No Correlation between PD-L1 and NIS Expression in Lymph Node Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
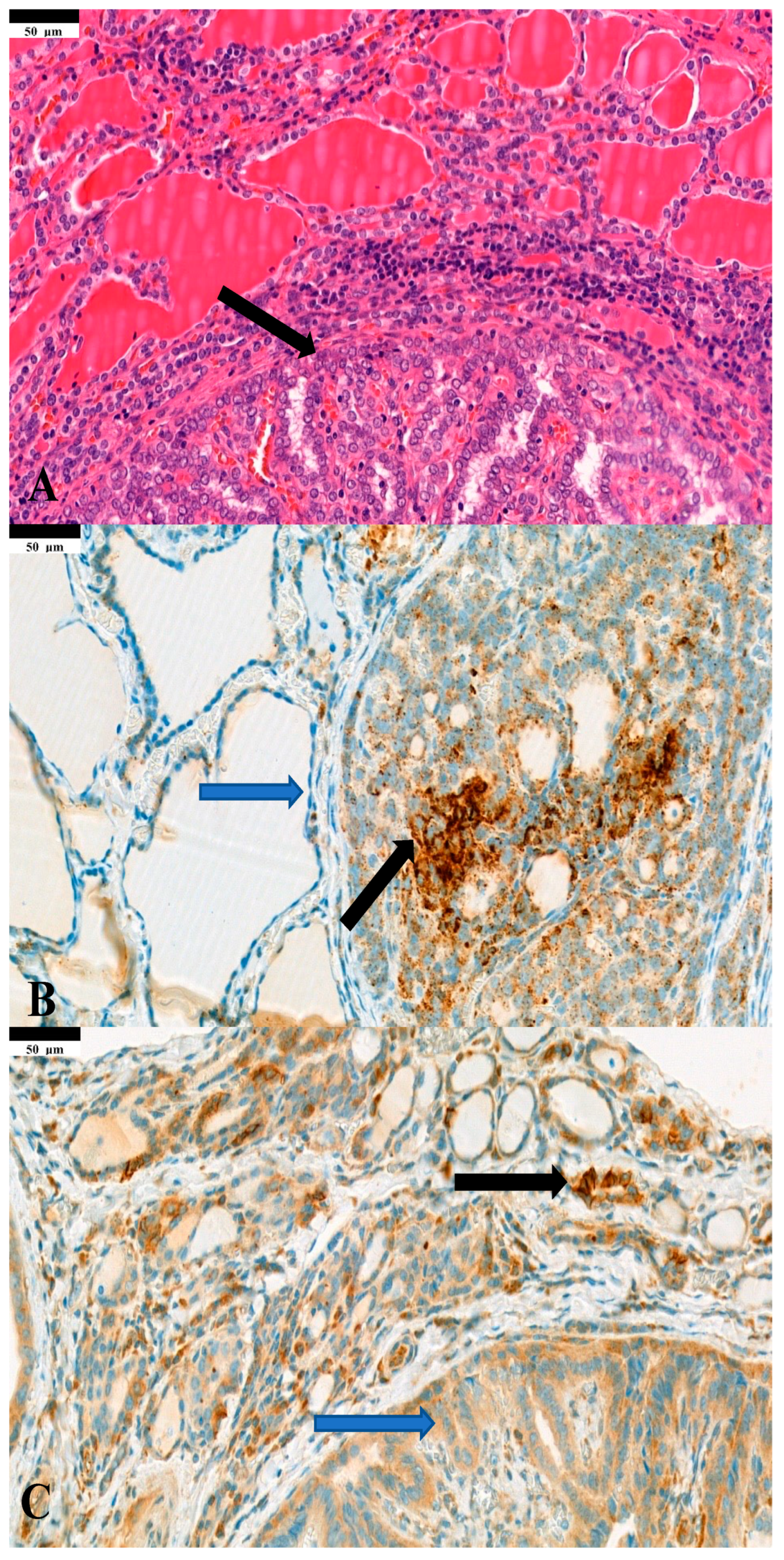
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Andréa, G.; Lassalle, S.; Guevara, N.; Mograbi, B.; Hofman, P. From biomarkers to therapeutic targets: The promise of PD-L1 in thyroid autoimmunity and cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1310–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagin, J.A.; Wells, S.A. Biologic and Clinical Perspectives on Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 75, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzman, S.P.; Sherman, S.I. Novel Drug Treatments of Progressive Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohán, O.; De la Vieja, A.; Paroder, V.; Riedel, C.; Artani, M.; Reed, M.; Ginter, C.S.; Carrasco, N. The sodium/iodide Symporter (NIS): Characterization, regulation, and medical significance. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 48–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Xu, J.; Cai, Y. Optical diagnostic imaging and therapy for thyroid cancer. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 26, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dohán, O.; Baloch, Z.; Bánrévi, Z.; Livolsi, V.; Carrasco, N. Rapid communication: Predominant intracellular overexpression of the Na+/I− symporter (NIS) in a large sampling of thyroid cancer cases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2697–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, M.; Gaweł, D.; Godlewska, M. Novel Inhibitor-Based Therapies for Thyroid Cancer—An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Huang, W. Molecular basis and targeted therapies for radioiodine refractory thyroid cancer. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 19, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Long, S.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, L.; Wang, S. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 964442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kornepati, A.V.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Curiel, T.J. Programmed death ligand 1 signals in cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, O.; Dai, G.; Riedel, C.; Ginter, C.S.; Paul, E.M.; Lebowitz, A.N.; Carrasco, N. Characterization of the thyroid Na+/I− symporter with an anti-COOH terminus antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 27, 5568–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadia, M.; Fookeerah, P.; Ali, S.; Shadbolt, B.; Greenaway, T.; Perampalam, S. PD-L1 expression in papillary thyroid cancer with and without lymphocytic thyroiditis: A cross sectional study. Pathology 2020, 52, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Veyhl, J.; Jessa, F.; Polyakova, O.; Alenzi, A.; MacMillan, C.; Ralhan, R.; Walfish, P.G. Programmed death-ligand 1 overexpression is a prognostic marker for aggressive papillary thyroid cancer and its variants. Oncotarget 2016, 31, 32318–32328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wapnir, I.L.; Van De Rijn, M.; Nowels, K.; Amenta, P.S.; Walton, K.; Montgomery, K.; Greco, R.S.; Dohán, O.; Carrasco, N. Immunohistochemical profile of the sodium/iodide symporter in thyroid, breast, and other carcinomas using high density tissue microarrays and conventional sections. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Deng, P.; Dai, W.; Wang, P.; Dong, Z.; Yang, C.; Tian, J.; Hu, T.; Yan, K. Association between programmed cell death ligand 1 expression and thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, 25315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, D.; Baraban, E.; Lisby, A.; Jalali-Farahani, S.; Zhang, P.; Livolsi, V. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Emerging from Hashimoto Thyroiditis Demonstrates Increased PD-L1 Expression, Which Persists with Metastasis. Endocr. Pathol. 2018, 29, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.L.; Marcello, M.A.; Ward, L.S. The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Niu, D.; Huang, X.; Jia, L.; Kang, Q.; Dou, F.; Ji, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-1 expression are correlated with distinctive clinicopathological features in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2017, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapanou, O.; Simeakis, G.; Vlassopoulou, B.; Alevizaki, M.; Saltiki, K. Advanced RAI-refractory thyroid cancer: An update on treatment perspectives. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2022, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | Mean (Min–Max) |
|---|---|
| PD-L1 (%) | 17.7 (0.0–90.0) |
| Range | 1.8 (1.0–3.0) |
| NIS total (%) | 18.7 (0.0–100.0) |
| NIS only citoplasmatic (%) | 17.2 (0.0–100.0) |
| NIS plasmamembrane (%) also present | 1.5 (0.0–30.0) |
| Clinicopathological Parameter | PD-L1 | NIS |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | NS | NS |
| Age | 0.0183 | NS |
| TNM stage | NS | NS |
| Tumor size | 0.0237 | NS |
| Multifocality | NS | NS |
| (Nr.) Number of metastatic lymph nodes | NS | NS |
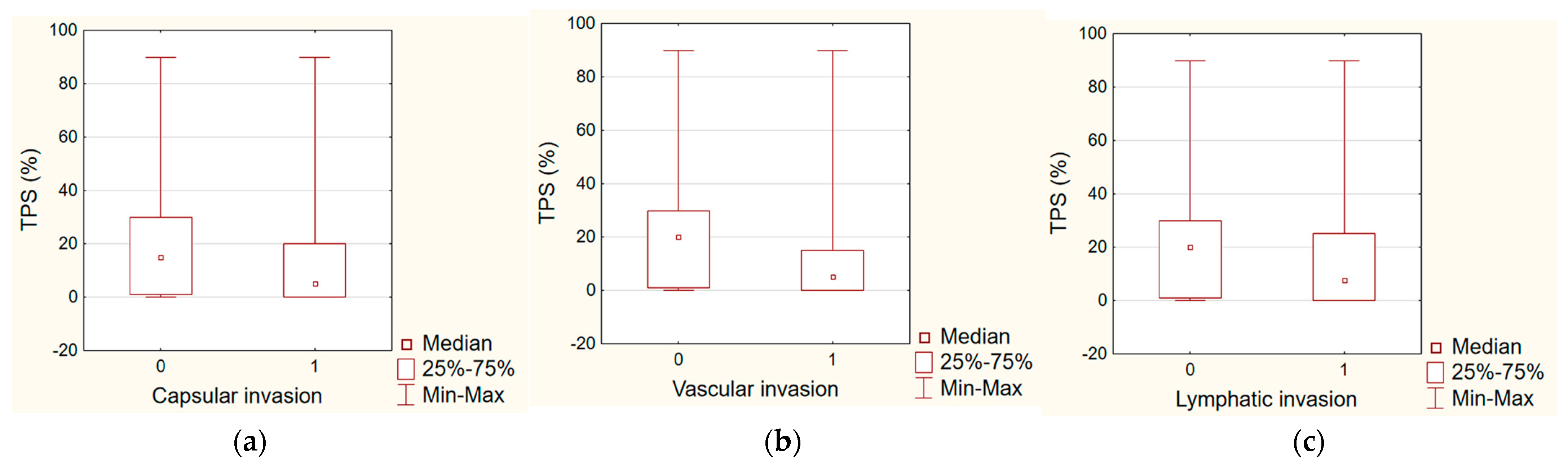
| Capsular invasion | NS | NS |
| Vascular invasion | 0.0165 | NS |
| Lymphatic invasion | NS | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernadett, L.; Alexandra, K.; Georgina, F.; Erika, T.; András, S.; Ilona, P.; Ferenc, O.; Orsolya, D. No Correlation between PD-L1 and NIS Expression in Lymph Node Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171858
Bernadett L, Alexandra K, Georgina F, Erika T, András S, Ilona P, Ferenc O, Orsolya D. No Correlation between PD-L1 and NIS Expression in Lymph Node Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(17):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171858
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernadett, Lévay, Kiss Alexandra, Fröhlich Georgina, Tóth Erika, Slezák András, Péter Ilona, Oberna Ferenc, and Dohán Orsolya. 2024. "No Correlation between PD-L1 and NIS Expression in Lymph Node Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma" Diagnostics 14, no. 17: 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171858
APA StyleBernadett, L., Alexandra, K., Georgina, F., Erika, T., András, S., Ilona, P., Ferenc, O., & Orsolya, D. (2024). No Correlation between PD-L1 and NIS Expression in Lymph Node Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 14(17), 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14171858






