Impact of Hip Exercises on Postural Stability and Function in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
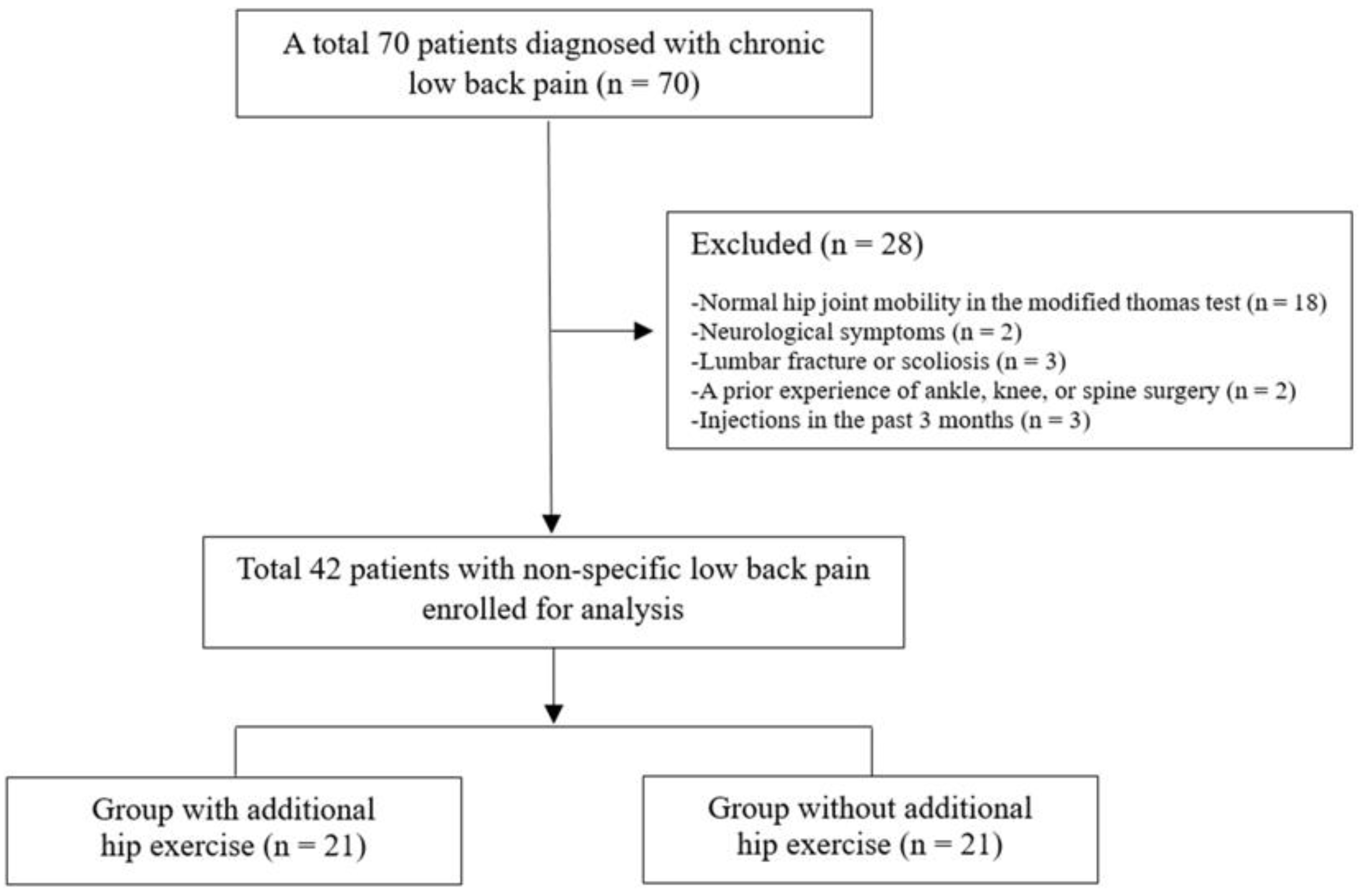
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. Outcome Measures
2.2.1. Hip Joint Mobility
2.2.2. Back Extensor Endurance
2.2.3. Postural Stability
2.2.4. Pain and Function (Disability)
2.2.5. Interventions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Between- and Within-Group Comparisons of Functional and Clinical Outcomes
3.3. Correlation and Predictor Factors
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dal Farra, F.; Lopomo, N.; Fascia, M.; Scalona, E.; Cimolin, V. How non-specific low back pain affects gait kinematics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture 2024, 114, S18–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, D.; Bain, C.; Williams, G.; March, L.; Brooks, P.; Blyth, F.; Woolf, A.; Vos, T.; Buchbinder, R. A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W.; Thomas, S. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. BMJ 2006, 332, 1430–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrcina, Z.; Woelfel, S.; Burcal, C. A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Core Stability Exercises in Patients with Non-Specific Low Back Pain. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2022, 17, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumitt, J.; Matheson, J.W.; Meira, E.P. Core stabilization exercise prescription, part 2: A systematic review of motor control and general (global) exercise rehabilitation approaches for patients with low back pain. Sports Health 2013, 5, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, C.S.; de Jesus, F.L.A.; Machado, M.B.; Ferreira, G.; Ayres, I.G.T.; de Aquino, L.M.; Fukuda, T.Y.; Gomes-Neto, M. Lower limb muscle strength in patients with low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2019, 19, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Amabile, A.H.; Bolte, J.H.; Richter, S.D. Atrophy of gluteus maximus among women with a history of chronic low back pain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.P.; Oliveira, D.; Fanasca, M.A.; Vechin, F.C. Shortening of hip flexor muscles and chronic low-back pain among resistance training practitioners: Applications of the modified Thomas test. Sport Sci. Health 2023, 19, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatefi, M.; Babakhani, F.; Ashrafizadeh, M. The effect of static stretching exercises on hip range of motion, pain, and disability in patients with non-specific low back pain. J. Exp. Orthop. 2021, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlaing, S.S.; Puntumetakul, R.; Wanpen, S.; Boucaut, R. Balance Control in Patients with Subacute Non-Specific Low Back Pain, with and without Lumbar Instability: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhe, A.; Fejer, R.; Walker, B. Is there a relationship between pain intensity and postural sway in patients with non-specific low back pain? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-Dulcina, K.; Armand, S.; Dominguez, D.E.; Genevay, S.; Vuillerme, N. Asymmetry of lumbar muscles fatigability with non-specific chronic low back pain patients. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Sal, A.; Alonso-Perez, J.L.; Sosa-Reina, M.D.; García-Noblejas-Fernández, J.A.; Balani-Balani, V.G.; Rossettini, G.; Villafañe, J.H. Effectiveness of Physical Activity in the Management of Nonspecific Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clael, S.; Campos, L.F.; Correia, K.L.; de Lucena, J.M.S.; Gentil, P.; Durigan, J.L.; Ribeiro, A.L.A.; Martins, W.R. Exercise interventions can improve muscle strength, endurance, and electrical activity of lumbar extensors in individuals with non-specific low back pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, K.; Heller, D.; Hazlewood, D.; Sharma, N.; Dos Santos, M. Is spinal mobilization effective for low back pain?: A systematic review. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigotsky, A.D.; Lehman, G.J.; Beardsley, C.; Contreras, B.; Chung, B.; Feser, E.H. The modified Thomas test is not a valid measure of hip extension unless pelvic tilt is controlled. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, A.; Močnik, R.; Titze, S.; Nakamura, M.; Tilp, M. The Influence of Stretching the Hip Flexor Muscles on Performance Parameters. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Frank, B.; Goto, S.; Blackburn, T.; Cates, S.; Clark, M.; Aguilar, A.; Fava, N.; Padua, D. Effect of Restricted Hip Flexor Muscle Length on Hip Extensor Muscle Activity and Lower Extremity Biomechanics in College-Aged Female Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 946–954. [Google Scholar]
- Sembrano, J.N.; Polly, D.W., Jr. How often is low back pain not coming from the back? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009, 34, E27–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, M.P.; Weisbach, P.C.; Glynn, P.E. The hips influence on low back pain: A distal link to a proximal problem. J. Sport Rehabil. 2009, 18, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, S.M.; San Juan, J.G.; Suprak, D.N.; Lyda, M.; Bies, A.J.; Boydston, C.R. Passive hip range of motion is reduced in active subjects with chronic low back pain compared to controls. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burns, S.A.; Mintken, P.E.; Austin, G.P.; Cleland, J. Short-term response of hip mobilizations and exercise in individuals with chronic low back pain: A case series. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2011, 19, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modrzewski, K.; Gagała, J. Deceptive low back pain and pseudoradicular signs in avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2004, 6, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, İ.; Yılmaz, M.; Kıvrak, A. Efficacy of autologous stem cell therapy in femoral head avascular necrosis: A comparative study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, F.; Azadinia, F.; Talebian, S.; Rasouli, O. Test-retest reliability of a load cell setup, Ito, and timed loaded standing tests for measuring muscle strength and endurance in older adults with and without hyperkyphosis. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2022, 58, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidstrand, J.; Horneij, E. Inter-rater reliability of three standardized functional tests in patients with low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, O.M.; Oakley, P.A.; Elabd, A.M. Prediction of Back Disability Using Clinical, Functional, and Biomechanical Variables in Adults with Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Karimi, H.; Gilani, S.A.; Hassan, D. Treatment of disability associated with chronic non-specific low back pain using core stabilization exercises in Pakistani population. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2019, 32, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juker, D.; McGill, S.; Kropf, P.; Steffen, T. Quantitative intramuscular myoelectric activity of lumbar portions of psoas and the abdominal wall during a wide variety of tasks. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, J.H.; Shapiro, R.; Pohl, M.B. Effects of a Hip Flexor Stretching Program on Running Kinematics in Individuals with Limited Passive Hip Extension. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 3338–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masset, D.F.; Piette, A.G.; Malchaire, J.B. Relation between functional characteristics of the trunk and the occurrence of low back pain. Associated risk factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998, 23, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henchoz, Y.; Kai-Lik So, A. Exercise and nonspecific low back pain: A literature review. Jt. Bone Spine 2008, 75, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhathami, K.; Alshehre, Y.; Brizzolara, K.; Weber, M.; Wang-Price, S. Effectiveness of Spinal Stabilization Exercises on Movement Performance in Adults with Chronic Low Back Pain. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2023, 18, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Ho, R.L.M.; Coombes, S.A. The effect of chronic low back pain on postural control during quiet standing: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Hänsel, F. Non-specific Low Back Pain and Postural Control During Quiet Standing-A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. An Approach to Examinations and Treatment of Lumbo-Pelvic-Hip Region; Churchill Livingstone: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, S.; Cassidy, S.; Peterson, B.; Spink, M.; Chuter, V. Gluteus medius muscle function in people with and without low back pain: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsufiany, M.B.; Lohman, E.B.; Daher, N.S.; Gang, G.R.; Shallan, A.I.; Jaber, H.M. Non-specific chronic low back pain and physical activity: A comparison of postural control and hip muscle isometric strength: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2020, 99, e18544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, M.G.; Ross, J.C.; McLean, I.P.; Porter, R.W. The natural history of trunk list, its associated disability and the influence of McKenzie management. Eur. Spine J. 1998, 7, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahn, S.E.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, B.H. Effects of Gluteal Muscle Strengthening Exercise-Based Core Stabilization Training on Pain and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain. Medicine 2024, 60, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brech, G.C.; Andrusaitis, S.F.; Vitale, G.F.; Greve, J.M. Correlation of disability and pain with postural balance among women with chronic low back pain. Clinics 2012, 67, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostelo, R.W.; Deyo, R.A.; Stratford, P.; Waddell, G.; Croft, P.; Von Korff, M.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C. Interpreting change scores for pain and functional status in low back pain: Towards international consensus regarding minimal important change. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008, 33, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.D.; Shin, D. Correlations Between Hip Extension Range of Motion, Hip Extension Asymmetry, and Compensatory Lumbar Movement in Patients with Nonspecific Chronic Low Back Pain. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e925080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Ambrose Lo, W.L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, C. The associations between lumbar proprioception and postural control during and after calf vibration in people with and without chronic low back pain. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1329437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, S.R.; Clark, R.D.; Webster, I.W. Postural stability and associated physiological factors in a population of aged persons. J. Gerontol. 1991, 46, M69–M76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, P.S.; Lee, D. Effects of Visual Input on Postural Stability and Compensatory Strategies in Adults with Chronic Low Back Pain. Vision 2025, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, İ.; Kıvrak, A. Lumbosacral fusion increases the risk of hip osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group with Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | Group without Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 8/13 | 9/12 | 1.0 |
| Age (years) a | 47.5 ± 4.5 | 45.6 ± 3.9 | 0.138 |
| Height (cm) a | 166.9 ± 9.2 | 168.5 ± 7.5 | 0.560 |
| Weight (kg) a | 61.3 ± 12.8 | 63.6 ± 9.7 | 0.527 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) a | 19.6 ± 2.4 | 20.1 ± 2.0 | 0.521 |
| Group with Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | Group Without Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | p-Value 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip joint mobility (right) | Pre-intervention | 18.0 ± 6.4 | 16.0 ± 6.9 | 0.187 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 2.0 (−1.4–6.9), 0.148 | |||
| Post-intervention | −5.9 ± 2.3 | −5.9 ± 1.5 | 0.943 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 0 (−1.2–1.2), 0 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Hip joint mobility (left) | Pre-intervention | 15.0 ± 7.9 | 14.0 ± 6.8 | 0.605 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −1.0 (−3.4–5.8), 0.067 | |||
| Post-intervention | −7.9 ± 3.4 | −6.6 ± 3.2 | 0.209 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −1.3 (−3.3–0.7), −0.193 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Back extensor endurance | Pre-intervention | 88.2 ± 10.2 | 85.2 ± 8.7 | 0.313 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 3.0 (−2.9–8.9), 0.156 | |||
| Post-intervention | 123.6 ± 15.3 | 120.3 ± 9.4 | 0.413 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 3.3 (−4.7–11.1), 0.128 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Postural stability (right) | Pre-intervention | 8.7 ± 1.5 | 9.5 ± 1.7 | 0.147 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −0.8 (−1.8–0.3), −0.242 | |||
| Post-intervention | 20.0 ± 1.6 | 16.1 ± 1.6 | <0.001 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 3.9 (1.9–4.9), 0.773 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Postural stability (left) | Pre-intervention | 9.0 ± 1.3 | 9.4 ± 1.5 | 0.305 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −0.4 (−1.3–0.4), −0.141 | |||
| Post-intervention | 18.2 ± 2.1 | 15.8 ± 3.6 | 0.01 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 2.4 (0.6–4.3), 0.377 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Group with Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | Group Without Additional Hip Exercises (n = 21) | p-Value 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | Pre-intervention | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 0.379 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 0.2 (−0.2–0.6), 0.141 | |||
| Post-intervention | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 0.657 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −0.1 (−0.5–0.3), −0.071 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| ODI | Pre-intervention | 43.0 ± 8.8 | 41.1 ± 8.4 | 0.488 |
| MD (95% CI), ES | 1.9 (−3.5–7.2), 0.109 | |||
| Post-intervention | 12.3 ± 2.8 | 18.4 ± 3.5 | <0.001 | |
| MD (95% CI), ES | −6.1 (from −8.0 to −4.1), −0.693 | |||
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Dependent Variables | Independent Variables | Standardized Coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | β | r2 | p-value | ||
| Hip joint mobility | VAS | 0.342 | 0.054 | 0.022 | 0.734 |
| ODI | 2.367 | 0.351 | 0.123 | 0.023 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leem, I.; Lee, G.B.; Wang, J.W.; Pyun, S.W.; Kum, C.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.-D. Impact of Hip Exercises on Postural Stability and Function in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101229
Leem I, Lee GB, Wang JW, Pyun SW, Kum C-J, Lee JH, Kim H-D. Impact of Hip Exercises on Postural Stability and Function in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(10):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeem, Inhwan, Gyu Bin Lee, Ji Won Wang, Sang Woo Pyun, Chang-Jun Kum, Jin Hyuck Lee, and Hyeong-Dong Kim. 2025. "Impact of Hip Exercises on Postural Stability and Function in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain" Diagnostics 15, no. 10: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101229
APA StyleLeem, I., Lee, G. B., Wang, J. W., Pyun, S. W., Kum, C.-J., Lee, J. H., & Kim, H.-D. (2025). Impact of Hip Exercises on Postural Stability and Function in Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain. Diagnostics, 15(10), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15101229







