Development and Performance Evaluation of T-prep24: A Novel Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction System Based on Silica Magnetic Beads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
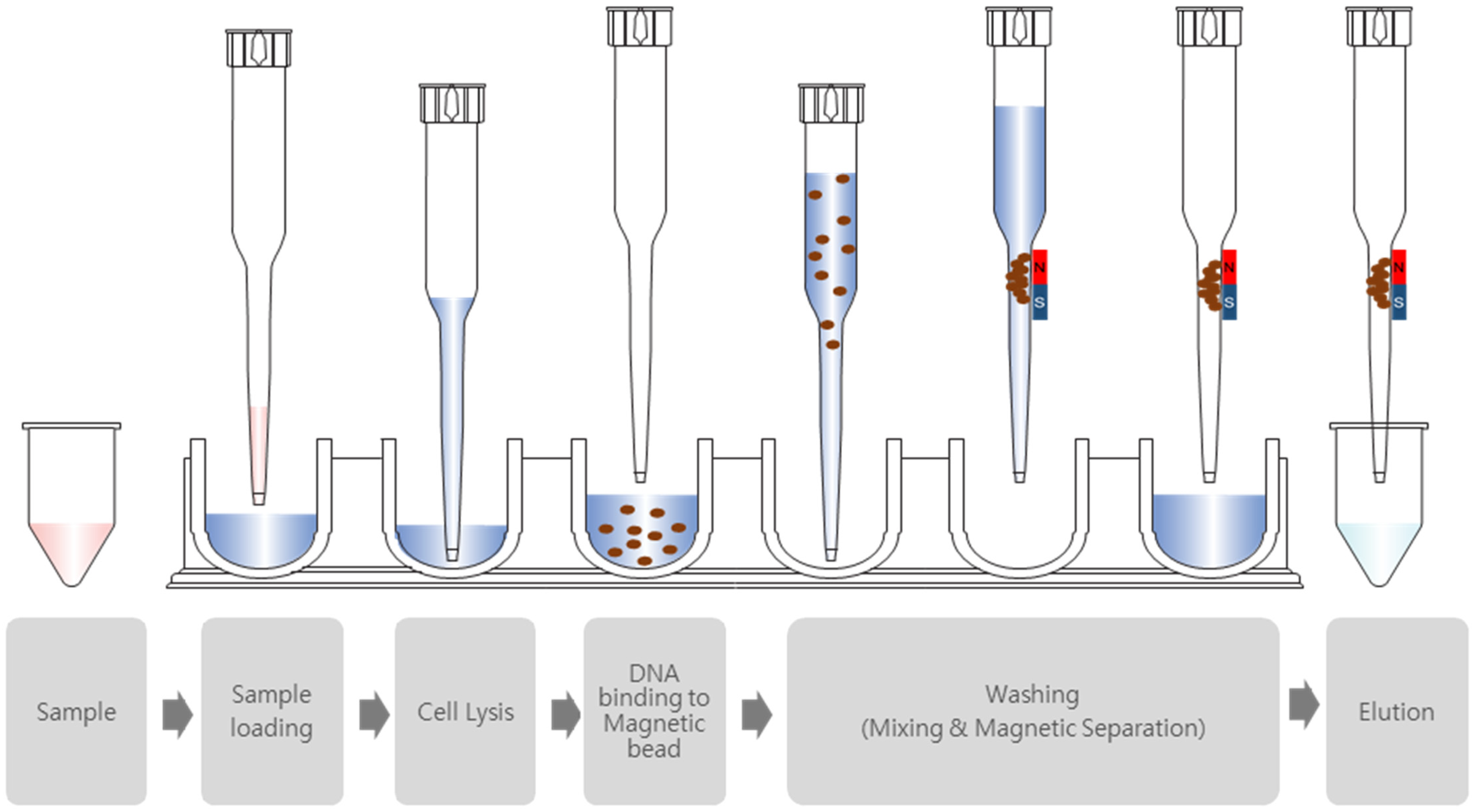
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.3. Measurement of Concentration and Quality of Extracted Nucleic Acid
2.4. Nucleic Acid Amplification Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Concentration and Purity of Extracted Nucleic Acid According to the Nucleic Acid Extraction System
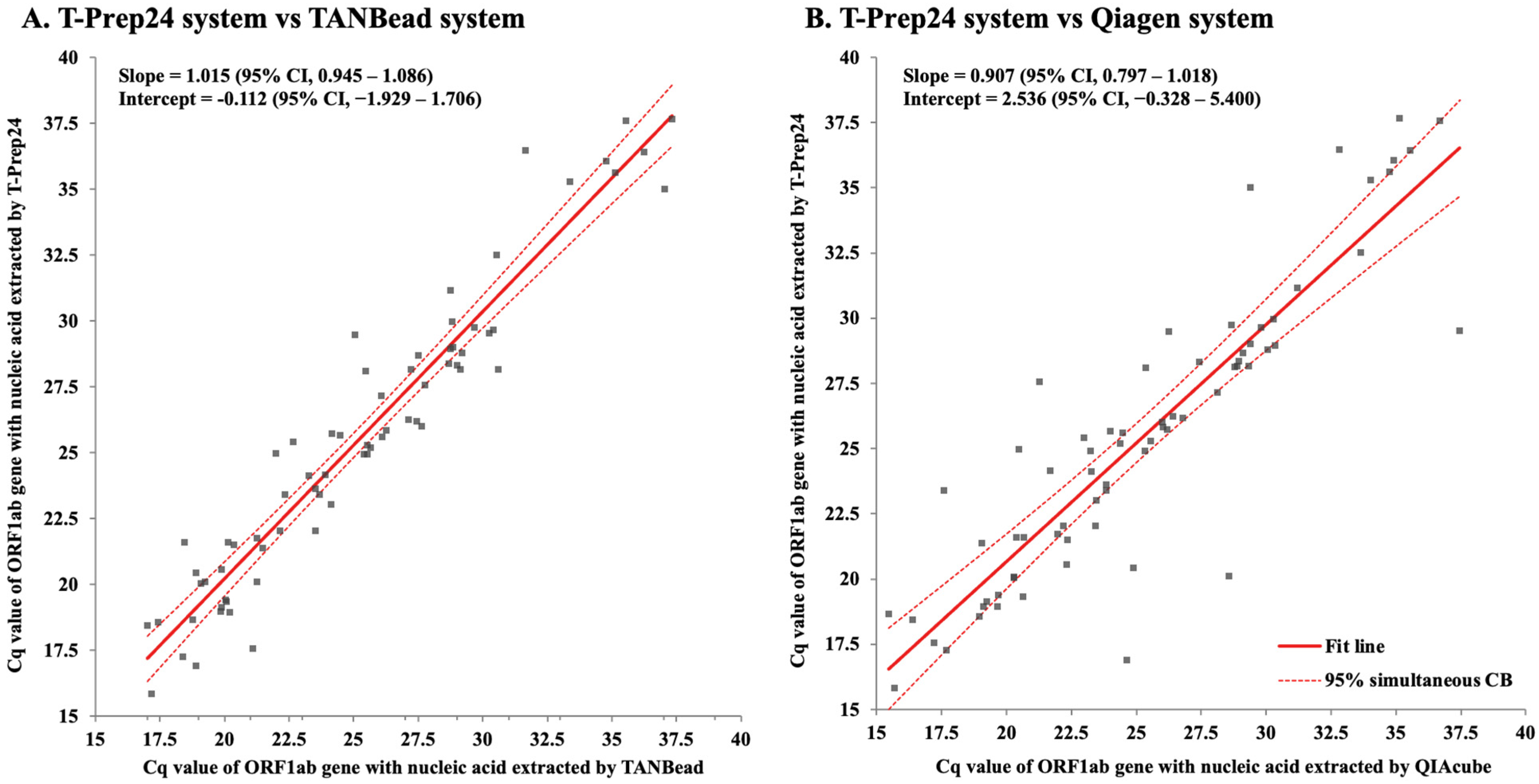
3.2. Result of SARS-CoV-2 PCR Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Li, T.; Yang, J.; Gu, L.; Wei, M. Molecular detection of Nocardia: Development and application of a real-time PCR assay in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H. Nucleic Acid Extraction Techniques. In Advanced Techniques in Diagnostic Microbiology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, R.; Sol, C.J.; Salimans, M.M.; Jansen, C.L.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; van der Noordaa, J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, J.A.; Ibe, C.O.; Moore, M.S.; Host, C.; Simon, G.L. Evaluation of a manual DNA extraction protocol and an isothermal amplification assay for detecting HIV-1 DNA from dried blood spots for use in resource-limited settings. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 54, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.L.; Wu, M.S.; Wu, P.C.; Chen, H.M.; Peng, Y.H.; Hsu, J.C.; Wang, D.Y. A collaborative study to establish the national standard for SARS-CoV-2 RNA nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAAT) in Taiwan. Biologicals 2022, 79, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laus, S.; Kingsley, L.A.; Green, M.; Wadowsky, R.M. Comparison of QIAsymphony automated and QIAamp manual DNA extraction systems for measuring Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in whole blood using real-time PCR. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, J.; Sato, Y.; Shinozaki, N.; Ye, B.; Tsuboi, A.; Nagasaki, M.; Yamashita, R. Comparison of Boiling and Robotics Automation Method in DNA Extraction for Metagenomic Sequencing of Human Oral Microbes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.H.; Kim, G.J.; Roh, K.H.; Sung, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, T.S.; Park, J.S.; Huh, H.J.; Park, Y.; et al. Update of Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomsgaard, A.S.; Rosenstierne, M.W. An alternative workflow for molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2—Escape from the NA extraction kit-shortage, Copenhagen, Denmark, March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Störmer, M.; Kleesiek, K.; Dreier, J. High-volume extraction of nucleic acids by magnetic bead technology for ultrasensitive detection of bacteria in blood components. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neidhöfer, C.; Bagniceva, M.; Wetzig, N.; Sieber, M.A.; Thiele, R.; Parčina, M. Pragmatic Considerations When Extracting DNA for Metagenomics Analyses of Clinical Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, R.U.; Ghani, E.; Rathore, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Ahmed, F.; Hussain, H. Evaluation of new-onset BK viruria in post-renal transplant recipients by quantitative PCR. Transpl. Immunol. 2024, 87, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, J.; Pingoud, A. Real-time polymerase chain reaction. Chembiochem 2003, 4, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijns, B.; Hoekema, T.; Oomens, L.; Tiggelaar, R.; Gardeniers, H. Performance of Spectrophotometric and Fluorometric DNA Quantification Methods. Analytica 2022, 3, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbolo, M.; Gottardi, M.; Corbo, V.; Fassan, M.; Mafficini, A.; Malpeli, G.; Lawlor, R.T.; Scarpa, A. DNA qualification workflow for next generation sequencing of histopathological samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Husin, A.; Sulong, S.; Yusoff, S.; Johan, M.F.; Yahaya, B.H.; Ang, C.Y.; Ghazali, S.; Cheong, S.K. Guideline for nucleic acid detection and analysis in hematological disorders. Malays. J. Pathol. 2015, 37, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
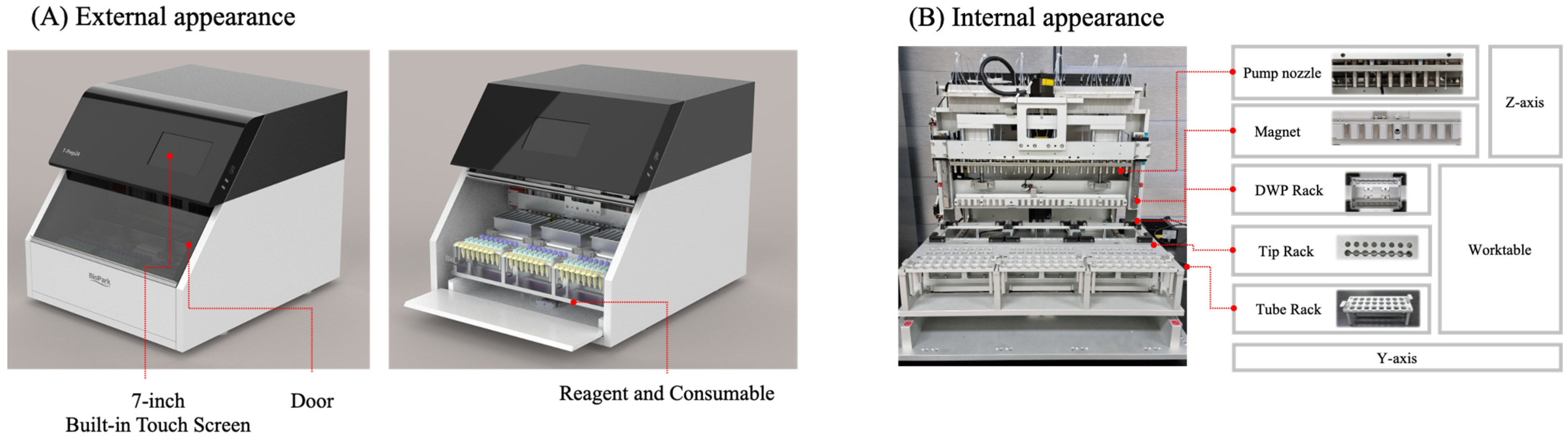
| T-Prep24 System | TANBead System | Qiagen System | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | BioPark Diagnostics Inc. (Seoul, Republic of Korea) | Taiwan Advanced Nanotech Inc. (Taoyuan City, Taiwan) | Qiagen (Hilden, Germany) |
| Extractor | T-Prep24 | SLA-E13200 | QIAcube |
| Technique | Nucleic acid capture by magnetic bead | Nucleic acid capture by magnetic bead | Nucleic acid capture by silica gel membrane |
| Extraction kit | BPDX-Viral DNA/RNA Extraction Kit | TANBead Nucleic acid extraction kit | QIAamp DSP Viral RNA Mini Kit |
| Sample loading volume | 200 μL | 140 μL | |
| Sample processing volume | 50–1200 μL | 50–1000 μL | |
| Elution volume | 50–100 μL | 70–100 μL | 50 μL |
| Maximum throughput | 24 samples/run | 32 samples/run | 12 samples/run |
| Running time | 30 min | 30–40 min | 20–40 min |
| Cost—extractor | $20,000 | $30,000 | $40,000 |
| Cost—extraction kit/test | $2–2.5/test | $3–4/test | $4–6/test |
| T-Prep24 System | TANBead System | Qiagen System | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration by Qubit, median (quartile range), ng/μL | 0.685 (0.258–1.493) | 0.985 (0.610–1.583) * | 4.710 (3.783–5.810) * |
| Concentration by Nanodrop, median (quartile range), ng/μL | 2.105 (0.539–8.841) | 7.961 (6.274–10.359) * | 83.275 (74.434–87.454) * |
| A260/A280 ratio | 1.528 (1.273–1.825) | 1.511 (1.412–1.611) | 2.652 (2.594–2.708) * |
| SARS-CoV-2 PCR results | |||
| Cq value of internal control, median (quartile range) | 25.02 (24.81–25.13) | 25.13 (25.01–25.26) | 25.26 (25.12–25.41) |
| Positive | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Cq value of ORF1ab, median (quartile range) | 25.35 (21.42–28.76) | 25.22 (20.54–28.79) | 24.76 (20.82–29.07) |
| Cq value of E gene, median (quartile range) | 24.21 (20.25–27.40) | 22.85 (18.71–26.91) | 22.86 (18.95–27.04) |
| Indeterminate | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Negative | 110 | 110 | 108 |
| Case Number | SARS-CoV-2 (T-Prep24) | SARS-CoV-2 (TANBead) | SARS-CoV-2 (QIAcube) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | Negative | Negative | Indeterminate (38.17/-) |
| 99 | Negative | Negative | Indeterminate (38.52/38.72) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.H.; Kwak, N.; Kim, D.; Chae, J.-C.; Jeong, S.H. Development and Performance Evaluation of T-prep24: A Novel Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction System Based on Silica Magnetic Beads. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121528
Park JH, Kwak N, Kim D, Chae J-C, Jeong SH. Development and Performance Evaluation of T-prep24: A Novel Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction System Based on Silica Magnetic Beads. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121528
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jung Ho, Naeun Kwak, Dokyun Kim, Jong-Chan Chae, and Seok Hoon Jeong. 2025. "Development and Performance Evaluation of T-prep24: A Novel Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction System Based on Silica Magnetic Beads" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121528
APA StylePark, J. H., Kwak, N., Kim, D., Chae, J.-C., & Jeong, S. H. (2025). Development and Performance Evaluation of T-prep24: A Novel Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction System Based on Silica Magnetic Beads. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121528






