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma (IP-SCC). Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, W.W.; Vrabec, D.P. Inverted papilloma of the nasal vault and paranasal sinuses: Spectrum of CT findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1994, 162, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Shenoy, J.; Chokkappan, K.; Chung, R. Imaging Features of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Pictorial Review. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2016, 45, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, S.; Kikuta, S.; Yoshida, M.; Ando, M.; Kondo, K.; Yamasoba, T. High CT attenuation values relative to the brainstem may predict squamous cell carcinoma arising from inverted papilloma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019, 139, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Jabarin, B.; Harvey, A.; Ham, J.; Javer, A.; Janjua, A.; Thamboo, A. Clinical evidence based review and systematic scientific review in the identification of malignant transformation of inverted papilloma. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 49, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.; Vivarrat-Perrin, L.; Champsaur, P.; Juhan, V.; Chagnaud, C.; Vidal, V.; Gaubert, J.Y.; Bartoli, J.M.; Dessi, P.; Zanaret, M.; et al. Radiological follow-up of inverted papilloma. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, M.; Kuroki, M.; Kato, H.; Shibata, H.; Yamada, N.; Okuda, H.; Terazawa, K.; Iinuma, R.; Ohkoshi, A.; Wakamori, S.; et al. CT scoring system for differentiating of sinonasal inverted papilloma and squamous cell carcinoma arising from inverted papilloma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 282, 2533–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroldi, R.; Farina, D.; Palvarini, L.; Lombardi, D.; Tomenzoli, D.; Nicolai, P. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of inverted papilloma: Differential diagnosis with malignant sinonasal tumors. Am. J. Rhinol. 2004, 18, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sham, C.L.; King, A.D.; van Hasselt, A.; Tong, M.C.F. The Roles and Limitations of Computed Tomography in the Preoperative Assessment of Sinonasal Inverted Papillomas. Am. J. Rhinol. 2008, 22, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, C.; Elefante, A.; Romano, A.; Cama, A.; Erra, M.; Ugga, L.; Brunetti, L.; Motta, G.; Califano, L.; Iengo, M.; et al. A multimodal diagnostic approach to inverted papilloma: Proposal of a novel diagnostic flow-chart. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2021, 50, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojiri, H.; Ujita, M.; Tada, S.; Fukuda, K. Potentially Distinctive Features of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma on MR Imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Xian, J. Value of magnetic resonance imaging including dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation between inverted papilloma and malignant tumors in the nasal cavity. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, G.; Yu, W.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Prediction of malignant sinonasal inverted papilloma transformation by preoperative computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Rhinol. J. 2020, 58, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafqat, I.; Ho, A.S.; Manzoor, D.; Balzer, B.; Wu, A.W. Management of FDG avid Benign Sinonasal Schneiderian Papilloma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, G.; Mühling, J.; Hassfeld, S. Inverted papilloma of paranasal sinuses. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 35, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katori, H.; Nozawa, A.; Tsukuda, M. Histopathological parameters of recurrence and malignant transformation in sinonasal inverted papilloma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Yang, A.; Kim, D.; Hojel, A.; Voevodsky, D.; Wang, J.; Tong, C.C.L.; Ungerer, H.; Palmer, J.N.; Kohanski, M.A.; et al. Deep learning classification of inverted papilloma malignant transformation using 3D convolutional neural networks and magnetic resonance imaging. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022, 12, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, F.; Sha, Y.; Ren, J. Development and validation of apparent diffusion coefficient histogram-based nomogram for predicting malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2023, 52, 20220301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yui, R.; Takahashi, M.; Noda, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sakurai, R.; Ohira, S.; Omura, K.; Otori, N.; Wada, K.; Kojima, H. Preoperative prediction of sinonasal papilloma by artificial intelligence using nasal video endoscopy: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Characteristics | SNIP-SCC n (8) | SNIP n (8) |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 88% (7) | 75% (6) |
| Female | 12.5% (1) | 25% (2) |
| Recurrence | 12.5% (1) | 62.5% (5) |
| * SCC synchronous | 75% (6) | 0% |
| * SCC metachronous | 25% (2) | 0% |
| Mean age at IP diagnosis (years, mean ± SD) * | 64 ± 15 | 50 ± 8 |
| Mean follow-up months (mean ± SD) * | 35 ± 18 | 66 ± 32 |
| Findings Only Found in SNIP-SCC | SNIP-SCC n (8) | SNIP n (8) |
|---|---|---|
| Orbit invasion | 12.5% (1) | 0% |
| Intracranial invasion | 25% (2) | 0% |
| Bone defect | ||
| Nasal cavity wall | 50% (4) | 0% |
| Maxillary | 50% (4) | 0% |
| Ethmoid | 25% (2) | 0% |
| Sphenoid | 12.5% (1) | 0% |
| Frontal | 25% (2) | 0% |
| Some differences between groups | SNIP-SCC n (8) | SNIP n (8) |
| Shape of tumor | ||
| Polypoid | 50% (4) | 75% (6) |
| Unsharp | 50% (4) | 25% (2) |
| Tumor location | ||
| Unilateral | 50% (4) | 87.5% (7) |
| Bilateral | 50% (4) | 12.5% (1) |
| Nasal cavity wall | 100% (8) | 100% (8) |
| Maxillary | 50% (4) | 62.5% (5) |
| Ethmoid | 87.5% (7) | 75% (6) |
| Sphenoid | 25% (2) | 0% |
| Frontal | 25% (2) | 37.5% (3) |
| CT enhancement * | 87.5% (7/8) | 62.5% (5/8) * |
| Site of hyperostosis on CT | ||
| Nasal cavity wall | 0% | 25% (2) |
| Maxillary | 12.5% (1) | 0% |
| Ethmoid | 0% | 25% (2) |
| Sphenoid | 0% | 0% |
| Frontal | 12.5% (1) | 0% |
| No differences between groups | SNIP-SCC n (8) | SNIP n (8) |
| Mean diameter of tumor, mm (range) | 57 (30–87) | 48 (20–70) |
| Surface of the tumor | ||
| Smooth | 25% (2) | 12.5% (1) |
| Rough | 75% (6) | 75% (6) |
| Tumor calcification | 25% (2) | 25% (2) |
| Only in SNIP-SCC Group | SNIP-SCC (n 5) | SNIP (n 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear atypia | 40% (2) | 0% |
| Maturation disturbance | 40% (2) | 0% |
| Dyskeratosis | 20% (1) | 0% |
| More often in SNIP-SCC group | SNIP-SCC (n 5) | SNIP (n 5) |
| Basaloid hyperplasia | 100% (5) | 40% (2) |
| Mitosis in basal cell layer | 80% (4) | 40% (2) |
| Loss of epithelial stratification | 80% (4) | 40% (2) |
| Mitosis above basal cell layer | 40% (2) | 20% (1) |
| Goblet cells | 40% (2) | 20% (1) |
| More often in SNIP group | SNIP-SCC (n 5) | SNIP (n 5) |
| Clear cell cytoplasm | 20% (1) | 60% (3) |
| Respiratory epithelium | 20% (1) | 40% (2) |
| Squamous cell metaplasia | 40% (2) | 60% (3) |
| Neutrophils | 60% (3) | 80% (4) |
| The same frequencies in both groups | SNIP-SCC (n 5) | SNIP (n 5) |
| Polarity disturbance | 80% (4) | 80% (4) |
| Micro-abscess | 60% (3) | 60% (3) |
| Eosinophils | 40% (2) | 40% (2) |
| Apoptotic cells | 20% (1) | 20% (1) |
| No observations | SNIP-SCC (n 5) | SNIP (n 5) |
| Atypical keratinization | 0% | 0% |
| Apoptotic keratinocyte | 0% | 0% |
| Atypical mitosis | 0% | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuusisto, N.; Hagström, J.; Kurdo, G.; Haapaniemi, A.; Markkola, A.; Mäkitie, A.; Lilja, M. Differences in Imaging and Histology Between Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma with and Without Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131645
Kuusisto N, Hagström J, Kurdo G, Haapaniemi A, Markkola A, Mäkitie A, Lilja M. Differences in Imaging and Histology Between Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma with and Without Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuusisto, Niina, Jaana Hagström, Goran Kurdo, Aaro Haapaniemi, Antti Markkola, Antti Mäkitie, and Markus Lilja. 2025. "Differences in Imaging and Histology Between Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma with and Without Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131645
APA StyleKuusisto, N., Hagström, J., Kurdo, G., Haapaniemi, A., Markkola, A., Mäkitie, A., & Lilja, M. (2025). Differences in Imaging and Histology Between Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma with and Without Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131645






