Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. DNA Isolation, HPV, p16+, and Proliferative Index Ki-67 Confirmation
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Group
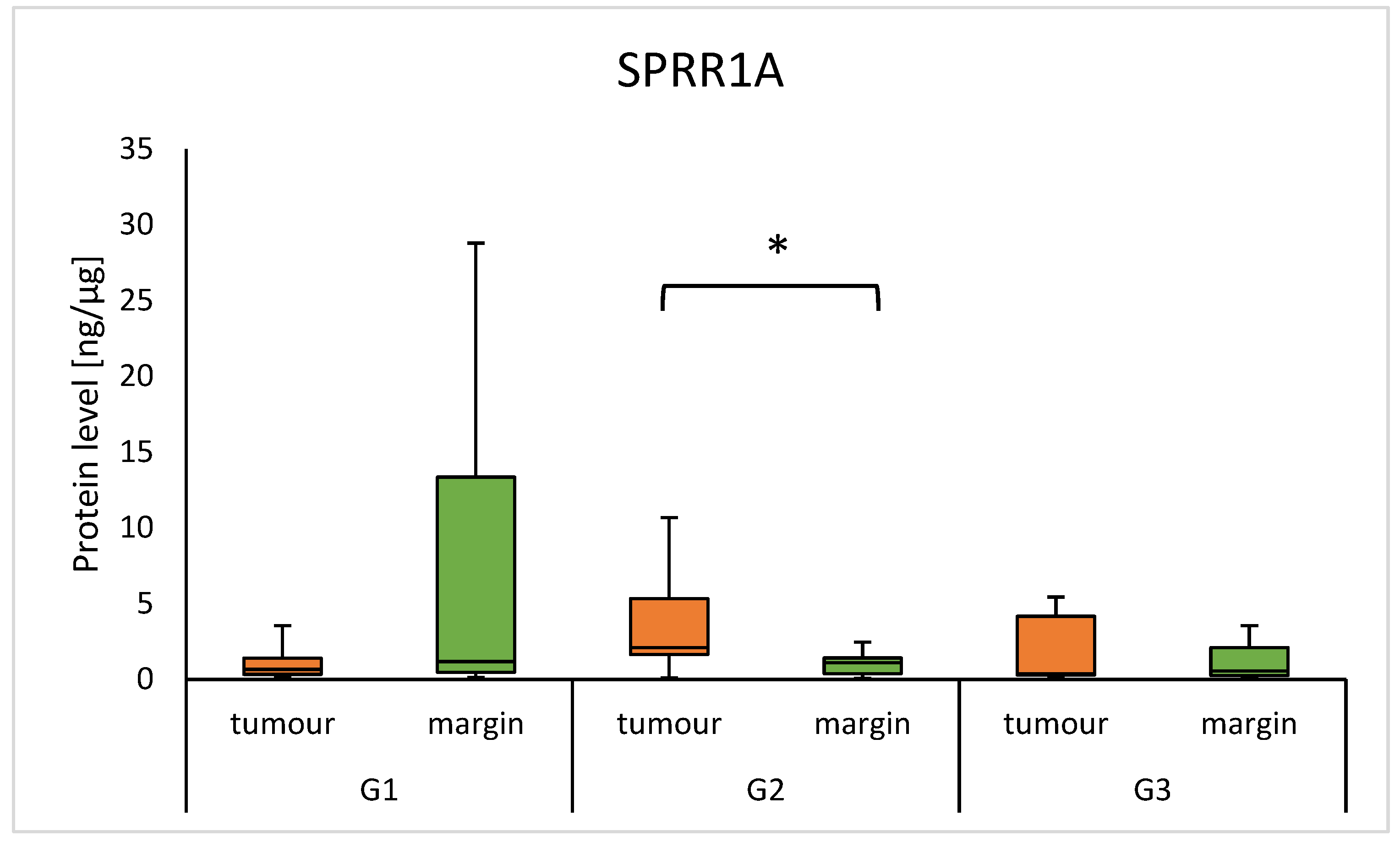
3.2. Protein Level of SPRR and Clinical Parameters
3.3. SPRR Protein Level and Tobacco Habit
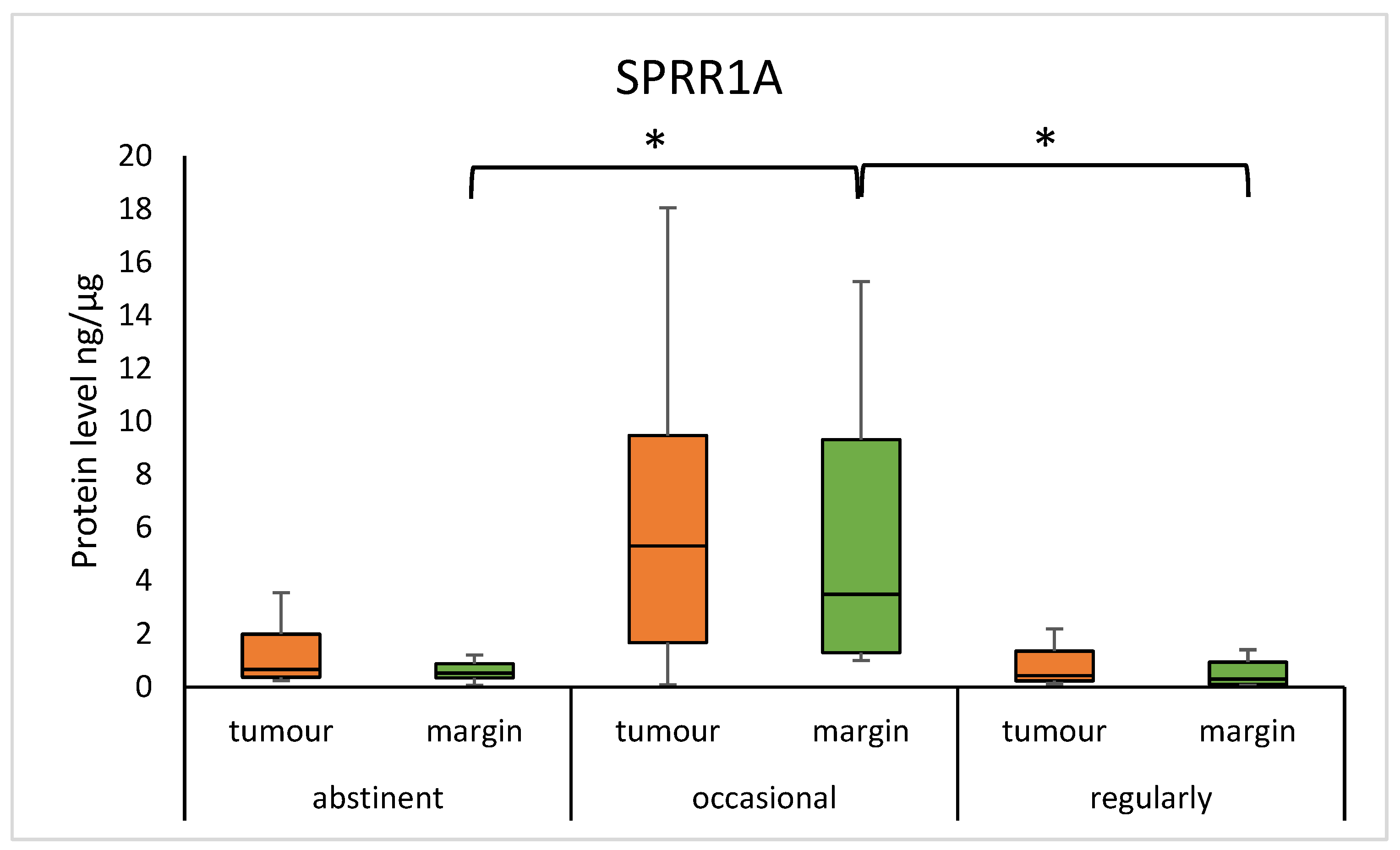
3.4. SPRR Protein Level and Alcohol Habit
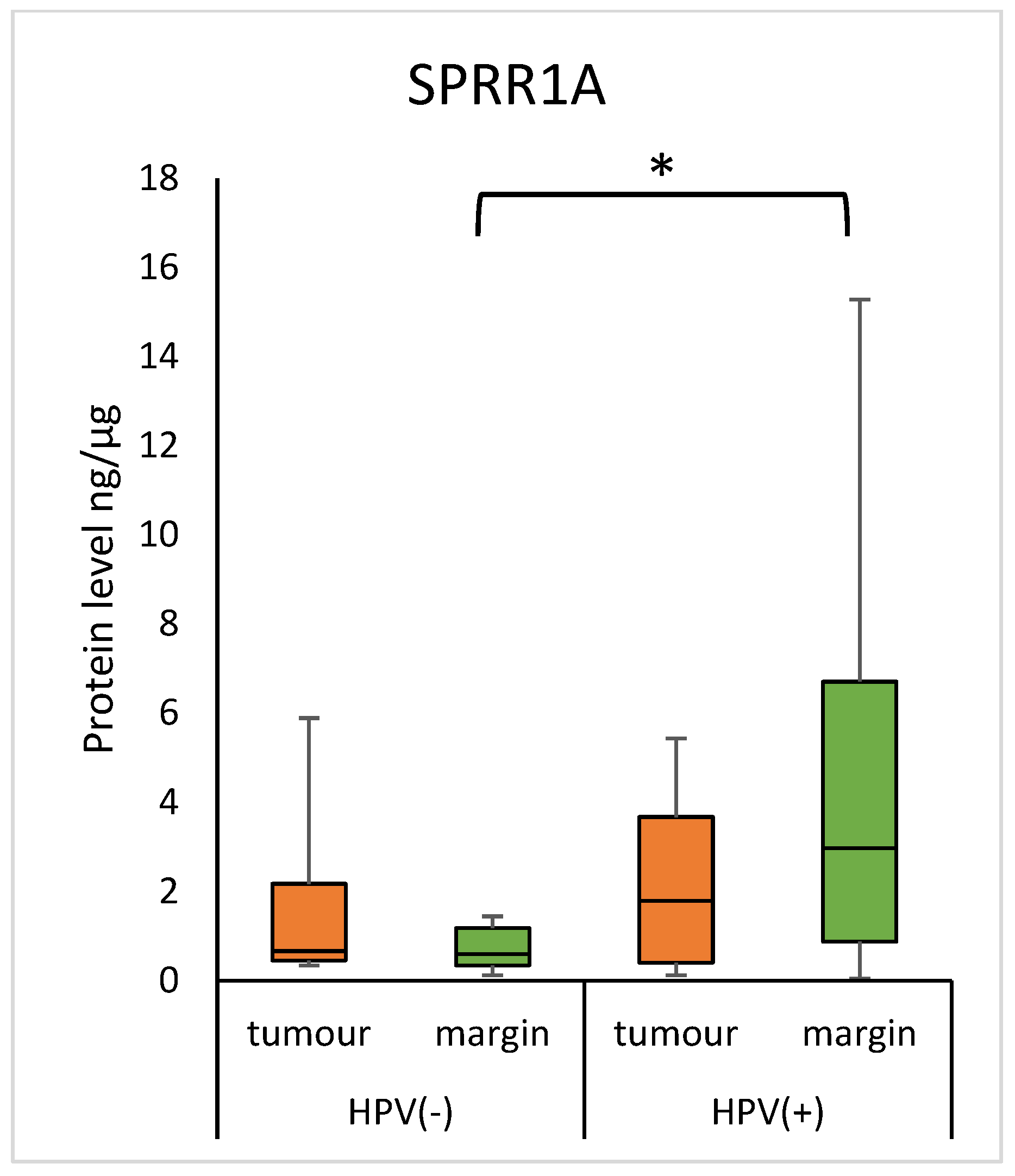
3.5. Concentration of SPRR Proteins and HPV Status
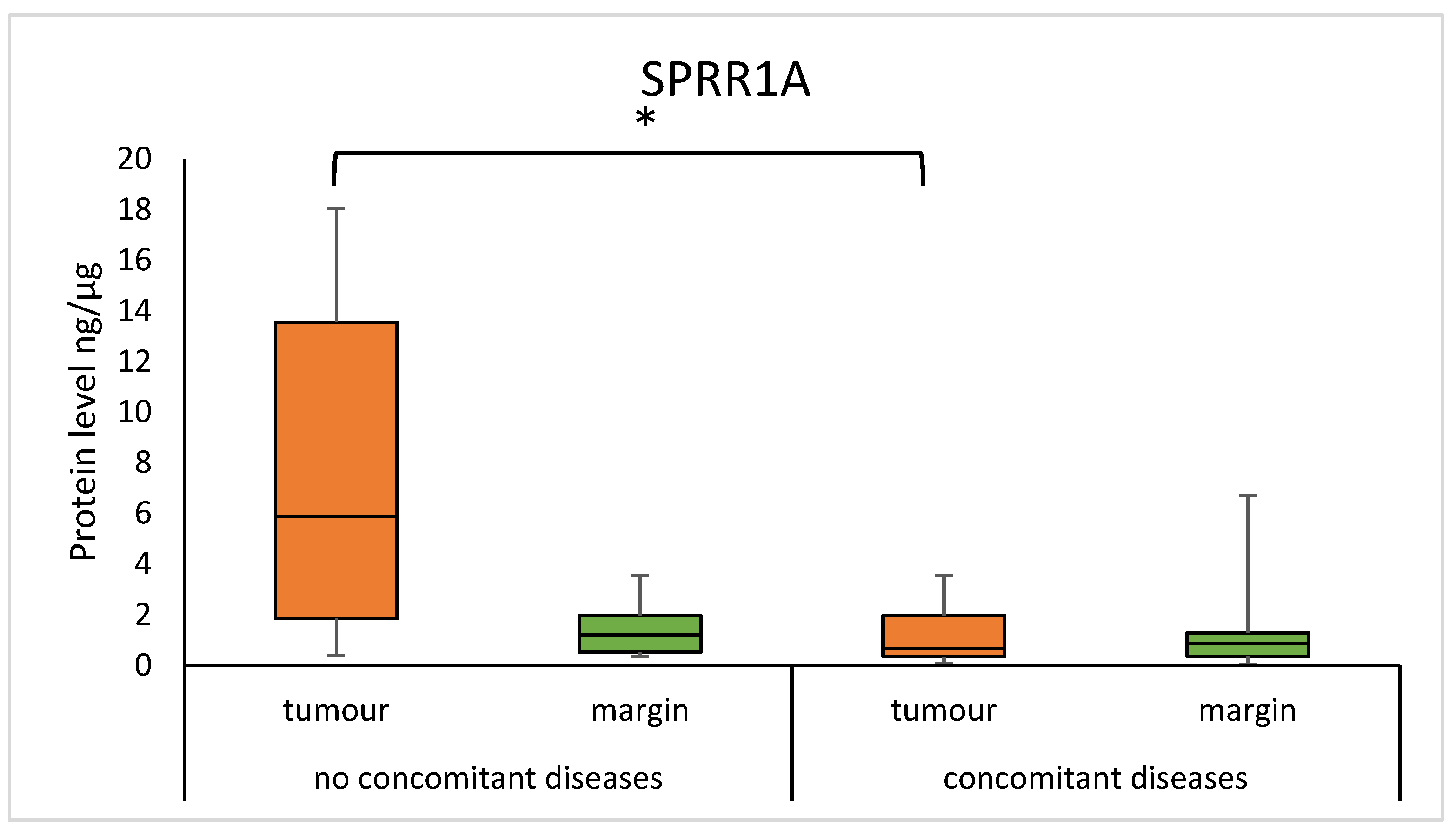
3.6. SPRR Protein Level in Tumour and Margin Samples in Patients with Concomitant Diseases
3.7. SPRR Protein Level in Tumour and Margin Samples According to Ki-67 Proliferation Index Ki-67 Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amaral, M.N.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Current Insights and Progress in the Clinical Management of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, F.; Buonaguro, L.; Caponigro, F.; Ionna, F.; Starita, N.; Annunziata, C.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Tornesello, M.L. Update on Head and Neck Cancer: Current Knowledge on Epidemiology; Risk Factors; Molecular Features and Novel Therapies. Oncology 2015, 89, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leemans, C.; Snijders, P.; Brakenhoff, R. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoli, A.; Gosavi, A.S.; Shirwadkar, U.P.; Wangdale, K.V.; Behera, S.K.; Kurrey, N.K.; Kalia, K.; Mandoli, A. Overview of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Risk factors; mechanisms; and diagnostics. Oral Oncol. 2021, 121, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Marekov, L.N.; Kim, S.; Brahim, J.S.; Park, M.H.; Steinert, P.M. Small proline-rich protein 1 is the major component of the cell envelope of normal human oral keratinocytes. FEBS Lett. 2000, 477, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carregaro, F.; Stefanini, A.C.B.; Henrique, T.; Tajara, E.H. Study of small proline-rich proteins (SPRRs) in health and disease: A review of the literature. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2013, 305, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabini, A.; Zimmer, Y.; Medová, M. Beyond keratinocyte differentiation: Emerging new biology of small proline-rich proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, N.J.; Varuzza, L.; Machado-Lima, A.; Lauretto, M.S.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Severino, P.; Nobrega, F.G.; Head and Neck Genome Project GENCAPO; Silva, W.A.; et al. Searching for molecular markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) by statistical and bioinformatic analysis of larynx-derived SAGE libraries. BMC Med. Genom. 2008, 1, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Yu, J.H.; Cho, Y.K.; Jung, C.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Gong, G.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, D.H. Expression of SPRR3 is associated with tumour cell proliferation in less advanced stages of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Qu, X.; Han, N.; Ruan, M.; Zhang, C. Decreased CSTA expression promotes lymphatic metastasis and predicts poor survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 126, 105116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Z. Small proline-rich repeat protein 3 enhances the sensitivity of esophageal cancer cells in response to DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, W. Small proline-rich protein 1A promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression and indicates unfavorable clinical outcomes. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 100, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nałęcz, D.; Świętek, A.; Hudy, D.; Wiczkowski, K.; Złotopolska, Z.; Strzelczyk, J.K. Assessment of Concentration KRT6 Proteins in Tumour and Matching Surgical Margin from Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heller-Milev, M.; Huber, M.; Panizzon, R. Expression of small proline rich proteins in neoplastic and inflammatory skin diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 143, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y. High SPRR1A expression is associated with poor survival in patients with colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3417–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, D.P.; Southwick, H.W.; Smejkal, W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin. Cancer 1953, 6, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakhuis, B.J.; Tabor, M.P.; Kummer, J.A.; Leemans, C.R.; Brakenhoff, R.H. A genetic explanation of Slaughter’s concept of field cancerization: Evidence and clinical implications. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1727–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Michifuri, Y.; Hirohashi, Y.; Torigoe, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Fujino, J.; Tamura, Y.; Tsukahara, T.; Kanaseki, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Sasaki, T.; et al. Small proline-rich protein-1B is overexpressed in human oral squamous cell cancer stem-like cells and is related to their growth through activation of MAP kinase signal. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, L.L.; Ma, J. Survival-related indicators ALOX12B and SPRR1A are associated with DNA damage repair and tumour microenvironment status in HPV 16-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 714. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hecht, S.S. Carcinogenic components of tobacco and tobacco smoke: A 2022 update. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaigzi, J.; Wright, P.S.; Oreffo, V.; An, G.; Wu, R.; Carlson, D.M. A small proline-rich protein regulated by vitamin A in tracheal epithelial cells is induced in lung tumours. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1993, 9, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraguti, G.; Terracina, S.; Petrella, C.; Greco, A.; Minni, A.; Lucarelli, M.; Agostinelli, E.; Ralli, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Raponi, G.; et al. Alcohol and Head and Neck Cancer: Updates on the Role of Oxidative Stress, Genetic, Epigenetics, Oral Microbiota, Antioxidants, and Alkylating Agents. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, A.; Kemény, L. Psoriasis and alcohol: Is cutaneous ethanol one of the missing links? Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetris, A.J.; Specht, S.; Nozaki, I.; Lunz, J.G., 3rd; Stolz, D.B.; Murase, N.; Wu, T. Small proline-rich proteins (SPRR) function as SH3 domain ligands; increase resistance to injury and are associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cholangiocytes. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.L.; Phillips, S.L.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Microarray analysis identifies differentiation-associated genes regulated by human papillomavirus type 16 E6. Virology 2013, 314, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, E.; Hohl, D.; Huber, M.; Brown, D. Infection with Human Papillomavirus alters expression of the small proline rich proteins 2 and 3. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, M.A.; Arroyo-Solera, I.; León, X.; Téllez-Gabriel, M.; Virós, D.; Gallardo, A.; Céspedes, M.V.; Casanova, I.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; Barnadas, A.; et al. The combined use of EFS, GPX2; and SPRR1A expression could distinguish favorable from poor clinical outcome among epithelial-like head and neck carcinoma subtypes. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1830–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyöngyösi, E.; Szalmás, A.; Ferenczi, A.; Póliska, S.; Kónya, J.; Veress, G. Transcriptional regulation of genes involved in keratinocyte differentiation by human papillomavirus 16 oncoproteins. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakubo, G.D.; Jakupciak, J.P.; Birch-Machin, M.A.; Parr, R.L. Clinical implications and utility of field cancerization. Cancer Cell Int. 2007, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradervand, S.; Yasukawa, H.; Muller, O.G.; Kjekshus, H.; Nakamura, T.; St Amand, T.R.; Yajima, T.; Matsumura, K.; Duplain, H.; Iwatate, M.; et al. Small proline-rich protein 1A is a gp130 pathway- and stress-inducible cardioprotective protein. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4517–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wie, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Dong, X. Serum Small Proline-Rich Protein 2A (SPRR2A) Is a Noninvasive Biomarker in Gastric Cancer. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 8493796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, K.M.; Wong, A.C.; Wu, B.; Horschman, M.; Zhao, H.; Brooks, J.D. Sprr2f protects against renal injury by decreasing the level of reactive oxygen species in female mice. Am. J. Physiol.—Ren. Physiol. 2020, 319, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M.L. Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer is a distinct epidemiologic, clinical, and molecular entity. Semin. Oncol. 2024, 31, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | n (%) |
|---|---|
| T classification | |
| T1 | 4 (6.56) |
| T2 | 6 (9.84) |
| T3 | 21 (34.43) |
| T4 | 30 (49.18) |
| Nodal status (N) | |
| N0 | 30 (49.18) |
| N1 | 11 (18.03) |
| N2 | 17 (27.87) |
| N3 | 3 (4.92) |
| Histological grading (G) | |
| G1 | 18 (29.51) |
| G2 | 33 (54.10) |
| G3 | 5 (8.20) |
| G4 | 2 (3.28) |
| NA * | 3 (4.92) |
| HPV status | |
| Yes | 17 (27.87) |
| No | 29 (47.54) |
| NA * | 15 (24.59) |
| p16 status | |
| Yes | 12 (19.67) |
| No | 47 (77.05) |
| NA * | 2 (3.28) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nałęcz, D.; Świętek, A.; Hudy, D.; Złotopolska, Z.; Opyrchał, J.; Aebisher, D.; Strzelczyk, J.K. Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131633
Nałęcz D, Świętek A, Hudy D, Złotopolska Z, Opyrchał J, Aebisher D, Strzelczyk JK. Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131633
Chicago/Turabian StyleNałęcz, Dariusz, Agata Świętek, Dorota Hudy, Zofia Złotopolska, Jakub Opyrchał, David Aebisher, and Joanna Katarzyna Strzelczyk. 2025. "Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131633
APA StyleNałęcz, D., Świętek, A., Hudy, D., Złotopolska, Z., Opyrchał, J., Aebisher, D., & Strzelczyk, J. K. (2025). Analysis of Selected Small Proline-Rich Proteins in Tissue Homogenates from Samples of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131633







