Investigating the Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluating Multiple Sclerosis Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Criteria
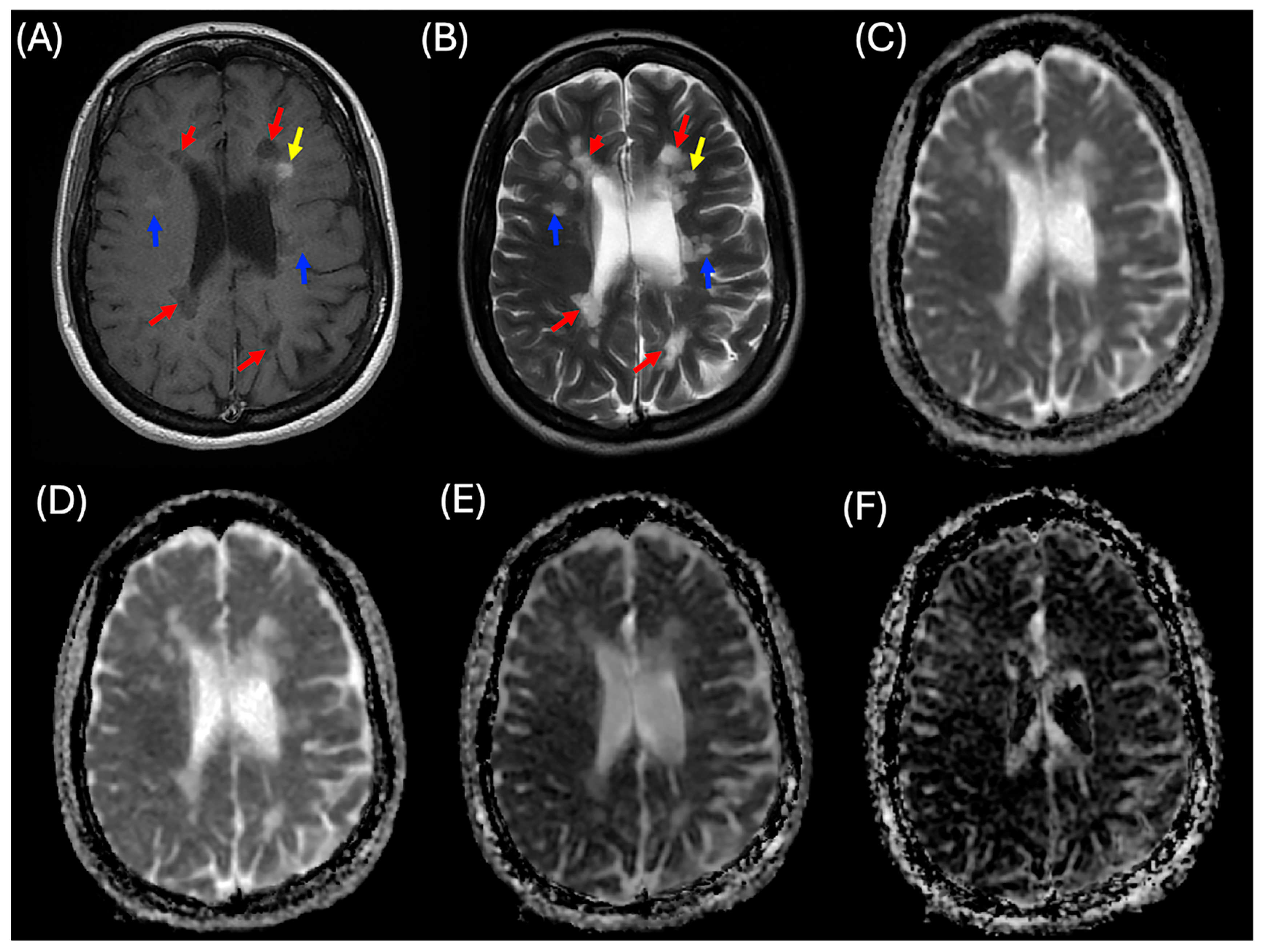
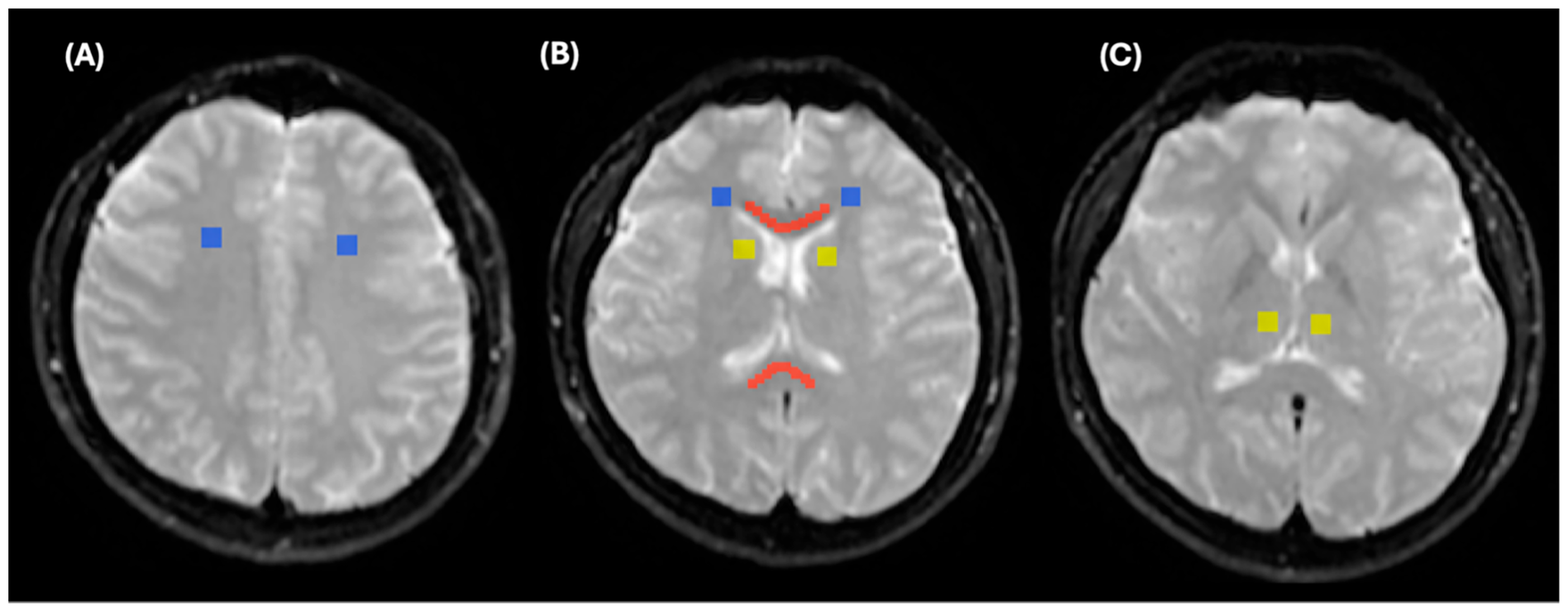
2.2. Lesion Analysis
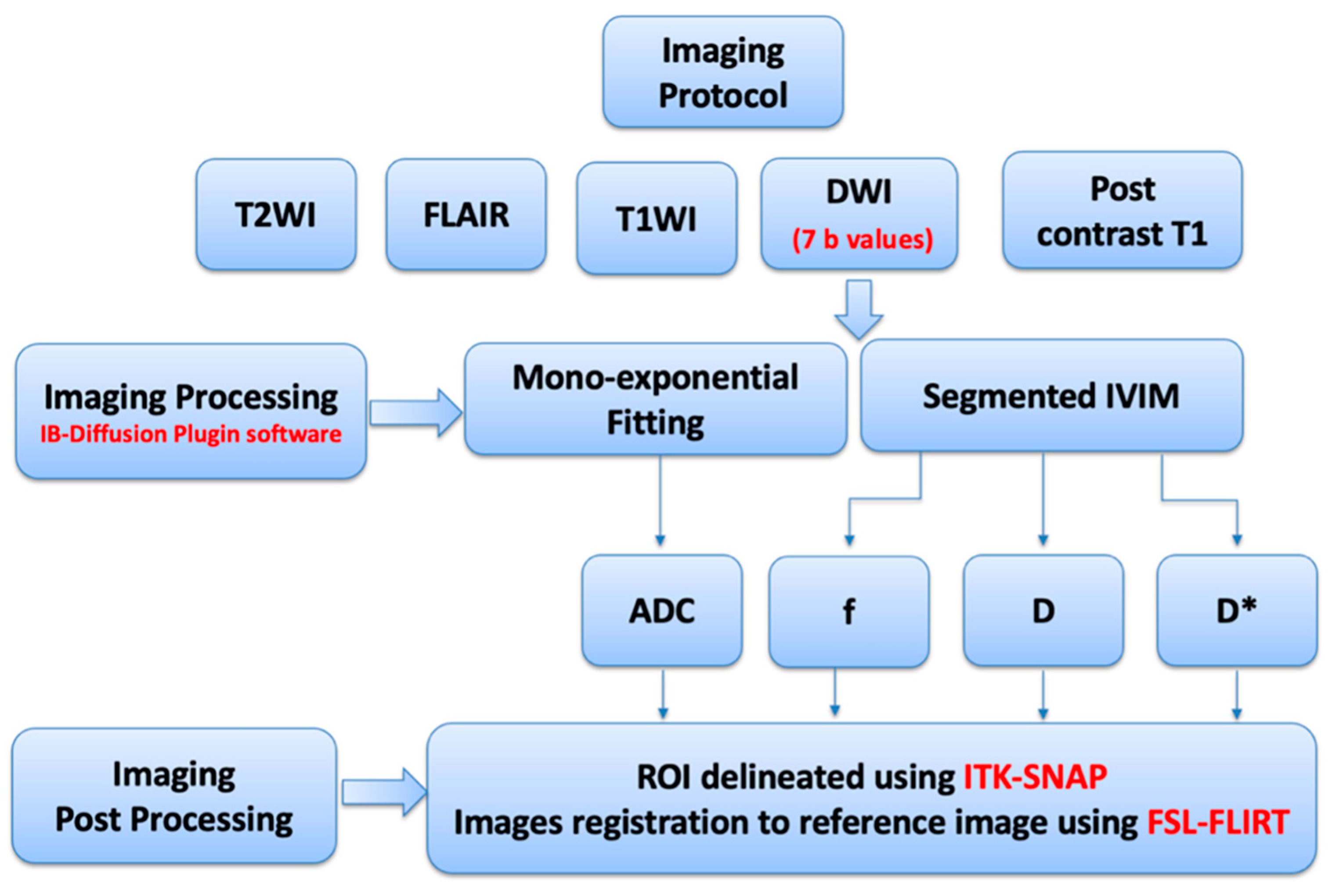
2.3. MRI Imaging Protocols
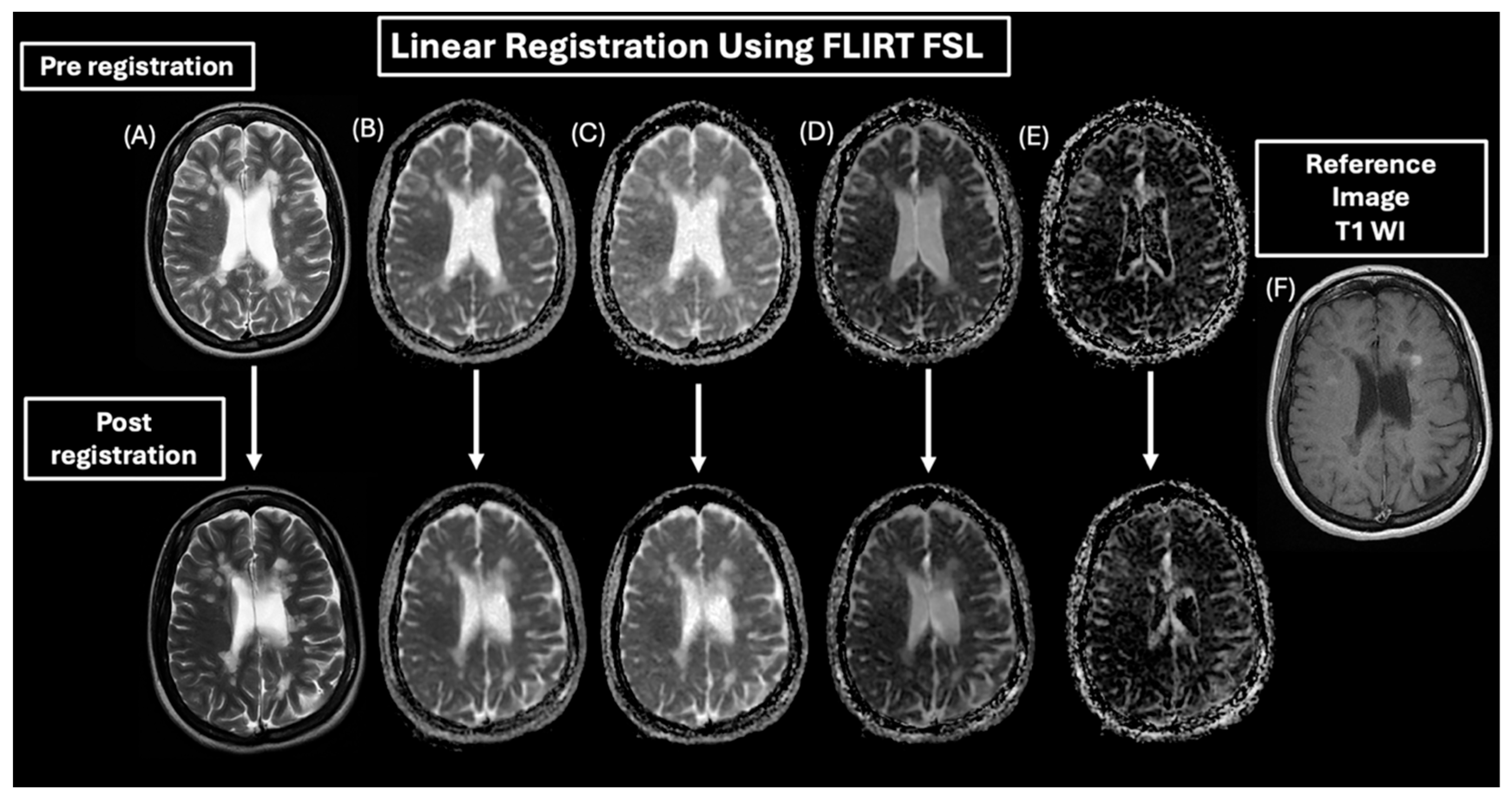
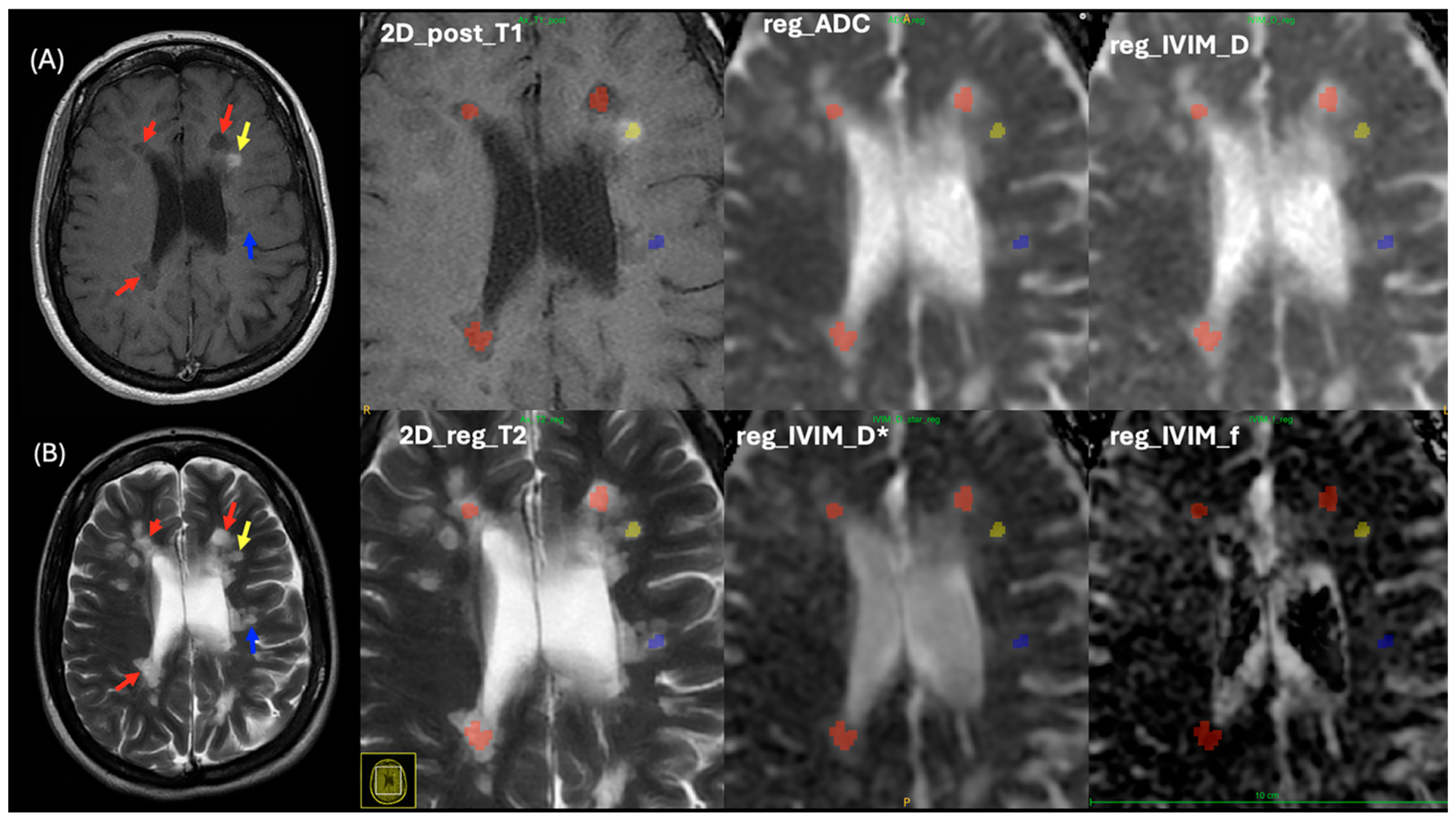
2.4. MRI Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. One-Way ANOVA
3.3. Multiple Comparisons of MRI Parameters
3.3.1. Control Regions vs. MS Lesions
3.3.2. Between MS Lesions
3.4. ROC Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison Between Controls and MS Lesions
4.2. Comparisons Between MS Lesion Types
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| IVIM | Intravoxel incoherent motion |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient |
| D | Pure molecular diffusion |
| D* | Pseudo-diffusion |
| WI | Weighted imaging |
| MS_E | MS enhanced lesions |
| MS_NE | MS non-enhanced lesions |
| MS_BH | MS black hole lesions |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| TR | Repetition time |
| TE | Echo time |
| GCC | Genu of the corpus callosum |
| SCC | Splenium of the corpus callosum |
| WM | White matter |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ROIs | Regions of interest |
References
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutzelnigg, A.; Lassmann, H. Pathology of multiple sclerosis and related inflammatory demyelinating diseases. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 122, 15–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Ciccarelli, O.; De Stefano, N.; Evangelou, N.; Kappos, L.; Rovira, A.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Tintorè, M.; Frederiksen, J.L.; et al. MRI criteria for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: MAGNIMS consensus guidelines. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lublin, F.D.; Reingold, S.C. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: Results of an international survey. Neurology 1996, 46, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriadis, N.; Van Pesch, V. A basic overview of multiple sclerosis immunopathology. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, P.; Oh, J.; Constable, R.T.; Evangelou, N.; Guttmann, C.R.G.; Henry, R.G.; Klawiter, E.C.; Mainero, C.; Massacesi, L.; McFarland, H.; et al. The central vein sign and its clinical evaluation for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: A consensus statement from the North American Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Cooperative. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Saindane, A.M.; Ge, Y.; Babb, J.S.; Johnson, G.; Mannon, L.J.; Herbert, J.; Grossman, R.I. Microvascular abnormality in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: Perfusion MR imaging findings in normal-appearing white matter. Radiology 2004, 231, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’haeseleer, M.; Hostenbach, S.; Peeters, I.; El Sankari, S.; Nagels, G.; De Keyser, J.; D’hooghe, M.B. Cerebral hypoperfusion: A new pathophysiologic concept in multiple sclerosis? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraian, M.A.; Radue, E.-W.; Haller, S.; Kappos, L. Black holes in multiple sclerosis: Definition, evolution, and clinical correlations. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitán, M.I.; Shea, C.D.; Evangelou, I.E.; Stone, R.D.; Fenton, K.M.; Bielekova, B.; Massacesi, L.; Reich, D.S. Evolution of the blood-brain barrier in newly forming multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, J.W.; Kidd, D.; Moseley, I.F.; Kenndall, B.E.; Thompson, A.J.; MacManus, D.G.; McDonald, W.I.; Miller, D.H. Serial gadolinium-enhanced MRI of the brain and spinal cord in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1996, 46, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, F.; Jeffries, N.; Richert, N.D.; Stone, R.D.; Ohayon, J.M.; McFarland, H.F.; Frank, J.A. Evolution of T1 black holes in patients with multiple sclerosis imaged monthly for 4 years. Brain 2003, 126, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brück, W.; Bistsch, A.; Brück, Y.; Brück, Y.; Stiefel, M.; Lassmann, H. Inflammatory central nervous system demyelination: Correlation of magnetic resonance imaging findings with lesion pathology. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Brück, W.; Chard, D.; Fazekas, F.; Geurts, J.J.G.; Enzinger, C.; Hametner, S.; Kuhlmann, T.; Preziosa, P.; Rovira, À.; et al. Association between pathological and MRI findings in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, W.I.; Compston, A.; Edan, G.; Goodkin, D.; Hartung, H.P.; Lublin, F.D.; McFarland, H.F.; Paty, D.W.; Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: Guidelines from the International Panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2001, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Talavage, T.M.; Cheng, J.X. New imaging techniques in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2008, 2, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miller, D.H.; Chard, D.T.; Ciccarelli, O. Clinically isolated syndromes. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, W.J.; Miller, D.H. Clinically isolated syndromes and the relationship to multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.J.; Yang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.J. Gadolinium deposition in brain: Current scientific evidence and future perspectives. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Heales, C. Evaluation of IVIM in the Spinal Cord of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Radiol. Technol. 2024, 95, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lipiński, K.; Bogorodzki, P. Evaluation of Whole Brain Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Imaging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Grenier, P.; Cabanis, E.; Laval-Jeantet, M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federau, C.; Sumer, S.; Becce, F.; Maeder, P.; O’Brien, K.; Meuli, R.; Wintermark, M. Intravoxel incoherent motion perfusion imaging in acute stroke: Initial clinical experience. Neuroradiology 2014, 56, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoal, A.M.; Leoni, R.F.; Dos Santos, A.C.; Paiva, F.F. Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI in neurological and cerebrovascular diseases. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 20, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, T.; Hébert, M.; Bilodeau, L.; Sebastiani, G.; Cerny, M.; Olivié, D.; Gao, Z.-H.; Sylvestre, M.-P.; Cloutier, G.; Nguyen, B.N.; et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI for the characterization of inflammation in chronic liver disease. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, B. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast lesions: Comparison with conventional DWI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e782–e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharzewska-Gondek, A.; Pokryszko-Dragan, A.; Maciej Gondek, T.; Kołtowska, A.; Gruszka, E.; Budrewicz, S.; Sąsiadek, M.; Bladowska, J. Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in normal appearing white matter may support the differential diagnosis between multiple sclerosis lesions and other white matter hyperintensities. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 397, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, K.G.; Haberg, A.K.; Skandsen, T.; Finnanger, T.G.; Vik, A. A longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study of the apparent diffusion coefficient values in corpus callosum during the first year after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus Farber, R.; Devilliers, L.; Miller, A.; Lublin, F.; Law, M.; Fatterpekar, G.; Delman, B.; Naidich, T. Differentiating multiple sclerosis from other causes of demyelination using diffusion weighted imaging of the corpus callosum. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, P.; Absinta, M. Emerging MRI biomarkers for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2024, 30, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca, M.A.; Preziosa, P.; Barkhof, F.; Brownlee, W.; Calabrese, M.; De Stefano, N.; Granziera, C.; Stefan, R.; Toosy, A.T.; Vidal-Jordana, À.; et al. Current and future role of MRI in the diagnosis and prognosis of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 44, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VandeBunte, A.M.; Fonseca, C.; Paolilo, E.W.; Gontrum, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Kramer, J.H.; Casaletto, K.B. Regional Vulnerability of the Corpus Callosum in the Context of Cardiovascular Risk. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2023, 36, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.; Chwojnicki, K.; Szurowska, E. The diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: What has changed in diagnostic criteria? Pol. J. Radiol. 2023, 88, e574–e581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nahas, A.R.; El-Assmy, A.M.; Mansour, O.; Sheir, K.Z. A prospective multivariate analysis of factors predicting stone disintegration by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: The value of high-resolution noncontrast computed tomography. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 1688–1693; discussion 1693–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Smith, S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, D.N.; Fischl, B. Accurate and robust brain image alignment using boundary based registration. NeuroImage 2009, 48, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of Anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, S.; Maldjian, J.A.; Grossman, R.I. Multiple sclerosis: Comparison of trace apparent diffusion coefficients with MR enhancement pattern of lesions. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 869–874. [Google Scholar]
- Eisele, P.; Szabo, K.; Griebe, M.; Rossmanith, C.; Förster, A.; Hennerici, M.; Gass, A. Reduced diffusion in a subset of acute MS lesions: A serial multiparametric MRI study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Gong, X.-Q.; Zheng, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.-M. Progress of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging in liver diseases. World J. Clin. Cases. 2020, 8, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, E.; Bammer, R.; Horsfield, M.S.; Rovaris, M.; Gass, A.; Ciccarelli, O.; Filippi, M. Diffusion MR imaging in multiple sclerosis: Technical aspects and challenges. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawlani, V.; Patel, M.D.; Davies, N.; Flintham, R.; Wesolowski, R.; Ughratdar, I.; Pohl, U.; Nagaraju, S.; Petrik, V.; Kay, A.; et al. Multiparametric MRI: Practical approach and pictorial review of a useful tool in the evaluation of brain tumours and tumour-like lesions. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Law, M.; Johnson, G.; Herbert, J.; Babb, J.S.; Mannon, L.J.; Grossman, R.I. Dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MR imaging of multiple sclerosis lesions: Characteriing hemodynamic impairment and inflammatory activity. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe, E.; Li, D.K.B.; Traboulsee, A.; Rauscher, A. What have we learned from perfusion MRI in multiple sclerosis? Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerfel, J.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; Brunecher, P.; Aktas, O.; McFarland, H.; Villringer, A.; Zipp, F. Changes in cerebral perfusion precede plaque formation in multiple sclerosis: A longitudinal perfusion MRI study. Brain 2004, 127 Pt 1, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummari, S.; Burra, K.G.; Reddy, V.R.; Das, S.; Anilkumar, C. Determination of Efficiency of 3D Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) in the Imaging of Multiple Sclerosis in Comparison With 2D FLAIR at 3-Tesla MRI. Cureus 2023, 15, e48136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Calabrese, M.; Sormani, M.P.; Rinaldi, F.; Perini, P.; Comi, G.; Gallo, P. Intracortical lesions: Relevance for new MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2010, 75, 1988–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurts, J.J.; Pouwels, P.J.; Uitdehaag, B.M.; Polman, C.H.; Barkhof, F.; Castelijns, J.A. Intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis: Improved detection with 3D double inversion-recovery MR imaging. Radiology 2005, 236, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Brück, W.; Parisi, J.E.; Lucchinetti, C.; Brück, W.; Parisi, J.; Scheithauer, B.; Rodriguez, M.; Lassmann, H. Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: Implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roine, T.; Jeurissen, B.; Perrone, D.; Aelterman, J.; Leemans, A.; Philips, W.; Sijbers, J. Isotropic non-white matter partial volume effects in constrained spherical deconvolution. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziosa, P.; Sangalli, F.; Esposito, F.; Moiola, L.; Martinelli, V.; Falini, A.; Comi, G.; Filippi, M. Clinical deterioration due to co-occurrence of multiple sclerosis and glioblastoma: Report of two cases. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhao, W.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Kuang, Q.; Xu, J.; Ji, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, M.; et al. MS or not MS: T2-weighted imaging (T2WI)-based radiomic findings distinguish MS from its mimics. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 61, 10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkossi, S.M.; Sayed, S.A.; Shehata, G.A.; Seif Eldein, G.S.; Ahmed, S.H.; Ali, A.H. Diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry in differentiating multiple sclerosis and its mimics. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2023, 54, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Controls | RR-MS Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size and number of examined ROIs in controls and MS patients | 29 58 CC, 116 WM, and 116 deep WM A total of 290 collected from different brain areas | 224 114 MS_E lesions 1613 MS_NE lesions 779 MS_BH lesions |
| Mean age ± SD | 28 ± 4.7 years | 36.3 ± 9.7 years |
| Gender (male and female) | 25 male and 4 female | 62 male and 162 female |
| Disease duration | N/A | 8.9 ± 4.7 years |
| EDSS (mean± SD, range) | N/A | (2.3 ± 1.95, 0–8) |
| Number of relapses (mean± SD, range) | N/A | (2.5 ± 1.95, 0–13) |
| IVIM Parameters | Groups | N | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADC | Corpus callosum | 58 | 0.75 ± 0.04 |
| WM | 116 | 0.75 ± 0.04 | |
| Deep WM | 116 | 0.76 ± 0.03 | |
| E | 114 | 0.97 ± 0.17 | |
| NE | 1613 | 1.06 ± 0.16 | |
| BH | 779 | 1.30 ± 0.21 | |
| D | Corpus callosum | 58 | 0.72 ± 0.04 |
| WM | 116 | 0.71 ± 0.04 | |
| Deep WM | 116 | 0.71 ± 0.03 | |
| E | 114 | 0.92 ± 0.16 | |
| NE | 1613 | 1.01 ± 0.16 | |
| BH | 779 | 1.23 ± 0.22 | |
| D* | Corpus callosum | 58 | 0.87 ± 0.09 |
| WM | 116 | 0.89 ± 0.08 | |
| Deep WM | 116 | 0.86 ± 0.11 | |
| E | 114 | 1.18 ± 0.25 | |
| NE | 1613 | 1.22 ± 0.19 | |
| BH | 779 | 1.47 ± 0.22 | |
| f | Corpus callosum | 58 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| WM | 116 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | |
| Deep WM | 116 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | |
| E | 114 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | |
| NE | 1613 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | |
| BH | 779 | 0.06 ± 0.03 |
| Outcome Variables | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC | Between groups | 70.08 | 5 | 14.07 | 482.52 | <0.0001 |
| Within groups | 81.04 | 2790 | 0.03 | |||
| D | Between groups | 63.08 | 5 | 12.62 | 433.60 | <0.0001 |
| Within groups | 81.18 | 2790 | 0.03 | |||
| D* | Between groups | 80.93 | 5 | 16.19 | 431.40 | <0.0001 |
| Within groups | 104.68 | 2790 | 0.04 | |||
| f | Between groups | 0.07 | 5 | 0.014 | 25.78 | <0.0001 |
| Within groups | 1.55 | 2790 | 0.001 |
| Healthy Control ROI | MS Lesion | IVIM Parameters | Mean Difference | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corpus callosum | E | ADC | −0.22 | All < 0.0001 |
| NE | −0.31 | |||
| BH | −0.54 | |||
| E | D | −0.20 | ||
| NE | −0.29 | |||
| BH | −0.51 | |||
| E | D* | −0.31 | ||
| NE | −0.35 | |||
| BH | −0.60 | |||
| E | f | −0.02 | ||
| NE | −0.01 | |||
| BH | −0.02 | |||
| WM | E | ADC | −0.22 | |
| NE | −0.31 | |||
| BH | −0.54 | |||
| E | D | −0.20 | ||
| NE | −0.30 | |||
| BH | −0.52 | |||
| E | D* | −0.28 | ||
| NE | −0.32 | |||
| BH | −0.58 | |||
| E | f | −0.02 | ||
| NE | −0.01 | |||
| BH | −0.10 | |||
| Deep WM | E | ADC | −0.24 | |
| NE | −0.32 | |||
| BH | −0.56 | |||
| E | D | −0.21 | ||
| NE | −0.30 | |||
| BH | −0.52 | |||
| E | D* | −0.31 | ||
| NE | −0.36 | |||
| BH | −0.61 | |||
| E | f | −0.02 | ||
| NE | −0.01 | |||
| BH | −0.02 |
| IVIM Parameters | MS Lesions | Mean Difference | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC | E | NE | −0.09 | All < 0.0001 |
| E | BH | −0.32 | ||
| NE | BH | −0.23 | ||
| D | E | NE | −0.09 | All < 0.0001 |
| E | BH | −0.22 | ||
| NE | BH | −0.22 | ||
| D* | E | NE | −0.04 | 0.264 |
| E | BH | −0.30 | Both < 0.0001 | |
| NE | BH | −0.25 | ||
| f | E | NE | 0.01 | <0.0001 |
| E | BH | 0.01 | 0.205 | |
| NE | BH | −0.005 | <0.0001 | |
| Type of MS vs. Controls | Cutoff Value for Detecting Lesions | Area Under the Curve | p-Value | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC | |||||
| BH vs. Controls | >0.84 | 0.996 | All < 0.001 | 98.0 (96.6–98.7) | 99.7 (97.9–100) |
| E vs. Controls | >0.83 | 0.967 | 89.5 (82.3–94.4) | 98.6 (96.5–99.6) | |
| NE vs. Controls | >0.83 | 0.989 | 94.5 (93.3–95.5) | 98.3 (96.0–99.4) | |
| D | |||||
| BH vs. Controls | >0.81 | 0.996 | All < 0.001 | 97.7 (96.4–98.6) | 99.6 (97.5–99.9) |
| E vs. Controls | >0.78 | 0.948 | 89.5 (82.3–94.4) | 96.6 (93.8–98.3) | |
| NE vs. Controls | >0.79 | 0.982 | 93.6 (92.2–94.7) | 98.3 (96.0–99.4) | |
| D* | |||||
| BH vs. Controls | >1.08 | 0.99 | All < 0.001 | 95.3 (93.5–96.6) | 99.0 (97.0–99.8) |
| E vs. Controls | >0.98 | 0.917 | 86.0 (78.2–91.8) | 89.7 (85.6–92.9) | |
| NE vs. Controls | >1.00 | 0.957 | 88.5 (86.8–90.0) | 92.8 (89.1–95.5) | |
| f | |||||
| BH vs. Controls | >0.05 | 0.715 | All < 0.001 | 56.7 (53.2–60.3) | 80.0 (74.2–83.8) |
| E vs. Controls | >0.05 | 0.728 | 61.4 (51.8–70.4) | 80.7 (75.7–85.1) | |
| NE vs. Controls | >0.05 | 0.67 | 49.8 (47.3–52.2) | 80.0 (74.9–84.4) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alomair, O.I.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Abujamea, A.H.; AlfIfi, A.Y.; Alashban, Y.I.; Kurniawan, N.D. Investigating the Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluating Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101260
Alomair OI, Alghamdi SA, Abujamea AH, AlfIfi AY, Alashban YI, Kurniawan ND. Investigating the Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluating Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101260
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlomair, Othman I., Sami A. Alghamdi, Abdullah H. Abujamea, Ahmed Y. AlfIfi, Yazeed I. Alashban, and Nyoman D. Kurniawan. 2025. "Investigating the Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluating Multiple Sclerosis Lesions" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101260
APA StyleAlomair, O. I., Alghamdi, S. A., Abujamea, A. H., AlfIfi, A. Y., Alashban, Y. I., & Kurniawan, N. D. (2025). Investigating the Role of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluating Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101260






