Utility and Challenges of Imaging in Peripheral Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
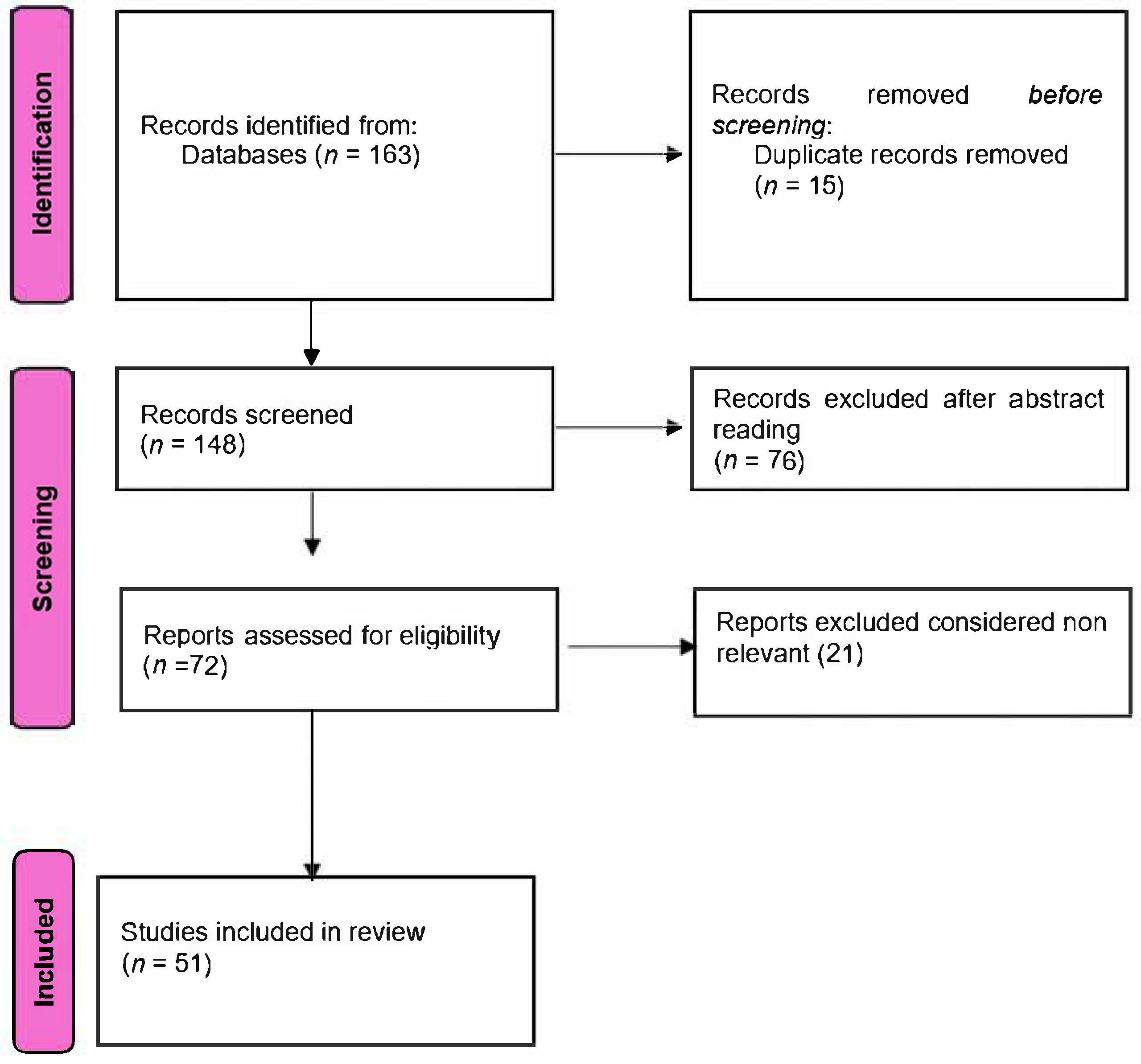
2. Materials and Methods
3. Imaging Modalities in Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis
3.1. Specific Vestibular Disorders and Imaging Utility
3.1.1. Vestibular Neuritis
3.1.2. Meniere’s Disease
3.1.3. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
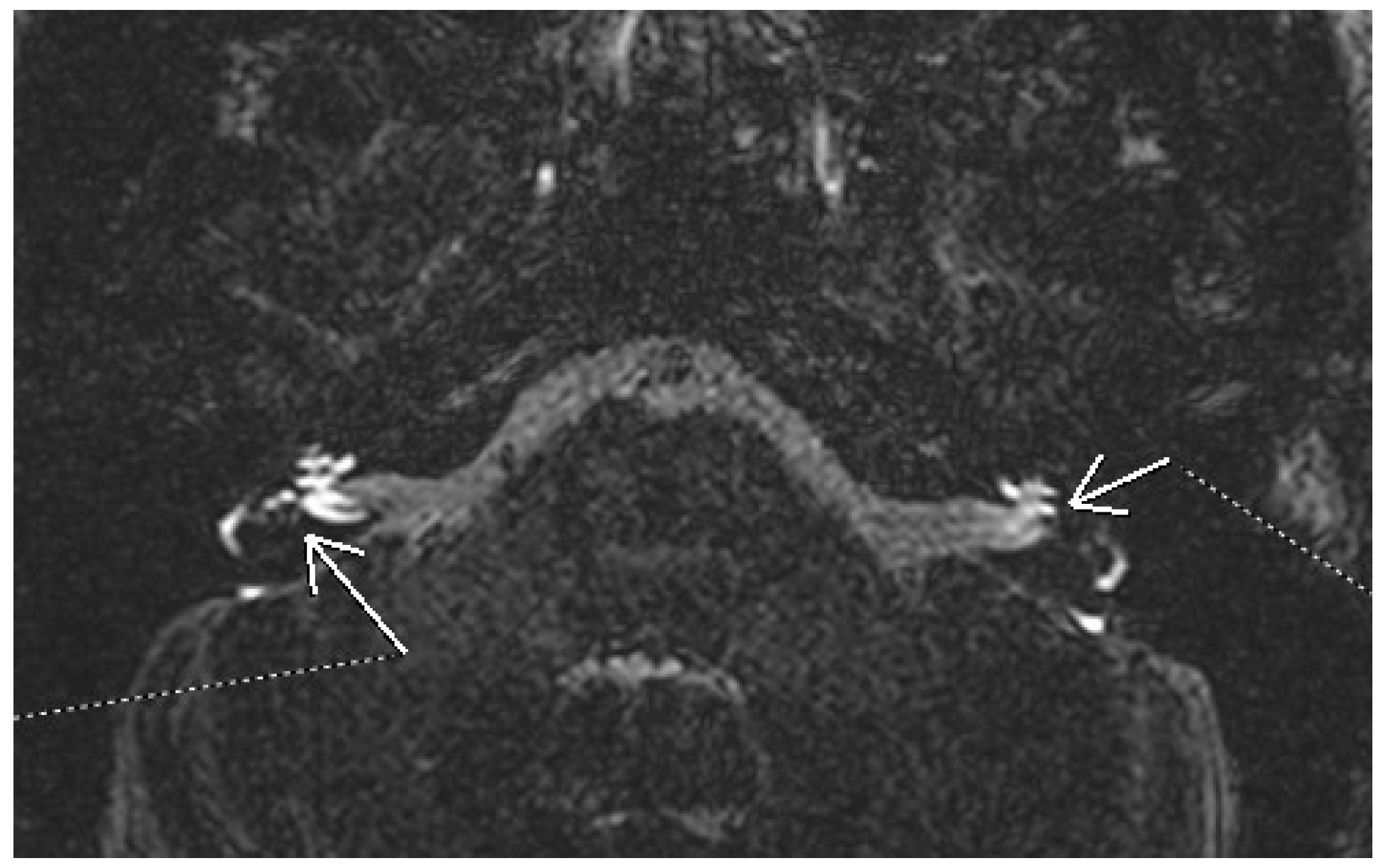
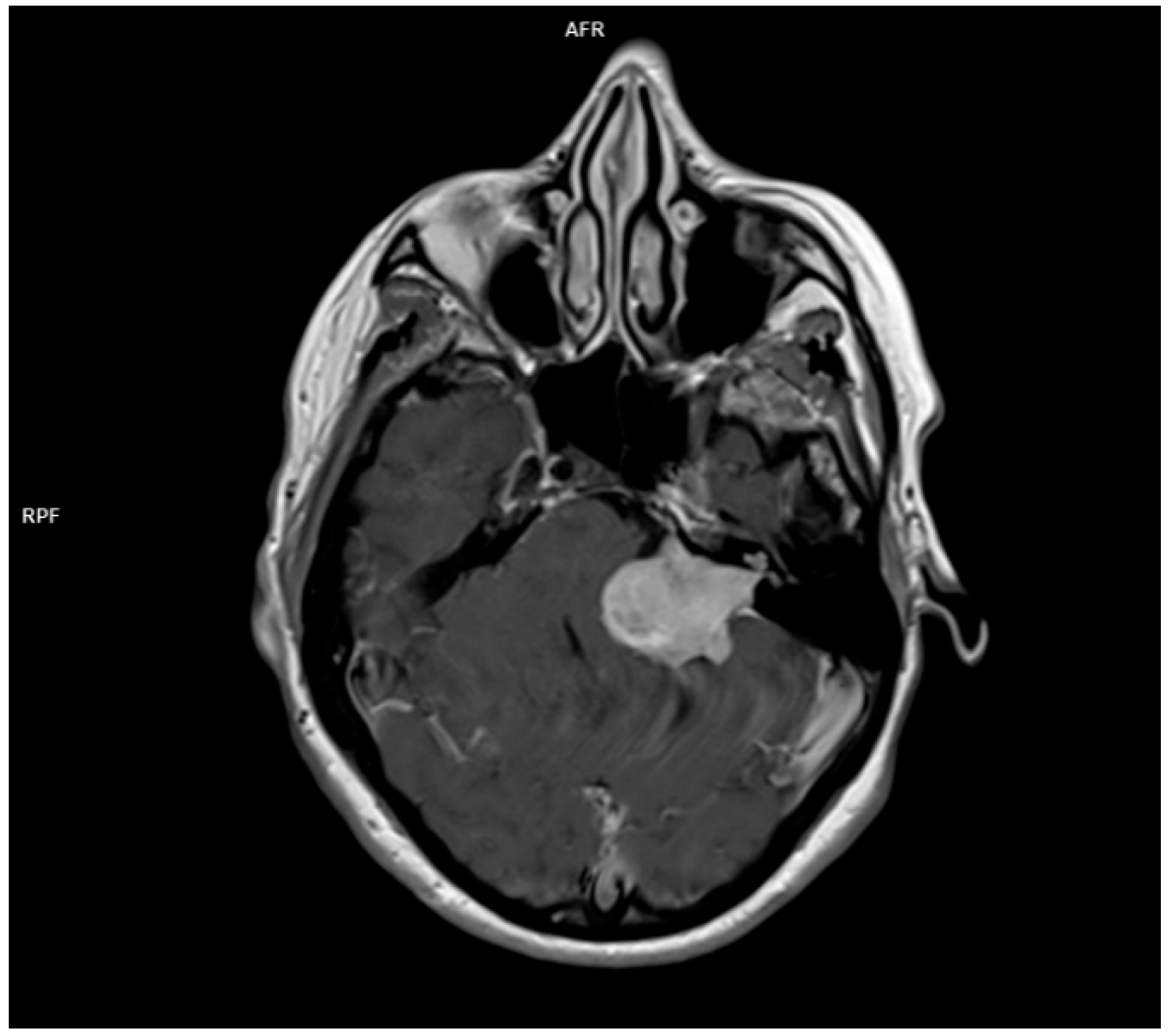
3.1.4. Acoustic Neuroma
3.1.5. Superior Canal Dehiscence
3.1.6. Differential Diagnosis with Central Vertigo
3.2. Other Imaging Modalities (Ultrasound and Functional Imaging)
3.3. Imaging Resolution Limitations and Lesion Detectability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuhauser, H.K. Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Teggi, R.; Manfrin, M.; Balzanelli, C.; Gatti, O.; Mura, F.; Quaglieri, S.; Pilolli, F.; de Zinis, L.R.; Benazzo, M.; Bussi, M. Prevalenza dei sintomi vertigine e instabilità in un campione di 2672 soggetti e correlazione con il sintomo cefalea. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2016, 36, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.W.; Bhattacharyya, N. Balance disorders in the elderly: Epidemiology and functional impact. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strupp, M.; Brandt, T. Peripheral vestibular disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, T.; Dieterich, M. The dizzy patient: Don’t forget disorders of the central vestibular system. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renga, V. Clinical Evaluation of Patients with Vestibular Dysfunction. Neurol. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3931548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Arbusow, V. Acute vestibulopathy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001, 14, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-S. Nystagmus and central vestibular disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemungal, B.M. Neuro-otological emergencies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2007, 20, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.G.; Zhang, L. Eye and head movements and vestibulo-ocular reflex in the context of indirect, referent control of motor actions. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 124, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, A.M.; Patel, M.; Arshad, Q. A brief review of the clinical anatomy of the vestibular-ocular connections—How much do we know? Eye 2015, 29, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, J.A.; Newman-Toker, D. Using the Physical Examination to Diagnose Patients with Acute Dizziness and Vertigo. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 50, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A. Diagnostic value of nystagmus: Spontaneous and induced ocular oscillations. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, S.D.; Bisdorff, A.; von Brevern, M.; Zee, D.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Perez-Fernandez, N.; Welgampola, M.S.; Della Santina, C.C.; Newman-Toker, D.E. Classification of vestibular signs and examination techniques: Nystagmus and nystagmus-like movements. J. Vestib. Res. 2019, 29, 57–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganança, M.M.; Caovilla, H.H.; Ganança, F.F. Eletronistagmografia versus videonistagmografia. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, S.A.; Adams, M.E. Efficient Use of Vestibular Testing. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 54, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.M.; Levin, D.C. The Overuse of Diagnostic Imaging and the Choosing Wisely Initiative. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, S.; Sriskandan, N. Imaging of dizziness. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, B. Vertigo and Disequilibrium: A Practical Guide to Diagnosis and Management, 2nd ed.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Patkar, D.; Yevankar, G.; Parikh, R. Radiology in Vertigo and Dizziness. Int. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Clin. 2012, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnizo, A.; Farah, K.; Lelli, D.A.; Tse, D.; Zakhari, N. Limited usefulness of routine head and neck CT angiogram in the imaging assessment of dizziness in the emergency department. Neuroradiol. J. 2021, 34, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, R.; Abu Awad, A.; Abu Shaheen, W.; Alwily, D.; Avraham, Y.; Najjar, R.; Merchavy, S.; Massoud, S. The “Vestibular Eye Sign”—“VES”: A new radiological sign of vestibular neuronitis can help to determine the affected vestibule and support the diagnosis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.-M.; Sun, H.-C.; Ju, F.-H. Recommendations for reducing exposure to medical X-ray irradiation (Review). Med. Int. 2022, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.E.; Matory, Y.L.; Dwyer, A.J.; Hill, S.C.; Girton, M.E.; Steinberg, S.M.; Knop, R.H.; Frank, J.A.; Hyams, D.; Doppman, J.L.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Soft Tissue Tumors of the Extremities. Ann. Surg. 1987, 205, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadera, S.; Smith, D. MRI Brain (Summary). Radiopaedia.org. 2015. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/mri-brain-summary?lang=us (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Strupp, M.; Bisdorff, A.; Furman, J.; Hornibrook, J.; Jahn, K.; Maire, R.; Newman-Toker, D.; Magnusson, M. Acute unilateral vestibulopathy/vestibular neuritis: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelein, S.; Lindemann, A.; Sinicina, I.; Horn, A.K.E.; Brandt, T.; Strupp, M.; Hüfner, K. Differential Involvement during Latent Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection of the Superior and Inferior Divisions of the Vestibular Ganglia: Implications for Vestibular Neuritis. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00331-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamec, I.; Skorić, M.K.; Handžić, J.; Habek, M. Incidence, seasonality and comorbidity in vestibular neuritis. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, M.; Maquet, C.; Horion, J.; Gillibert, A.; Toupet, M.; Bolognini, B.; Magne, N.; Kahn, L.; Hautefort, C.; Attyé, A. Detection of intralabyrinthine abnormalities using post-contrast delayed 3D-FLAIR MRI sequences in patients with acute vestibular syndrome. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.; Chung, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.W.; Park, D.W.; Kim, T.Y. Clinical value of 4-hour delayed gadolinium-Enhanced 3D FLAIR MR Images in Acute Vestibular Neuritis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navi, B.B.; Kamel, H.; Shah, M.P.; Grossman, A.W.; Wong, C.; Poisson, S.N.; Whetstone, W.D.; Josephson, S.A.; Johnston, S.C.; Kim, A.S. Rate and Predictors of Serious Neurologic Causes of Dizziness in the Emergency Department. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloh, R.W. Prosper Ménière and His Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai-Van, H.; Bounaix, M.-J.; Fraysse, B. Menière’s Disease. Drugs 2001, 61, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Mizukoshi, K.; Shojaku, H.; Watanabe, I.; Hinoki, M.; Kitahara, M. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Meniere’s Disease in Japan. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 1995, 115, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basura, G.J.; Adams, M.E.; Monfared, A.; Schwartz, S.R.; Antonelli, P.J.; Burkard, R.; Bush, M.L.; Bykowski, J.; Colandrea, M.; Derebery, J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Ménière’s Disease. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 162, S1–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K. Audiological Assessment in Meniere’s Disease. In Up to Date on Meniere’s Disease; InTech: Toyama, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorba, A.; Skarżyński, P.H.; Corazzi, V.; Bianchini, C.; Aimoni, C.; Hatzopoulos, S. Assessment Tools for Use in Patients with Ménière Disease: An Update. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 6144–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay-Rivest, E.; Friedmann, D.; Roland, J. Imaging for Menière Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1964–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, H.; Konishi, K.; Sakamaoto, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsushita, N.; Oishi, M.; Iguchi, H.; Inoue, Y. Practical 3DCT imaging of the vestibular aqueduct for Meniere’s disease. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2015, 135, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, T.; Toyama, Y.; Inamoto, R.; Mori, N. Evaluation of the vestibular aqueduct in Ménière’s disease using multiplanar reconstruction images of CT. Auris Nasus Larynx 2012, 39, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasamy, A.; Veillon, F.; Fleury, A.; Eliezer, M.; Abu Eid, M.; Romain, B.; Vuong, H.; Rohmer, D.; Charpiot, A.; Sick, H.; et al. Imaging of the saccule for the diagnosis of endolymphatic hydrops in Meniere disease, using a three-dimensional T2-weighted steady state free precession sequence: Accurate, fast, and without contrast material intravenous injection. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2017, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.-H.; Shen, A.; Keil, S.; Kraemer, N.; Westhofen, M. Radiological findings of the cochlear aqueduct in patients with Meniere’s disease using high-resolution CT and high-resolution MRI. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 271, 3325–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Naganawa, S.; Teranishi, M.; Tagaya, M.; Nakata, S.; Sone, M.; Otake, H.; Kato, K.; Iwata, T.; Nishio, N. Endolymphatic hydrops revealed by intravenous gadolinium injection in patients with Meniere’s disease. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2009, 130, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaerts, A. MRI in Menière’s Disease. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2018, 102, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, G.; Russo, F.M.L.; Calloni, S.F.; Sina, C.; Barozzi, S.; Di Berardino, F.; Scola, E.; Palumbo, G.; Zanetti, D.; Triulzi, F.M. MR imaging of endolymphatic hydrops in Ménière’s disease: Not all that glitters is gold. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Naganawa, S.; Pyykkö, I.; Gibson, W.P.; Sone, M.; Nakata, S.; Teranishi, M. Grading of endolymphatic hydrops using magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2009, 129, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baráth, K.; Schuknecht, B.; Naldi, A.M.; Schrepfer, T.; Bockisch, C.; Hegemann, S. Detection and Grading of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Menière Disease Using MR Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, M.; Poillon, G.; Lévy, D.; Guichard, J.-P.; Toupet, M.; Houdart, E.; Attyé, A.; Hautefort, C. Clinical and radiological characteristics of patients with collapse or fistula of the saccule as evaluated by inner ear MRI. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2020, 140, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrulle, F.; Chaton, V.; Risoud, M.; Farah, H.; Charley, Q.; Vincent, C. The round window sign: A sensitive sign to detect perilymphatic fistulae on delayed postcontrast 3D-FLAIR sequence. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6303–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, A.; Osaki, Y.; Kitahara, T.; Imai, T.; Uno, A.; Nishiike, S.; Fujita, N.; Inohara, H. Endolymphatic hydrops in Meniere’s disease detected by MRI after intratympanic administration of gadolinium: Comparison with sudden deafness. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 2011, 131, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehling, D.A.; Silverstein, M.D.; Mohr, D.N.; Beatty, C.W.; Offord, K.P.; Ballard, D.J. Benign Positional Vertigo: Incidence and Prognosis in a Population-Based Study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, V.; Granato, G.; Mascolo, A.; Tortora, S.; Basso, L.; Farriciello, A.; Coppola, P.; Manfredonia, M.; Toro, F.; Tarallo, A.; et al. Advanced neuroimaging techniques in the clinical routine: A comprehensive MRI case study. J. Adv. Health Care 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M.P.; Pinder, D.K. The Epley (canalith repositioning) manoeuvre for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD003162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halker, R.B.; Barrs, D.M.; Wellik, K.E.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Demaerschalk, B.M. Establishing a Diagnosis of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Through the Dix-Hallpike and Side-Lying Maneuvers. Neurol. 2008, 14, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Radiopaedia.org. 2017. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/benign-paroxysmal-positional-vertigo?lang=us (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluwe, L.; Mautner, V.; Heinrich, B.; Dezube, R.; Jacoby, L.B.; Friedrich, R.E.; MacCollin, M. Molecular study of frequency of mosaicism in neurofibromatosis 2 patients with bilateral vestibular schwannomas. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, R.; Sharma, R.; Bagley, J.H.; Hatef, J.; Friedman, A.H.; Adamson, C. Vestibular schwannomas in the modern era: Epidemiology, treatment trends, and disparities in management. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthies, C.; Samii, M. Management of 1000 Vestibular Schwannomas (Acoustic Neuromas): Clinical Presentation. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, M.; Zhou, L.-F.; Zhang, R.; Lang, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, P.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Clinical features of intracranial vestibular schwannomas. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasamy, A.; Nicolas-Ong, C.; Vuong, H.; Charpiot, A.; Veillon, F. Extension patterns of vestibular schwannomas towards the middle ear: Three new cases and review of the literature. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koos, W.T.; Day, J.D.; Matula, C.; Levy, D.I. Neurotopographic considerations in the microsurgical treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, L.R.; Jacoby, C.G.; Turski, P.A.; Houston, L.W.; Strother, C.M.; Sackett, J.F. Cerebellopontine angle-petromastoid mass lesions: Comparative study of diagnosis with MR imaging and CT. Radiology 1987, 162, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Gaillard, F. Vestibular schwannoma. Radiopaedia.org. 2008. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/vestibular-schwannoma?lang=us (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Hofmann, E.; Choné, L. Neuroradiologische Bildgebung des Akustikusneurinoms (Vestibularisschwannoms). HNO 2011, 59, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulkens, T.H.; Parizel, P.M.; Martin, J.J.; Degryse, H.R.; Van de Heyning, P.H.; Forton, G.E.; De Schepper, A.M. Acoustic schwannoma: MR findings in 84 tumors. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 160, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallari, V.; Apa, E.; Monzani, D.; Genovese, E.; Marchioni, D.; Soloperto, D.; Sacchetto, L. Cochlear Implantation Following Transcanal Infrapromontorial Approach for Vestibular Schwannoma: A Case Series. Audiol. Res. 2022, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss as the initial symptom in patients with acoustic neuroma. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 953265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, C.-H. Vestibular Schwannoma Presenting as Acute Vertigo Mimicking Vestibular Neuritis. Case Rep. Neurol. 2022, 14, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, C.J.; Weg, N.; Minor, L.B.; Zinreich, S.J. CT Evaluation of Bone Dehiscence of the Superior Semicircular Canal as a Cause of Sound- and/or Pressure-induced Vertigo. Radiology 2003, 226, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.P.; Lesser, J.C.C.; Alarcón, A.V. Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Syndrome—Diagnosis and Surgical Management. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 21, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addams-Williams, J.; Wu, K.; Ray, J. The experiments behind the Tullio phenomenon. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2014, 128, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuman, A.G.; Rizvi, S.S.; Pirouet, C.W.; Heidenreich, K.D. Hennebert’s sign in superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome: A Video Case Report. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, L.B. Superior canal dehiscence syndrome. Am. J. Otol. 2000, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.W.; Carey, J.P.; Minor, L.B. Canal dehiscence. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, B.K.; van de Berg, R.; van Rompaey, V.; Bisdorff, A.; Hullar, T.E.; Welgampola, M.S.; Carey, J.P. Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome: Diagnostic criteria consensus document of the committee for the classification of vestibular disorders of the Bárány Society. J. Vestib. Res. 2021, 31, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Raufer, S.; Guan, X.; Halpin, C.F.; Lee, D.J.; Nakajima, H.H. Superior Canal Dehiscence Similarly Affects Cochlear Pressures in Temporal Bones and Audiograms in Patients. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noij, K.S.; Rauch, S.D. Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP) Testing for Diagnosis of Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browaeys, P.; Larson, T.; Wong, M.; Patel, U. Can MRI Replace CT in Evaluating Semicircular Canal Dehiscence? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, H. Posterior Circulation Stroke and Vestibular Syndromes. In Oxford Textbook of Vertigo and Imbalance; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwergal, A.; Dieterich, M. Vertigo and dizziness in the emergency room. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, M.; Peksa, G.D.; Carlson, J.N. Head impulse, nystagmus, and test of skew examination for diagnosing central causes of acute vestibular syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD015089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datar, S.; Rabinstein, A.A. Cerebellar Hemorrhage. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, H.T.; Yildirim, A.; Ekmekci, B.; Eskut, N.; Gunbey, H.P. False-Negative Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Acute Stroke and its Frequency in Anterior and Posterior Circulation Ischemia. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2014, 38, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankalia, D.; Kothari, S.; Phalgune, D.S. Diagnosing Stroke in Acute Vertigo. Neurol. India 2021, 69, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, G.; Huang, L.; Gong, Q. A prospective study on the application of HINTS in distinguishing the localization of acute vestibular syndrome. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, C.L.; Bunn, L.; Koohi, N.; Schmidtmann, G.; Freeman, J.; Kaski, D. Clinician’s perspectives in using head impulse-nystagmus-test of skew (HINTS) for acute vestibular syndrome: UK experience. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattah, J.C.; Talkad, A.V.; Wang, D.Z.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Newman-Toker, D.E. HINTS to Diagnose Stroke in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome. Stroke 2009, 40, 3504–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, A.S.; Majrashi, N.A.; Shubayr, N.A.; Alatwah, S.M.; Alyami, J. Radiographers’ awareness level of MRI-induced vertigo and their perspectives on the post-examination care provided to patients in Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2022, 53, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botwe, B.; Antwi, W.; Vormawor, A.; Oblitey, J. Cognisance of magnetic resonance imaging-induced vertigo and supported care: A study among a cohort of MRI radiographers in a country in West Africa. Radiography 2021, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, A.C.L.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Oliveira, M.d.L.; Macedo-Soares, A.; Topciu, F.R.; Bittar, R.S.M. Magnetic resonance angiography and transcranial Doppler ultrasound findings in patients with a clinical diagnosis of vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Clinics 2020, 75, e1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagururu, N.V.; Akbar, A.; Ward, B.K. Using magnetic resonance imaging to improve diagnosis of peripheral vestibular disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 439, 120300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varangot-Reille, C.; Herranz-Gomez, A.; de la Nava, J.; Suso-Martí, L.; Cuenca-Martínez, F. The experience of vertigo: A systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Brain Imaging Behav. 2022, 16, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taciuc, I.-A.; Dumitru, M.; Vrinceanu, D.; Gherghe, M.; Manole, F.; Marinescu, A.; Serboiu, C.; Neagos, A.; Costache, A. Applications and challenges of neural networks in otolaryngology (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2024, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, V.; Cavaliere, C.; Di Cecca, A.; Ciccarelli, G.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M.; Federico, G. Sex differences in functional brain networks involved in interoception: An fMRI study. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 1130025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Vestibular Disorder | Primary Symptoms | Diagnostic Methods | Imaging Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vestibular neuritis | Vertigo, imbalance, nausea | Clinical examination, VNG | MRI (for differential diagnosis) |
| Meniere’s disease | Vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus | Clinical examination, audiometry | MRI (for hydrops) |
| BPPV | Positional vertigo | Dix–Hallpike maneuver | Not typically required |
| Acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma) | Unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, imbalance | Audiometry, VNG, MRI | MRI (gold standard), essential for diagnosis |
| Superior canal dehiscence | Autophony, sound intolerance, vertigo | Audiometry, VEMP, CT | CT for confirmation, MRI (optional) |
| Feature | HINTS Examination | MRI (DWI Sequence) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Bedside test to differentiate central vs. peripheral AVS | Imaging to detect structural CNS lesions (e.g., stroke) |
| Sensitivity for stroke (early) | High (approaching 100% in expert hands) [83] | Lower in early phase (misses up to 20% of posterior strokes) [82] |
| Specificity | High when correctly performed | High |
| Time to result | Immediate (bedside) | Delayed (requires scanner availability) |
| Availability | Requires clinical expertise, no equipment | Dependent on MRI access |
| Limitations | Operator dependent, limited use in episodic vertigo | Limited sensitivity in hyperacute stroke, not feasible in all settings |
| Best use scenario | Emergency room, acute continuous vertigo | Confirmation of suspected central lesion, atypical presentation |
| Complementarity | Should be used first in AVS, may guide need for MRI | Ideal as a follow-up when central cause is suspected or HINTS is inconclusive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musat, G.C.; Sarafoleanu, C.; Preda, M.A.; Tataru, C.P.; Mitroi, G.G.; Musat, A.A.M.; Radu, M.; Musat, O. Utility and Challenges of Imaging in Peripheral Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101272
Musat GC, Sarafoleanu C, Preda MA, Tataru CP, Mitroi GG, Musat AAM, Radu M, Musat O. Utility and Challenges of Imaging in Peripheral Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusat, Gabriela Cornelia, Codrut Sarafoleanu, Mihai Alexandru Preda, Calin Petru Tataru, George G. Mitroi, Andreea Alexandra Mihaela Musat, Mihnea Radu, and Ovidiu Musat. 2025. "Utility and Challenges of Imaging in Peripheral Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis: A Narrative Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101272
APA StyleMusat, G. C., Sarafoleanu, C., Preda, M. A., Tataru, C. P., Mitroi, G. G., Musat, A. A. M., Radu, M., & Musat, O. (2025). Utility and Challenges of Imaging in Peripheral Vestibular Disorder Diagnosis: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101272





