Predicting Clinical Response to Monoclonal TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Transcriptomic Approach Based on Transmembrane TNF Reverse Signaling and Nrf2 Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Methods
2.1.1. Donors
2.1.2. Cell Culture
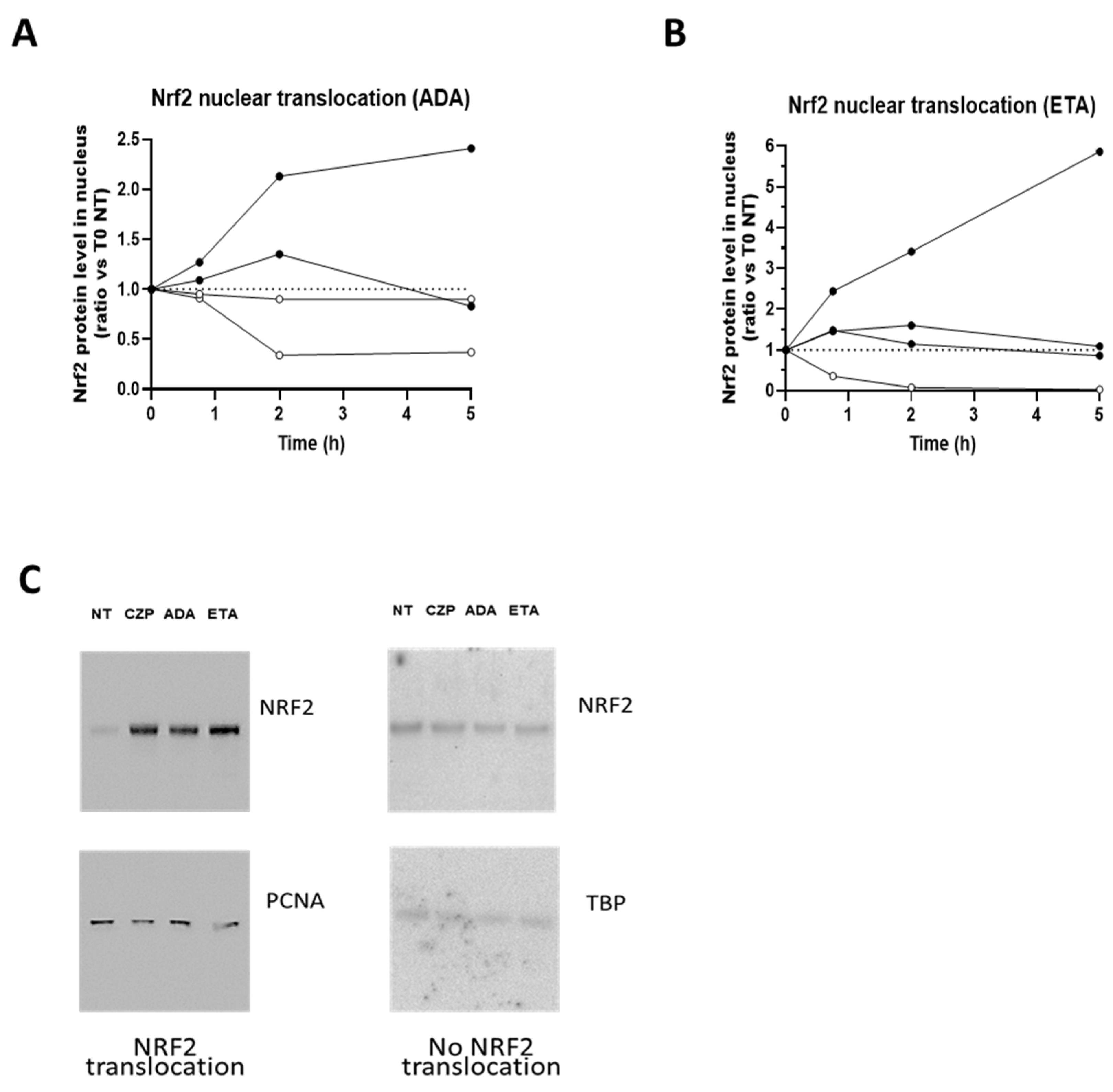
2.1.3. Cell Fractionation and Western Blot Analysis
2.1.4. RNA Extraction and Quantification by RT q PCR
2.1.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TNFis Are Able to Induce Nrf2 Translocation
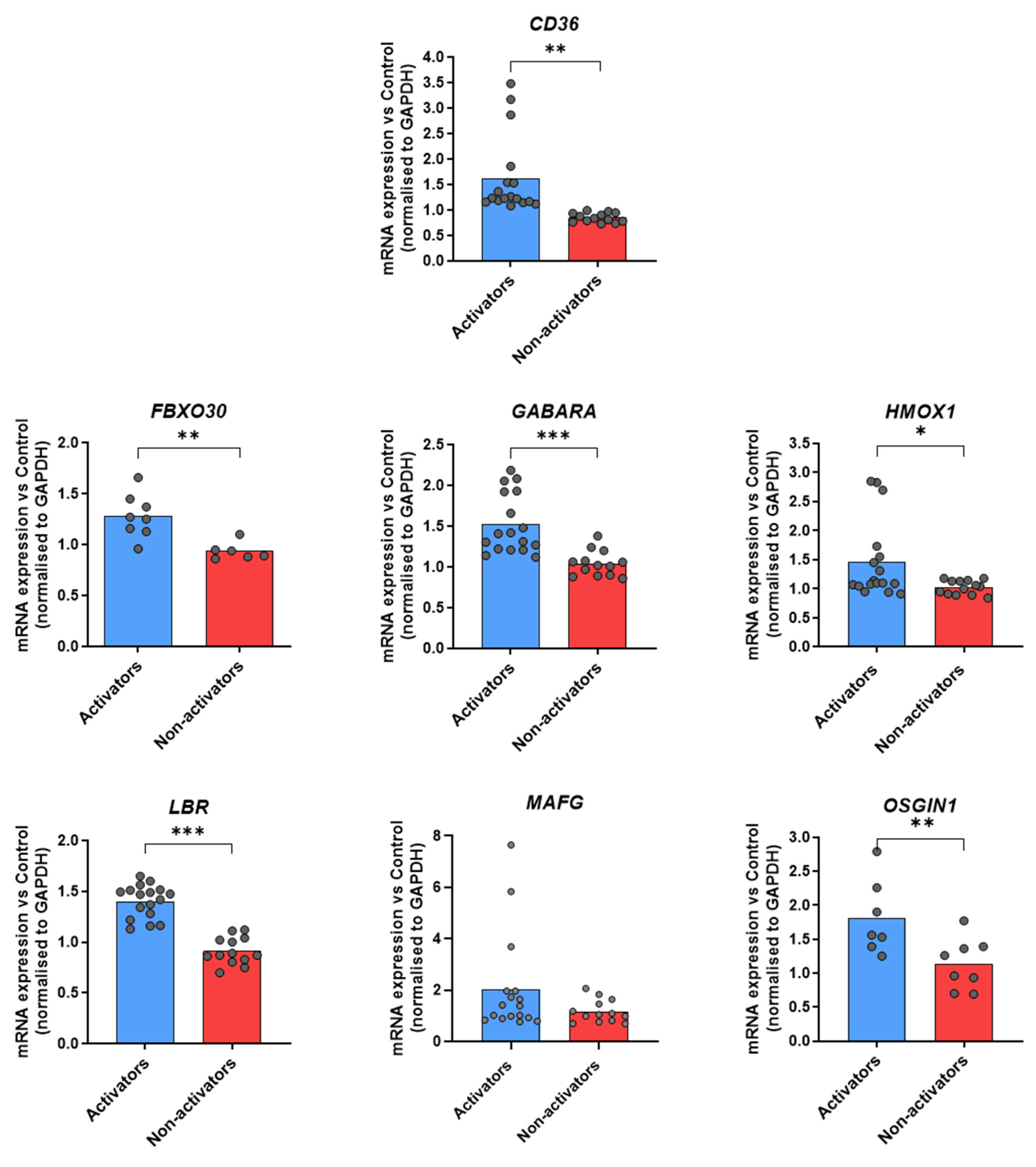
3.2. Identification of Target Genes Indicating a Transcriptional Activation of tmTNF Nrf2 Signaling in Healthy Donors
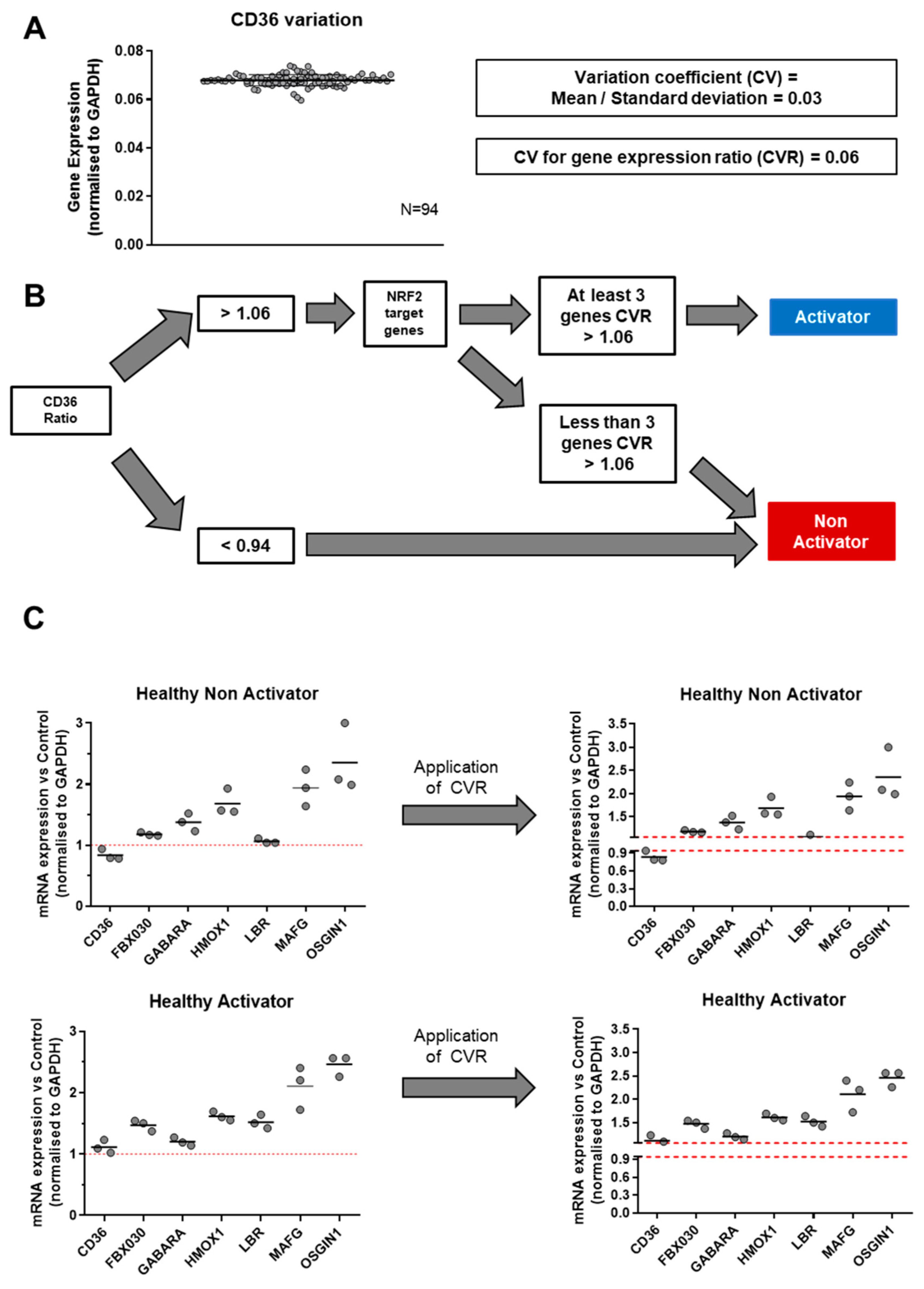
3.3. Identification of Experimental Variation of mRNA Measurement and Definition of tmTNF Nrf2 Activator/Non-Activator Status
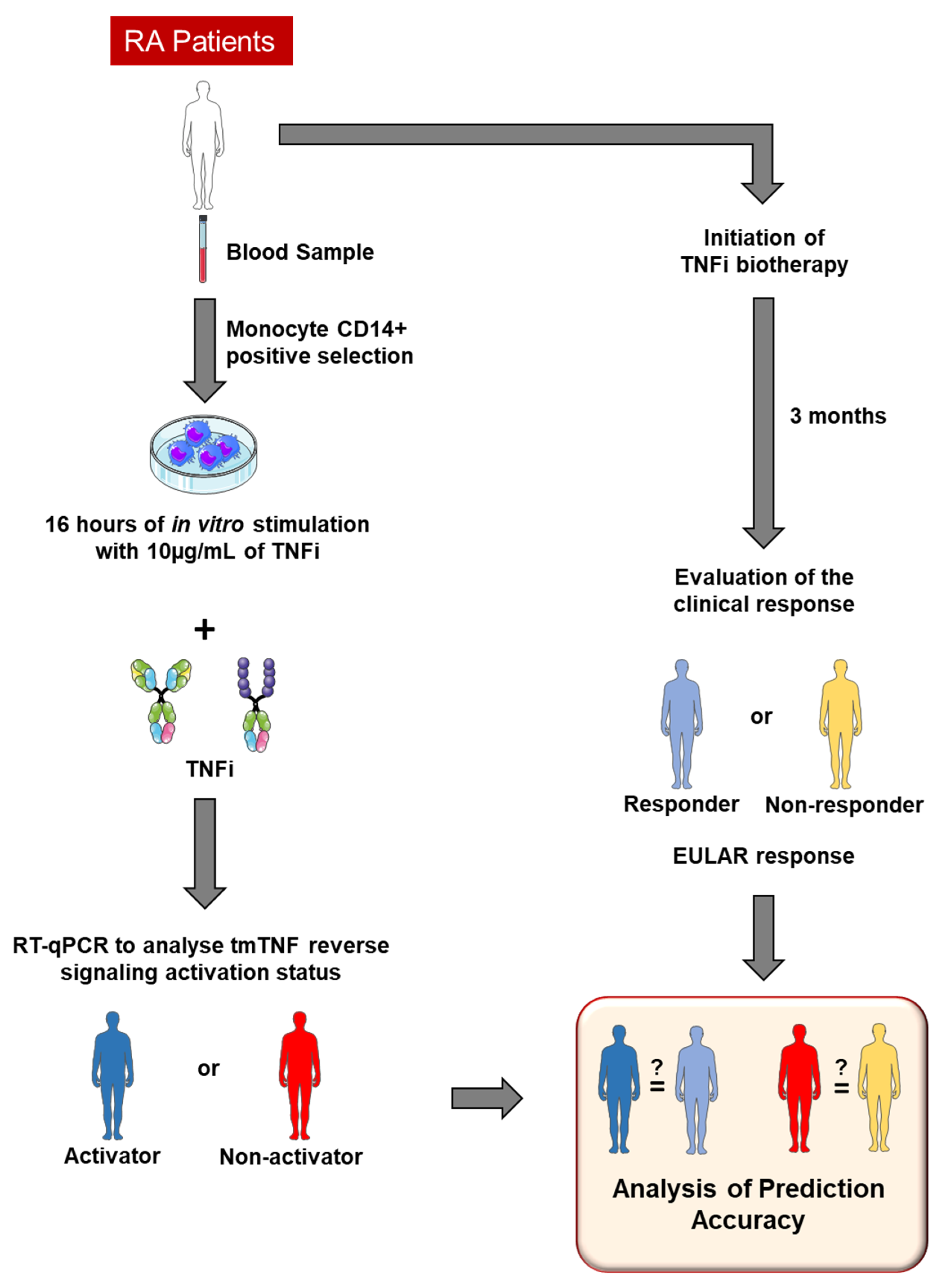
3.4. Experimental Protocol to Predict TNFi Clinical Response Depending on tmTNF Nrf2 Activator Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schett, G.; McInnes, I.B.; Neurath, M.F. Reframing Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases through Signature Cytokine Hubs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daien, C.; Hua, C.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Cantagrel, A.; Dubremetz, M.; Dougados, M.; Fautrel, B.; Mariette, X.; Nayral, N.; Richez, C.; et al. Update of French society for rheumatology recommendations for managing rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottenberg, J.-E.; Brocq, O.; Perdriger, A.; Lassoued, S.; Berthelot, J.-M.; Wendling, D.; Euller-Ziegler, L.; Soubrier, M.; Richez, C.; Fautrel, B.; et al. Non-TNF-Targeted Biologic vs a Second Anti-TNF Drug to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients with Insufficient Response to a First Anti-TNF Drug: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.C. Pharmacology of TNF blockade in rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic inflammatory diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, L.C.; l’Ami, M.J.; Ruwaard, J.; Hart, M.H.; Heer, P.O.; Bloem, K.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Boers, M.; Alvarez, D.F.; et al. Dynamics of circulating TNF during adalimumab treatment using a drug-tolerant TNF assay. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissner, G.; Kolch, W.; Scheurich, P. Ligands working as receptors: Reverse signaling by members of the TNF superfamily enhance the plasticity of the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2004, 15, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.F.; Baron, M.; Constantin, A.; Degboé, Y.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.-L. Anti-TNF certolizumab pegol induces antioxidant response in human monocytes via reverse signaling. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maicas, N.; Ferrándiz, M.L.; Brines, R.; Ibáñez, L.; Cuadrado, A.; Koenders, M.I.; van den Berg, W.B.; Alcaraz, M.J. Deficiency of Nrf2 accelerates the effector phase of arthritis and aggravates joint disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2011, 15, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, K.; Simons, N.; Sayegh, S.; Baron, M.; Degboé, Y.; Boyer, J.-F.; Kruglov, A.; Nedospasov, S.; Novarino, J.; Aloulou, M.; et al. Evidence for tmTNF reverse signaling in vivo: Implications for an arginase-1-mediated therapeutic effect of TNF inhibitors during inflammation. iScience 2021, 24, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Garde, M.D.B.; Martinez, F.O.; Melgert, B.N.; Hylkema, M.N.; Jonkers, R.E.; Hamann, J. Chronic exposure to glucocorticoids shapes gene expression and modulates innate and adaptive activation pathways in macrophages with distinct changes in leukocyte attraction. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrchen, J.; Steinmüller, L.; Barczyk, K.; Tenbrock, K.; Nacken, W.; Eisenacher, M.; Nordhues, U.; Sorg, C.; Sunderkötter, C.; Roth, J. Glucocorticoids induce differentiation of a specifically activated, anti-inflammatory subtype of human monocytes. Blood 2007, 109, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gestel, A.M.; Prevoo, M.L.; van ’t Hof, M.A.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; van de Putte, L.B.; van Riel, P.L. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chorley, B.N.; Campbell, M.R.; Wang, X.; Karaca, M.; Sambandan, D.; Bangura, F.; Xue, P.; Pi, J.; Kleeberger, S.R.; Bell, D.A. Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: Influence on retinoid X receptor alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 7416–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruck, C.J.; Fragoulis, A.; Gurzynski, A.; Brandenburg, L.-O.; Kan, Y.W.; Chan, K.; Hassenpflug, J.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Varoga, D.; Lippross, S.; et al. Role of oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: Insights from the Nrf2-knockout mice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusch, U.; Rossol, M.; Baerwald, C.; Hauschildt, S.; Wagner, U. Outside-to-inside signaling through transmembrane tumor necrosis factor reverses pathologic interleukin-1beta production and deficient apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis monocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2612–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Cotton, A.; Attipoe, L.; Ciurtin, C.; Doré, C.J.; Ehrenstein, M.R. Regulatory T cells as a biomarker for response to adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 978–980.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, A.; Ly, B.; Bitoun, S.; Nocturne, G.; Rivière, E.; Manson, J.J.; Matucci, A.; Pallardy, M.; De Vries, N.; Mariette, X. Restoration of Default Blood Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Polarization with Adalimumab But Not Etanercept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 832117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmüller, B.; Häupl, T.; Hernandez, M.M.; Grützkau, A.; Kuban, R.-J.; Tandon, N.; Voss, J.W.; Salfeld, J.; Kinne, R.W.; Burmester, G.R. CD11c as a transcriptional biomarker to predict response to anti-TNF monotherapy with adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meusch, U.; Krasselt, M.; Rossol, M.; Baerwald, C.; Klingner, M.; Wagner, U. In vitro response pattern of monocytes after tmTNF reverse signaling predicts response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deora, A.; Hegde, S.; Lee, J.; Choi, C.-H.; Chang, Q.; Lee, C.; Eaton, L.; Tang, H.; Wang, D.; Lee, D.; et al. Transmembrane TNF-dependent uptake of anti-TNF antibodies. MAbs 2017, 9, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, A.D.; Hunt, N.H.; Wanigasekara, Y.; Bloomfield, G.; Wallach, D.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Chaudhri, G. A casein kinase I motif present in the cytoplasmic domain of members of the tumour necrosis factor ligand family is implicated in “reverse signalling”. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, S.; Boldt, S.; Kolch, W.; Haffner, S.; Kazak, S.; Janosch, P.; Holler, E.; Andreesen, R.; Eissner, G. LPS resistance in monocytic cells caused by reverse signaling through transmembrane TNF (mTNF) is mediated by the MAPK/ERK pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymakcalan, Z.; Sakorafas, P.; Bose, S.; Scesney, S.; Xiong, L.; Hanzatian, D.K.; Salfeld, J.; Sasso, E.H. Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 131, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini Kadijani, A.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Sorrentino, D.; Mirzaei, A.; Shahrokh, S.; Balaii, H.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Mays, J.L.; Reza Zali, M. Transmembrane TNF-α Density, but not Soluble TNF-α Level, is Associated with Primary Response to Infliximab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Monoclonal | Etanercept | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Women (%) | 9/15 (60.0) | 5/10 (50.0) | 0.697 |
| Age (IQR) | 63.3 (58.0–70.0) | 61.0 (55.5–67.5) | 0.402 |
| ACPA positive | 14/15 (93.3) | 9/10 (90.0) | 0.999 |
| RF positive | 13/15 (86.7) | 8/9 (88,9) | 0.999 |
| Erosion | 6/15 (40.0) | 6/10 (60.0) | 0.428 |
| Baseline DAS28 (IQR) | 4.82 (4.15–5.58) | 4.60 (3.91–5.31) | 0.521 |
| Molecule | DAS28 M0 | DAS28 M3 | Prediction of Response | Clinical Evolution | Predictive Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANTIBODIES | |||||
| GOL | 5.09 | 4.47 | − | − | |
| GOL | 4.50 | 2.00 | + | + | |
| ADA | 5.40 | 3.10 | + | + | |
| GOL | 4.58 | 2.35 | + | + | |
| ADA | 3.78 | 1.04 | + | + | |
| ADA | 4.79 | 1.21 | + | + | |
| ADA | 7.10 | 5.16 | − | − | |
| GOL | 4.15 | 2.94 | + | + | |
| IFX | 4.39 | 2.61 | + | + | |
| ADA | 6.02 | 5.37 | − | − | |
| IFX | 5.60 | 3.17 | − | − | |
| ADA | 2.62 | 1.40 | + | + | |
| GOL | 3.78 | 4.16 | + | − | |
| ADA | 4.92 | 3.04 | + | + | |
| ADA | 5.58 | 3.15 | + | + | |
| ETANERCEPT | |||||
| ETA | 3.72 | 1.73 | − | + | |
| ETA | 5.88 | 2.50 | − | + | |
| ETA | 4.55 | 2.25 | − | + | |
| ETA | 4.64 | 2.56 | − | + | |
| ETA | 5.12 | 2.59 | +? | + | |
| ETA | 3.55 | 2.69 | − | + | |
| ETA | 4.63 | 2.82 | +? | + | |
| ETA | 6.03 | 1.40 | − | + | |
| ETA | 3.97 | 1.50 | + | + | |
| ETA | 4.18 | 2.12 | + | + | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diallo, K.; Degboé, Y.; Baron, M.; Bellin-Robert, A.; Boyer, J.-F.; Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Constantin, A.; Rauwel, B.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.-L. Predicting Clinical Response to Monoclonal TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Transcriptomic Approach Based on Transmembrane TNF Reverse Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101232
Diallo K, Degboé Y, Baron M, Bellin-Robert A, Boyer J-F, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Constantin A, Rauwel B, Cantagrel A, Davignon J-L. Predicting Clinical Response to Monoclonal TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Transcriptomic Approach Based on Transmembrane TNF Reverse Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101232
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiallo, Katy, Yannick Degboé, Michel Baron, Anaïs Bellin-Robert, Jean-Frédéric Boyer, Adeline Ruyssen-Witrand, Arnaud Constantin, Benjamin Rauwel, Alain Cantagrel, and Jean-Luc Davignon. 2025. "Predicting Clinical Response to Monoclonal TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Transcriptomic Approach Based on Transmembrane TNF Reverse Signaling and Nrf2 Activation" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101232
APA StyleDiallo, K., Degboé, Y., Baron, M., Bellin-Robert, A., Boyer, J.-F., Ruyssen-Witrand, A., Constantin, A., Rauwel, B., Cantagrel, A., & Davignon, J.-L. (2025). Predicting Clinical Response to Monoclonal TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Transcriptomic Approach Based on Transmembrane TNF Reverse Signaling and Nrf2 Activation. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101232






