Sample Collection and Processing in Volatile Organic Compound Analysis for Gastrointestinal Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Volatile Organic Compounds as Biomarkers
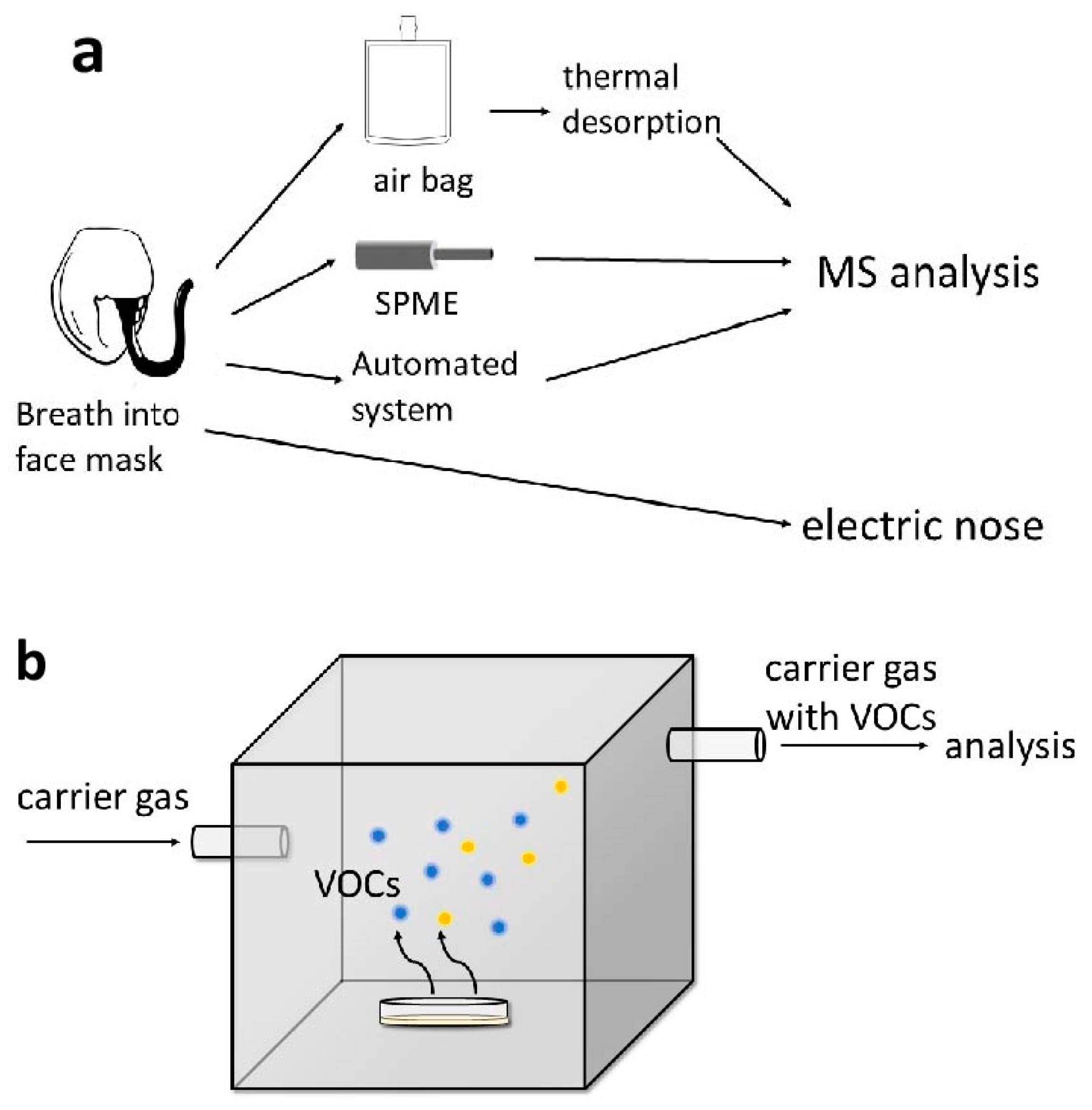
3. Breath
4. Urine
5. Feces
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.A.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.C.; Nilsson, M.; Grabsch, H.I.; van Grieken, N.C.; Lordick, F. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2020, 396, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanth, P.; Inadomi, J.M. Screening and prevention of colorectal cancer. BMJ 2021, 374, n1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretthauer, M.; Wieszczy, P.; Løberg, M.; Kaminski, M.F.; Werner, T.F.; Helsingen, L.M.; Mori, Y.; Holme, Ø.; Adami, H.-O.; Kalager, M. Estimated Lifetime Gained with Cancer Screening Tests: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecere, S.; Ciuffini, C.; Chiappetta, M.F.; Petruzziello, L.; Papparella, L.G.; Spada, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Barbaro, F. Increasing the accuracy of colorectal cancer screening. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2023, 23, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrift, A.P.; Wenker, T.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Global burden of gastric cancer: Epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabe, K.; Inoue, K.; Kamada, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, M.; Haruma, K. Endoscopic screening for gastric cancer in Japan: Current status and future perspectives. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Tao, J.; Li, J.; Tao, S. Volatile organic compounds analysis as a potential novel screening tool for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, N.K.; de Meij, T.G.; Oort, F.A.; Ben Larbi, I.; Mulder, C.J.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; van der Schee, M.P. The scent of colorectal cancer: Detection by volatile organic compound analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabińska, N.; Flynn, C.; Ratcliffe, N.; Belluomo, I.; Myridakis, A.; Gould, O.; Fois, M.; Smart, A.; Devine, T.; Costello, B.L. A literature survey of all volatiles from healthy human breath and bodily fluids: The human volatilome. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, P.; Lian, A.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Chi, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Luo, S.; et al. Blood volatile compounds as biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezmale, L.; Leja, M.; Lescinska, A.M.; Pčolkins, A.; Kononova, E.; Bogdanova, I.; Polaka, I.; Stonans, I.; Kirsners, A.; Ager, C.; et al. Identification of Volatile Markers of Colorectal Cancer from Tumor Tissues Using Volatilomic Approach. Molecules 2023, 28, 5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochalski, P.; Leja, M.; Gasenko, E.; Skapars, R.; Santare, D.; Sivins, A.; Aronsson, D.E.; Ager, C.; Jaeschke, C.; Shani, G.; et al. Ex vivo emission of volatile organic compounds from gastric cancer and non-cancerous tissue. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vietro, N.; Aresta, A.; Rotelli, M.T.; Zambonin, C.; Lippolis, C.; Picciariello, A.; Altomare, D.F. Relationship between cancer tissue derived and exhaled volatile organic compound from colorectal cancer patients. Preliminary results. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 180, 113055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.; Rispoli, G.; Anania, G.; Zonta, G.; Malagù, C. Chemoresistive Nanosensors Employed to Detect Blood Tumor Markers in Patients Affected by Colorectal Cancer in a One-Year Follow Up. Cancers 2023, 15, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, N.; Georgiou Delisle, T.; Chen, M.; Benton, S.; Abulafi, M. Faecal immunochemical test is superior to symptoms in predicting pathology in patients with suspected colorectal cancer symptoms referred on a 2WW pathway: A diagnostic accuracy study. Gut 2021, 70, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.; Wassie, M.M.; Winter, J.M.; Lathlean, T.J.; Young, G.P.; Symonds, E.L. Progress in the field of noninvasive diagnostics for colorectal cancer: A systematic review for the accuracy of blood-based biomarkers for detection of advanced pre-cancerous lesions. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 23, 1233–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, A.; Arasaradnam, R. Colorectal cancer diagnostic biomarkers: Beyond faecal haemoglobin. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 66, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, M.; Loree, J.M.; Kasi, P.M.; Parikh, A.R. Using Circulating Tumor DNA in Colorectal Cancer: Current and Evolving Practices. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Lahouel, K.; Lo, S.N.; Wang, Y.; Kosmider, S.; Wong, R.; Shapiro, J.; Lee, M.; Harris, S.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis Guiding Adjuvant Therapy in Stage II Colon Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moding, E.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Diehn, M. Detecting Liquid Remnants of Solid Tumors: Circulating Tumor DNA Minimal Residual Disease. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2968–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lena, M.; Porcelli, F.; Altomare, D.F. Volatile organic compounds as new biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A review. Color. Dis. 2016, 18, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markar, S.R.; Chin, S.T.; Romano, A.; Wiggins, T.; Antonowicz, S.; Paraskeva, P.; Ziprin, P.; Darzi, A.; Hanna, G.B. Breath Volatile Organic Compound Profiling of Colorectal Cancer Using Selected Ion Flow-tube Mass Spectrometry. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenhuis, E.G.M.; Schoenaker, I.J.H.; de Groot, J.W.B.; Fiebrich, H.B.; de Graaf, J.C.; Brohet, R.M.; van Dijk, J.D.; van Westreenen, H.L.; Siersema, P.D.; de Vos tot Nederveen Cappel, W.H. Feasibility of volatile organic compound in breath analysis in the follow-up of colorectal cancer: A pilot study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škapars, R.; Gašenko, E.; Broza, Y.Y.; Sīviņš, A.; Poļaka, I.; Bogdanova, I.; Pčolkins, A.; Veliks, V.; Folkmanis, V.; Lesčinska, A.; et al. Breath Volatile Organic Compounds in Surveillance of Gastric Cancer Patients following Radical Surgical Management. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miekisch, W.; Kischkel, S.; Sawacki, A.; Liebau, T.; Mieth, M.; Schubert, J.K. Impact of sampling procedures on the results of breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononova, E.; Mežmale, L.; Poļaka, I.; Veliks, V.; Anarkulova, L.; Vilkoite, I.; Tolmanis, I.; Ļeščinska, A.M.; Stonāns, I.; Pčolkins, A.; et al. Breath Fingerprint of Colorectal Cancer Patients Based on the Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ke, C.; Wang, X.; Chi, C.; Guo, L.; Luo, S.; Guo, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, E. Noninvasive detection of colorectal cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal, H.; Leja, M.; Funka, K.; Lasina, I.; Skapars, R.; Sivins, A.; Ancans, G.; Kikuste, I.; Vanags, A.; Tolmanis, I.; et al. Breath testing as potential colorectal cancer screening tool. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xiaoan, F.; Xu, K.; He, H.; Jiang, N. A stability study of carbonyl compounds in Tedlar bags by a fabricated MEMS microreactor approach. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depalma, N.; Di Lena, M.; Porcelli, F.; Travaglio, E.; Longobardi, F.; Demarinis Loiotile, A.; Tedesco, G.; De Gennaro, G.; Altomare, D.F. Detection of colorectal polyps by exhaled VOCs. Preliminary data. Tech. Coloproctol. 2014, 18, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, M.; Pistillo, S.; Porcelli, F.; Giuratrabocchetta, S.; Travaglio, E.; Salvemini, I.; Di Gennaro, R.; Trizio, L.; Rinaldi, M.; De Gennaro, G.; et al. Colorectal cancer screening by breath analysis: A specific pattern of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can discriminate between patients and health. Tech. Coloproctol. 2012, 16, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezi, A.; Picciariello, A.; Fan, X.; Sharma, R.; Zang, W.; Vincenti, L.; Altomare, D.F. Colorectal cancer diagnosis by a portable breath analyzer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2023, 66, e370–e371. [Google Scholar]
- Weggler, B.A.; Gruber, B.; Teehan, P.; Jaramillo, R.; Dorman, F.L. Chapter 5—Inlets and sampling. In Separation Science and Technology; Snow, N.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 2020; Volume 12, pp. 141–203. [Google Scholar]
- Altomare, D.F.; Di Lena, M.; Porcelli, F.; Trizio, L.; Travaglio, E.; Tutino, M.; Dragonieri, S.; Memeo, V.; de Gennaro, G. Exhaled volatile organic compounds identify patients with colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Chi, C.; Liu, D.; Guo, L.; Li, E.; Wang, C. Volatile organic metabolites identify patients with gastric carcinoma, gastric ulcer, or gastritis and control patients. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, D.F.; Picciariello, A.; Rotelli, M.T.; De Fazio, M.; Aresta, A.; Zambonin, C.G.; Vincenti, L.; Trerotoli, P.; De Vietro, N. Chemical signature of colorectal cancer: Case–control study for profiling the breath print. BJS Open 2020, 4, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodfield, G.; Belluomo, I.; Laponogov, I.; Veselkov, K.; Lin, G.; Myridakis, A.; Ayrton, O.; Španěl, P.; Vidal-Diez, A.; Romano, A.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of a Noninvasive Breath Test for Colorectal Cancer: COBRA1 Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1447–1449.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.T.; Romano, A.; Doran, S.L.F.; Hanna, G.B. Cross-platform mass spectrometry annotation in breathomics of oesophageal-gastric cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Huang, J.; Abbassi-Ghadi, N.; MacKenzie, H.A.; Veselkov, K.A.; Hoare, J.M.; Lovat, L.B.; Spanel, P.; Smith, D.; Hanna, G.B. Mass spectrometric analysis of exhaled breath for the identification of volatile organic compound biomarkers in esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markar, S.R.; Wiggins, T.; Antonowicz, S.; Chin, S.T.; Romano, A.; Nikolic, K.; Evans, B.; Cunningham, D.; Mughal, M.; Lagergren, J.; et al. Assessment of a noninvasive exhaled breath test for the diagnosis of oesophagogastric cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Atkins, G.; Acevedo-Moreno, L.A.; Grove, D.; Dweik, R.A.; Tonelli, A.R.; Brown, J.M.; Allende, D.S.; Aucejo, F.; Rotroff, D.M. Breath Metabolomics Provides an Accurate and Noninvasive Approach for Screening Cirrhosis, Primary, and Secondary Liver Tumors. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.J.; Seo, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Song, K.Y.; Park, C.H.; Lee, H.H. Advanced Diagnostic Technology of Volatile Organic Compounds Real Time analysis Analysis From Exhaled Breath of Gastric Cancer Patients Using Proton-Transfer-Reaction Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 560591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Che, X.; Su, H.; Mai, Z.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Exhaled breath analysis using on-line preconcentration mass spectrometry for gastric cancer diagnosis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, F.; Lv, Y.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, B. Volatolomics analysis of exhaled breath and gastric-endoluminal gas for distinguishing early upper gastrointestinal cancer from benign. J. Breath Res. 2023, 17, 036004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amal, H.; Leja, M.; Funka, K.; Skapars, R.; Sivins, A.; Ancans, G.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Kikuste, I.; Lasina, I.; Haick, H. Detection of precancerous gastric lesions and gastric cancer through exhaled breath. Gut 2016, 65, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Acevedo, C.M.; Jaimes-Mogollón, A.L.; Gualdrón-Guerrero, O.E.; Welearegay, T.G.; Martinez-Marín, J.D.; Caceres-Tarazona, J.M.; Sánchez- Acevedo, Z.C.; Beleño-Saenz, K.J.; Cindemir, U.; österlund, L.; et al. Exhaled breath analysis for gastric cancer diagnosis in Colombian patients. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28805–28817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharra, A.; Broza, Y.Y.; Yu, G.; Mao, W.; Shen, D.; Deng, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; et al. Exhaled breath diagnostics of lung and gastric cancers in China using nanosensors. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Cai, Y.; Yi, Y.; Li, K.; Ren, X.; Jiang, D.; Ge, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Noninvasive Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer Based on Breath Analysis with a Tubular Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensor. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poļaka, I.; Mežmale, L.; Anarkulova, L.; Kononova, E.; Vilkoite, I.; Veliks, V.; Ļeščinska, A.M.; Stonāns, I.; Pčolkins, A.; Tolmanis, I.; et al. The Detection of Colorectal Cancer through Machine Learning-Based Breath Sensor Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Keulen, K.E.; Jansen, M.E.; Schrauwen, R.W.M.; Kolkman, J.J.; Siersema, P.D. Volatile organic compounds in breath can serve as a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker for the detection of advanced adenomas and colorectal cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermans, V.N.E.; Li, Z.; Jongen, A.C.H.M.; Wu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ji, J.; Bouvy, N.D. Pilot Study: Detection of Gastric Cancer From Exhaled Air Analyzed With an Electronic Nose in Chinese Patients. Surg. Innov. 2018, 25, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziel, J.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Air sampling and analysis of volatile organic compounds with solid phase microextraction. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, G.; Ye, N.; Kou, X.; Zhu, F.; Shen, J.; Ouyang, G. Solid-phase microextraction: An appealing alternative for the determination of endogenous substances—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gilio, A.; Palmisani, J.; Ventrella, G.; Facchini, L.; Catino, A.; Varesano, N.; Pizzutilo, P.; Galetta, D.; Borelli, M.; Barbieri, P.; et al. Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling. Molecules 2020, 25, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, D.F.; Picciariello, A.; De Vietro, N.; Aresta, A.M.; Rotelli, M.; Trerotoli, P.; Vincenti, L.; DeFazio, M.; Zambonin, C. A new non-invasive method for colorectal cancer detection: The breath biopsy. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2020, 63, e451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciariello, A.; De Vietro, N.; Aresta, A.M.; Rotelli, M.T.; Lopinto, M.; Vincenti, L.; Iambrenghi, O.C.; Trerotoli, P.; Altomare, D.F. Breath biopsy: A non-invasive method for screening and early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Color. Dis. 2019, 21, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Picciariello, A.; Zang, W.; Sharma, R.; Dezi, A.; Vincenti, L.; Fan, X.; Altomare, D.F. Rapid breath analysis for colorectal cancer detection using an automated portable gas chromatography device. Color. Dis. 2022, 24, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcillo, A.; Baca Cabrera, J.C.; Widdig, A.; Birkemeyer, C. A comparison between mobile and stationary gas chromatography–mass spectrometry devices for analysis of complex volatile profiles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzak, T.; Wojnowski, W.; Piotrowicz, G.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Sample preparation and recent trends in volatolomics for diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Doran, S.; Belluomo, I.; Hanna, G.B. High-Throughput Breath Volatile Organic Compound Analysis Using Thermal Desorption Proton Transfer Reaction Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10204–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.E.; Fehervari, M.; Boshier, P.R.; Chin, S.T.; Lin, G.P.; Romano, A.; Kumar, S.; Hanna, G.B. Mass-Spectrometry Analysis of Mixed-Breath, Isolated-Bronchial-Breath, and Gastric-Endoluminal-Air Volatile Fatty Acids in Esophagogastric Cancer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3740–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Escarpa, A. Nanomaterials meet surface-enhanced Raman scattering towards enhanced clinical diagnosis: A review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehada, N.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Pariente, E.S.; Brönstrup, G.; Christiansen, S.; Johnson, D.W.; Leja, M.; Davies, M.P.; Liran, O.; et al. Silicon Nanowire Sensors Enable Diagnosis of Patients via Exhaled Breath. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7047–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhleh, M.K.; Amal, H.; Jeries, R.; Broza, Y.Y.; Aboud, M.; Gharra, A.; Ivgi, H.; Khatib, S.; Badarneh, S.; Har-Shai, L.; et al. Diagnosis and Classification of 17 Diseases from 1404 Subjects via Pattern Analysis of Exhaled Molecules. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanevelt, J.; Schoenaker, I.J.H.; Brohet, R.M.; Schrauwen, R.W.M.; Baas, F.J.N.; Tanis, P.J.; van Westreenen, H.L.; de Vos tot Nederveen Cappel, W.H. Alteration of the Exhaled Volatile Organic Compound Pattern in Colorectal Cancer Patients after Intentional Curative Surgery—A Prospective Pilot Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljevs, E.; Polaka, I.; Lauka, L.; Zvaigzne, L.; Ozola, A.; Jaeschke, C.; Leja, M.; Haick, H. Food ingestion influence on Sniffphone E-Nose Device breath profile. Helicobacter 2018, 23, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepers, M.; Al-Difaie, Z.; Brandts, L.; Peeters, A.; van Grinsven, B.; Bouvy, N.D. Diagnostic Performance of Electronic Noses in Cancer Diagnoses Using Exhaled Breath: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2219372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Liere, E.; van Dijk, L.J.; Bosch, S.; Vermeulen, L.; Heymans, M.W.; Burchell, G.L.; de Meij, T.G.J.; Ramsoekh, D.; de Boer, N.K.H. Urinary volatile organic compounds for colorectal cancer screening: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 186, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, J.A.; van der Schee, M.P.; Edge, A.S.L.; Boyle, B.; Savage, R.S.; Arasaradnam, R.P. The application of FAIMS gas analysis in medical diagnostics. Analyst 2015, 140, 6775–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaradnam, R.P.; McFarlane, M.J.; Ryan-Fisher, C.; Westenbrink, E.; Hodges, P.; Thomas, M.G.; Chambers, S.; O’Connell, N.; Bailey, C.; Harmston, C.; et al. Detection of colorectal cancer (CRC) by urinary volatile organic compound analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozdiak, E.; Wicaksono, A.N.; Covington, J.A.; Arasaradnam, R.P. Colorectal cancer and adenoma screening using urinary volatile organic compound (VOC) detection: Early results from a single-centre bowel screening population (UK BCSP). Tech. Coloproctology 2019, 23, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widlak, M.M.; Neal, M.; Daulton, E.; Thomas, C.L.; Tomkins, C.; Singh, B.; Harmston, C.; Wicaksono, A.; Evans, C.; Smith, S.; et al. Risk stratification of symptomatic patients suspected of colorectal cancer using faecal and urinary markers. Color. Dis. 2018, 20, O335–O342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulind, C.E.; Gould, O.; Costello, B.L.; Allison, J.; White, P.; Ewings, P.; Wicaksono, A.N.; Curtis, N.J.; Pullyblank, A.; Jayne, D.; et al. Urinary Volatile Organic Compound Testing in Fast-Track Patients with Suspected Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, M.; Millard, A.; Hall, H.; Savage, R.; Constantinidou, C.; Arasaradnam, R.; Nwokolo, C. Urinary volatile organic compounds and faecal microbiome profiles in colorectal cancer. Color. Dis. 2019, 21, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.; Greenwood, R.; Lewis, S.; Corfe, B.; Sarkar, S.; Rooney, P.; Probert, C. The use of volatile organic compounds emitted from stool as a biomarker for colonic neoplasia. Gut 2016, 65, A28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratiu, I.A.; Mametov, R.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B. Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor (µ-CTE) as a new sampling system for VOCs emitted by feces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śmiełowska, M.; Ligor, T.; Kupczyk, W.; Szeliga, J.; Jackowski, M.; Buszewski, B. Screening for volatile biomarkers of colorectal cancer by analyzing breath and fecal samples using thermal desorption combined with GC-MS (TD-GC-MS). J. Breath Res. 2023, 17, 047102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alustiza, M.; Ripoll, L.; Canals, A.; Murcia, O.; Martínez-Roca, A.; García-Heredia, A.; Giner-Calabuig, M.; Jover, R.; Vidal, L. A novel non-invasive colorectal cancer diagnostic method: Volatile organic compounds as biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 542, 117273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa dos Reis, L.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Graphene oxide/Fe3O4 as sorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography to determine 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meij, T.G.; Larbi, I.B.; Van Der Schee, M.P.; Lentferink, Y.E.; Paff, T.; Terhaar Sive Droste, J.S.; Mulder, C.J.; Van Bodegraven, A.A.; De Boer, N.K. Electronic nose can discriminate colorectal carcinoma and advanced adenomas by fecal volatile biomarker analysis: Proof of principle study. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, G.; Malagù, C.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Pezzoli, A.; De Togni, A.; Palmonari, C. Clinical validation results of an innovative non-invasive device for colorectal cancer preventive screening through fecal exhalation analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonta, G.; Anania, G.; Fabbri, B.; Gaiardo, A.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Landini, N.; Malagù, C.; Scagliarini, L.; Guidi, V. Preventive screening of colorectal cancer with a device based on chemoresistive sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, G.; Anania, G.; Astolfi, M.; Feo, C.; Gaiardo, A.; Gherardi, S.; Giberti, A.; Guidi, V.; Landini, N.; Palmonari, C.; et al. Chemoresistive sensors for colorectal cancer preventive screening through fecal odor: Double-blind approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibe, A.; Ota, M.; Takeshita, A.; Tsuboi, H.; Kizuka, S.; Oka, H.; Suwa, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Suwa, H.; et al. Detection of gas components as a novel diagnostic method for colorectal cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2018, 2, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Method of Collection | Method of Analysis | Real-Time Analysis | Identification of Individual Compounds | Duration of Procedure | Target | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tedlar® bag, TD | GC-MS | no | yes | ~2 h | CRC | 96 | 83 | [35] |
| Visually CO2-controlled sampling, SPME | GC-MS | - | CRC | - | - | [28] | ||
| SPME | GC-MS | - | GC | - | - | [36] | ||
| ReCIVA®, TD | GC-MS | - | CRC | 79–90 | 86–93 | [37,38] | ||
| ReCIVA®, TD | Multi-MS a | no | yes | - | Esophageal-gastric cancer | - | - | [39] |
| Nalophan bag | SIFT-MS | yes | selected | - | CRC | 96 | 76 | [23] |
| Nalophan bag | SIFT-MS | - | Esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma | 86.7 | 81.2 | [40] | ||
| Steel breath bag | SIFT-MS | - | Esophagogastric cancer | 80 | 81 | [41] | ||
| Mylar® bag | SIFT-MS | Hepatocellular cancer | 73 | 71 | [42] | |||
| Tedlar® bag, TD | PTR-TOF-MS | yes | selected | - | GC | 61 | 94 | [43] |
| Tedlar® bag, TD | SPI-MS | yes | partly | - | GC | 95.8 | 96.5 | [44] |
| BioVOC™, Tedlar® bag | UVP-TOFMS b | yes | partly | - | Upper gastrointestinal cancer | 92.3 | 100 | [45] |
| Mylar® bag | nanoarray | yes | no | - | CRC | 85 | 94 | [29] |
| Mylar® bag | nanoarray | - | Precancerous gastric lesions and gastric carcinoma | 73 | 98 | [46] | ||
| BioVOC™ | nanoarray | 15 min for sampler 20 min for sensor | GC | 100 | 93 | [47] | ||
| Tenax® TA sorption tube | nanoarray | - | GC | 100 | 98 | [48] | ||
| Tedlar® bag | SERS | no | partly | - | GC | 91.23 | 88.52 | [49] |
| e-nose | yes | no | - | CRC | 63.3 | 84.2 | [50] | |
| Aeonose™ | 15 min | CRC | 95 | 64 | [51] | |||
| Aeonose™ | GC | 81 | 71 | [52] | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Min, Y.; Pang, K.; Wu, D. Sample Collection and Processing in Volatile Organic Compound Analysis for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141563
Zheng W, Min Y, Pang K, Wu D. Sample Collection and Processing in Volatile Organic Compound Analysis for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141563
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Weiyang, Yiyang Min, Ke Pang, and Dong Wu. 2024. "Sample Collection and Processing in Volatile Organic Compound Analysis for Gastrointestinal Cancers" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141563
APA StyleZheng, W., Min, Y., Pang, K., & Wu, D. (2024). Sample Collection and Processing in Volatile Organic Compound Analysis for Gastrointestinal Cancers. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141563






