Unilateral Renal Agenesis: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Issues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prenatal Diagnosis
2.1. Prenatal Ultrasound of Normal Kidneys
2.2. Prenatal Ultrasound in Unilateral Renal Agenesis
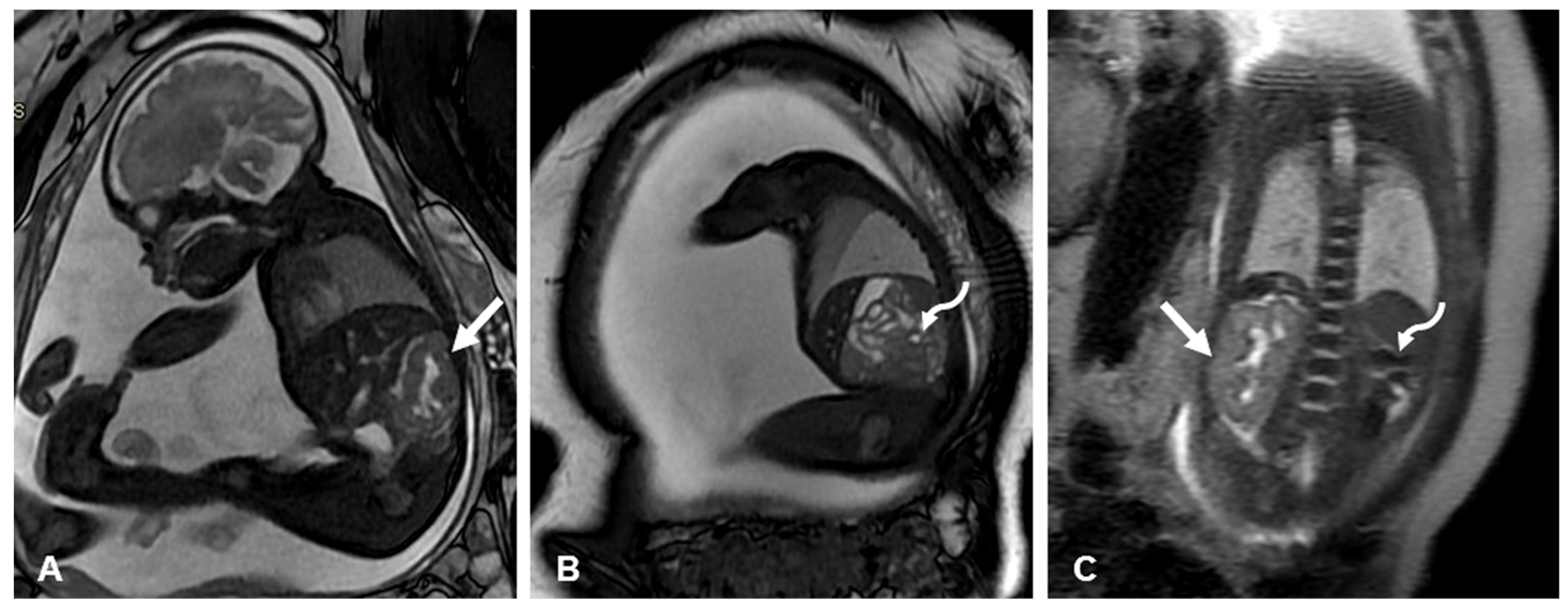
2.2.1. Empty Renal Fossa
2.2.2. ‘Lying Down’ Adrenal Gland
2.2.3. Contralateral Renal Hypertrophy
2.2.4. Absent Ipsilateral Renal Artery
3. Prenatal Evaluations
3.1. Prenatal Imaging Assessment
3.2. Prenatal Genetic Evaluation
4. Postnatal Evaluations
4.1. Birth Defect Registries
4.2. Early Postnatal Screening with Abdominal/Renal Ultrasound
5. Further Pediatric Evaluations
5.1. Urinary and Extra-Urinary Anomalies
5.2. Renal Function Tests
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Cheng, H.H.; Abbas, A.; Snijders, R.J.; Gosden, C. Fetal renal defects: Associated malformations and chromosomal defects. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 1992, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesel, A.; Queisser-Luft, A.; Clementi, M.; Bianca, S.; Stoll, C.; EUROSCAN Study Group. Prenatal detection of congenital renal malformations by fetal ultrasonographic examination: An analysis of 709,030 births in 12 European countries. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 48, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, T.; Sairam, S.; Kumarasiri, S. Ultrasound diagnosis of fetal renal abnormalities. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2014, 28, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Shazly, S.A.; Blumenfeld, Y.J.; Jelin, E.; Ruano, R. Update on the prenatal diagnosis and outcomes of fetal bilateral renal agenesis. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2019, 74, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM); Jelin, A. Renal agenesis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, B28–B30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaud Gonzalez, A.M.; Joseph, C.; Stover, S.R.; Nassr, A.; Koh, C.J.; Angelo, J.R.; Braun, M.C. Fetal nephrology: A quaternary care center experience. Kidney360 2023, 4, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, W.L.M.; Leung, A.K.C.; Rogers, R.C. Unilateral renal agenesis. Adv. Pediatr. 1995, 42, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeds, J.W. Borderline genitourinary tract abnormalities. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 1998, 19, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, M.; Moshiri, M.; Phillips, G.; Biyyam, D.; Dubinsky, T. Fetal genitourinary anomalies. A pictorial review with postnatal correlation. Ultrasound Q. 2011, 27, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileto, A.; Itani, M.; Katz, D.S.; Siebert, J.R.; Dighe, M.K.; Dubinsky, T.J.; Moshiri, M. Fetal urinary tract anomalies: Review of pathophysiology, imaging, and management. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westland, R.; Schreuder, M.F.; Ket, J.C.; van Wijk, J.A. Unilateral renal agenesis: A systematic review on associated anomalies and renal injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, M.F. Life with one kidney. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, E.L. Normal and Abnormal Development of the Kidney; Year Book Medical Publishers: Chicago, IL, USA, 1972; pp. 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.Y.; Holznagel, D.E.; Ameli, J.R.; Sohaey, R. Prenatal diagnosis of renal developmental anomalies associated with an empty renal fossa. Ultrasound Q. 2010, 26, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.S.; Dashe, J.S. Unilateral renal agenesis. In Obstetric Imaging: Fetal Diagnosis and Care, 2nd ed.; Copel, J.A., D’Alton, M.E., Feltovich, H., Gratacos, E., Odibo, A.O., Platt, L.D., Tutschek, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 43–45.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulak, O.; Ozgüner, G.; Malas, M.A. Size and location of the kidneys during the fetal period. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.L.; Cooper, J.; Eisenberg, P.; Mandel, F.S.; Gross, B.R.; A Goldman, M.; Barzel, E.; Rawlinson, K.F. Normal length of fetal kidneys: Sonographic study in 397 obstetric patients. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1991, 157, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konje, J.C.; Okaro, C.I.; Bell, S.C.; de Chazal, R.; Taylor, D.J. A cross-sectional study of changes in fetal renal size with gestation in appropriate- and small-for-gestational-age fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitty, L.S.; Altman, D.G. Charts of fetal size: Kidney and renal pelvis measurements. Prenat. Diagn. 2003, 23, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, S.H.; Damen-Elias, H.A.; Stigter, R.H.; van der Doef, R.; Goldschmeding, R.; de Jong, T.P.V.M.; Westers, P.; Visser, G.H.A.; Pistorius, L.R. Size and volume charts of fetal kidney, renal pelvis and adrenal gland. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 40, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heling, K.S.; Chaoui, R. Ultrasound diagnosis of malformations of the fetal kidneys and urinary system. Ultraschall Med. 2024, 45, 232–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. AIUM Practice Parameter for the performance of detailed second- and third-trimester diagnostic obstetric ultrasound examinations. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 3093–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, M.; Tsukahara, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Kasuga, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Mayumi, M. Renal aplasia is the predominant cause of congenital solitary kidneys. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesrobian, H.G.; Rushton, H.G.; Bulas, D. Unilateral renal agenesis may result from in utero regression of multicystic renal dysplasia. J. Urol. 1993, 150 Pt 2, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Iwanaga, J.; Loukas, M.; Oskouian, R.J.; Tubbs, R.S. Pelvic kidney: A review of the literature. Cureus 2018, 10, e2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubihal, V.; Razik, A.; Sharma, S.; Das, C.J. Unveiling the confusion in renal fusion anomalies: Role of imaging. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4254–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, D.M.; Thompson, H.O.; Armstrong, B.; Woods, J.R. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of unilateral fetal renal agenesis. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 1990, 18, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanty, P.; Romero, R.; Kepple, D.; Stoney, D.; Coggins, T.; Fleischer, A.C. Prenatal diagnoses in unilateral empty renal fossa. J. Ultrasound Med. 1990, 9, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, A.; Batukan, C. Sonographic findings of fetuses with an empty renal fossa and normal amniotic fluid volume. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2004, 19, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.S.; Benson, C.B.; Lebowitz, R.L. The clinical significance of an empty renal fossa on prenatal sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2005, 24, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Moon, M.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, S.H. Measurement of compensatory hyperplasia of the contralateral kidney: Usefulness for differential diagnosis of fetal unilateral empty renal fossa. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 34, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, E.; Tutus, S. Empty fetal renal fossa results of a tertiary center. Perinat. J. 2021, 29, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.R.; Bowie, J.D.; Andreotti, R.F.; Fields, S.I. Sonographic evaluation of fetal adrenal glands. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1982, 139, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, C.K.; Filly, R.A.; Callen, P.W. The “lying down” adrenal sign: A sonographic indicator of renal agenesis or ectopia in fetuses and neonates. J. Ultrasound Med. 1992, 11, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majmudar, A.; Cohen, H.L. “Lying-down” adrenal sign: There are exceptions to the rule among fetuses and neonates. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, T.D.; Malhotra, A.; Webb, J.A.; Savage, M.O.; Reznek, R.H. Embryology of the adrenal glands and its relevance to diagnostic imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2005, 60, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochat, P.; Febvey, O.; Bacchetta, J.; Bérard, E.; Cabrera, N.; Dubourg, L. Towards adulthood with a solitary kidney. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 2311–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, J.; Peters, C.A.; Estroff, J.A.; Allred, E.N.; Benacerraf, B.R. Human fetal compensatory renal growth. J. Urol. 1993, 150 Pt 2, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazebrook, K.N.; McGrath, F.P.; Steele, B.T. Prenatal compensatory renal growth: Documentation with US. Radiology 1993, 189, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.M.; Nowak, A.; Hartle, R.; Tush, B. Fetal compensatory renal hypertrophy with a unilateral functioning kidney. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 15, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Lotan, D.; Dekel, B.; Kivilevitch, Z.; Hazan, Y.; Achiron, R.; Gilboa, Y. Prenatal compensatory renal growth in unilateral renal agenesis. Prenat. Diagn. 2016, 36, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindryckx, A.; Raaijmakers, A.; Levtchenko, E.; Allegaert, K.; De Catte, L. Analysis of renal blood flow and renal volume in normal fetuses and in fetuses with a solitary functioning kidney. Prenat. Diagn. 2017, 37, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorne, N.; Shepard, T.; Barr, M. Compensatory renal growth in human fetuses with unilateral renal agenesis. Teratology 1991, 44, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houat, A.P.; Guimaraes, C.T.S.; Takahashi, M.S.; Rodi, G.P.; Gasparetto, T.P.D.; Blasbalg, R.; Velloni, F.G. Congenital anomalies of the upper urinary tract: A comprehensive review. Radiographics 2021, 41, 462–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleper, R. Mechanisms of compensatory renal growth. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2012, 10, 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Altinkaya, S.; Turgut, U.K.; Narin, R. Determining the location and position of renal arteries on the aorta during the second-trimester ultrasound examination of non-anomalous fetuses: A cross-sectional study. Perinat. J. 2024, 32, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- DeVore, G.R. The value of color Doppler sonography in the diagnosis of renal agenesis. J. Ultrasound Med. 1995, 14, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, W.; Stagiannis, K.D.; Flack, N.J.; Fisk, N.M. Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of renal agenesis with color flow imaging in severe second-trimester oligohydramnios. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1995, 173, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, A.S.; Hillman, K.A. Unilateral renal agenesis and the congenital solitary functioning kidney: Developmental, genetic and clinical perspectives. BJU Int. 2007, 99, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedl, A. Renal abnormalities and their developmental origin. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschen, G.W.; Blakemore, K.; Al-Kouatly, H.B.; Fridkis, G.; Baschat, A.; Gearhart, J.; Jelin, A.C. The genetic etiologies of bilateral renal agenesis. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonni, G.; Koçak, Ç.; Grisolia, G.; Rizzo, G.; Júnior, E.A.; Werner, H.; Ruano, R.; Sepulveda, W.; Bonasoni, M.P.; Lituania, M.; et al. Clinical presentations and diagnostic imaging of VACTERL association. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2023, 42, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragan, D.C.; Casale, A.J.; Rink, R.C.; Cain, M.P.; Weaver, D.D. Genitourinary anomalies in the CHARGE association. J. Urol. 1999, 161, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Ma, A.; Wilson, M.; Williams, G.; Curotta, J.; Munns, C.F.; Mehr, S. CHARGE syndrome: A review. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 50, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsell, D.G.; Bao, C.; White, T.P.; Chan, E.; Matsell, E.; Cojocaru, D.; Catapang, M.; Pediatric Nephrology Clinical Pathway Development Team. Outcomes of solitary functioning kidneys–renal agenesis is different than multicystic dysplastic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogelova, H.; Bouchalova, K.; Smakal, O.; Halek, J.; Langova, K.; Cizkova, K. Early diagnosis of solitary functioning kidney: Comparing the prognosis of kidney agenesis and multicystic dysplastic kidney. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, C.M.; Chasen, S.T. Unilateral fetal renal abnormalities: Are they really isolated? J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, O.; Beloosesky, R.; Gover, A.; Bronshtein, M. Unilateral renal agenesis diagnosed on early prenatal transvaginal scans. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2019, 21, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Faghihimehr, A.; Gharavi, M.; Mancuso, M.; Sreedher, G. Fetal MR imaging in urogenital system anomalies. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 3487–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, G.E.; Millischer, A.E.; Mahallati, H.; Siauve, N.; Melbourne, A.; Grevent, D.; Vinit, N.; Heidet, L.; Aigrain, Y.; Ville, Y.; et al. The use of fetal MRI for renal and urogenital tract anomalies. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkemeier, K. MR Imaging of the fetal genitourinary tract. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2024, 32, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurichesse Delmas, H.; Kohler, M.; Doray, B.; Lémery, D.; Francannet, C.; Quistrebert, J.; Marie, C.; Perthus, I. Congenital unilateral renal agenesis: Prevalence, prenatal diagnosis, associated anomalies. Data from two birth-defect registries. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi-Dain, L.; Maya, I.; Peleg, A.; Reches, A.; Banne, E.; Baris, H.N.; Tenne, T.; Singer, A.; Ben-Shachar, S. Microarray analysis in pregnancies with isolated unilateral kidney agenesis. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lin, N.; Su, L.; Wu, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, L. Copy number variations associated with fetal congenital kidney malformations. Mol. Cytogenet. 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.Y.; Fu, F.; Li, R.; Yu, Q.X.; Du, K.; Zhang, W.W.; Deng, Q.; Li, L.S.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in the evaluation of fetal congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract detected by ultrasonography. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, B.; Wang, C.; Hu, P.; Qiao, F.; Xu, Z. Molecular diagnostic in fetuses with isolated congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract by whole-exome sequencing. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Qian, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, W. Genetic analysis of congenital unilateral renal agenesis in children based on next-generation sequencing. Pediatr. Res. 2025, 97, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.D.; Baird, P.A. Renal agenesis in British Columbia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1985, 21, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Robert, E.; Källén, B. Epidemiologic characteristics of kidney malformations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 16, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Hayashida, M.; Yanagihara, T.; Yoshida, J.; Takeda, S.; Tatsuma, N.; Tsugu, H.; Hino, Y.; Munakata, E.; Murakami, M. Ultrasound screening for renal and urinary tract anomalies in healthy infants. Pediatr. Int. 2003, 45, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruessner, S.E.; Klein, K.; Peter, C.; Bueltmann, E.; Wagner, J.; Klingmueller, V. Ultrasound screening of the kidneys and urinary tract in 11.887 newborn infants: A 10-year experience. Open J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 2, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urisarri, A.; Gil, M.; Mandia, N.; Aldamiz-Echevarría, L.; Iria, R.; González-Lamuño, D.; Couce, M.-L. Retrospective study to identify risk factors for chronic kidney disease in children with congenital solitary functioning kidney detected by neonatal renal ultrasound screening. Medicine 2018, 97, e11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyuz, A.; Tekin, M. The diagnostic efficacy of and requirement for postnatal ultrasonography screening for congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiulo, V.A.; Caiulo, S.; Gargasole, C.; Chiriacò, G.; Latini, G.; Cataldi, L.; Mele, G. Ultrasound mass screening for congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, S.; Sessa, A.S.; Riccio, S.; Capalbo, D.; Reginelli, A.; Cappabianca, S.; Rambaldi, P.F.; del Giudice, E.M.; Polito, C.; Marzuillo, P. Early renal ultrasound in patients with congenital solitary kidney can guide follow-up strategy reducing costs while keeping long-term prognostic information. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, O.M.; Albedaiwi, K.; Al Harbi, B.; Al Otay, A.; Al Ghanbar, M.; Nakshabandi, Z. Unilateral renal agenesis: Necessity of postnatal evaluation in a contemporary series. Urology 2016, 98, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krill, A.; Cubillos, J.; Gitlin, J.; Palmer, L.S. Abdominopelvic ultrasound: A cost-effective way to diagnose solitary kidney. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 2201–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabnar, J.; Rus, R.R. Is renal scintigraphy really a necessity in the routine diagnosis of congenital solitary kidney? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2019, 35, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, H.; Bayazit, A.K.; Büyükçelik, M.; Soran, M.; Noyan, A.; Anarat, A. Associated anomalies in children with congenital solitary functioning kidney. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2005, 21, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneyama, K.; Yamataka, A.; Satake, S.; Yanai, T.; Lane, G.J.; Kaneko, K.; Yamashiro, Y.; Miyano, T. Associated urologic anomalies in children with solitary kidney. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 39, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.A.; Shapiro, L.R.; Stangel, J.J.; Klein, R.M.; Addonizio, J.C. The MURCS association: Müllerian duct aplasia, renal aplasia, and cervicothoracic somite dysplasia. J. Pediatr. 1979, 95, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Yadav, R.; Qi, B.; Wen, J.; Gang, X.; Banerjee, S. Kallmann syndrome: Diagnostics and management. Clin. Chim. Acta 2025, 565, 119994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.T.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Lteif, A. Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser anomaly and its associated malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 135, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Sheu, J.C.; Tsai, P.S.; Lee, M.D.; Lin, T.H.; Tsai, J.D. Zinner syndrome in children: Clinical presentation, imaging findings, diagnosis, and outcome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasic, I.; Topalovic, D.; Pavicevic, P.; Cvejic, S.; Milivojevic, S. Zinner syndrome in childhood and adolescence: Report of four cases and review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2025, 21, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi, K.K.; Garg, H.; Yu, R.N.; Chow, J.S. Zinner syndrome in pediatric age group: An underdiagnosed entity. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2024, 20, 705.e1–705.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.L.; Sanha, N.; Pereira, H.; Martins, A.; Costa, C. Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich syndrome also known as obstructed hemivagina and ipsilateral renal anomaly: A case report and a comprehensive review of literature. Radiol. Case Rep. 2023, 18, 2771–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.A.; Aguilar, L.; Heyward, Q.; Wheeler, C.; Caldamone, A. Screening for Mullerian anomalies in patients with unilateral renal agenesis: Leveraging early detection to prevent complications. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2018, 14, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walawender, L.; Santhanam, N.; Davies, B.; Fei, Y.F.; McLeod, D.; Becknell, B. Müllerian anomalies in girls with congenital solitary kidney. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acien, P.; Acien, M. Unilateral renal agenesis and female genital tract pathologies. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2010, 89, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Song, S.; Gao, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, R.; Yan, Y.; Huang, R.; Li, L.; Zhu, L. Clinical characteristics of 415 patients with obstructed hemivagina and ipsilateral renal anomaly syndrome: A nationwide multicenter retrospective study. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2025, S1477–S5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, M.F.; Langemeijer, M.E.; Bokenkamp, A.; Delemarre-Van de Waal, H.A.; Van Wijk, J.A. Hypertension and microalbuminuria in children with congenital solitary kidneys. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2008, 44, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzuillo, P.; Polito, C. Congenital solitary kidney in childhood: Not so bad. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, T.; Patzer, L.; John, U.; Dušek, J.; Vondrák, K.; Janda, J.; Misselwitz, J. Blood pressure, renal function, and proteinuria in children with unilateral renal agenesis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2006, 29, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, K.A.; Halili, L.; Guerra, A.; Geier, P.; Keays, M.; Guerra, L. Renal function in children with a congenital solitary functioning kidney: A systematic review. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2021, 17, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Scola, C.; Ammenti, A.; Bertulli, C.; Bodria, M.; Brugnara, M.; Camilla, R.; Capone, V.; Casadio, L.; Chimenz, R.; Conte, M.L.; et al. Management of the congenital solitary kidney: Consensus recommendations of the Italian Society of Pediatric Nephrology. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 2185–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K. Congenital solitary functioning kidney: Evaluations to do which, when, and how. Child. Kidney Dis. 2024, 28, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngelaki, A.; Mitsigiorgi, R.; Goadsby, J.; Hamed, K.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H. Routine 36-week scan: Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2025, 65, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

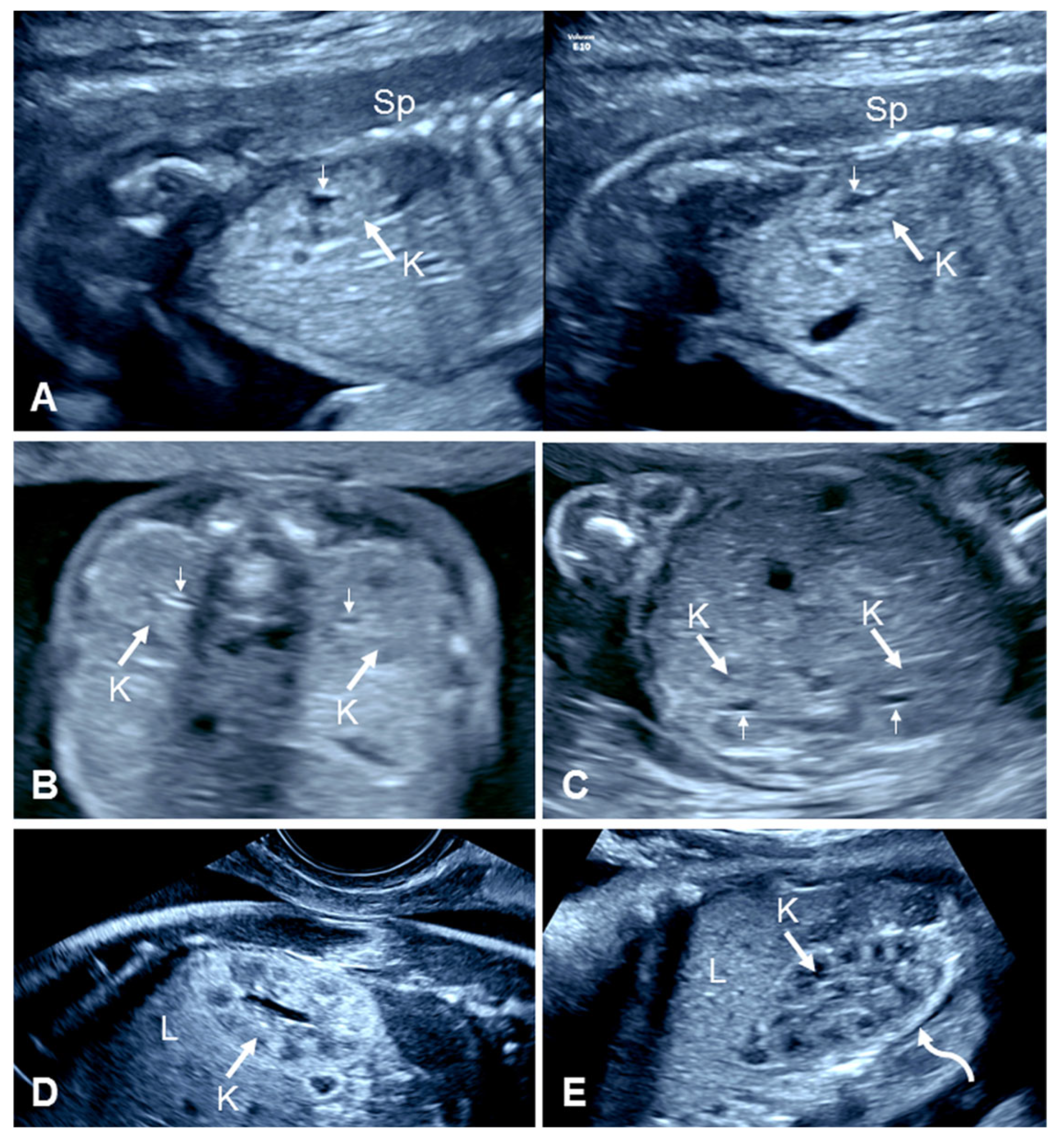
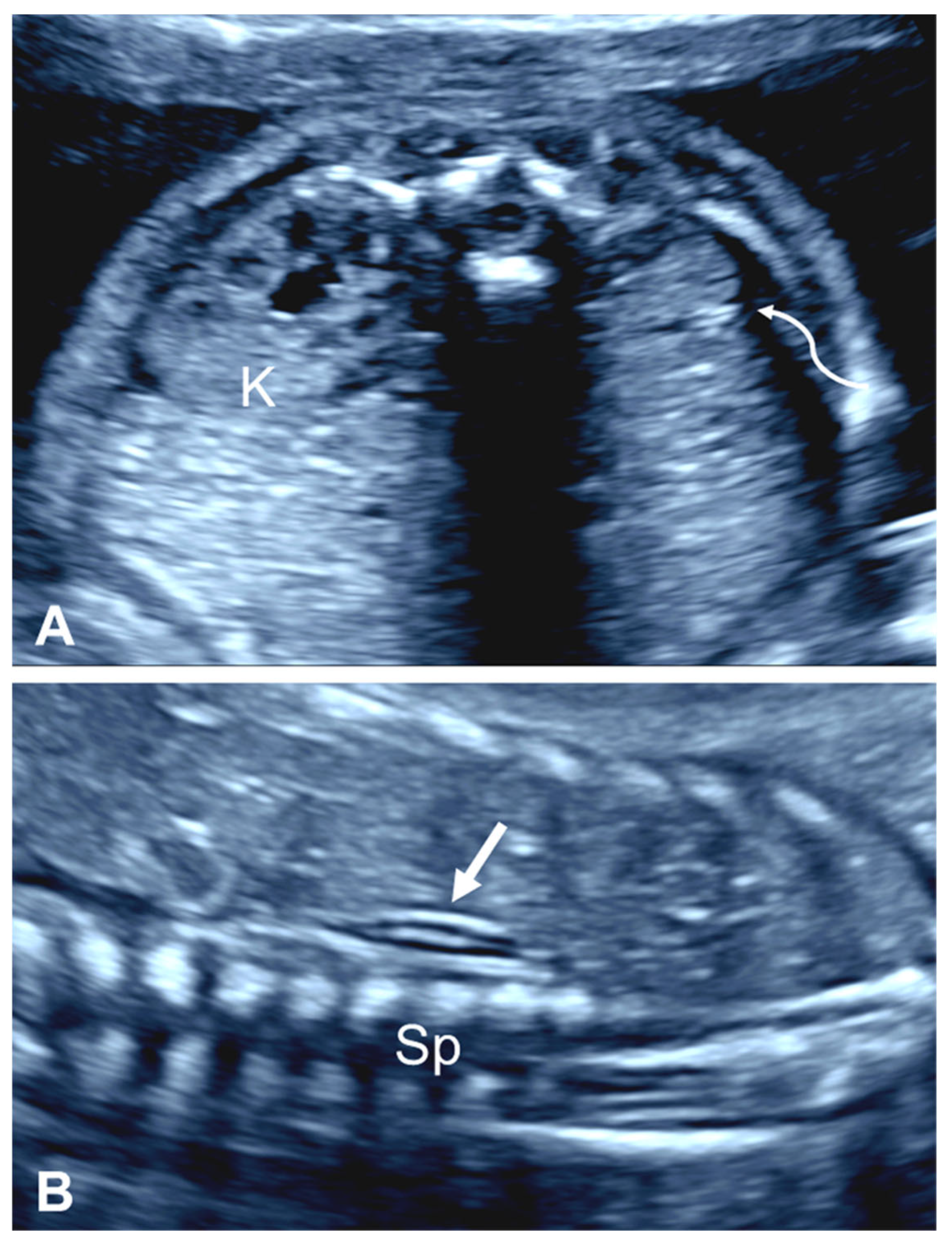
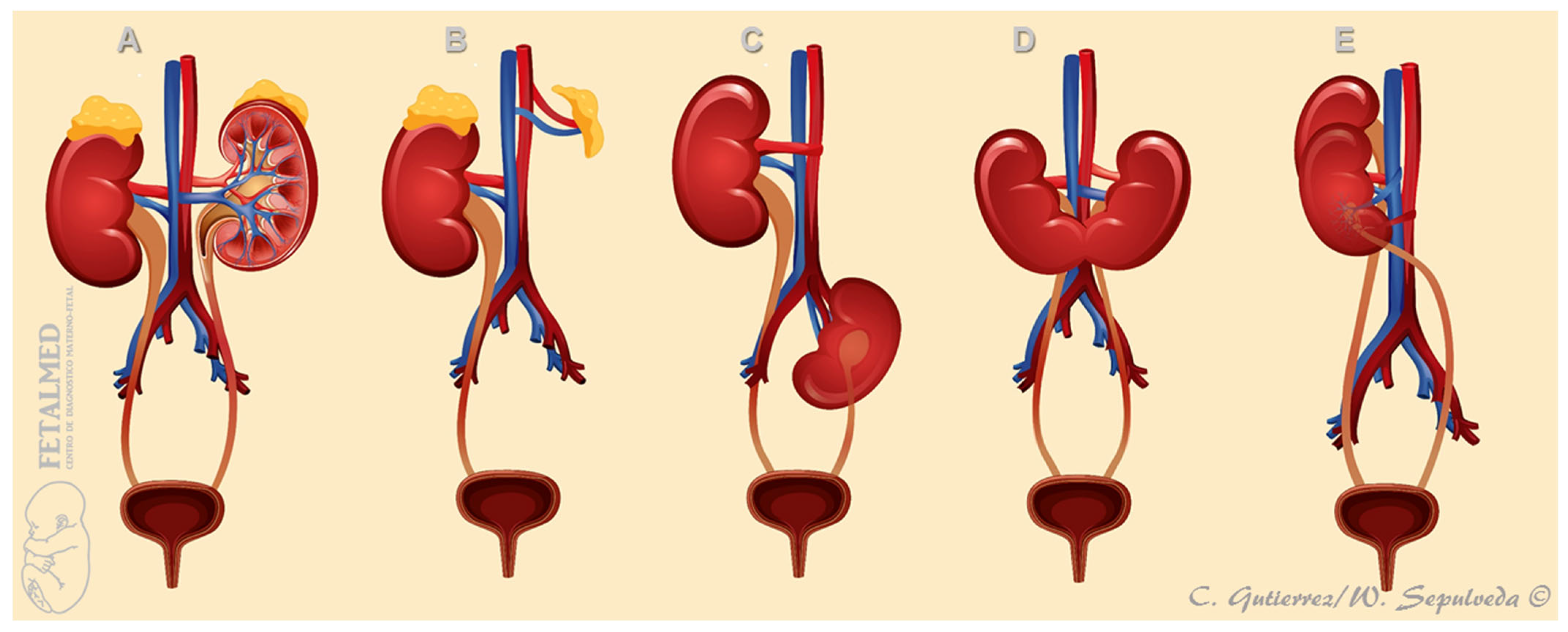
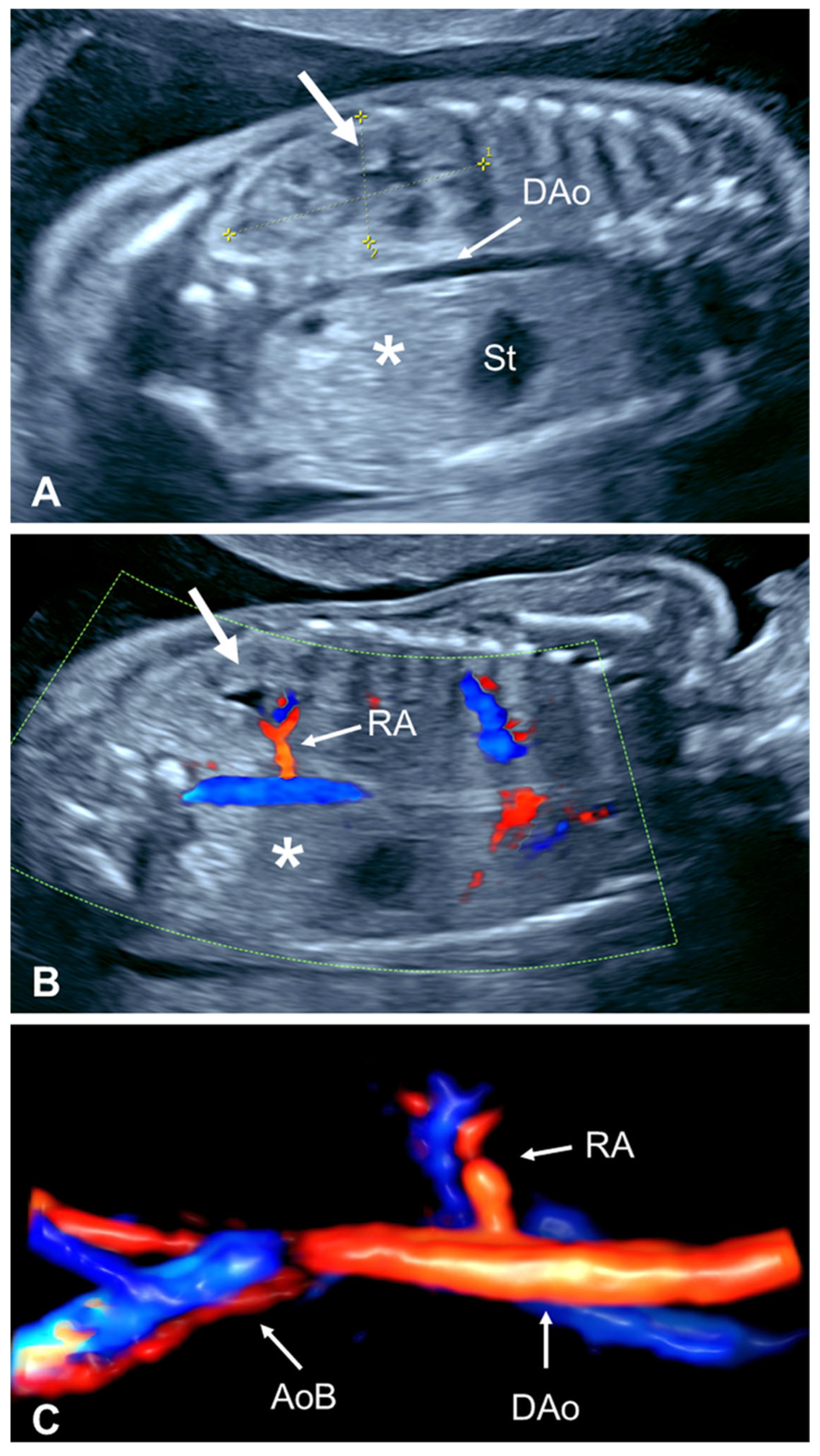
| First Author, Year | Cases (n) | GA at Diagnosis (Weeks) | URA (n (%)) | Pelvic Kidney n (%) | Horseshoe Kidney n (%) | CFRE n (%) | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeanty [28], 1990 | 6 | 28-Term | 3 (50) | 2 (33) | 1 (17) | ||
| Yuksel [29], 2004 | 40 | 18–37 * | 13 (32) | 24 (60) | 2 (5) | 1 (3) | |
| Chow [30], 2005 | 93 † | 17–39 | 44 (47) | 35 (38) | 4 (4) | 10 (11) † | |
| Cho [31], 2009 | 24 | 12 (50) | 6 (25) | 6 (25) ‡ | |||
| Toprak [32], 2021 | 10 | 17–24 | 2 (20) | 3 (30) | 4 (40) | 1 (10) | |
| Total | 173 | 74 (43) | 70 (40) | 6 (3) | 7 (4) | 16 (9) |
| First Author, Year | Study Period (Years) | Country | Deliveries (n) | Cases of URA (n) | Prevalence | Isolated/ Non-Isolated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wilson [68], 1985 | 1966–1982 | Canada | 625,132 | 90 | 1.4/10,000 | NR |
| Harris [69], 2000 | 1978–1993 1973–1993 1983–1992 | France Sweden USA | 1,418,519 2,191,790 2,221,735 =5,832,044 * | =407 * | =0.7/10,000 * | 56/56 48/75 58/114 =162/245 * |
| Laurichesse Delmas [62], 2017 | 1995–2013 | France | 447,885 | 177 | 4.0/10,000 | 106/71 |
| Total | 6,905,061 | 674 | 1.0/10,000 | 268/316 (46%/54%) † |
| First Author, Year | Population Screened (n) | Urinary Anomalies Detected (n (%)) | URA (n) | Characteristics and Age at Screening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tsuchiya [70], 2003 | 5700 | 198 (3.5) | 2 | Low-risk population; no anomalies detected on prenatal US Routine US at 1 month of age |
| Gruessner [71], 2012 | 11,887 | 335 (2.8) | 11 | Routine US at 3–10 days of life |
| Urisarri [72], 2018 | 32,900 | * 128 (0.4) | 74 | Retrospective observational study in newborn infants. Prenatal diagnosis of URA in 28 (38%) cases and diagnosis in the first week of life in 46 (62%) |
| Gulyuz [73], 2023 | 2629 | 121 (4.6) | 9 | Infants of 6 weeks to 3 months of age undergoing urinary tract US during routine pediatric care. Anomalies detected antenatally in 75 cases (6 URA) and postnatally in 46 cases (3 URA) |
| Caiulo [74], 2012 | 17,783 | 171 (1.0) | 0 | Routine US at 2 months of age |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sepulveda, W.; Wong, A.E.; Tonni, G.; Grisolia, G.; Ranzini, A.C. Unilateral Renal Agenesis: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Issues. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131572
Sepulveda W, Wong AE, Tonni G, Grisolia G, Ranzini AC. Unilateral Renal Agenesis: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Issues. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSepulveda, Waldo, Amy E. Wong, Gabriele Tonni, Gianpaolo Grisolia, and Angela C. Ranzini. 2025. "Unilateral Renal Agenesis: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Issues" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131572
APA StyleSepulveda, W., Wong, A. E., Tonni, G., Grisolia, G., & Ranzini, A. C. (2025). Unilateral Renal Agenesis: Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Issues. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131572






