Abstract
Background: Juvenile spondyloarthritis (JSpA) is a heterogeneous group of diseases. An international consensus group developed the axial juvenile SpA (AxJSpA) classification criteria for this purpose, defining a homogeneous group of patients diagnosed with jSpA and experiencing axial symptoms before the age of 18 years. Aim: To validate this new set of criteria in our pediatric SpA patients. Methods: This study was held in the Hacettepe University Department of Pediatric Rheumatology. Juvenile SpA patients suspected of axial disease diagnosed and followed at the same center between 2005 and 2024 were included. Patients who had other etiologies for axial symptoms, including chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis, mechanical back pain–overuse injuries, amplified pain/growing pains, and SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis) served as the control group. Results: In total, 123 JSpA patients and 74 controls were included in this study. The sensitivity/specificity of the new criteria were 61%/77% with an area under curve value of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68–0.83) in our cohort. Among different criteria sets, European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria were the most sensitive (sensitivity/specificity 91%/68%), and ASAS peripheral criteria (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society) were the most specific (sensitivity/specificity 67%/84%) in our cohort when compared to ASAS axial criteria (sensitivity/specificity 74%/65%), ILAR (International League of Associations for Rheumatology) (sensitivity/specificity 85%/81%), and ILAR + SI (sacroiliitis) (sensitivity/specificity 67%/74%) criteria. Conclusions: The area under the curve of the new AxJSpA criteria was similar to that of the original report; however, both sensitivity and specificity were lower in our cohort, possibly due to factors like earlier disease presentation and a lower prevalence of chronic structural changes on MRI.
1. Introduction
Juvenile spondyloarthritis (JSpA) encompasses a group of heterogeneous diseases characterized by peripheral arthritis, axial involvement, enthesitis, acute anterior uveitis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and HLA-B27 positivity. The prevalence of JSpA can vary significantly, ranging from 10 to 30% of all juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients, depending on the geographic area [1,2,3,4]. Children with JSpA have a significant disease burden and relatively poor outcomes compared to other types of JIA [5]. Among children with JSpA [6], 10% to 20% of patients develop ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in adulthood [7]. Patients with JSpA share many similarities with adult spondyloarthritis; however, there are also significant differences between the two. Inflammatory back pain is not as prominent, and the sacroiliac and other vertebral joints are less frequently affected in juvenile disease [8]. In contrast, children often present with hip and peripheral arthritis, along with enthesitis. In pediatric cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may misinterpret certain physiological bone marrow changes as sacroiliitis [9]. A significant proportion of children with JSpA experience “silent” axial disease, which refers to axial involvement without back pain. Even in cases without reported back pain, MRI scans reveal evidence of both acute disease and chronic destructive changes [10].
Several diagnostic and/or classification criteria have been proposed for JSpA and adult-onset spondyloarthropathies. The International League of Associations for Rheumatology (ILAR) JIA classification criteria are the most commonly used pediatric criteria; however, there is ongoing debate about their performance in classifying juvenile spondyloarthropathies [11]. These classification criteria primarily categorize patients with JSpA as either enthesitis-associated arthritis or psoriatic arthritis. These criteria do not include inflammatory-bowel-disease-related arthritis, juvenile ankylosing spondylitis, or Reiter’s syndrome, which are well-defined forms of JSpA. Furthermore, the enthesitis-related arthritis category and stringent classification criteria often lead to many patients being classified as having undifferentiated arthritis [12]. On the other hand, the SpA International Society (ASAS) currently categorizes adult SpAs using two sets of criteria. One set is for patients experiencing axial involvement, while the other is for those with peripheral symptoms [13,14,15]. There are two types of axial SpA (axSpA). These are radiographic axSpA, which is characterized by the presence of clear radiographic axial disease and is known as AS, and non-radiographic axSpA [11].
Early recognition of JSpA and, especially, axial involvement is crucial for reducing long-term disease burden and preventing irreversible damage by starting earlier and more aggressive treatment. Recently, an international collaboration developed the axial juvenile SpA (AxJSpA) classification criteria, aimed at identifying juvenile patients with axial symptoms before 18 years of age, and they validated it in an independent group [16]. We designed the present study to validate the recently published AxJSpA classification criteria in a cohort of JSpA patients and to assess the effectiveness of the ASAS axial SpA criteria [13], the ILAR ERA criteria [17], the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis [11], the ASAS peripheral SpA criteria [15], and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria for adults [18]. We hypothesize that the new AxJSpA classification criteria will provide a valid and reliable tool for classifying juvenile spondyloarthritis with axial involvement in a pediatric cohort.
The AxJSpA criteria demonstrated moderate specificity and sensitivity in our JSpA cohort. The observed variability among the existing classification criteria highlights the diagnostic challenges in juvenile spondyloarthritis. Importantly, early detection of axial involvement is crucial for optimal disease management and timely intervention.
2. Materials and Methods
We retrospectively evaluated the medical records of SpA patients under 18 years of age at diagnosis and followed up for at least 6 months at the Pediatric Rheumatology Department of Hacettepe University, Ankara, between January 2005 and January 2024. We enrolled 123 SpA patients (113 ERA, 10 PsA) and validated the AxJSpA classification criteria using real patient data analysis (Supplementary Figure S1).
We included controls similar to the reference study, which had other etiologies for axial symptoms, including chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) (n = 44), mechanical back pain–overuse injuries (n = 18), amplified pain/growing pains (n = 8), and SAPHO syndrome (n = 4). Patients with familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) with sacroiliitis, as well as those with sacroiliitis secondary to infections, drugs, undifferentiated arthritis, or reactive arthritis, were excluded from the study. These conditions represent distinct pathophysiological entities that could mimic SpA and confound the classification process; therefore, they were excluded to maintain consistency with the original AxJSpA validation study. Demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations, laboratory findings, and the items of AxJSpA classification criteria, ASAS classification criteria for axial and peripheral SpA, ILAR ERA criteria, the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis, and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria for adults were also assessed (Table 1 and Table 2). Regarding the control group’s classification, an experienced pediatric rheumatologist’s expert opinion (SO) was used as the gold standard. The classification was based on a thorough review of clinical, imaging, and laboratory findings, ensuring the exclusion of conditions that could mimic axial involvement. The sensitivities and specificities of AxJSpA classification criteria, ASAS classification criteria for axial and peripheral SpA, ILAR ERA criteria, the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis, and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria for SpA patients were also evaluated according to the features registered at disease diagnosis. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values were calculated using cross-tabulation against the clinician-based diagnosis (gold standard). This study has been approved by the Hacettepe University Ethics Commission (approval number: GO 21/665). All participants provided informed consent.

Table 1.
Axial Juvenile Spondyloarthritis (AxJSpA) criteria weights and scoring [16].

Table 2.
Classification criteria for juvenile spondyloarthritis.
3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by using the SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) version 29.0 package program. Descriptive statistics were presented as frequency, percentage, median, minimum (min), and maximum (max). The variables were investigated using visual (histograms, probability plots) and analytical methods (Kolmogorov–Smirnov) to determine whether they were normally distributed. The Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test (when Chi-square test assumptions did not hold due to low expected cell counts) was used to analyze relationships between categorical variables. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare non-normally distributed continuous variables. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of the AxJSpA classification criteria against the gold standard clinician’s diagnosis were calculated and used to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the AxJSpA classification criteria and compared with the ASAS axial SpA criteria [13], the ILAR ERA criteria [17], the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis [11], the ASAS peripheral SpA criteria [15], and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria for adults [18]. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to determine a suggested cut-off probability for the AxJSpA classification criteria in our pediatric cohort.
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Features of the Patients
This study included 123 JSpA patients (26% female) and 74 non-JSpA (47.3% female) controls. The control group consisted of patients with CNO (n = 44), mechanical pain (n = 18), growth pain (n = 8), and SAPHO syndrome (n = 4). The mean age at diagnosis was 13 ± 2.8 years in the JSpA patients and 10.73 ± 3.8 years in the control group. Table 3 summarizes the patient demographics and clinical characteristics.

Table 3.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients.
The disease duration at the time of diagnosis was frequently 12 weeks or more in the case and control groups at 90.2% and 78.4%, respectively (p = 0.021). Hips or the groin were the most common areas of localization of pain in JSpA patients (n = 98, 80%) and controls (n = 42, 56.8%) (p 0.001). Acute disease onset was observed in 69.9% (n = 86) of patients with JSpA, whereas an insidious onset pattern was more common than acute onset among individuals in the control group (33.8%, n = 25). Peripheral arthritis and enthesitis were more common in the case group (both p < 0.01). Morning stiffness was commonly more prolonged (≥30 min in 36.6%) in the JSpA patients than the control group.
4.2. Sensitivity and Specificity of the New AxJSpA Classification Criteria in JSpA Patients
The new AxJSpA criteria were validated in our cohort, and the validity of the new classification system was compared to that of the ASAS axial SpA criteria [14], the ILAR ERA criteria [17], the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis [11], the ASAS peripheral SpA criteria [15], and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria [18] for adults. In our cohort, the AxJSpA criteria had a specificity of 77% and a sensitivity of 61% with an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68–0.83) (Figure 1).
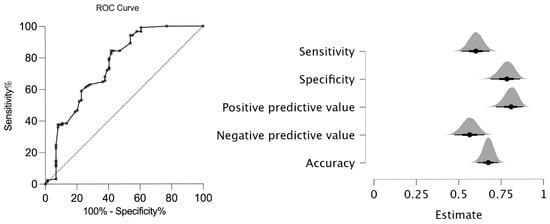
Figure 1.
ROC analysis and performance of the new AxJSpA criteria in JSpA patients. (ROC: receiver operator curve; JspA: juvenile spondyloarthritis).
Comparison with ILAR ERA criteria [17], the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis [11], ASAS axial and peripheral SpA [14], and ESSG [18] criteria for adults showed that the sensitivity of the EESG criteria (92%) was the highest, while the highest specificity was that of the ASAS peripheral criteria (84%). The new AxJSpA criteria had the lowest negative predictive value (53.7%), together with a relatively high positive predictive value (81.30%) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Sensitivity, specificity, and negative and positive predictive values of different criteria for the classification of juvenile spondyloarthritis patients.
The results of the sensitivity and specificity of each parameter of the new AxJSpA classification criteria are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Sensitivity and specificity of each criterion in juvenile spondyloarthritis patients.
5. Discussion
This is the first external validation of the new AxJSpA classification criteria in a JSpA population. Our study cohort and the original validation cohort were comparable in terms of gender distribution, age at diagnosis, and HLA-B27 positivity; however, notable differences included a higher frequency of peripheral arthritis, a lower prevalence of MRI-detected chronic structural changes, and a predominance of acute disease onset in our cohort. In contrast to the original validation cohort, our patients had a lower frequency of uveitis and inflammatory bowel disease, while the rate of enthesitis was similar between the two groups.
In our cohort, we have found a similar sensitivity (61%) but a relatively low specificity (77%) with a similar area under the curve of 0.75 (95% CI: 0.68–0.83) than those reported by Weiss et al. [16]. The original study reported a specificity of 97.5%, a sensitivity of 64.3%, and an area under the curve of 0.81 (95% CI: 0.76–0.86) in their validation cohort according to the new AxJSpA classification using the threshold score of ≥55 (out of 100). Imaging typical of sacroiliitis was regarded as a required but insufficient criterion for AxJSpA classification. Comparing our study to the original one, we found relatively low sensitivity and a low negative predictive value of 53.70%. One reason may be the lack of chronic sacroiliac lesions in our patient group. Many of our patients were evaluated early in the disease course, often at the onset of axial symptoms, allowing for the detection of active inflammatory lesions before the development of structural damage. In parallel, several factors may also account for the relatively lower specificity observed in our cohort.
In the original study, imaging evidence of juvenile SpA was required alongside clinical symptoms. However, MRI interpretation in children can be challenging due to thick cartilaginous growth plates, which may be falsely interpreted as sacroiliitis [10]. Variability in radiologist expertise and institutional criteria may further contribute to inconsistencies. Additionally, conditions like CNO can show sacroiliitis-like changes on MRI [19], and the presence of such cases in our control group may have contributed to lower specificity.
It is worth noting that while imaging evidence is necessary to surpass the classification threshold, there are cases of JSpA with imaging evidence of typical axial disease in juvenile SpA that are below the threshold. These were cases for which clinical criteria levels had a low score. Similarly, there were cases that had near maximum level scoring for each of the clinical domains but no imaging evidence typical of juvenile SpA. While 43 out of 49 patients who were false negatives had clinical features compatible with SpA, they did not have sufficient MRI findings, and 37 of these patients had peripheral arthritis, while 31 had enthesitis. Twenty-one patients did not fulfill the criteria due to the presence of acute sacroiliitis on MRI but no chronic structural lesions. Analyzing the individual parameters of the AxJSpA classification criterion reveals a sensitivity of 47.9% for structural lesions but a specificity of 78.3%. Given the classification criteria’s emphasis on specificity, it makes sense to incorporate chronic changes into the criteria. However, the lower frequency of chronic changes in our study may have contributed to the low sensitivity.
A study examining the occurrence of sacroiliitis at diagnosis in cases of JSpA revealed that fifteen children with JSpA exhibited sacroiliac arthritis according to the ILAR definition [11], although not with MRI [10]. Other investigations have indicated that the primary presentation of early illness in children is peripheral arthritis and enthesitis, rather than inflammatory back pain [20]. The early detection of axial disease has been enabled by the increased use of MRI [21,22]. Anti-TNF agents have demonstrated efficacy in clinically enhancing the signs and symptoms of the disease [23,24]. Patients with axial disease experience varying effects on spinal radiographic progression as a result of biologic therapy [25]. In our cohort, the early detection of axial disease enabled the timely initiation of biologic therapy, potentially limiting radiographic progression.
In addition, patients with a family history of spondyloarthritis have a higher risk of developing both sacroiliitis and persistent active disease [26]. In our cohort, 17 (13.8%) JSpA patients had a SpA family history. Family history of SpA was shown to contribute significantly to specificity for the new AxJSpA criteria.
The criterion validity of the new classification system was compared to that of the ASAS axial SpA criteria [14], the ILAR ERA criteria [17], the ILAR ERA definition of sacroiliitis [11], the ASAS peripheral SpA criteria [15], and the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) criteria [18] for adults. These results showed that the ESSG criteria had the highest sensitivity at 92% (113/123), while the new jAxSPA criteria had the lowest sensitivity at 61% (74/123). ASAS peripheral at 84% (62/74) had the highest specificity, followed by ASAS axial criteria with the lowest specificity.
In a study examining the performance of ILAR and ASAS classification criteria in ERA patients, the sensitivities of ILAR and ASAS criteria for axial SpA and peripheral SpA at diagnosis were 74.0%, 21.3%, and 85.1%, respectively. Specificities were 100%, 99.1%, and 90.9% at diagnosis. We did not differentiate ERA patients with axial involvement, and the control group differed in terms of quantity and content, leading to differences in specificity and sensitivity. We excluded patients with only peripheral involvement and enthesitis from our study, while the previous study, which used a different design, included psoriatic arthritis, oligoarticular JIA, and polyarticular JIA patients in its control group. Given the frequency of peripheral arthritis in our patient cohort, the inclusion of synovitis as an alternative entry criterion in the ESSG criteria may explain its high sensitivity, providing a wide range of options beyond the entry criteria. Similarly, in another study, the sensitivity and specificity of the ESSG criteria were high at 85.4% and 96.4%, respectively [27].
ASAS criteria for SpA validated in 2982 rheumatic children [28], revealed 78.7% for sensitivity and 92.2% for specificity. Sensitivity of the criterion “inflammatory back pain” was only 9.1% in children. The ASAS axial SpA criteria indicate that a history of back pain for a minimum of three months is necessary as an entry criterion prior to conducting MRI and/or radiographic investigations of the sacroiliac joints. In the absence of back pain, there seems to be no obvious clinical rationale for conducting MRI studies of the sacroiliac joints and spine in children. These may explain the low sensitivity of our study group to ASAS axial criteria. The additional criteria of uveitis, psoriasis, IBD, and the absence of a prior infection history in patients with peripheral arthritis within this criterion may account for the low sensitivity of our cohort to ASAS peripheral criteria.
Our study has several limitations. Our data are retrospective; not all data were available for certain time points. We used expert opinions as a gold standard. The duration of follow-up was heterogeneous. Our center performed MRI examinations based on the clinical judgement of the treating physician, primarily when there was lumbosacral pain. As discussed earlier, axial disease can be clinically silent. Our population was followed in a tertiary center, with recruitment likely biased towards more severe cases.
This is the first external validation of the newly proposed AxJSpA criteria using an independent pediatric cohort. In our cohort, the AxJSpA criteria demonstrated high specificity but relatively low sensitivity, likely influenced by the strong emphasis on structural MRI findings, which are often absent in early-stage or mild pediatric cases. Although reducing the weight of such imaging findings might improve sensitivity, this may increase misclassification in children with non-inflammatory back pain. These results underscore the need for prospective validation studies to refine the scoring thresholds and optimize diagnostic performance across diverse pediatric populations. Furthermore, we suggest that similar to the ASAS framework, a separate set of criteria could be considered for SpA patients with prominent peripheral involvement but without axial disease to ensure the inclusion of clinically relevant non-axial cases and improve cohort homogeneity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/diagnostics15121498/s1, Figure S1: Annual Distribution of Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Diagnoses at Hacettepe University (2005–2024).
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception or design of this study or to the generation, analysis, and/or interpretation of data and agree to be accountable for the integrity of the work herein. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the submitted version. No person who fulfills the criteria for authorship has been excluded as an author. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Hacettepe University (protocol code: GO 21/665; SBA 23/252; 2023-10-24).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request, subject to ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare the absence of any present or potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Nordal, E.; Zak, M.; Aalto, K.; Berntson, L.; Fasth, A.; Herlin, T.; Lahdenne, P.; Nielsen, S.; Straume, B.; Rygg, M. Ongoing disease activity and changing categories in a long-term nordic cohort study of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2809–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modesto, C.; Antón, J.; Rodriguez, B.; Bou, R.; Arnal, C.; Ros, J.; Tena, X.; Rodrigo, C.; Rotés, I.; Hermosilla, E.; et al. Incidence and prevalence of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Catalonia (Spain). Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oen, K.; Duffy, C.M.; Tse, S.M.; Ramsey, S.; Ellsworth, J.; Chédeville, G.; Chetaille, A.L.; Saint-Cyr, C.; Cabral, D.A.; Spiegel, L.R.; et al. Early outcomes and improvement of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis enrolled in a Canadian multicenter inception cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunjir, V.; Venugopalan, A.; Chopra, A. Profile of Indian patients with juvenile onset chronic inflammatory joint disease using the ILAR classification criteria for JIA: A community-based cohort study. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.F.; Beukelman, T.; Schanberg, L.E.; Kimura, Y.; Colbert, R.A. Enthesitis-related arthritis is associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status in comparison with other categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, A.; Minden, K.; Listing, J.; Foeldvari, I.; Sieper, J.; Rudwaleit, M. Course of patients with juvenile spondyloarthritis during 4 years of observation, juvenile part of GESPIC. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.S.; Raza, K.; Jones, S.D.; Kennedy, L.G.; Calin, A. Juvenile onset ankylosing spondylitis–more girls than we thought? J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 735–737. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, M. Spondylarthropathies in children--are they different from those in adults? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.F.; Chauvin, N.A.; Roth, J. Imaging in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.F.; Xiao, R.; Biko, D.M.; Chauvin, N.A. Assessment of Sacroiliitis at Diagnosis of Juvenile Spondyloarthritis by Radiography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Clinical Examination. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.E.; Southwood, T.R.; Manners, P.; Baum, J.; Glass, D.N.; Goldenberg, J.; He, X.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.; Orozco-Alcala, J.; Prieur, A.M.; et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgos-Vargas, R.; Rudwaleit, M.; Sieper, J. The place of juvenile onset spondyloarthropathies in the Durban 1997 ILAR classification criteria of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. International League of Associations for Rheumatology. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudwaleit, M.; Landewé, R.; van der Heijde, D.; Listing, J.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Davis, J.; Dijkmans, B.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): Classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudwaleit, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Listing, J.; Akkoc, N.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Chou, C.T.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Dougados, M.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): Validation and final selection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudwaleit, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Akkoc, N.; Brandt, J.; Chou, C.T.; Dougados, M.; Huang, F.; Gu, J.; Kirazli, Y.; et al. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.F.; Brandon, T.G.; Aggarwal, A.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Colbert, R.A.; Horneff, G.; Laxer, R.M.; Minden, K.; Ravelli, A.; Ruperto, N.; et al. Classification Criteria for Axial Disease in Youth with Juvenile Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.E.; Southwood, T.R.; Baum, J.; Bhettay, E.; Glass, D.N.; Manners, P.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.; Suarez-Almazor, M.; Orozco-Alcala, J.; Prieur, A.M. Revision of the proposed classification criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Durban, 1997. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Dougados, M.; van der Linden, S.; Juhlin, R.; Huitfeldt, B.; Amor, B.; Calin, A.; Cats, A.; Dijkmans, B.; Olivieri, I.; Pasero, G.; et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydıngöz, Ü.; Yıldız, A.E.; Ayaz, E.; Batu, E.D.; Özen, S. Preferential involvement of the pelvis and hips along with active sacroiliitis in chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis: MRI of 97 patients from a single tertiary referral center. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 4979–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Vargas, R. The assessment of the spondyloarthritis international society concept and criteria for the classification of axial spondyloarthritis and peripheral spondyloarthritis: A critical appraisal for the pediatric rheumatologist. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2012, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoff, C.E.; Feist, E.; Burova, E.; Eshed, I.; Bollow, M.; Hamm, B.; Hermann, K.G. Magnetic resonance imaging of active sacroiliitis: Do we really need gadolinium? Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 71, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, S.; Ergen, F.B.; Taydaş, O.; Sağ, E.; Bilginer, Y.; Aydıngöz, Ü.; Özen, S. Spinal involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: What do we miss without imaging? Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez-Roca, C.; Iglesias, E.; Torrente-Segarra, V.; Bou, R.; Sánchez-Manubens, J.; Calzada-Hernández, J.; Hernández, S.; Ricart, S.; Antón, J. Efficacy and safety of TNF-alpha antagonists in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis who started treatment under 4 years of age. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnithorne, K.J.; Cron, R.Q.; Beukelman, T. Attainment of inactive disease status following initiation of TNF-α inhibitor therapy for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Enthesitis-related arthritis predicts persistent active disease. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, T.J.P.; Lopes, A.; Fisher, C.; Ciurtin, C.; Sen, D.; Hall-Craggs, M.A. Sacroiliac Joint Ankylosis in Young Spondyloarthritis Patients Receiving Biologic Therapy: Observation of Serial Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goirand, M.; Breton, S.; Chevallier, F.; Duong, N.P.; Uettwiller, F.; Melki, I.; Mouy, R.; Wouters, C.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Job-Deslandre, C.; et al. Clinical features of children with enthesitis-related juvenile idiopathic arthritis/juvenile spondyloarthritis followed in a French tertiary care pediatric rheumatology centre. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2018, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liao, Z.; Yu, D.; Li, T.; Gu, J. Evaluation of the European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) classification criteria in a Chinese population. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Prieur, A.M.; Listrat, V.; Dougados, M.; Amor, B. Criteria for classification of spondylarthropathies in children. Arch. Fr. Pediatr. 1993, 50, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).