Automated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation in Computed Tomography Using nnU-Net: Integration with TotalSegmentator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohorts
2.2. PET/CT Acquisition Parameters
2.3. Manual BAT Annotation Procedure
2.4. Automated BAT Segmentation Using nnU-Net
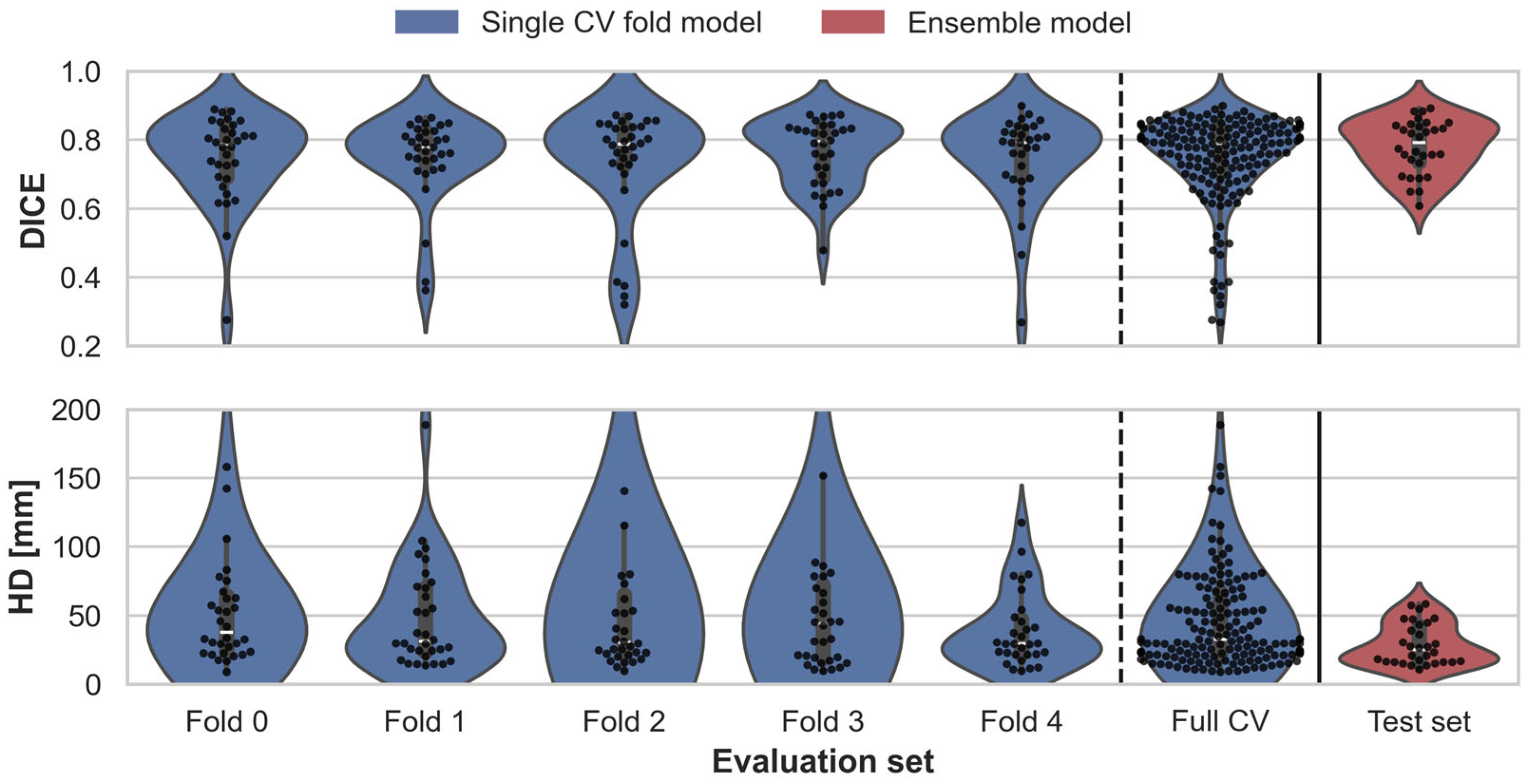
2.5. Evaluation
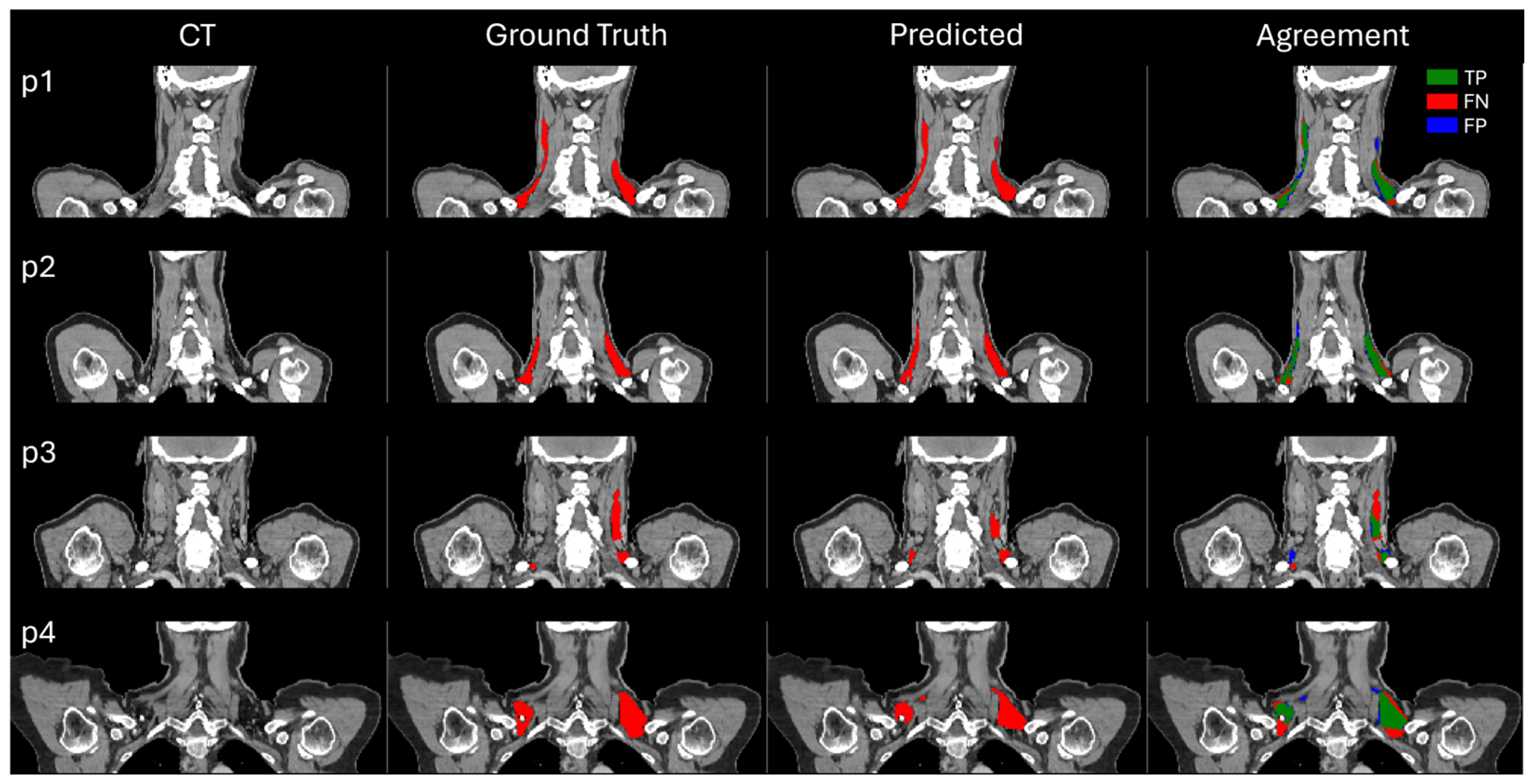
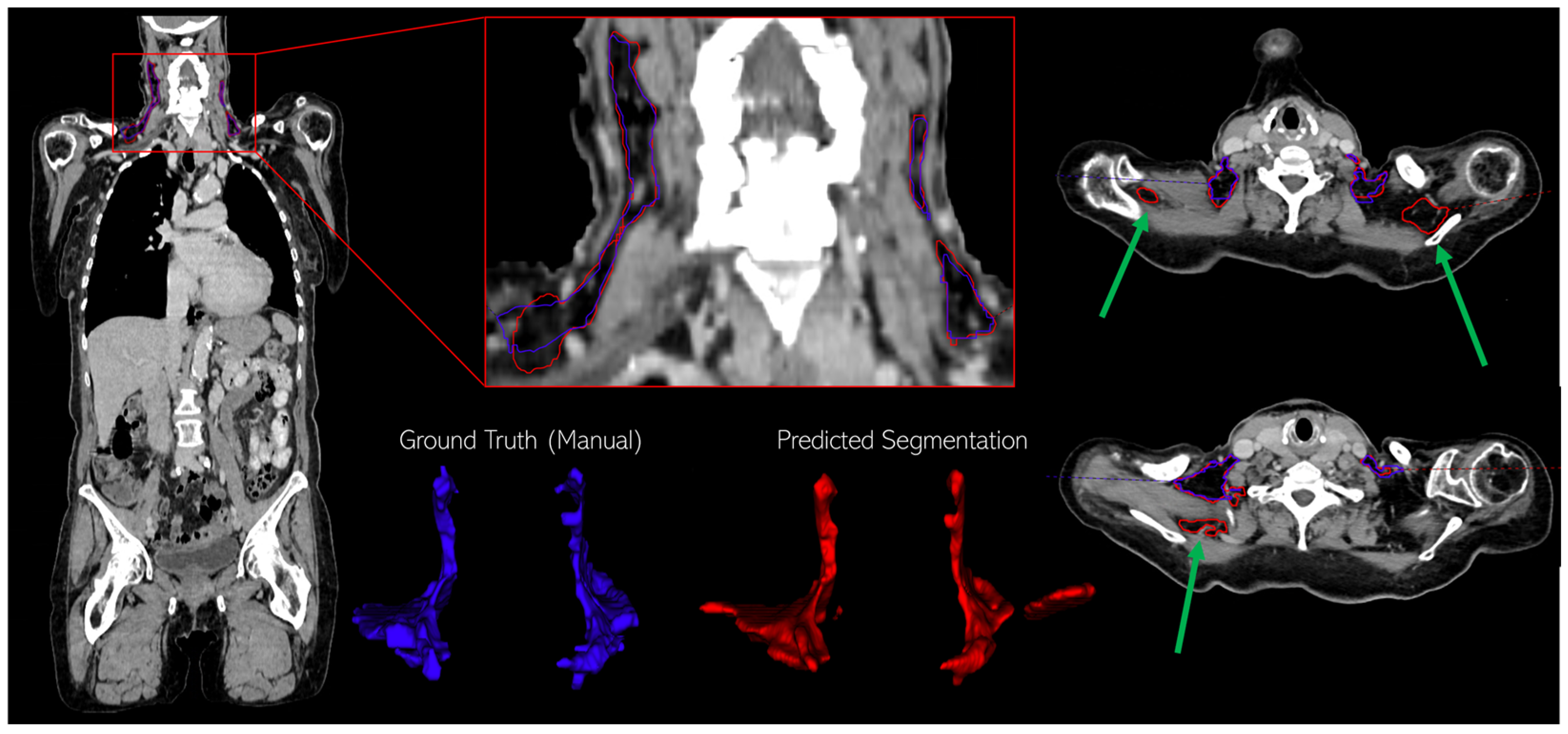
2.5.1. BAT Segmentation Quality
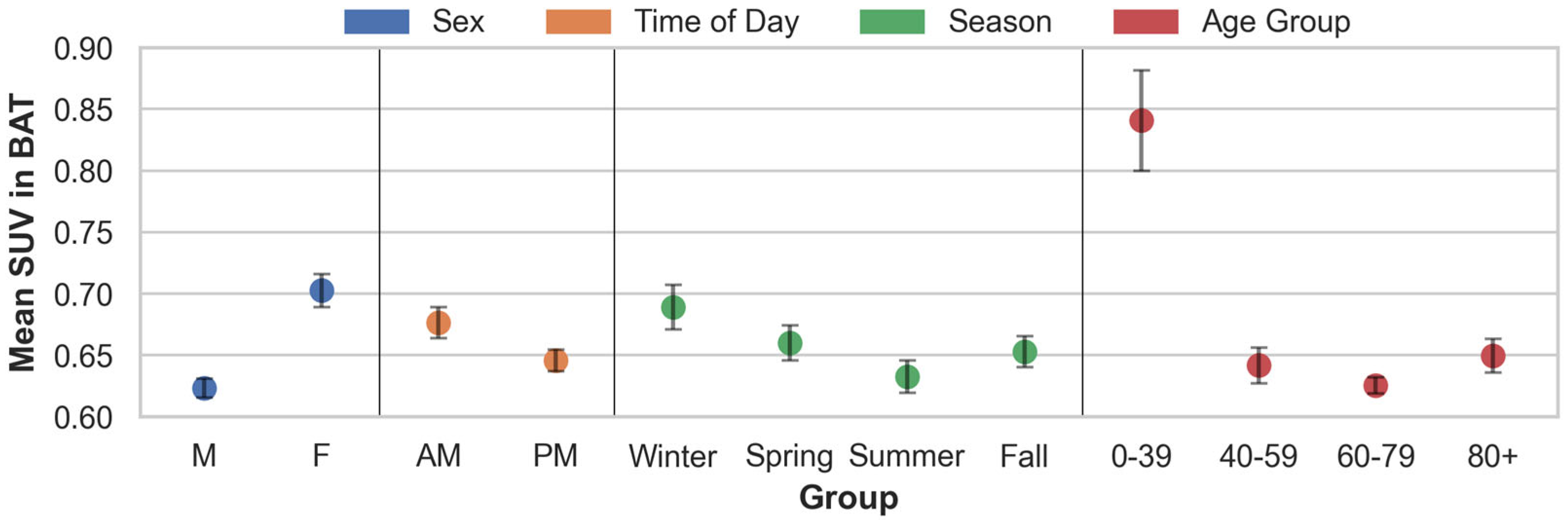
2.5.2. Descriptive Analyses
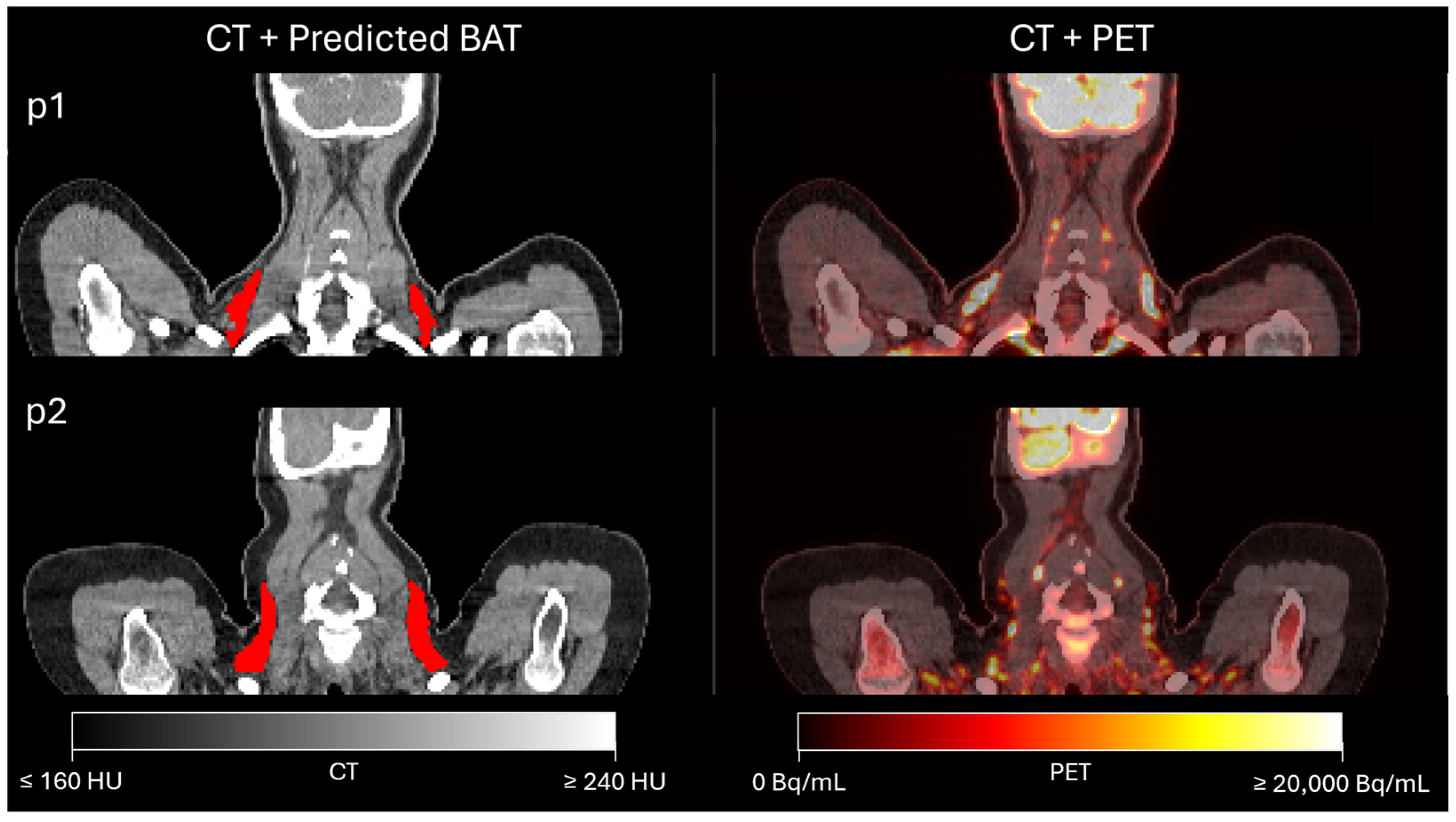
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of BAT Segmentation Performance
3.2. Findings from the Descriptive Analyses in Patients with Lymphoma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown Adipose Tissue: Function and Physiological Significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.; Seale, P. Brown and beige fat: Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulier, B.; Montfort, L.; Richelle, F.; Brichant, C. Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) causing unusual cervical and scapular uptake of 18F-FDG in a young patient with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2015, 99, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gunawardana, S.C. Therapeutic value of brown adipose tissue: Correcting metabolic disease through generating healthy fat. Adipocyte 2012, 1, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whitehead, A.; Krause, F.N.; Moran, A.; MacCannell, A.D.; Scragg, J.L.; McNally, B.D.; Boateng, E.; Murfitt, S.A.; Virtue, S.; Wright, J.; et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue regulate systemic metabolism through a metabolite interorgan signaling axis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lin, J.D. The brown fat secretome: Metabolic functions beyond thermogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ustione, A.; Wilkerson, E.M.; Balakrishnan, R.; Thurmond, D.C.; Goldfarb, D.; Piston, D.W. Insulin-Independent Regulation of Type 1 Diabetes via Brown Adipocyte-Secreted Proteins and the Novel Glucagon Regulator Nidogen-2. bioRxiv, 2024; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Chaudhari, A.J.; Ramirez, A.; Sen, F.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Sidossis, L.S.; Klein, S.; et al. The Role of Brown Adipose Tissue in Branched-chain Amino Acid Clearance in People. iScience 2024, 27, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Hu, Z.; Cui, L.; Zhao, M.; Su, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. βAR-mTOR-lipin1 pathway mediates PKA-RIIβ deficiency-induced adipose browning. Theranostics 2024, 14, 5316–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilder-Smith, A.J.; Yang, S.; Weikert, T.; Bremerich, J.; Haaf, P.; Segeroth, M.; Ebert, L.C.; Sauter, A.; Sexauer, R. Automated Detection, Segmentation, and Classification of Pericardial Effusions on Chest CT Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Crandall, J.; Kasal, K.; Wahl, R. A Comparison of Semi-Automated Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation Methods. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1400. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.Y.; Cypess, A.M.; Laughlin, M.R.; Haft, C.R.; Hu, H.H.; Bredella, M.A.; Enerbäck, S.; Kinahan, P.E.; Lichtenbelt, W.M.; Lin, F.I.; et al. Brown Adipose Reporting Criteria in Imaging STudies (BARCIST 1.0): Recommendations for Standardized FDG-PET/CT Experiments in Humans. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Tellez, B.; Nahon, K.J.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Abreu-Vieira, G.; Llamas-Elvira, J.M.; Van Velden, F.H.P.; Arias-Bouda, L.M.P.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Boon, M.R.; Ruiz, J.R.; et al. The impact of using BARCIST 1.0 criteria on quantification of BAT volume and activity in three independent cohorts of adults. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.C.; Turkington, T.G.; Wilson, J.M.; Wong, T.Z. A systematic review of the factors affecting accuracy of SUV measurements. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, E.; Strand, R.; Forslund, A.; Bergsten, P.; Weghuber, D.; Ahlström, H.; Kullberg, J. Automated segmentation of human cervical-supraclavicular adipose tissue in magnetic resonance images. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Xu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, B.; Bai, J.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Using Artificial Intelligence to Detect COVID-19 and Community-acquired Pneumonia Based on Pulmonary CT: Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy. Radiology 2020, 296, E65–E71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.F.P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-Net and its variants for medical image segmentation: Theory and applications. arXiv, 2020; arXiv:2011.01118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserthal, J.; Breit, H.-C.; Meyer, M.T.; Pradella, M.; Hinck, D.; Sauter, A.W.; Heye, T.; Boll, D.T.; Cyriac, J.; Yang, S.; et al. TotalSegmentator: Robust Segmentation of 104 Anatomic Structures in CT Images. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, e230024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeghiazaryan, V.; Voiculescu, I. Family of boundary overlap metrics for the evaluation of medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerig, G.; Jomier, M.; Chakos, M. Valmet: A new validation tool for assessing and improving 3D object segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2001, 2208, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Tang, C.; Cui, B.; Cui, B.; Somasundaram, A.; Somasundaram, A.; Raspe, J.; Raspe, J.; et al. Automated segmentation of the human supraclavicular fat depot via deep neural network in water-fat separated magnetic resonance images. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 4699–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Barrios, A.; Dirakvand, G.; Pervin, S. Human brown adipose tissue and metabolic health: Potential for therapeutic avenues. Cells 2021, 10, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, M.E.; Aldiss, P.; Pope, M.; Budge, H. Recent advances in our understanding of brown and beige adipose tissue: The good fat that keeps you healthy. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lidell, M.E.; Orava, J.; Heglind, M.; Westergren, R.; Niemi, T.; Taittonen, M.; Laine, J.; Savisto, N.-J.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Functional Brown Adipose Tissue in Healthy Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, N.C.; Grunewald, Z.I.; Gastecki, M.L.; Woodford, M.L.; Welly, R.J.; Clookey, S.L.; Ball, J.R.; Gaines, T.L.; Karasseva, N.G.; Kanaley, J.A.; et al. Deletion of UCP1 enhances ex vivo aortic vasomotor function in female but not male mice despite similar susceptibility to metabolic dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2017, 313, E402–E412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypess, A.M.; Lehman, S.; Williams, G.; Tal, I.; Rodman, D.; Goldfine, A.B.; Kuo, F.C.; Palmer, E.L.; Tseng, Y.H.; Doria, A.; et al. Identification and Importance of Brown Adipose Tissue in Adult Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Nonshivering thermogenesis and its adequate measurement in metabolic studies. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, Y. The emerging role of circadian rhythms in the development and function of thermogenic fat. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1175845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yong, I.T.H.; Thorn, N.; Ganatra, R.; Perkins, A.C.; Symonds, M.E. Brown adipose tissue and seasonal variation in humans. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Perspective: Does brown fat protect against diseases of aging? Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 9, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdvibulvech, C.; Li, Q.; Duffy, V.G. Empowering Zero-Shot Object Detection: A Human-in-the-Loop Strategy for Unveiling Unseen Realms in Visual Data. In Digital Human Modeling and Applications in Health, Safety, Ergonomics and Risk Management; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonoli, T.A.; Berger, L.K.; Indrakanti, A.K.; Vishwanathan, N.; Weiß, J.; Jung, M.; Berkarda, Z.; Rau, A.; Reisert, M.; Küstner, T.; et al. TotalSegmentator MRI: Sequence-Independent Segmentation of 59 Anatomical Structures in MR images. arXiv, 2024; arXiv:2405.19492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Cohort | Age [Years] | Weight [kg] | Height [m] | BMI | BAT Vol. [mL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train (n = 159) | |||||
| Men (n = 75 (47%)) | 15.3 | 14.4 | 0.08 | 4.7 | 66.3 |
| Women (n = 84 (53%)) | 16.0 | 16.2 | 0.06 | 5.4 | 72.1 |
| Test (n = 30) | |||||
| Men (n = 16 (53%)) | 20.3 | 11.7 | 0.07 | 3.7 | 47.9 |
| Women (n = 14 (47%)) | 20.2 | 21.6 | 0.06 | 6.8 | 66.7 |
| LymphBAT-7107 (n = 7107) | |||||
| Men (n = 4011 (56%)) | 16.2 | 15.8 | 0.07 | 4.5 | - |
| Women (n = 3096 (44%)) | 17.0 | 16.0 | 0.6 | 5.5 | - |
| Model | Evaluation Set | [mm] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single fold model | Validation Fold 0 (n = 32) | 0.022 | 0.025 | 13.0 |
| Validation Fold 1 (n = 32) | 0.021 | 0.024 | 6.6 | |
| Validation Fold 2 (n = 32) | 0.028 | 0.030 | 24.4 | |
| Validation Fold 3 (n = 32) | 0.017 | 0.021 | 20.6 | |
| Validation Fold 4 (n = 31) | 0.023 | 0.026 | 4.7 | |
| Combined Validation set (n = 159) | 0.010 | 0.011 | 7.2 | |
| Ensemble model | Test set (n = 30) | 0.014 | 0.019 | 2.7 |
| Grouping | # | Mean | SEM | Welch’s t-Test (p-Values) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | F | |||||
| M | 4011 | 0.623 | 0.004 | *** 1.47 × 10−23 | ||
| F | 3096 | 0.703 | 0.007 | – | ||
| Time of day | PM | |||||
| AM | 2884 | 0.676 | 0.006 | *** 9.44 × 10−5 | ||
| PM | 4223 | 0.645 | 0.004 | – | ||
| Season | Spring | Summer | Fall | |||
| Winter | 1734 | 0.689 | 0.009 | * 0.0132 | *** 8.54 × 10−7 | * 1.44 × 10−3 |
| Spring | 1740 | 0.660 | 0.007 | – | ** 5.93 × 10−3 | 0.4880 |
| Summer | 1896 | 0.633 | 0.007 | – | – | * 0.0270 |
| Fall | 1737 | 0.653 | 0.006 | – | – | – |
| Age group | 40–59 | 60–79 | 80+ | |||
| 0–39 | 876 | 0.841 | 0.021 | *** 7.08 × 10−19 | * 2.49 × 10−23 | *** 1.18 × 10−17 |
| 40–59 | 1570 | 0.642 | 0.007 | – | * 0.0448 | 0.4352 |
| 60–79 | 3938 | 0.625 | 0.003 | – | – | ** 2.20 × 10−3 |
| 80+ | 723 | 0.650 | 0.007 | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jørgensen, K.; Høi-Hansen, F.E.; Loos, R.J.F.; Hinge, C.; Andersen, F.L. Automated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation in Computed Tomography Using nnU-Net: Integration with TotalSegmentator. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242786
Jørgensen K, Høi-Hansen FE, Loos RJF, Hinge C, Andersen FL. Automated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation in Computed Tomography Using nnU-Net: Integration with TotalSegmentator. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(24):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242786
Chicago/Turabian StyleJørgensen, Kasper, Frederikke Engel Høi-Hansen, Ruth J. F. Loos, Christian Hinge, and Flemming Littrup Andersen. 2024. "Automated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation in Computed Tomography Using nnU-Net: Integration with TotalSegmentator" Diagnostics 14, no. 24: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242786
APA StyleJørgensen, K., Høi-Hansen, F. E., Loos, R. J. F., Hinge, C., & Andersen, F. L. (2024). Automated Supraclavicular Brown Adipose Tissue Segmentation in Computed Tomography Using nnU-Net: Integration with TotalSegmentator. Diagnostics, 14(24), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14242786






