Novel Splice Variant in the HES7 Gene in Vietnamese Patient with Spondylocostal Dysostosis 4: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
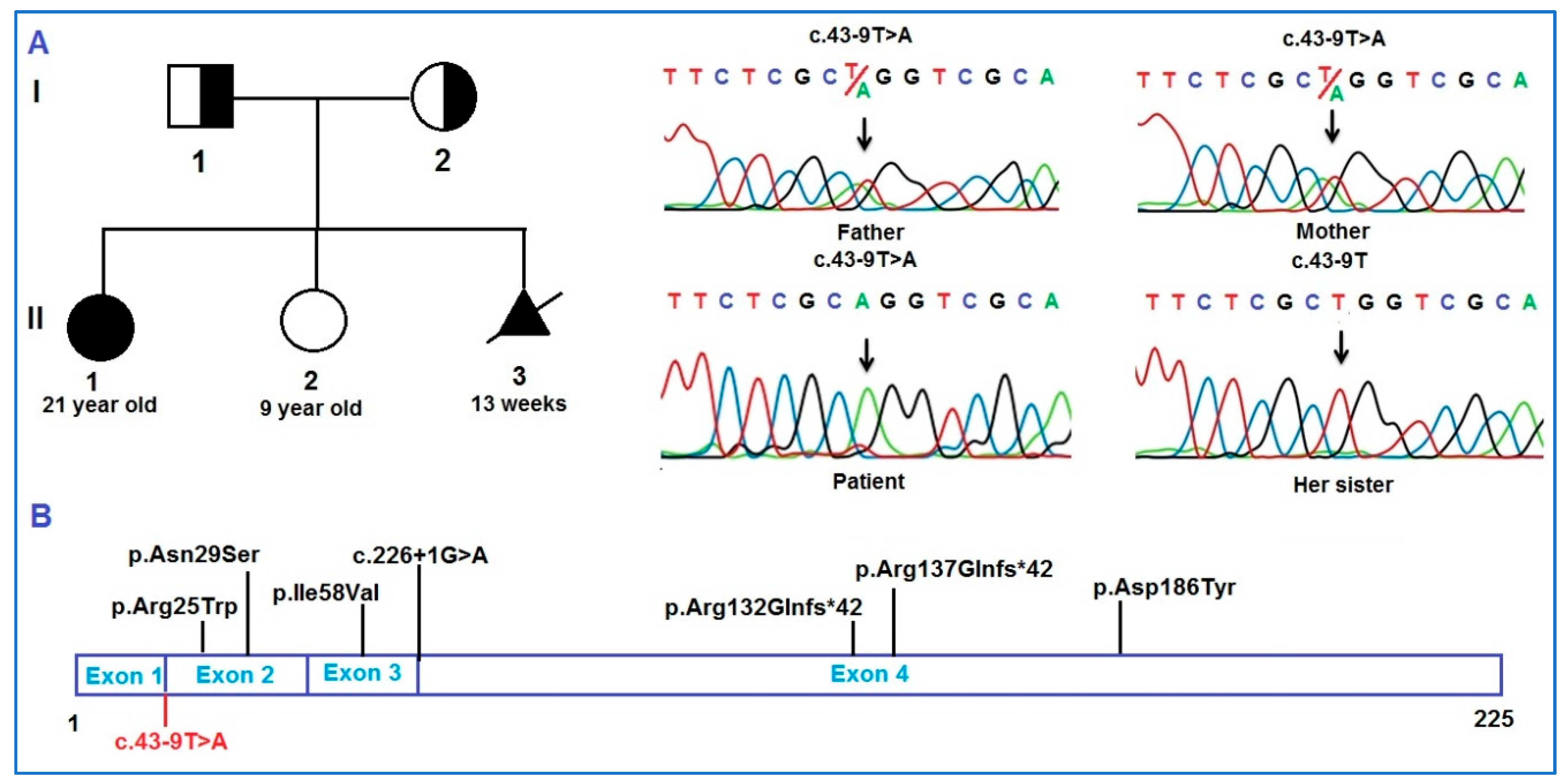
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McAlister, W.H. Spondylocostal dysostosis. Sci. Direct 1973, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geister, K.A.; Camper, S.A. Advances in skeletal dysplasia genetics. Annu. Rev. Gen. Hum. Genet. 2015, 16, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdon, W.E.; Lampl, B.S.; Cornier, A.S.; Ramirez, N.; Turnpenny, P.D.; Vitale, M.G.; Seimon, L.P.; Cowles, R.A. Clinical and radiological distinction between spondylothoracic dysostosis (Lavy-Moseley syndrome) and spondylocostal dysostosis (Jarcho-Levin syndrome). Pediatr. Radiol. 2011, 41, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Chapman, G.; Dunwoodie, S.L. The mouse notches up another success: Understanding the causes of human vertebral malformation. Mamm. Genome 2011, 22, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourquie, O. Vertebrate segmentation: From cyclic gene networks to scoliosis. Cell 2011, 145, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canalis, E. Notch in skeletal physiology and disease. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, M.P.; Kusumi, K.; Frayling, T.M.; McKeown, C.; Garrett, C.; Lander, E.S.; Krumlauf, R.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ellard, S.; Turnpenny, P.D. Mutations in the human delta homologue, DLL3, cause axial skeletal defects in spondylocostal dysostosis. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumi, K.; Mimoto, M.S.; Covello, K.L.; Beddington, R.S.; Krumlauf, R.; Dunwoodie, S.L. DLL3 pudgy mutation differentially disrupts dynamic expression of somite genes. Genesis 2004, 39, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittock, N.V.; Sparrow, D.B.; Wouters, M.A.; Sillence, D.; Ellard, S.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; Turnpenny, P.D. Mutated MESP2 causes spondylocostal dysostosis in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Chapman, G.; Wouters, M.A.; Whittock, N.V.; Ellard, S.; Fatkin, D.; Turnpenny, P.D.; Kusumi, K.; Sillence, D.; Dunwoodie, S.L. Mutation of the Lunatic Fringe gene in humans causes spondylocostal dysostosis with a severe vertebral phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Guillén-Navarro, E.; Fatkin, D.; Dunwoodie, S.L. Mutation of Hairy-and-Enhancer-of-Split-7 in humans causes spondylocostal dysostosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 3761–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Ming, X.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Shinawi, M.; Shen, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Xie, H.; et al. TBX6 null variants and a common hypomorphic allele in congenital scoliosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney-Leo, A.M.; Sparrow, D.B.; Harris, J.E.; Gardiner, B.B.; Marshall, M.S.; O’Reilly, V.C.; Shi, H.; Brown, M.A.; Leo, P.J.; Zanki, A.; et al. Compound heterozygous mutations in RIPPLY2 associated with vertebral segmentation defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, T.; Nashabat, M.; Alghanem, B.; Alhallaj, A.; Boudjelal, M.; Umair, M.; Alarifi, S.; Alfares, A.; Mohrij, S.A. Delta like-1 gene mutation: A novel cause of congenital vertebral malformation. Front. Genet. 2019, 510, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnpenny, P.D.; Sloman, M.; Dunwoodie, S. Spondylocostal Dysostosis, Autosomal Recessive; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews®: Seattle, WA, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Nobrega, A.; Maia-Fernandes, A.C.; Andrade, R.P. Altered cogs of the clock: Insights into the embryonic etiology of spondylocostal dysostosis. J. Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umair, M.; Younus, M.; Shafiq, S.; Nayab, A.; Alfadhel, M. Clinical genetics of spondylocostal dysostosis: A mini review. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 996364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Sillence, D.; Wouters, M.A.; Turnpenny, P.D.; Dunwoodie, S.L. Two novel missense mutations in HAIRY-AND-ENHANCER-OF-SPLIT-7 in a family with spondylocostal dysostosis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, D.B.; Faqeih, E.A.; Sallout, B.; Alswaid, A.; Ababneh, F.; Al-Sayed, M.; Rukban, H.; Eyaid, W.M.; Kageyama, R.; Ellard, S.; et al. Mutation of HES7 in a large extended family with spondylocostal dysostosis and dextrocardia with situs inversus. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2013, 161A, 2244–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, M.; Dieux-Coeslier, A.; Baujat, G.; Schaefer, E.; Judith, S.O.; Bazin, A.; Pinson, L.; Attie-Bitach, T.; Baumann, C.; Fradin, M.; et al. Diagnostic strategy in segmentation defect of the vertebrae: A retrospective study of 73 patients. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 55, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiao, B. A novel homozygous HES7 splicing variant causing spondylocostal dysostosis 4: A case report. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1201999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Arshad, A.; Ullah, A.; Steenackers, E.; Mortier, G.; Ahmad, W.; Arshad, M.; Khan, S.; Hayat, A.; Khan, I.; et al. Identification of a novel nonsense variant in the DLL3 gene underlying spondylocostal dysostosis in a consanguineous Pakistani family. Mol. Syndromol. 2023, 14, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnpenny, P.D.; Whittock, N.; Duncan, J.; Dunwoodie, S.; Kusumi, K.; Ellard, S. Novel mutations in DLL3, a somitogenesis gene encoding a ligand for the Notch signalling pathway, cause a consistent pattern of abnormal vertebral segmentation in spondylocostal dysostosis. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Lai, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Guan, S.; Kuo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Peng, M.; et al. Trio-whole-exome sequencing and preimplantation genetic diagnosis for unexplained recurrent fetal malformations. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafe, L.; Giunta, C.; Gassner, M.; Steinmann, B.; Superti-Furga, A. A cluster of autosomal recessive spondylocostal dysostosis caused by three newly identified DLL3 mutations segregating in a small village. Clin. Genet. 2003, 64, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampietro, P.F.; Raggio, C.L.; Reynolds, C.; Ghebranious, N.; Burmester, J.K.; Glurich, I.; Rasmussen, K.; McPherson, E.; Pauli, R.M.; Shukla, S.K.; et al. DLL3 as a candidate gene for vertebral malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical application of whole-exome sequencing across clinical indications: Abnormality of skeletal system. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddirevula, S.; Alsahli, S.; Alhabeeb, L.; Patel, N.; Alzahrani, F.; Shamseldin, H.E.; Anazi, S.; Ewida, N.; Alsaif, H.S.; Mohamed, J.Y.; et al. Expanding the phenome and variome of skeletal dysplasia. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornier, A.S.; Staehling-Hampton, K.; Delventhal, K.M.; Saga, Y.; Caubet, J.F.; Sasaki, N.; Ellard, S.; Young, E.; Ramirez, N.; Carlo, S.E.; et al. Mutations in the MESP2 gene cause spondylothoracic dysostosis/Jarcho-Levin syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmann, S.; Koller, H.; Sticht, H.; Kraus, C.; Krumbiegel, M.; Uebe, S.; Ekici, A.B.; Reis, A.; Thiel, C.T. Clinical and molecular delineation of spondylocostal dysostosis type 3. Clin. Genet. 2021, 99, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Kou, I.; Mizumoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Kawakami, N.; Nakajima, M.; Otomo, N.; Ogura, Y.; Miyake, N.; Matsumoto, N.; et al. Screening of known disease genes in congenital scoliosis. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengryn, P.; da Costa Silveira, K.; Oborn, C.; Soltys, C.L.; Beke, A.; Chacon-Fonseca, I.; Damseh, N.; Rodriguez, M.Q.; Badilla-Porras, R.; Kannu, P. Functional characterization of novel Lunatic Fringe variants in spondylocostal dysostossis type—III with scoliosis. Hum. Mutat. 2023, 2023, 5989733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, N.; Mizumoto, S.; Lu, H.F.; Takeda, K.; Campos-Xavier, B.; Mittaz-Crettol, L.; Guo, L.; Takikawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, S.; et al. Identification of novel LFNG mutations in spondylocostal dysostosis. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecca, M.; Bedeschi, M.F.; Izzi, C.; Dordoni, C.; Rinaldi, B.; Peluso, F.; Caraffi, S.G.; Prefumo, F.; Signorelli, M.; Zanzucchi, M.; et al. Identification of bi-allelic LFNG variants in three patients and further clinical and molecular refinement of spondylocostal dysostosis 3. Clin. Genet. 2023, 104, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mizumoto, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Dan, M.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; et al. Identification of a novel LFNG variant in a Chinese fetus with spondylocostal dysostosis and a systematic review. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 69, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, M.; Duffourd, Y.; Jouan, T.; Poe, C.; Jean-Marçais, N.; Verloes, A.; St-Onge, J.; Riviere, J.B.; Petit, F.; Pierquin, G.; et al. Autosomal recessive variations of TBX6, from congenital scoliosis to spondylocostal dysostosis. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, N.; Takeda, K.; Kawai, S.; Kou, I.; Guo, L.; Osawa, M.; Alev, C.; Kawakami, N.; Miyake, N.; Matsumoto, N.; et al. Bi-allelic loss of function variants of TBX6 causes a spectrum of malformation of spine and rib including congenital scoliosis and spondylocostal dysostosis. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, D.B.; McInerney-Leo, A.; Gucev, Z.S.; Gardiner, B.; Marshall, M.; Leo, P.J.; Chapman, D.L.; Tasic, V.; Shishko, A.; Brown, M.A.; et al. Autosomal dominant spondylocostal dysostosis is caused by mutation in TBX6. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegler, M.; Roth, C.; Schumann, E.; Kogan, J.; Totten, E.; Guillen Sacoto, M.J.; Abou Jamra, R.; Hornemann, F. Congenital cervical spine malformation due to bi-allelic RIPPLY2 variants in spondylocostal dysostosis type 6. Clin. Genet. 2021, 99, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, E.R.; Andersen, E.F.; Cherry, A.M.; Kantarci, S.; Kearney, H.; Patel, A.; Raca, G.; Ritter, D.I.; South, S.T.; Thorland, E.C.; et al. Technical standards for the interpretation and reporting of constitutional copy number variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics (ACMG) and the clinical genome resource (ClinGen). Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampietro, P.F.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; Kusumi, K.; Pourquie, O.; Tassy, O.; Offiah, A.C.; Cornier, A.S.; Alman, B.A.; Blank, R.D.; Raggio, C.L.; et al. Progress in the understanding of the genetic etiology of vertebral segmentation disorders in humans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1151, 38–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gucev, Z.S.; Tasic, V.; Pop-Jordanova, N.; Sparrow, D.B.; Dunwoodie, S.L.; Ellard, S.; Young, E.; Turnpenny, P.D. Autosomal dominant spondylocostal dysostosis in three generations of a Macedonian family: Negative mutation analysis of DLL3, MESP2, HES7, and LFNG. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offiah, A.; Alman, B.; Cornier, A.S.; Giampietro, P.F.; Tassy, O.; Wade, A.; Turnpenny, P.D. Pilot assessment of a radiologic classification system for segmentation defects of the vertebrae. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Alkhatib, B.; Serra, R. Development of the axial skeleton and intervertebral disc. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2019, 133, 49–90. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, M.M.; Takahashi, Y.; Endo, M.; Saga, Y. The Mesp2 transcription factor establishes segmental borders by suppressing Notch activity. Nature 2005, 19435, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, M.; Sasaki, N.; Oginuma, M.; Kiso, M.; Igarashi, K.; Aizaki, K.; Aizaki, K.; Kanno, J.; Saga, Y. The negative regulation of Mesp2 by mouse Ripply2 is required to establish the rostro-caudal patterning within a somite. Development 2007, 134, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shifley, E.T.; VanHorn, K.M.; Perez-Balaguer, A.; Franklin, J.D.; Weinstein, M.; Cole, S.E. Oscillatory lunatic fringe activity is crucial for segmentation of the anterior but not posterior skeleton. Development 2008, 135, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, Y.; Sakata, R.; Komatsu, S.; Shiota, K.; Yamada, S.; Kageyama, R. Dynamic expression and essential functions of Hes7 in somite segmentation. Genes. Dev. 2001, 15, 2642–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, N. TBX6-associated congenital scoliosis (TACS) as a clinically distinguishable subtype of congenital scoliosis: Further evidence supporting the compound inheritance and TBX6 gene dosage model. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Kou, I.; Kawakami, N.; Iida, A.; Nakajima, M.; Ogura, Y.; Imagawa, E.; Miyake, N.; Matsumoto, N.; Yasuhiko, Y.; et al. Compound heterozygosity for null mutations and a common hypomorphic risk haplotype in TBX6 causes congenital scoliosis. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Yuan, D.; Zuo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Qiu, G.; Huang, S.; Giampietro, P.F.; et al. Progress and perspective of TBX6 gene in congenital vertebral malformations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57430–57441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, A.; Koshida, S.; Takada, S. Activator-to-repressor conversion of T-box transcription factors by the Ripply family of Groucho/TLEassociated mediators. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 3236–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Serey-Gaut, M.; Scala, M.; Reversade, B.; Ruaud, L.; Cabrol, C.; Musacchia, F.; Torella, A.; Accogli, A.; Escande-Beillard, N.; Langlais, J.; et al. Congenital posterior cervical spine malformation due to biallelic c.240-4T>G RIPPLY2 variant: A discrete entity. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer-Zirnsak, B.; Segebrecht, L.; Schubach, M.; Charles, P.; Alderman, E.; Brown, K.; Cadieux-Dion, M.; Cartwright, T.; Chen, Y.; Costin, C.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of the notch ligand DLL1 causes variable neurodevelopmental disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, M.; Hosalkar, H.; Gill, I.; Noordeen, H. Spondylocostal dysostosis: Thirteen new cases treated by conservative and surgical means. Spine 2004, 29, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, T.; Kedes, L.; Hamamori, Y. HES and HERP families: Multiple effectors of the notch signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 194, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Matsui, T.; Yamao, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Tamada, K.; Takumi, T.; Kohno, K.; Oba, S.; Ishii, S.; Sakumura, Y.; et al. The period of the somite segmentation clock is sensitive to notch activity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3541–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bello-Rojas, S.; Bagnall, M.W. Clonally related, notch-differentiated spinal neurons integrate into distinct circuits. Elife 2022, 11, e83680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, Y.; Masamizu, Y.; Liu, T.; Nakayama, R.; Deng, C.X.; Kageyama, R. The initiation and propagation of Hes7 oscillation are cooperatively regulated by Fgf and notch signaling in the somite segmentation clock. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Gessler, M. Delta-notch–and then? Protein interactions and proposed modes of repression by hes and hey bHLH factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4583–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Protein | Phenotype | Number of Related Variants/ Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLL3 (AR) OMIM 602768 NM_016941.4 19q13.2 | Delta protein | Spondylocostal dysostosis 1 (OMIM 277300) | 34 related variants [7,8] |
| MESP2 (AR) OMIM 605195 NM_001039958.2 15q26.1 | Basically transcription factor | Spondylocostal dysostosis 2 (OMIM 608681) | 10 related variants [9] |
| LFNG (AR) OMIM 602576 NM_001040167.2 7p22.3 | Glycosyl transferase | Spondylocostal dysostosis 3 (OMIM 609813) | 17 related variants [10] |
| HES7 (AR) OMIM 608059 NM_001165967.2 17p13.1 | Transcriptional repressor protein | Spondylocostal dysostosis 4 (OMIM 613686) | 8 related variants [11] |
| TBX6 (AR/AD) OMIM 602427 NM_004608.3 16p11.2 | T-box transcription factor | Spondylocostal dysostosis 5 (OMIM 122600) | 7 related variants [12] |
| RIPPLY2 (AR) OMIM 609891 NM_001009994.2 6q14.2 | Transcriptional repressor protein | Spondylocostal dysostosis 6 (OMIM 616566) | 2 related variants [13] |
| DLL1 (AR) OMIM 606582 NM_005618.4 6q27 | Delta ligand | Spondylocostal dysostosis 7 | 1 related variants [14] |
| Gene | Position in cDNA | Position in Protein | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLL3 | c.535G>T | p.Glu179* | [22] |
| c.621C>A | p.Cys207* | [23] | |
| c.661C>T | p.Arg221* | [24] | |
| c.712C>T | p.Arg238* | [25] | |
| c.805G>A | p.Gly269Arg | [26] | |
| c.926G>A | p.Cys309Tyr | [23] | |
| c.980G>A | p.Cys327Tyr | [27] | |
| c.1086C>A | p.Cys362* | [23] | |
| c.1136G>A | p.Cys379Tyr | [28] | |
| c.1138C>T | p.Arg380Cys | [20] | |
| c.1154G>A | p.Gly385Asp | [7] | |
| c.1164C>A | p.Cys388* | [20] | |
| c.1511G>A | p.Gly504Asp | [7] | |
| c.329delT | p.Val110Glyfs*22 | [28] | |
| c.395delG | p.Gly132Glufs*109 | [23] | |
| c.593insGCGGT | p.Ser198ins5 | [7] | |
| c.599_603dupGCGGT | p.Pro202Alafs*41 | [25] | |
| c.602_614dup13 | p.Pro206Serfs*14 | [23] | |
| c.602delG | p.Gly201Valfs*40 | [23] | |
| c.603ins5 | p.Pro206Serfs*14 | [23] | |
| c.614ins13 | p.? | [23] | |
| c.615delC | p.Arg205 | [25] | |
| c.618delC | p.Cys207Alafs*34 | [25] | |
| c.868_870+8del11 | p.? | [23] | |
| c.945_946delAT | p.Ala317Argfs*17 | [25] | |
| c.948_949delTG | p.Ala317Argfs*17 | [23] | |
| c.1183_1184insCGCTGC | p.Cys395delinsSerLeuArg | [20] | |
| c.1238_1255dup18 | p.His413_Ala418dup | [23] | |
| c.1256ins18 | p.? | [23] | |
| c.1291_1307dup17 | p.Pro437Thrfs*117 | [25] | |
| c.1285–1301dup | p.? | [25] | |
| c.1365_1381del17 | p.Cys455Trpfs*5 | [23] | |
| c.1418delC | p.Ala473Glufs*75 | [23] | |
| c.1440delG | p.Pro481Argfs*67 | [25] | |
| MESP2 | c.307G>T | p.Gln103* | [29] |
| c.367G>T | p.Gln123* | [20] | |
| c.373C>G | p.Leu125Val | [29] | |
| c.376G>T | p.Glu123* | [20] | |
| c.688C>T | p.Gln230* | [29] | |
| c.737G>A | p.Trp246* | [17] | |
| c.1166A>G | p.Glu389Gly | [17] | |
| c.599delA | p.Gln200Argfs*281 | [17] | |
| c.180_193dup14 | p.Glu65Alafs*60 | [17] | |
| c.500_503dupACCG | p.Gly169Profs*199 | [17] | |
| LFNG | c.446C>T | p.Thr149Ile | [30] |
| c.467T>G | p.Leu156Arg | [31] | |
| c.521G>T | p.Arg174Leu | [32] | |
| c.564C>A | p.Phe188Leu | [10] | |
| c.583T>C | p.Trp195Arg | [20] | |
| c.601G>A | p Asp201Asn | [33] | |
| c.761C>T | p.Thr254Met | [28] | |
| c.766G>A | p.Gly256Ser | [32] | |
| c.842C>G | p.Thr281Lys | [20] | |
| c.856C>T | p. Arg286Trp | [31] | |
| c.890T>G | p.Val297Gly | [34] | |
| c.1063G>A | p.Asp355Asn | [34] | |
| c.1078C>T | p.Arg360Cys | [35] | |
| c.44dupG | p.Ala16Argfs*135 | [20] | |
| c.372delG | p. Lys124Asnfs*21 | [33] | |
| c.822-5C>T | [34] | ||
| c.863dupC | p.Asp289* | [34] | |
| HES7 | c.73C>T | p.Arg25Trp | [11] |
| c.86A>G | p.Asn29Ser | [20] | |
| c.172G>A | p.Ile58Val | [18] | |
| c.556G>T | p.Asp186Tyr | [18] | |
| c.43-9T>A | This study | ||
| c.226+1G>A | [21] | ||
| c.400_409dup10 | p.Arg137Glnfs*42 | [19] | |
| TBX6 | c.422C>T | p.Leu141Pro | [36] |
| c.449G>A | p.Arg150His | [37] | |
| c.661C>A | p.His221Asp | [17] | |
| c.699G>C | p.Trp233Cys | [36] | |
| c.1311G>C | p.*437Cys | [38] | |
| c.1148C>A | p.Ser383* | [17] | |
| c.994delG | p.Glu332Lysfs*166 | [17] | |
| RIPPLY2 | c.238A>T | p.Arg80* | [39] |
| c.240-4T>G | [39] | ||
| DLL1 | c.1534G>A | p.Gly512Arg | [14] |
| In Silico Prediction Tools | Wildtype | Mutant | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| EX-SKIP | −144.498 | Exon skipping | |
| Fruitfly | 0.66 | 0.99 | Acceptor loss |
| MaxEntScan | 9.51 | 2.24 | Damage variant |
| NetGene2 | 0.67 | 0.97 | Acceptor loss |
| Spliceailookup | - | 0.91 | Acceptor loss |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.M.; Lien, N.T.K.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, N.L.; Nguyen, S.B.T.; Bui, T.H.C.; Tung, N.V.; Thanh, L.T.; Xuan, N.T.; Tran, V.K.; et al. Novel Splice Variant in the HES7 Gene in Vietnamese Patient with Spondylocostal Dysostosis 4: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131587
Nguyen HM, Lien NTK, Tran TH, Nguyen NL, Nguyen SBT, Bui THC, Tung NV, Thanh LT, Xuan NT, Tran VK, et al. Novel Splice Variant in the HES7 Gene in Vietnamese Patient with Spondylocostal Dysostosis 4: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131587
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Ha Minh, Nguyen Thi Kim Lien, Thinh Huy Tran, Ngoc Lan Nguyen, Suong Bang Thi Nguyen, Thi Hong Chau Bui, Nguyen Van Tung, Le Tat Thanh, Nguyen Thi Xuan, Van Khanh Tran, and et al. 2025. "Novel Splice Variant in the HES7 Gene in Vietnamese Patient with Spondylocostal Dysostosis 4: A Case Report and Literature Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131587
APA StyleNguyen, H. M., Lien, N. T. K., Tran, T. H., Nguyen, N. L., Nguyen, S. B. T., Bui, T. H. C., Tung, N. V., Thanh, L. T., Xuan, N. T., Tran, V. K., & Hoang, N. H. (2025). Novel Splice Variant in the HES7 Gene in Vietnamese Patient with Spondylocostal Dysostosis 4: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131587






