Convolutional Neural Network–Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a hybrid architecture that allows for the integration of any CNN and ViT encoder within component blocks. Each component block is carefully designed to capture the low-range and long-range dependencies effectively.
- We introduce a gated attention control mechanism, which selectively emphasizes the important features through channel-, spatial-, and element-wise attention. This mechanism modulates and refines the feature representations by dynamically controlling the flow of relevant information.
- We present a multi-scale fusion module that captures single-level and multi-level features. This module uses an Inception-style design to combine fine-grained, medium-scale, and large-scale features across multiple branches, ensuring more comprehensive feature representation.
2. Related Work
2.1. Pulmonary Disease Detection Based on CNN Architecture
2.2. Pulmonary Disease Detection Based on Transformer Architecture
2.3. Gated Mechanisms
2.4. Attention Mechanisms
2.5. Graph-Based Hybrid Models
3. Methods
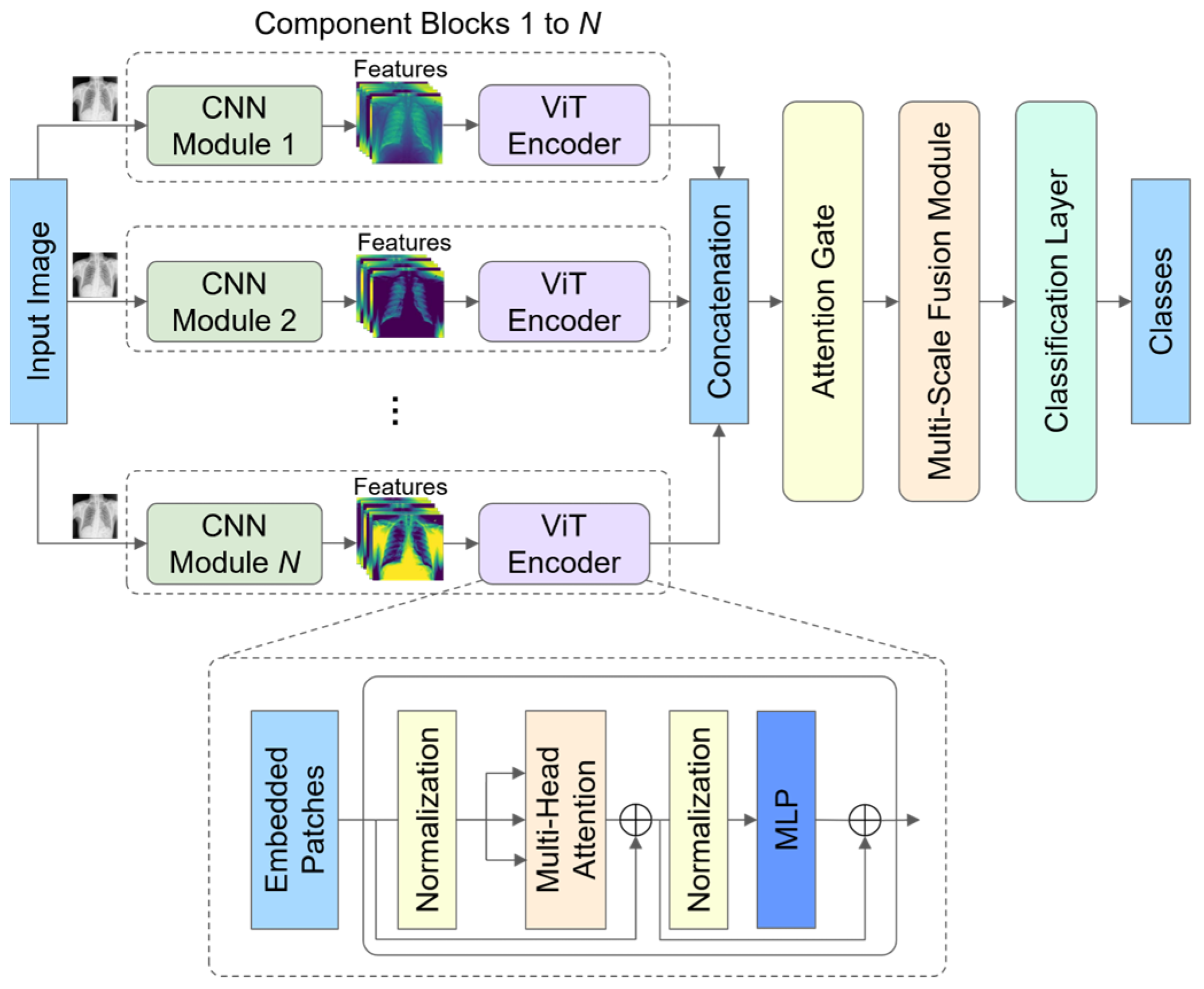
3.1. Model Architecture
3.2. Component Blocks
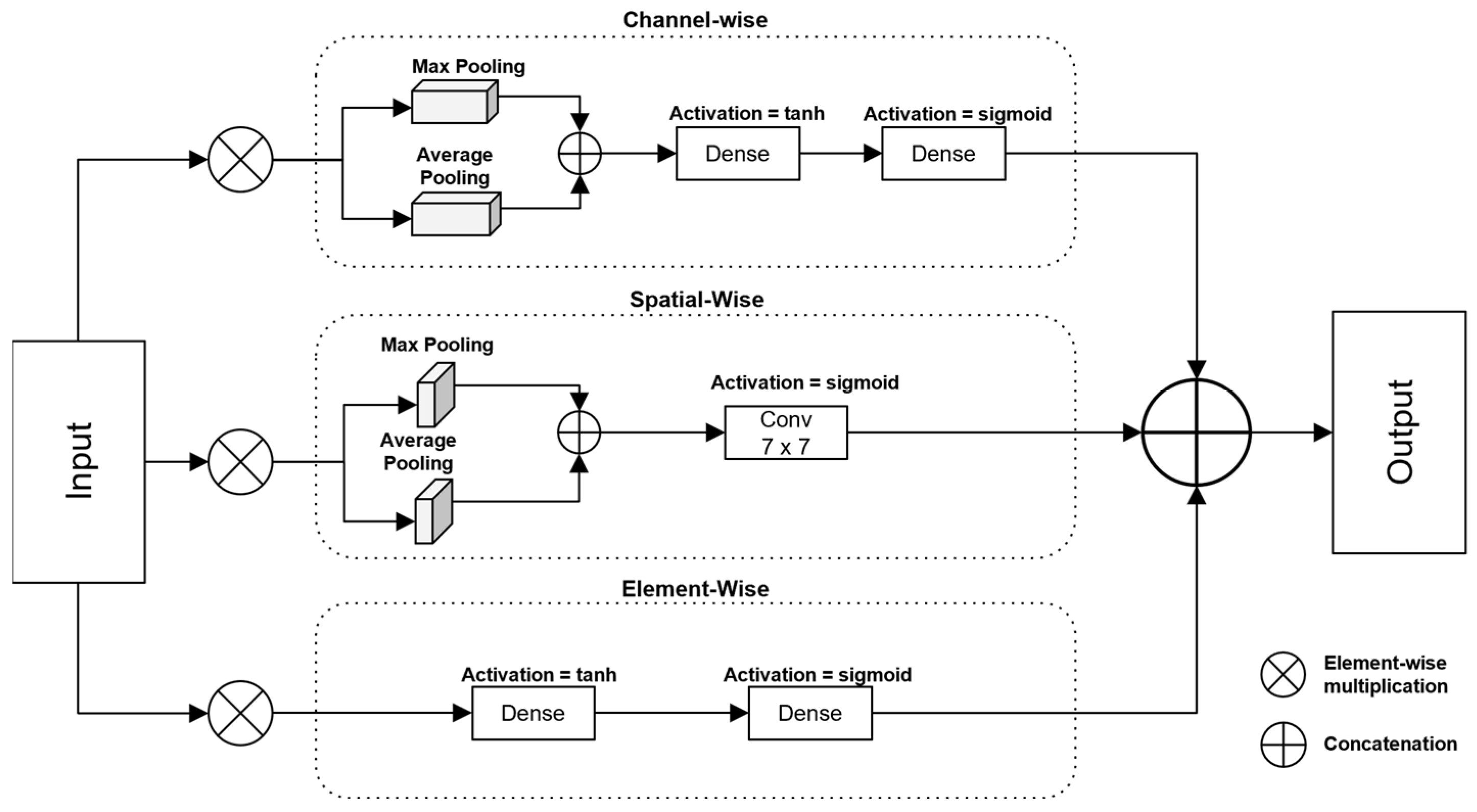
3.3. Gated Mechanism with Attention
3.3.1. Channel-Wise Attention
3.3.2. Element-Wise Attention
3.3.3. Spatial-Wise Attention
3.3.4. Combining Attention
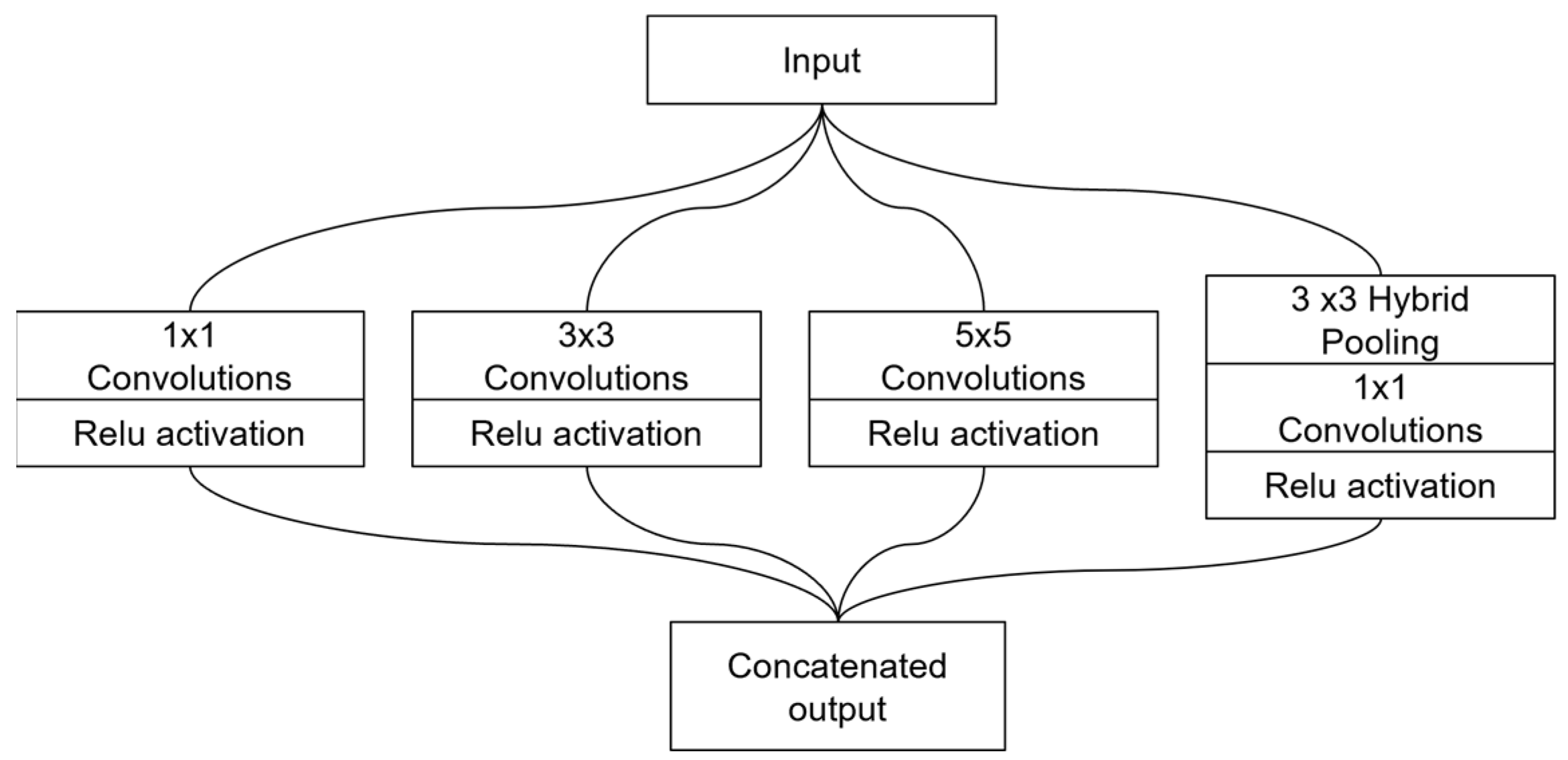
3.4. Multi-Scale Fusion Module
3.5. Classification Layer
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Dataset Description
- Normal class: the normal class was assembled from the various datasets mentioned above.
4.2. Experimental Parameters and Environment
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
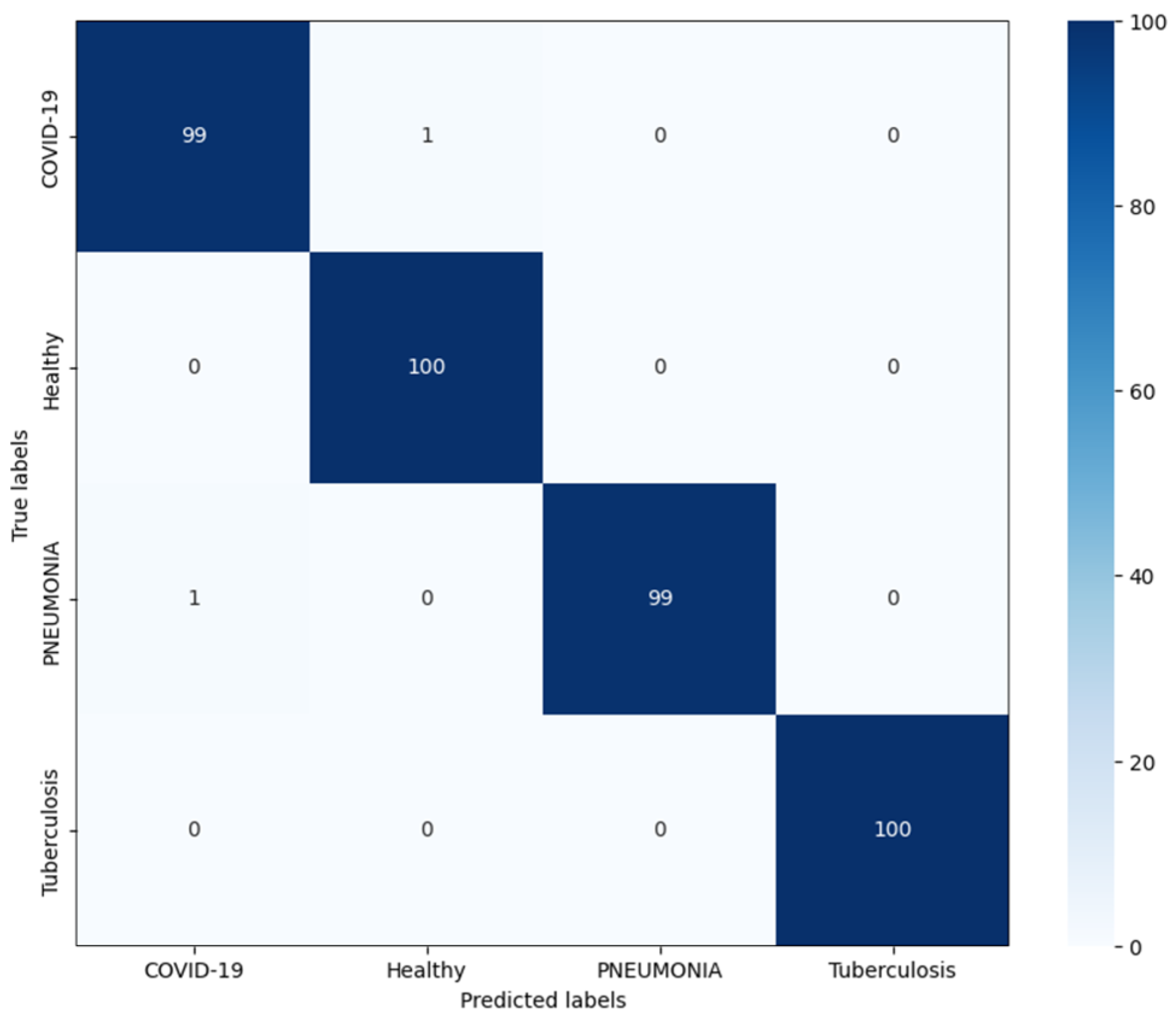
4.4. Classification Results of the Proposed Model
4.5. Ablation Studies
4.6. Comparison with Existing Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022; WHO Press, World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729 (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Showkatian, E.; Salehi, M.; Ghaffari, H.; Reiazi, R.; Sadighi, N. Deep learning-based automatic detection of tuberculosis disease in chest X-ray images. Pol. J. Radiol. 2022, 87, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Chest Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection: Summary of Current WHO Recommendations and Guidance on Programmatic Approaches; WHO Press, World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241511506 (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Acharya, V.; Dhiman, G.; Prakasha, K.; Bahadur, P.; Choraria, A.; M, S.; J, S.; Prabhu, S.; Chadaga, K.; Viriyasitavat, W.; et al. AI-assisted tuberculosis detection and classification from chest X-rays using a deep learning normalization-free network model. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2399428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotei, E.; Thirunavukarasu, R. Ensemble technique coupled with deep transfer learning framework for automatic detection of tuberculosis from chest X-ray radiographs. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshmrani, G.M.M.; Ni, Q.; Jiang, R.; Pervaiz, H.; Elshennawy, N.M. A deep learning architecture for multi-class lung diseases classification using chest X-ray (CXR) images. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 64, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, G. DS-TransUNET: Dual SWIN Transformer U-Net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Rauf, Z.; Sohail, A.; Rehman, A.; Asif, H.M.; Asif, A.; Farooq, U. A survey of the vision transformers and its CNN-transformer based variants. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09880. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Rauf, Z.; Khan, A.R.; Rathore, S.; Khan, S.H.; Shah, S.; Farooq, U.; Asif, H.; Asif, A.; Zahoora, U.; et al. A recent survey of vision transformers for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00634. [Google Scholar]
- Yunusa, H.; Qin, S.; Chukkol, A.H.A.; Yusuf, A.A.; Bello, I.; Lawan, A. Exploring the Synergies of Hybrid CNNs and ViTs Architectures for Computer Vision: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02941. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, M.; Hosseini, S. A deep convolutional neural network approach using medical image classification. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, S.; Antani, S. Modality-specific deep learning model ensembles toward improving TB detection in chest radiographs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27318–27326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayakumar, R.; Acharya, V.; Alazab, M. A multichannel EfficientNet deep learning-based stacking ensemble approach for lung disease detection using chest X-ray images. Clust. Comput. 2022, 26, 1181–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikaladevi, N.; Revathi, A. Deep learning framework for the robust prognosis of tuberculosis from radiography images based on fused linear triangular interpolation. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urooj, S.; Suchitra, S.; Krishnasamy, L.; Sharma, N.; Pathak, N. Stochastic learning-based artificial neural network model for an automatic tuberculosis detection system using chest X-ray images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103632–103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.; Redondo, R.P.D.; Dahou, A.; Elaziz, M.A.; Kayed, M. Pneumonia detection on chest X-ray images using ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, G. CCT: Lightweight Compact Convolutional Transformer for lung disease CT image classification. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1066999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Qin, Z.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Smahi, A.; Jackson, J.; Qadri, S.F.; Muaad, A.Y.; Monday, H.N.; Nneji, G.U. Automated lung-related pneumonia and COVID-19 detection based on novel feature extraction framework and vision transformer approaches using chest X-ray images. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Hong, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. A COVID-19 medical image classification algorithm based on transformer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Gulcehre, C.; Paine, T.; Hoffman, M.; Pascanu, R. Improving the gating mechanism of recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.09890. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, G.; Jin, Y.K.; Qi, G.; Yang, X.; Bai, L. Palmprint recognition based on gating mechanism and adaptive feature fusion. Front. Neurorobotics 2023, 17, 1203962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Han, X. Spatial and channel attention modulated network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) Workshops, Singapore, 20–23 May 2021; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Oza, P.; Hacihaliloglu, I.; Patel, V.M. Medical transformer: Gated axial-attention for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.01507. [Google Scholar]
- Matlock, M.K.; Datta, A.; Dang, N.L.; Jiang, K.; Swamidass, S.J. Deep learning long-range information in undirected graphs with wave networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Long, C.; Xu, W.; Xiao, C. Dual Graph Convolutional Networks with Transformer and Curriculum Learning for Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, China, 20–24 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, N.W.; Jia, N.Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Punn, N.S.; Agarwal, S. Inception U-Net architecture for semantic segmentation to identify nuclei in microscopy cell images. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 1551–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Hartley Spectral pooling for deep learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M. Rethinking computer-aided tuberculosis diagnosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2646–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, S.; Candemir, S.; Antani, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Lu, P.; Thoma, G.R. Two public chest X-ray datasets for computer-aided screening of pulmonary diseases. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2014, 4, 475–477. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Kadir, M.A.; Islam, K.R.; Islam, K.F.; Mazhar, R.; Hamid, T.; Islam, M.T.; Kashem, S.; Mahbub, Z.B.; et al. Reliable tuberculosis detection using chest X-ray with deep learning, segmentation and visualization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191586–191601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Chauhan, D.; Rout, C. Role of Gist and PHOG Features in computer-aided diagnosis of tuberculosis without segmentation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A Tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafai, W.; El-Samie, F.A. Extensive COVID-19 X-Ray and CT Chest Images Dataset (Version V3, Vol. 3) [Dataset]. Mendeley Data. 2020. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/8h65ywd2jr/3 (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Kermany, D.; Goldbaum, M.H.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.S.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Wu, C.; Carr, C.; Shih, G.; Dulkowski, J.; Chen, L.; Prevedello, L.; Kohli, M.; McDonald, M.; Kalpathy, P.; et al. RSNA pneumonia detection challenge [Dataset]. Kaggle. 2018. Available online: https://kaggle.com/competitions/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.06993. [Google Scholar]
- Margarat, G.S.; Hemalatha, G.; Mishra, A.; Shaheen, H.; Maheswari, K.; Tamijeselvan, S.; Kumar, U.P.; Banupriya, V.; Ferede, A.W. Early diagnosis of tuberculosis using deep learning approach for IoT-based healthcare applications. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 303, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. CutMix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.04899. [Google Scholar]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. RandAugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.13719. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why should I trust you?”: Explaining the predictions of any classifier. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.04938. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Barhoumi, Y.; Rasool, G. ScopeFormer: N-CNN-VIT Hybrid Model for Intracranial Hemorrhage Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.04575. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R.; Liang, J. Add-Vit: CNN-Transformer Hybrid Architecture for small data paradigm processing. Neural Process. Lett. 2024, 56, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Taj, I.; Usman, S.M.; Shah, S.N.H.; Imran, A.S.; Khalid, S. A hybrid approach of vision transformers and CNNs for detection of ulcerative colitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05709. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, B.Z.; Khabsa, M.; Fang, H.; Ma, H. Linformer: Self-attention with linear complexity. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04768. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, J.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; Tallec, C.; Richemond, P.H.; Buchatskaya, E.; Doersch, C.; Pires, B.A.; Guo, Z.D.; Azar, M.G.; et al. Bootstrap your own latent: A new approach to self-supervised Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07733. [Google Scholar]
- Choromanski, K.; Likhosherstov, V.; Dohan, D.; Song, X.; Gane, A.; Sarlos, T.; Hawkins, P.; Davis, J.; Mohiuddin, A.; Kaiser, L.; et al. Rethinking attention with performers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufuk, F.; Savaş, R. COVID-19 pneumonia: Lessons learned, challenges, and preparing for the future. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 28, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hyperparameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of ViT encoder layers | 6 |
| Hidden dimension | 32 |
| Multi-layer perceptron dimension | 64 |
| Number of multi-head self-attention blocks | 2 |
| Dropout rate | 0.5 |
| Patch size | 8 |
| Image channels | 3 |
| Image size | 224 × 224 |
| Epoch | 51 |
| Category | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 99.0% | 99.5% |
| Healthy | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100.0% | |
| Pneumonia | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 99.0% | |
| Tuberculosis | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100.0% |
| Data Augmentation | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
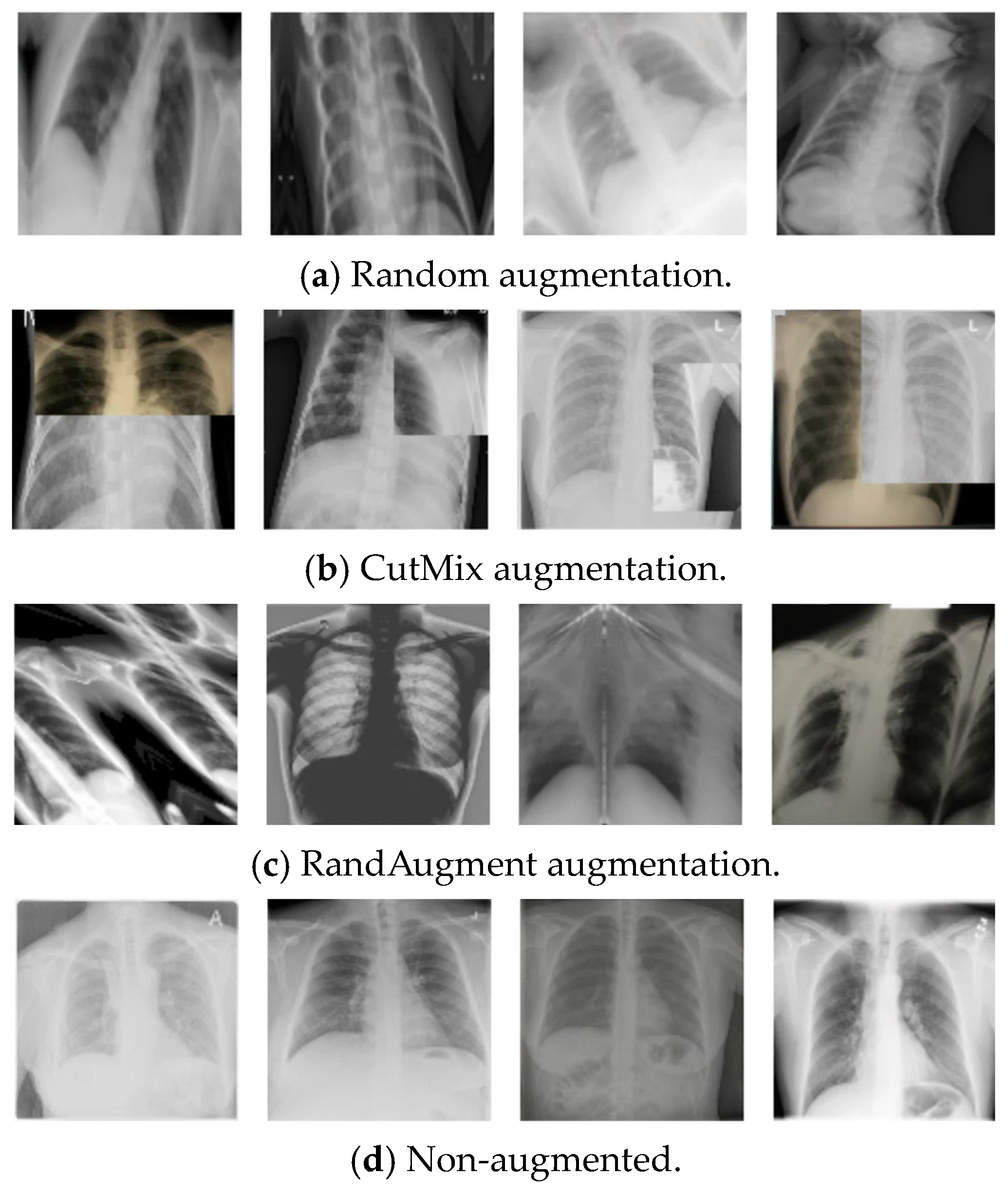
| CutMix [44] | 99.50% |
| RandAugment [45] | 99.50% |
| Without augmentation | 98.25% |
| Models | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
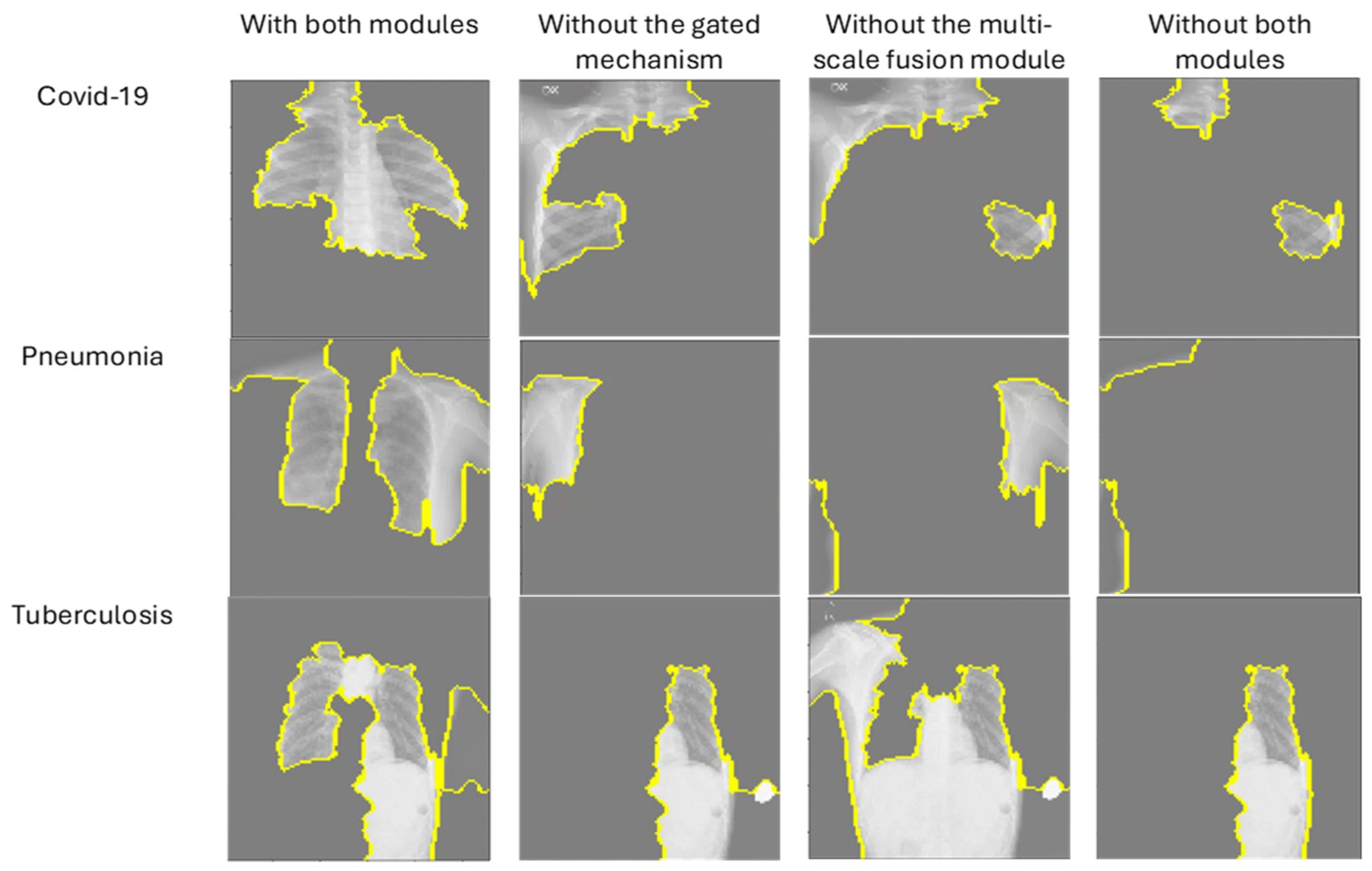
| Without the gated mechanism | 99.25% |
| Without the multi-scale fusion module | 99.00% |
| With both modules | 99.50% |
| Models | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 1 component block (CNN model: EfficientNetB3 [41]) | 96.50% |
| 2 component blocks (CNN models: EfficientNetB3 and DenseNet-121 [42]) | 99.50% |
| 3 component blocks (CNN models: EfficientNetB3, DenseNet-121, and MobileNet [47]) | 99.55% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chibuike, O.; Yang, X. Convolutional Neural Network–Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242790
Chibuike O, Yang X. Convolutional Neural Network–Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(24):2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242790
Chicago/Turabian StyleChibuike, Okpala, and Xiaopeng Yang. 2024. "Convolutional Neural Network–Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification" Diagnostics 14, no. 24: 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242790
APA StyleChibuike, O., & Yang, X. (2024). Convolutional Neural Network–Vision Transformer Architecture with Gated Control Mechanism and Multi-Scale Fusion for Enhanced Pulmonary Disease Classification. Diagnostics, 14(24), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242790






