Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views
Abstract
1. Introduction
Goals of This Investigation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurements
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Ethics Approval
3. Results
Limitations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olaisen, S.; Smistad, E.; Espeland, T.; Hu, J.; Pasdeloup, D.; Østvik, A.; Aakhus, S.; Rösner, A.; Malm, S.; Stylidis, M.; et al. Automatic measurements of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction by artificial intelligence: Clinical validation in real time and large databases. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 25, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukas, M.; Burns, D. Basic Ultrasound Physics. In Essential Ultrasound Anatomy; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, P.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Pu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Deng, Y.; et al. Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Assessment and Grading: Multiview Versus Single View. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2023, 36, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asch, F.M.; Mor-Avi, V.; Rubenson, D.; Goldstein, S.; Saric, M.; Mikati, I.; Surette, S.; Chaudhry, A.; Poilvert, N.; Hong, H.; et al. Deep learning–based automated echocardiographic quantification of left ventricular ejection fraction: A point-of-care solution. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, e012293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, T.; Farina, J.M.; Chao, C.-J.; Ayoub, C.; Jeong, J.; Patel, B.N.; Banerjee, I.; Arsanjani, R. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sveric, K.M.; Ulbrich, S.; Dindane, Z.; Winkler, A.; Botan, R.; Mierke, J.; Trausch, A.; Heidrich, F.; Linke, A. Improved assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction using artificial intelligence in echocardiography: A comparative analysis with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 394, 131383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldaas, O.M.; Igata, S.; Raisinghani, A.; Kraushaar, M.; DeMaria, A.N. Accuracy of left ventricular ejection fraction determined by automated analysis of handheld echocardiograms: A comparison of experienced and novice examiners. Echocardiography 2019, 36, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor-Avi, V.; Khandheria, B.; Klempfner, R.; Cotella, J.I.; Moreno, M.; Ignatowski, D.; Guile, B.; Hayes, H.J.; Hipke, K.; Kaminski, A.; et al. Real-Time Artificial Intelligence–Based Guidance of Echocardiographic Imaging by Novices: Image Quality and Suitability for Diagnostic Interpretation and Quantitative Analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e015569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; DeCara, J.M. Point-of-care ultrasound. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadon, Z.; Steinmetz, Y.; Levi, N.; Orlev, A.; Belman, D.; Butnaru, A.; Carasso, S.; Glikson, M.; Alpert, E.A.; Gottlieb, S. Artificial Intelligence-Powered Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Analysis Using the LVivoEF Tool for COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.; Bae, R.; Hong, H.; Thomas, Y.; Surette, S.; Cadieu, C.; Chaudhry, A.; Martin, R.P.; McCarthy, P.M.; Rubenson, D.S.; et al. Utility of a deep-learning algorithm to guide novices to acquire echocardiograms for limited diagnostic use. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, E.; Herling, A.; Mazuz, M.; Tsaban, G.; Gat, T.; Kobal, S.; Fuchs, L. Artificial Intelligence (AI) versus POCUS Expert: A Validation Study of Three Automatic AI-Based, Real-Time, Hemodynamic Echocardiographic Assessment Tools. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Kosaka, Y.; Haga, A.; Sata, M.; Kusunose, K. Artificial intelligence-assisted interpretation of systolic function by echocardiogram. Open Heart 2023, 10, e002287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth-Hansen, A.K.; Magelssen, M.I.; Andersen, G.N.; Graven, T.; Kleinau, J.O.; Landstad, B.; Løvstakken, L.; Skjetne, K.; Mjølstad, O.C.; Dalen, H. Real-time automatic quantification of left ventricular function by hand-held ultrasound devices in patients with suspected heart failure: A feasibility study of a diagnostic test with data from general practitioners, nurses and cardiologists. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e063793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Bartko, P.; Geller, W.; Dannenberg, V.; König, A.; Binder, C.; Goliasch, G.; Hengstenberg, C.; Binder, T. A machine learning algorithm supports ultrasound-naive novices in the acquisition of diagnostic echocardiography loops and provides accurate estimation of LVEF. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 37, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motazedian, P.; Marbach, J.A.; Prosperi-Porta, G.; Parlow, S.; Di Santo, P.; Abdel-Razek, O.; Jung, R.; Bradford, W.B.; Tsang, M.; Hyon, M.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound with artificial intelligence-assisted assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’driscoll, J.M.; Hawkes, W.; Beqiri, A.; Mumith, A.; Parker, A.; Upton, R.; McCourt, A.; Woodward, W.; Dockerill, C.; Sabharwal, N.; et al. Left ventricular assessment with artificial intelligence increases the diagnostic accuracy of stress echocardiography. Eur. Heart J. Open 2022, 2, oeac059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, S.-L.; Sachpekidis, V.; Kantartzi, V.; Styliadis, I.; Nihoyannopoulos, P. Clinical validation of an artificial intelligence-assisted algorithm for automated quantification of left ventricular ejection fraction in real time by a novel handheld ultrasound device. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2023, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, N.J.; Schnobrich, D.; Mathews, B.K.; Tierney, D.M.; Jensen, T.P.; Dancel, R.; Cho, J.; Dversdal, R.K.; Mints, G.; Bhagra, A.; et al. Point-of-Care Ultrasound for Hospitalists: A Position Statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 14, E1–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Goudie, A.; Chiorean, L.; Cui, X.W.; Gilja, O.H.; Dong, Y.; Abramowicz, J.S.; Vinayak, S.; Westerway, S.C.; Nolsøe, C.P.; et al. Point of Care Ultrasound: A WFUMB Position Paper. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.A.; Holden, S.; Vela, J.; Rathleff, M.S.; Jensen, M.B. Point-of-Care Ultrasound in General Practice: A Systematic Review. Ann. Fam. Med. 2019, 17, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunose, K.; Haga, A.; Abe, T.; Sata, M. Utilization of artificial intelligence in echocardiography. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Nicolosi, G.L.; Granato, A.; Bonanomi, A.; Rigamonti, E.; Lombardo, M. Influence of chest wall conformation on reproducibility of main echocardiographic indices of left ventricular systolic function. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2024, 72, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharqi, M.; Ismavel, V.A.; Arnold, L.; Choudhury, S.S.; Solomi, V.C.; Rao, S.; Nath, T.; Rani, A.; Goel, I.; Kakoty, S.D.; et al. Focused Cardiac Ultrasound to Guide the Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Pregnant Women in India. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2022, 35, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satılmış Siliv, N.; Yamanoglu, A.; Pınar, P.; Yamanoglu, N.G.C.; Torlak, F.; Parlak, I. Estimation of cardiac systolic function based on mitral valve movements: An accurate bedside tool for emergency physicians in dyspneic patients. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.; Ionescu, A. The pocket echocardiograph: A useful new tool? Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2008, 9, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, D.G.; Ku, B.S.; Carr, B.G.; Everett, W.W.; Okusanya, O.; Horan, A.; Gracias, V.H.; Dean, A.J. Directed bedside transthoracic echocardiography: Preferred cardiac window for left ventricular ejection fraction estimation in critically ill patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2007, 25, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, E.S.; Di Achille, P.; Kopparapu, K.; Andrews, C.T.; Singh, P.; Reeder, C.; Al-Alusi, M.; Khurshid, S.; Haimovich, J.S.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Deep learning–enabled assessment of left heart structure and function predicts cardiovascular outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 1936–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskings, E.M.; Eissa, M.; Alllard, R.V.; MirGhassemi, A.; McFaul, C.M.; Miller, E.C. Point-of-care ultrasound use in emergencies: What every anaesthetist should know. Anaesthesia 2023, 78, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, R.; Robert-Halabi, M.; Pichette, M.; Vinet, A.; Sauvé, C.; Dilorenzo, M.; Le, V.; Piette, E.; Brunet, M.; Bédard, W.; et al. Left ventricular ejection fraction using a simplified wall motion score based on mid-parasternal short axis and apical four-chamber views for non-cardiologists. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

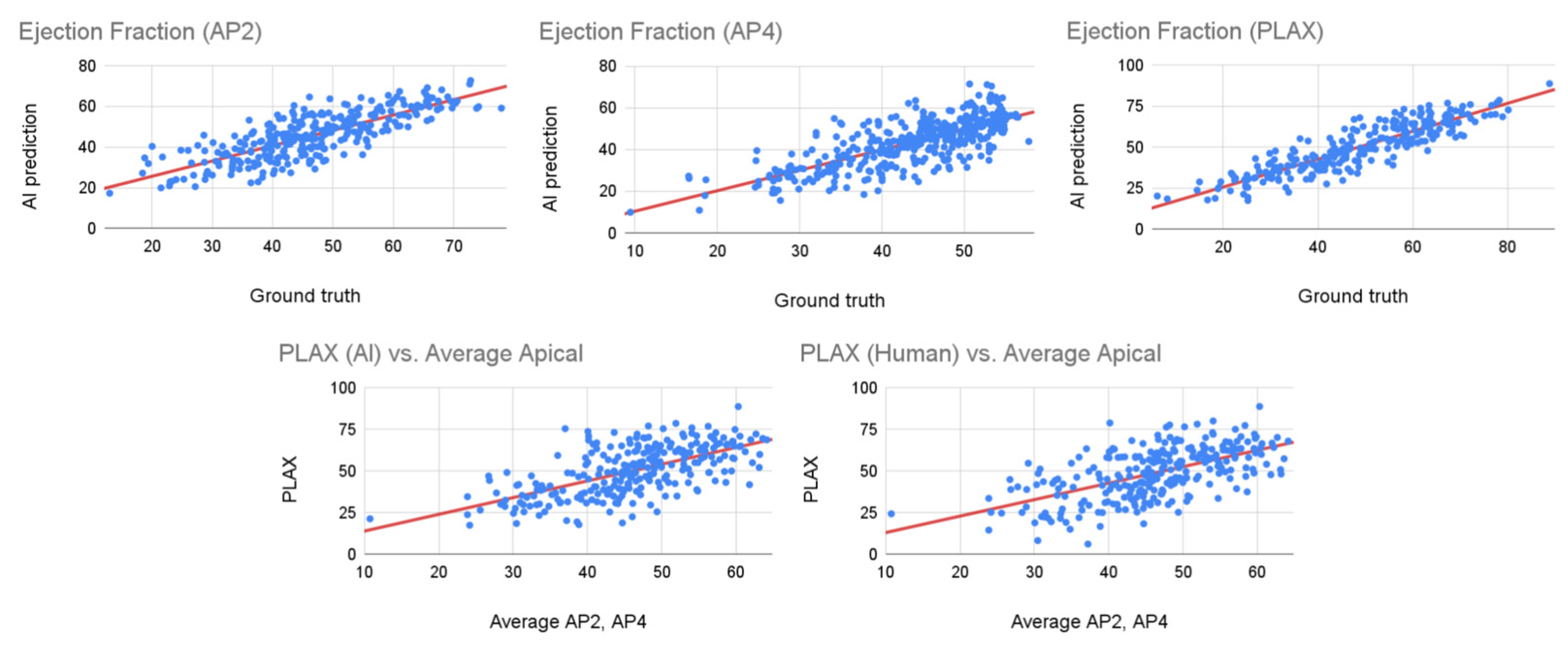

| Apical 2 | Apical 4 | PLAX | AP vs. PLAX (Expert) | AP vs. PLAX (AI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 7.58 | 7.45 | 7.29 | 12.57 | 12.16 |
| Pearson’s R | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.62 |
| Bias | −0.88 | −0.15 | 1.43 | 2.66 | 4.09 |
| SD | 7.54 | 7.45 | 7.16 | 12.31 | 11.47 |
| Min | −18.77 | −19.81 | −16.80 | −31.1 | −25.90 |
| IQR: 25% | −6.25 | −4.25 | −3.40 | −6.56 | −3.44 |
| IQR: 50% | −0.98 | −0.01 | 1.14 | 3.31 | 4.34 |
| IQR: 75% | 3.84 | 3.69 | 5.84 | 11.54 | 10.81 |
| Max | 20.31 | 20.76 | 19.36 | 38.75 | 38.47 |
| Apical 2 | Apical 4 | PLAX | AP vs. PLAX (Expert) | AP vs. PLAX (AI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 172 | 237 | 124 | 119 | 117 |
| TN | 81 | 89 | 120 | 66 | 68 |
| FP | 27 | 33 | 10 | 19 | 17 |
| FN | 24 | 48 | 14 | 64 | 66 |
| Accuracy | 83% | 80% | 91% | 69% | 69% |
| Sensitivity | 88% | 83% | 90% | 65% | 64% |
| Specificity | 75% | 73% | 92% | 78% | 80% |
| PPV | 86% | 88% | 93% | 86% | 87% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vega, R.; Kwok, C.; Rakkunedeth Hareendranathan, A.; Nagdev, A.; Jaremko, J.L. Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161719
Vega R, Kwok C, Rakkunedeth Hareendranathan A, Nagdev A, Jaremko JL. Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(16):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161719
Chicago/Turabian StyleVega, Roberto, Cherise Kwok, Abhilash Rakkunedeth Hareendranathan, Arun Nagdev, and Jacob L. Jaremko. 2024. "Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views" Diagnostics 14, no. 16: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161719
APA StyleVega, R., Kwok, C., Rakkunedeth Hareendranathan, A., Nagdev, A., & Jaremko, J. L. (2024). Assessment of an Artificial Intelligence Tool for Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Echocardiograms from Apical and Parasternal Long-Axis Views. Diagnostics, 14(16), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14161719





