BioInnovate AI: A Machine Learning Platform for Rapid PCR Assay Design in Emerging Infectious Disease Diagnostics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assay Development
2.2. Training Data Pre-Processing
2.3. Model Training, Validation, and Metrics Evaluation
2.4. Development of a User Interface
3. Results
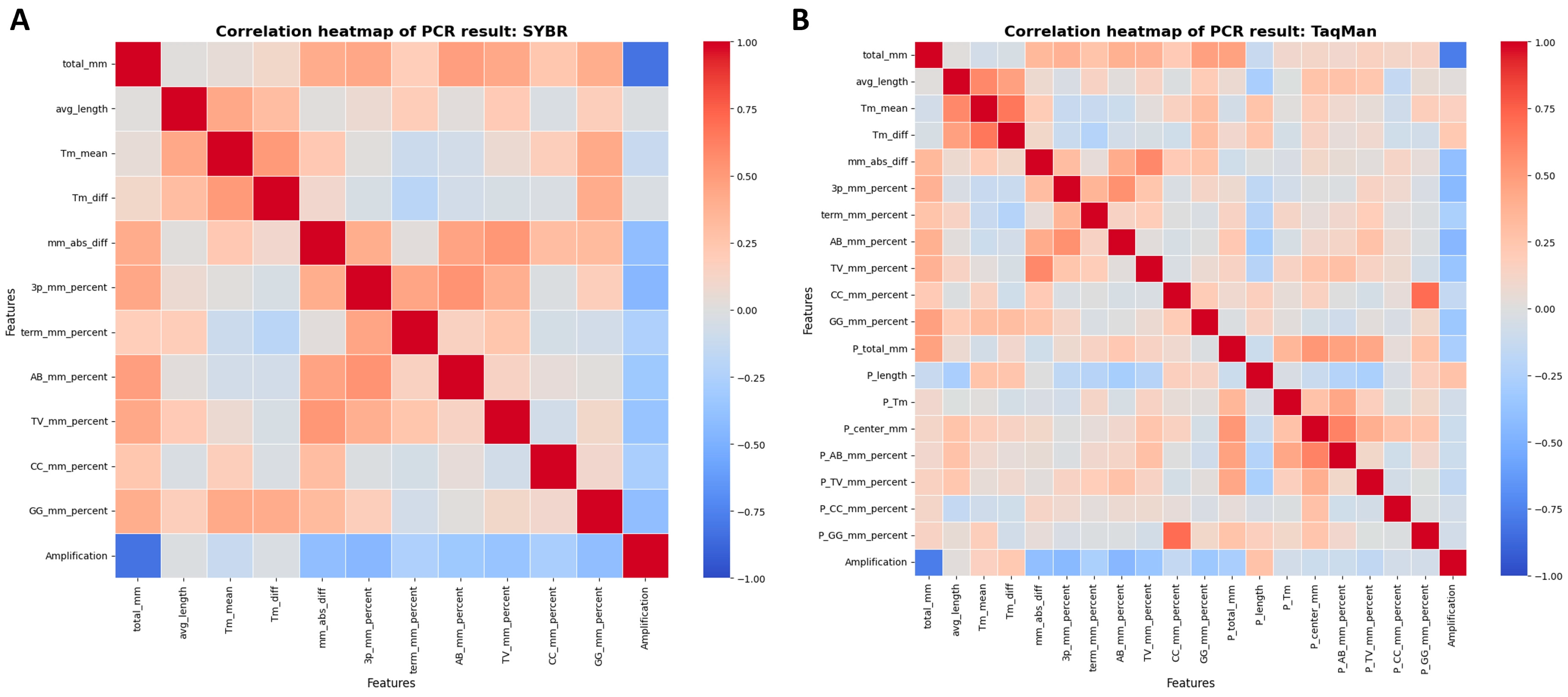
3.1. Key Influencers in Amplification Success
3.2. Model Validation and Performance Metrics Overview
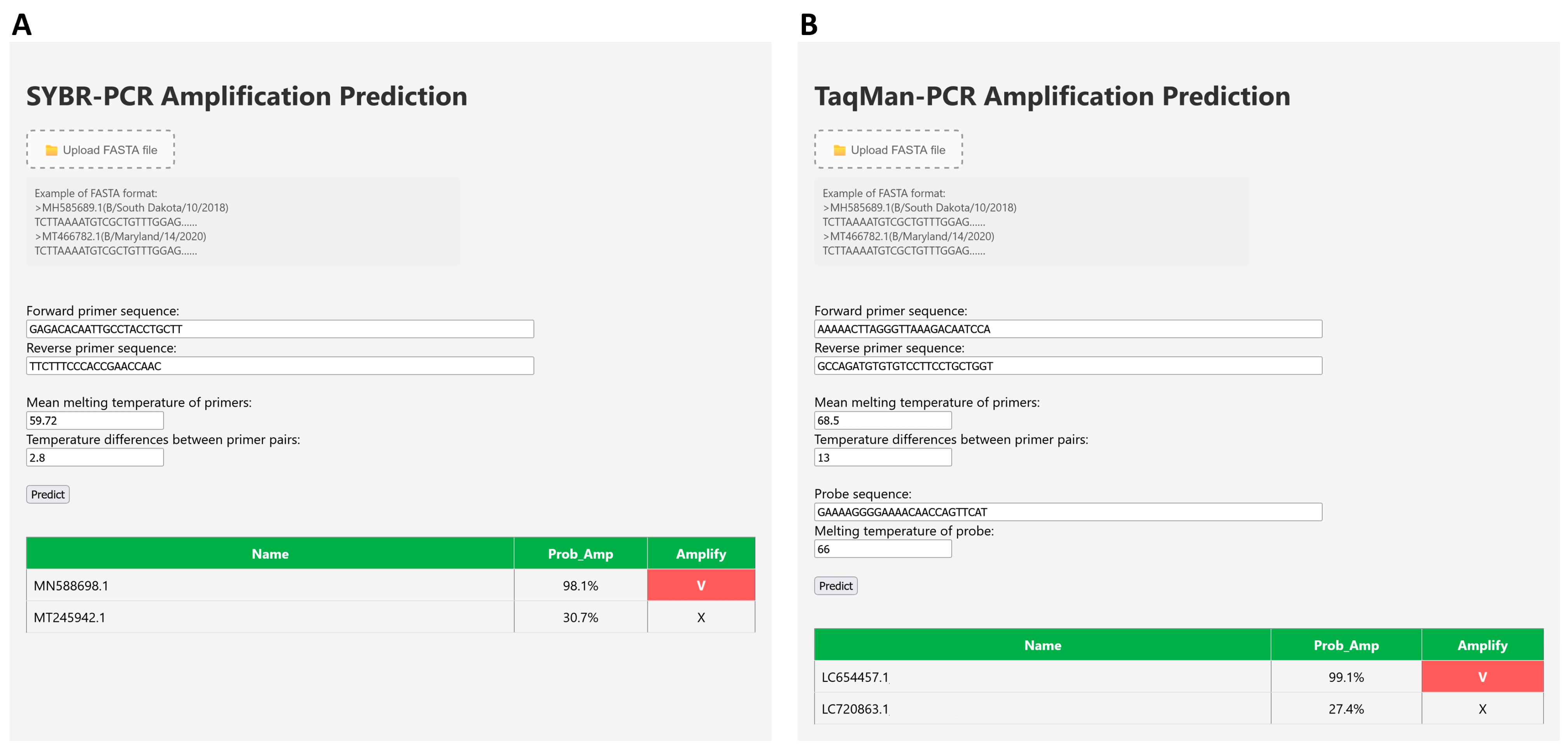
3.3. Development of User Interface
3.4. Practical Implementation and Impact on PCR Assay Design
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| qPCR | quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| EID | Emerging Infectious Disease |
| Tm | Melting Temperature |
| RFC | Random Forest Classifier |
| LGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GBC | Gradient Boosting Classifier |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
References
- World Health Organization Regional Office for South-East Asia. A Brief Guide to Emerging Infectious Diseases and Zoonoses; WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Babiker, A.; Immergluck, K.; Stampfer, S.D.; Rao, A.; Bassit, L.; Su, M.; Nguyen, V.; Stittleburg, V.; Ingersoll, J.M.; Bradley, H.L.; et al. Single-Amplicon Multiplex Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR with Tiled Probes To Detect SARS-CoV-2 spike Mutations Associated with Variants of Concern. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0144621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennerster, R.; Snyder, C.M.; Tan, B.J. Calculating the Costs and Benefits of Advance Preparations for Future Pandemics. IMF Econ. Rev. 2023, 71, 611–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Fang, Y.-H.D. Classification of the ICU Admission for COVID-19 Patients with Transfer Learning Models Using Chest X-Ray Images. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azhary, K.; Ghazi, B.; Kouhen, F.; El Bakkouri, J.; Chamlal, H.; El Ghanmi, A.; Badou, A. Clinical Impact of Neutrophil Variation on COVID-19 Complications. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.L.T.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Le-Quy, V.; To, T.B.; Tran, H.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hoang, Y.; Nguyen, A.T.; Dam, L.T.P.; Nguyen, N.L.; et al. The Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Outcomes in Vietnam. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.; Madaan, A.; Singh, S.; Chandra, S. Burden of Coronavirus Disease-19 on Cardiovascular System. J. Med Sci. 2021, 41, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breman, J.G.; Heymann, D.L.; Lloyd, G.; McCormick, J.B.; Miatudila, M.; Murphy, F.A.; Muyembé-Tamfun, J.-J.; Piot, P.; Ruppol, J.-F.; Sureau, P.; et al. Discovery and Description of Ebola Zaire Virus in 1976 and Relevance to the West African Epidemic During 2013–2016. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S93–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.S.; Iuliano, A.D.; Reed, C.; Meltzer, M.I.; Shay, D.K.; Cheng, P.Y.; Bandaranayake, D.; Breiman, R.F.; Brooks, W.A.; Buchy, P.; et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Verma, V.K. Next-Generation Sequencing and Its Application: Empowering in Public Health Beyond Reality. In Microbial Technology for the Welfare of Society; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 313–341. [Google Scholar]
- Salk, J.J.; Schmitt, M.W.; Loeb, L.A. Enhancing the accuracy of next-generation sequencing for detecting rare and subclonal mutations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Alotaibi, J.; Natto, Z.S.; Alkhaibari, R.S.; Alawad, E.; Alshammari, H.M.; Alwarthan, S.; Alhajri, M.; Almogbel, M.S.; et al. Unleashing the power of artificial intelligence for diagnosing and treating infectious diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.H.; Mahmanzar, M.; Rahimian, K.; Mahdavi, B.; Tokhanbigli, S.; Moradi, B.; Sisakht, M.M.; Deng, Y. Global landscape of SARS-CoV-2 mutations and conserved regions. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.-J.; Lin, T.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-K.; Perng, C.-L.; Chang, F.-Y.; Shang, H.-S. Pioneering Klebsiella Pneumoniae Antibiotic Resistance Prediction With Artificial Intelligence-Clinical Decision Support System–Enhanced Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: Retrospective Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e58039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Jian, M.-J.; Chang, C.-K.; Lin, H.-H.; Yu, C.-M.; Perng, C.-L.; Chang, F.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. Artificial intelligence-clinical decision support system for enhanced infectious disease management: Accelerating ceftazidime-avibactam resistance detection in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, C.; Crowley, J.; Jerome, K.R.; Kuypers, J. Comparison of FilmArray Respiratory Panel and laboratory-developed real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction assays for respiratory virus detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberger, J.A.; Wilcox, T.M.; Mason, D.H.; Franklin, T.W.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Schwartz, M.K. eDNAssay: A machine learning tool that accurately predicts qPCR cross-amplification. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, N.; Wang, R.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. Preparing the developing world for the next pandemic: Evidence from China’s R&D blueprint for emerging infectious diseases. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, A.-K.; Laakso, S.; Piiparinen, P.; Aittakorpi, A.; Lindfors, M.; Huopaniemi, L.; Piiparinen, H.; Mäki, M. Rapid identification of bacterial pathogens using a PCR- and microarray-based assay. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kang, N.; An, K.; Kim, D.; Koo, J.; Kim, M.-S. MRPrimerV: A database of PCR primers for RNA virus detection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D475–D481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosy, J.R.; Rose, S.D.; Beltz, K.R.; Rupp, S.M.; Powers, K.M.; Behlke, M.A.; Walder, J.A. RNase H-dependent PCR (rhPCR): Improved specificity and single nucleotide polymorphism detection using blocked cleavable primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Hu, J.; Lyu, X.; Huang, H.; Cheng, X. Exploring the Interdisciplinary Nature of Precision Medicine: Network Analysis and Visualization. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e23562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechita, L.C.; Tutunaru, D.; Nechita, A.; Voipan, A.E.; Voipan, D.; Tupu, A.E.; Musat, C.L. AI and Smart Devices in Cardio-Oncology: Advancements in Cardiotoxicity Prediction and Cardiovascular Monitoring. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

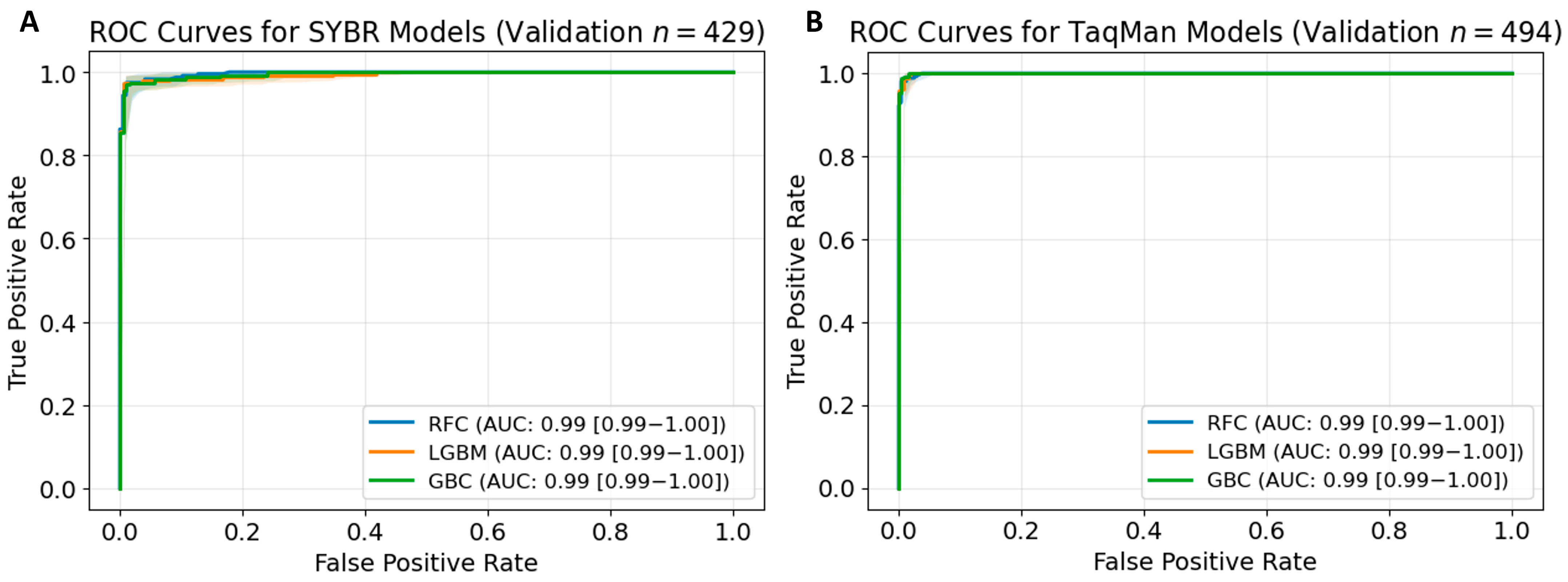
| Training AUC | Validating AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | F1 Score | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYBR models | ||||||||
| RFC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| LGBM | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| GBC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| TaqMan models | ||||||||
| RFC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| LGBM | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| GBC | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-H.; Chang, C.-K.; Perng, C.-L.; Hung, K.-S.; Yanagihara, K.; Shang, H.-S.; Jian, M.-J. BioInnovate AI: A Machine Learning Platform for Rapid PCR Assay Design in Emerging Infectious Disease Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121445
Lin H-H, Chung H-Y, Lin T-H, Chang C-K, Perng C-L, Hung K-S, Yanagihara K, Shang H-S, Jian M-J. BioInnovate AI: A Machine Learning Platform for Rapid PCR Assay Design in Emerging Infectious Disease Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121445
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hung-Hsin, Hsing-Yi Chung, Tai-Han Lin, Chih-Kai Chang, Cherng-Lih Perng, Kuo-Sheng Hung, Katsunori Yanagihara, Hung-Sheng Shang, and Ming-Jr Jian. 2025. "BioInnovate AI: A Machine Learning Platform for Rapid PCR Assay Design in Emerging Infectious Disease Diagnostics" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121445
APA StyleLin, H.-H., Chung, H.-Y., Lin, T.-H., Chang, C.-K., Perng, C.-L., Hung, K.-S., Yanagihara, K., Shang, H.-S., & Jian, M.-J. (2025). BioInnovate AI: A Machine Learning Platform for Rapid PCR Assay Design in Emerging Infectious Disease Diagnostics. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121445







