Distribution of Microaneurysms and Hemorrhages in Accordance with the Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type Diabetes Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Building the Algorithm
2.3. Aim
2.4. Design
2.5. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Retinography of T2DM patients from MESSIDOR and MIRADATASET were included.
- Retinography of other datasets and with low quality were excluded.
2.6. Sample Size
2.7. Methods
2.8. Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy
- No DR, level 0: (μA = 0) AND (H = 0)
- Mild-DR, level 1: (0 < μA ≤ 5) AND (H = 0)
- Moderate-DR, level 2: ((5 < μA < 15) OR (0 < H < 5)) AND (NV = 0)
- Severe-DR, level 3: (μA ≥ 15) OR (H ≥ 5) OR (NV = 1)
2.9. Ethics and Consent
2.10. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Two Databases MESSIDOR and MIRADATASET
3.2. MESSIDOR Database Study
3.2.1. Microaneurysm Count
3.2.2. Hemorrhages Count
3.3. Analysis of the MIRADATASET Database
3.3.1. Microaneurysm Count
3.3.2. Hemorrhage Count
3.4. Results at Central Ring
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Ed. Brussels. Belgium. 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/ (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriguer, F.; Goday, A.; Bosch-Comas, A.; Bordiú, E.; Calle-Pascual, A.; Carmena, R.; Casamitjana, R.; Castaño, L.; Castell, C.; Catalá, M.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in Spain: The Di@bet.es Study. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo-Martínez, G.; Valdés, S.; Soriguer, F.; Vendrell, J.; Urrutia, I.; Pérez, V.; Ortega, E.; Ocón, P.; Montanya, E.; Menéndez, E.; et al. Incidence of diabetes mellitus in Spain as results of the nation-wide cohort diabetes study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Section 12, Retinopathy, Neuropathy, and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S185–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, R.R.A.; Jonas, J.B.; Bron, A.M.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Friedman, D.S.; Keeffe, J.E.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; et al. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Prevalence and causes of vision loss in high-income countries and in Eastern and Central Europe in 2015: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avidor, D.; Loewenstein, A.; Waisbourd, M.; Nutman, A. Cost-effectiveness of diabetic retinopathy screening programs using telemedicine: A systematic review. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2020, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanchi, F.; Diabetic Retinopathy Guidelines Working Group. The Royal College of Ophthalmologists’ clinical guidelines for diabetic retinopathy: A summary. Eye 2013, 7, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Sun, J.; Kawasaki, R.; Ruamviboonsuk, P.; Gupta, N.; Lansingh, V.C.; Maia, M.; Mathenge, W.; Moreker, S.; Muqit, M.M.; et al. Guidelines on Diabetic Eye Care: The International Council of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2018, 25, 1608–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Yanagihara, R.T.; Lee, C.S.; Blazes, M.; Jung, H.C.; Chee, Y.E.; Gencarella, M.D.; Gee, H.; Maa, A.Y.; Cockerham, G.C.; et al. Multicenter, Head-to-Head, Real-World Validation Study of Seven Automated Artificial Intelligence Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Systems. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.; Pires, I.; Rosa, A.; Duarte, L.; Bernardes, R.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Microaneurysm turnover is a biomarker for diabetic retinopathy progression to clinically significant macular edema: Findings for type 2 diabetics with nonproliferative retinopathy. Ophthalmologica 2009, 223, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.S. Deep Learning-Based Methods for Extracting Fundus Image Landmarks and Signs of Eye Diseases. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona, Spain, 2022. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10803/687502 (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRID). Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/open-access/indian-diabetic-retinopathy-image-dataset-idrid (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Methods for Evaluating Segmentation and Indexing Techniques Dedicated to Retinal Ophthalmology MESSIDOR. Available online: https://www.adcis.net/en/third-party/messidor/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- RetinaReadRisk (RRR). Available online: https://www.iispv.cat/cas-dxit/retinareadrisk-rrr/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs—An extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology 1991, 98 (Suppl. S5), 786–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Klein, R.E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Global Diabetic Retinopathy Project Group. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, L.M.; Bursell, S.E.; Cavallerano, J.; Gardner, W.K.; Strong, J. Joslin Vision Network Validation Study: Pilot image stabilization phase. J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1998, 69, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Tan, T.E. The Diabetic Retinopathy “Pandemic” and Evolving Global Strategies: The 2023 Friedenwald Lecture. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Bressler, N.M. Artificial Intelligence with Deep Learning Technology Looks into Diabetic Retinopathy Screening. JAMA 2016, 316, 2366–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Heijden, A.A.; Abramoff, M.D.; Verbraak, F.; Van Hecke, M.V.; Liem, A.; Nijpels, G. Validation of automated screening for referable diabetic retinopathy with the IDx-DR device in the Hoorn Diabetes Care System. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vought, R.; Vought, V.; Shah, M.; Szirth, B.; Bhagat, N. EyeArt artificial intelligence analysis of diabetic retinopathy in retinal screening events. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 4851–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.; Bandello, F.; Tejerina, A.N.; Vujosevic, S.; Varano, M.; Egan, C.; Sivaprasad, S.; Menon, G.; Massin, P.; Verbraak, F.D.; et al. Characterization of Retinal Disease Progression in a 1-Year Longitudinal Study of Eyes with Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy in Diabetes Type 2. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5698–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, R.; Nunes, S.; Pereira, I.; Torrent, T.; Rosa, A.; Coelho, D.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Computer-assisted microaneurysm turnover in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmologica 2009, 223, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.; Ribeiro, L.; Lobo, C.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Three different phenotypes of mild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy with different risks for development of clinically significant macular edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 4595–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Lobo, C. Phenotypes and biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 41, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munuera-Gifre, E.; Saez, M.; Juvinyà-Canals, D.; Rodríguez-Poncelas, A.; Barrot-De-La–Puente, J.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Romero-Aroca, P.; Barceló, M.A.; Coll-De-Tuero, G. Analysis of the location of retinal lesions in central retinographies of patients with Type 2 diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e13–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Mohr, S.; Du, Y.D.; Kern, T.S. Non-uniform distribution of lesions and biochemical abnormalities within the retina of diabetic humans. Curr. Eye Res. 2003, 27, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Fundus photographic risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy. ETDRS report number 12. Ophthalmology 1991, 98 (Suppl. S5), 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domalpally, A.; Barrett, N.; Reimers, J.; Blodi, B. Comparison of Ultra-Widefield Imaging and Standard Imaging in Assessment of Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2021, 1, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
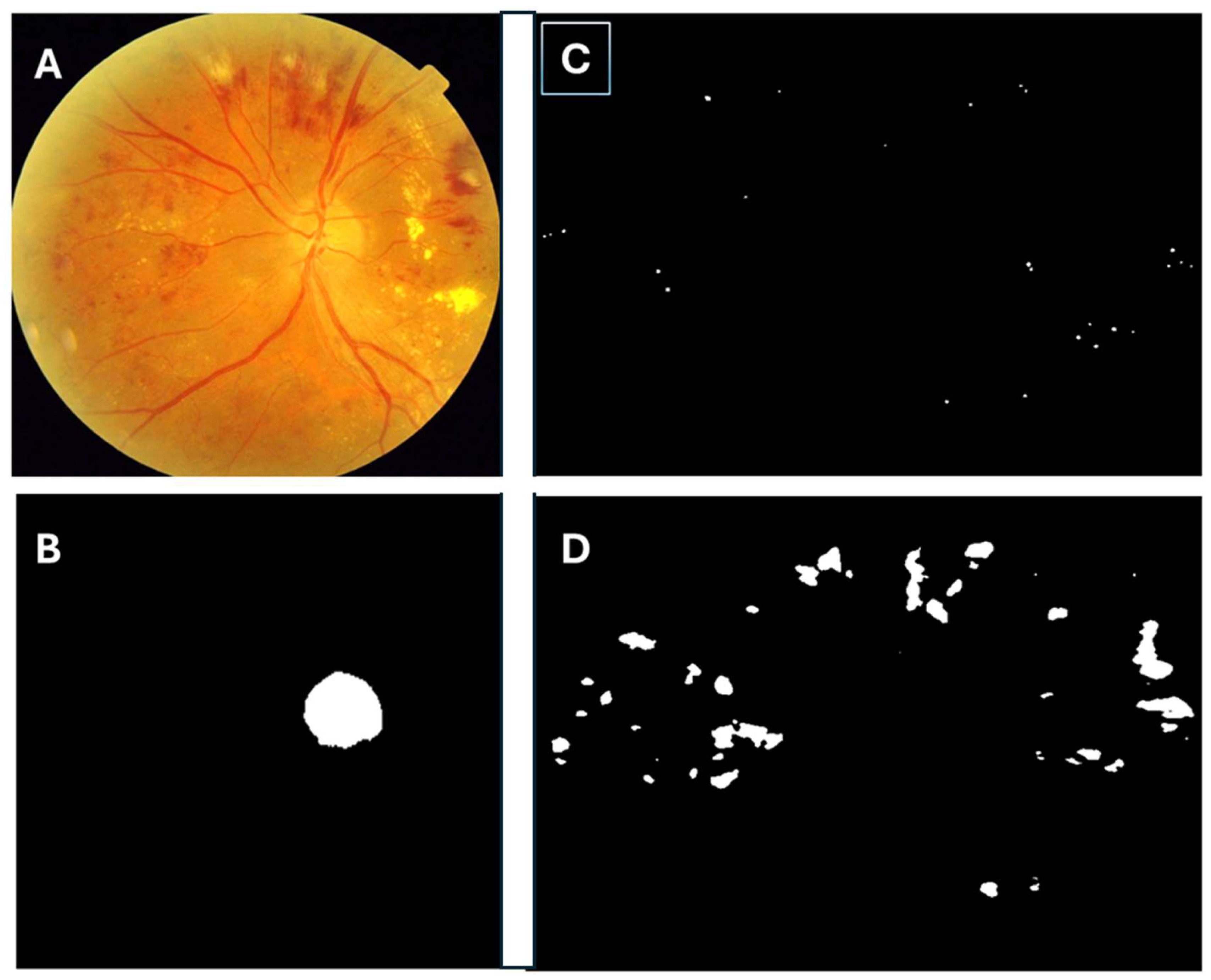
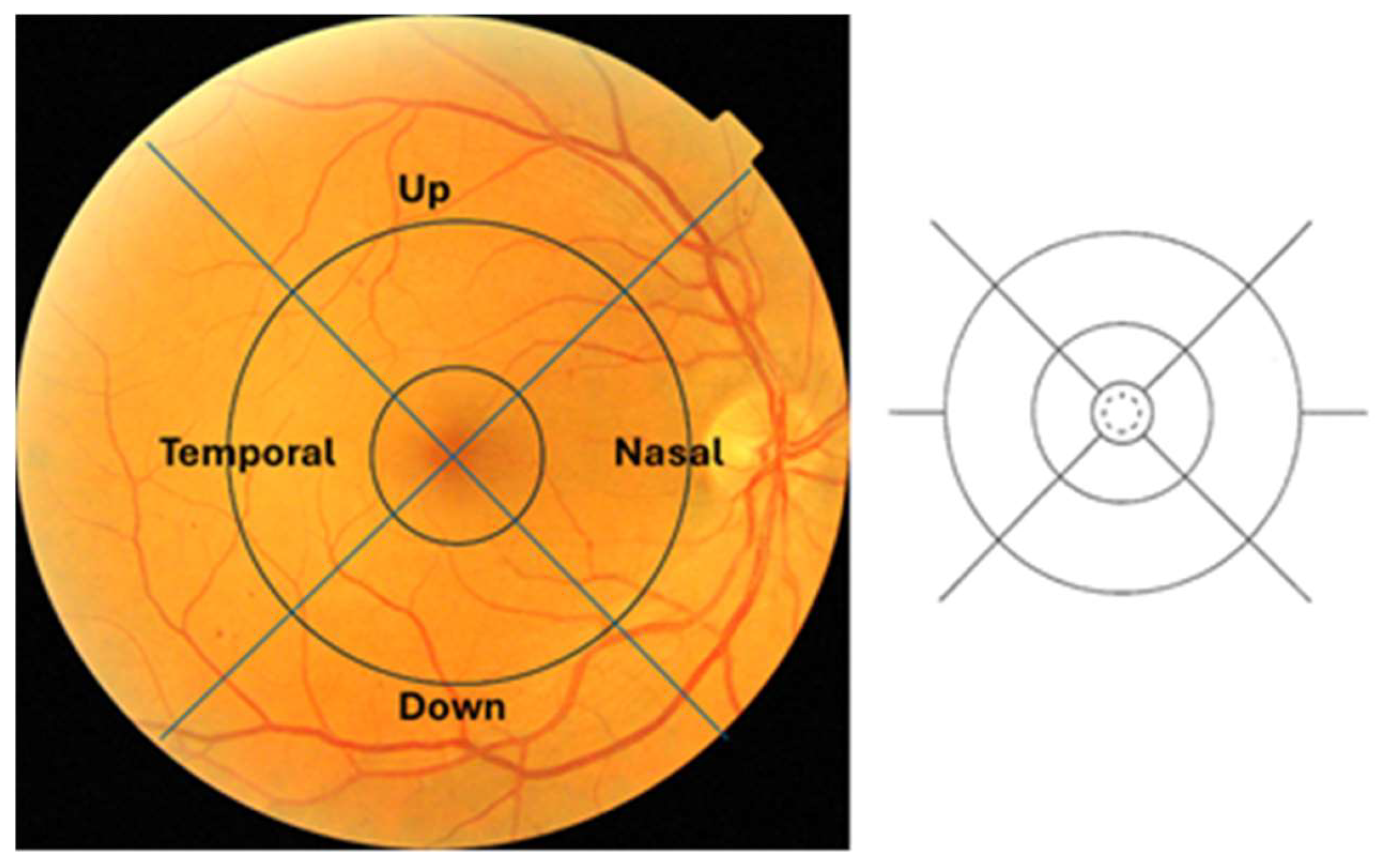
| Classification | MESSIDOR | MIRADATASET |
|---|---|---|
| No DR | 609 | 37,218 |
| Mild-DR | 182 | 715 |
| Moderate-DR | 162 | 1290 |
| Severe-DR | 261 | 1469 |
| Total | 1200 | 40,692 |
| Microaneurysms | Type of DR | UP | TEMPORAL | NASAL | DOWN | ANOVA |
| Mild-DR | 1.25 ± 0.71 | 1.01 ± 1.08 | 0.38 ± 0.62 | 0.86 ± 0.92 | <0.001 | |
| Moderate-DR | 1.64 ± 0.92 | 1.50 ± 2.07 | 0.65 ± 1.13 | 1.01 ± 1.27 | <0.001 | |
| Severe-DR | 2.47 ± 2.80 | 5.50 ± 6.52 | 1.86 ± 2.22 | 3.10 ± 3.23 | <0.001 | |
| ANOVA test | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Hemorrhages | Type of DR | UP | TEMPORAL | NASAL | DOWN | |
| Mild-DR | 1.07 ± 0.27 | 1.53 ± 0.77 | 1.12 ± 0.48 | 1.17 ± 0.64 | <0.001 | |
| Moderate-DR | 1.26 ± 0.50 | 1.69 ± 0.98 | 1.29 ± 0.55 | 1.31 ± 0.58 | <0.001 | |
| Severe-DR | 2.08 ± 3.44 | 4.98 ± 6.55 | 1.96 ± 2.66 | 2.18 ± 3.22 | <0.001 | |
| ANOVA test | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Microaneurysms | Type of DR | UP | TEMPORAL | NASAL | DOWN | ANOVA Test |
| Mild-DR | 1.65 ± 1.10 | 1.18 ± 1.51 | 1.86 ± 1.16 | 1.01 ± 1.25 | <0.001 | |
| Moderate-DR | 1.04 ± 1.33 | 2.23 ± 2.85 | 1.47 ± 1.72 | 1.76 ± 2.05 | <0.001 | |
| Severe-DR | 4.72 ± 4.19 | 7.51 ± 7.72 | 5.16 ± 4.78 | 7.46 ± 7.67 | <0.001 | |
| ANOVA test | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Hemorrhages | Type of DR | UP | TEMPORAL | NASAL | DOWN | ANOVA test |
| Mild-DR | 1.34 ± 0.76 | 1.39 ± 0.80 | 1.24 ± 0.56 | 1.29 ± 0.64 | <0.001 | |
| Moderate-DR | 1.52 ± 0.85 | 1.76 ± 1.25 | 1.55 ± 0.88 | 1.45 ± 0.85 | <0.001 | |
| Severe-DR | 2.28 ± 3.25 | 3.13 ± 4.81 | 2.47 ± 3.79 | 3.19 ± 5.30 | <0.001 | |
| ANOVA test | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Database | Lesions | Quadrants | Significance, (t Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MESSIDOR | Microaneurysms | Temporal versus nasal | p < 0.001, (t = 8.53), |
| Temporal versus upper | p = 0.02, (t = 6.89), | ||
| Temporal versus inferior | p = 0.03, (t = 5.34) | ||
| Hemorrhages | Temporal versus nasal | p < 0.001, (t = 7.72) | |
| Temporal versus upper | p = 0.02, (t = 6.33) | ||
| Temporal versus inferior | p = 0.02, (t = 6.19). | ||
| MIRADATASET | Microaneurysms | Temporal versus nasal | p = 0.03, (t = 3.53) |
| Temporal versus upper | p = 0.02, (t = 4.89) | ||
| Temporal versus inferior | p = 0.87, (t = 1.04) | ||
| Hemorrhages | Temporal versus nasal | p = 0.03, (t = 2.72), | |
| Temporal versus upper | p = 0.04, (t = 2.33) | ||
| Temporal versus inferior | p = 0.91, (t = 1.02). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Aroca, P.; Garcia-Curto, E.; Pascual-Fontanilles, J.; Valls, A.; Moreno, A.; Baget-Bernaldiz, M. Distribution of Microaneurysms and Hemorrhages in Accordance with the Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type Diabetes Patients. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141547
Romero-Aroca P, Garcia-Curto E, Pascual-Fontanilles J, Valls A, Moreno A, Baget-Bernaldiz M. Distribution of Microaneurysms and Hemorrhages in Accordance with the Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type Diabetes Patients. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141547
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Aroca, Pedro, Eugeni Garcia-Curto, Jordi Pascual-Fontanilles, Aida Valls, Antonio Moreno, and Marc Baget-Bernaldiz. 2024. "Distribution of Microaneurysms and Hemorrhages in Accordance with the Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type Diabetes Patients" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141547
APA StyleRomero-Aroca, P., Garcia-Curto, E., Pascual-Fontanilles, J., Valls, A., Moreno, A., & Baget-Bernaldiz, M. (2024). Distribution of Microaneurysms and Hemorrhages in Accordance with the Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type Diabetes Patients. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141547








