Community Point of Care Testing in Diagnosing and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. POCT Devices for Kidney Disease: Accuracy, Precision and Acceptability
3. The Role of Point of Care Testing (POCT) in Kidney Disease
3.1. Screening for CKD
3.2. Dose Adjustment of Prescribed Medications in Patients with Renal Impairment
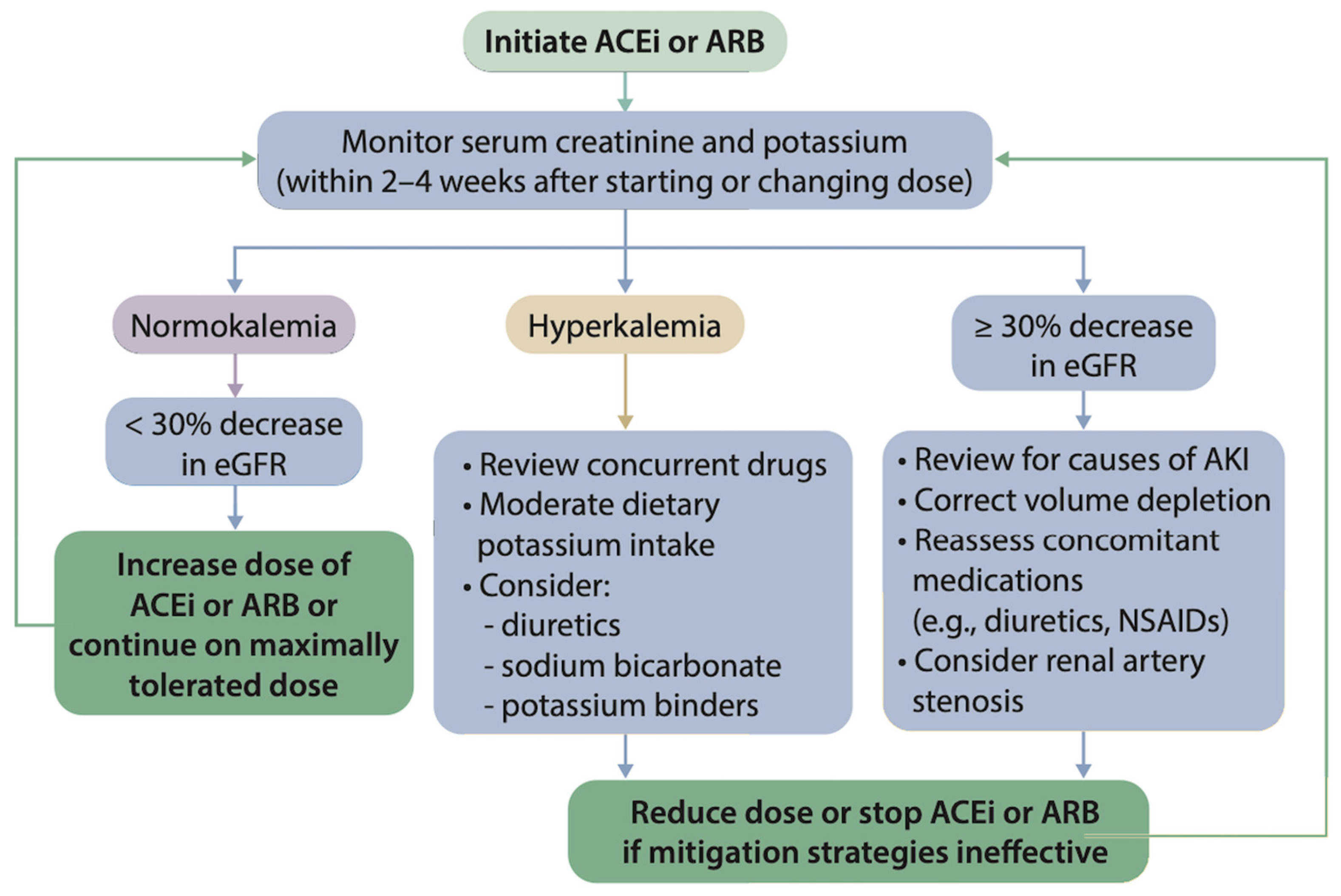
3.3. Monitoring of CKD
4. Patient and Healthcare Professional Perspectives on POCT for Kidney Disease
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounkpatin, H.O.; Harris, S.; Fraser, S.D.S.; Day, J.; Mindell, J.S.; Taal, M.W.; O’Donoghue, D.; Roderick, P.J. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in adults in England: Comparison of nationally representative cross-sectional surveys from 2003 to 2016. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, D.C.; Liu, Y.; Boulware, L.E. Disparities in the burden, outcomes, and care of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrity, B.H.; Kramer, H.; Vellanki, K.; Leehey, D.; Brown, J.; Shoham, D.A. Time trends in the association of ESRD incidence with area-level poverty in the US population. Hemodial. Int. 2016, 20, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, S.J.; Schachter, M.; Er, L.; Djurdjev, O.; Levin, A. A systematic review of ethnic differences in the rate of renal progression in CKD patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.C.N.; Gregg, E.W.; Sargent, J.; Horton, R. Reducing global diabetes burden by implementing solutions and identifying gaps: A Lancet Commission. Lancet 2016, 387, 1494–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, R.; Dreyer, G.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Hull, S.A. Ethnic differences in the progression of chronic kidney disease and risk of death in a UK diabetic population: An observational cohort study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, G.; Hull, S.; Mathur, R.; Chesser, A.; Yaqoob, M.M. Progression of chronic kidney disease in a multi-ethnic community cohort of patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, P.E.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Chronic Kidney Disease: Assessment and Management. NICE Guideline NG203. 2021. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng203 (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- NICE. Evidence Reviews for Cystatin C Based Equations to Estimate GFR in Adults, Children and Young People. 2021 Jan. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng203/update/NG203/documents/evidence-review-13 (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Kerr, M. Chronic Kidney Disease in England: The Human and Financial Cost. 2012. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/improvement-hub/wp-content/uploads/sites/44/2017/11/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-in-England-The-Human-and-Financial-Cost.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Crews, D.C.; Bello, A.K.; Saadi, G.; World Kidney Day Steering Committee. Burden, access and disparities in kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppa, P.B.; Müller, C.; Schlichtiger, A.; Schlebusch, H. Point-of-care testing (POCT): Current techniques and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junker, R.; Schlebusch, H.; Luppa, P.B. Point-of-Care Testing in Hospitals and Primary Care. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2010, 107, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortune Business Insights. Market Research Report: Point of Care Diagnostics Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/point-of-care-diagnostics-market-101072 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Myers, G.L. Recommendations for Improving Serum Creatinine Measurement: A Report from the Laboratory Working Group of the National Kidney Disease Education Program. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Evaluation of Total Analytical Error for Quantitative Medical Laboratory Measurement Procedures; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Health and Human Services. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) Proficiency Testing Regulations Related to Analytes and Acceptable Performance. Federal Register. 4 February 2019. Volume 84, pp. 1536–1566. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2019-02-04/pdf/2018-28363.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- van der Heijden, C.; Roosens, L.; Cluckers, H.; Van Craenenbroeck, A.H.; Peeters, B. Analytical and clinical performance of three hand-held point-of-care creatinine analyzers for renal function measurements prior to contrast-enhanced imaging. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 497, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosack, C.S.; de Kieviet, W.; Bayrak, K.; Milovic, A.; Page, A.L. Evaluation of the Nova StatSensor® XpressTM Creatinine Point-Of-Care Handheld Analyzer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straseski, J.A.; Lyon, M.E.; Clarke, W.; DuBois, J.A.; Phelan, L.A.; Lyon, A.W. Investigating Interferences of a Whole-Blood Point-of-Care Creatinine Analyzer: Comparison to Plasma Enzymatic and Definitive Creatinine Methods in an Acute-Care Setting. Clin Chem. 2011, 57, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, K.L.; Bagherpoor, S.; Diker, P.; Cursio, C.; DuBois, J.; Yip, P.M. Evaluation of the analytical performance of the Nova StatSensor creatinine meter and reagent strip technology for whole blood testing. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpi-Steiner, N.L.; Williamson, E.E.; Karon, B.S. Comparison of Three Whole Blood Creatinine Methods for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate Before Radiographic Contrast Administration. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataatmadja, M.; Fung, A.W.S.; Jacobson, B.; Ferera, J.; Bernstein, E.; Komenda, P.; Mattman, A.; Seccombe, D.; Levin, A. Performance of StatSensor Point-of-Care Device for Measuring Creatinine in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Postkidney Transplantation. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2020, 7, 2054358120970716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lint, C.L.; van der Boog, P.J.M.; Romijn, F.P.H.T.M.; Schenk, P.W.; van Dijk, S.; Rövekamp, T.J.M.; Kessler, A.; Siekmann, L.; Rabelink, T.J.; Cobbaert, C.M. Application of a point of care creatinine device for trend monitoring in kidney transplant patients: Fit for purpose? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2015, 53, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Williams, C.J.; Lendrem, C.; Smithson, J.; Allinson, C.; Robinson, J.; Walker, A.; Winter, A.; Simpson, A.J.; Newton, J.; et al. Patient Self-Testing of Kidney Function at Home, a Prospective Clinical Feasibility Study in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begos, D.; Milojkovic, B. MO382: Validation of a Handheld Point-of-Care Creatinine/EGFR Meter for Evaluating Renal Function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37 (Suppl. S3), gfac069-015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currin, S.; Gondwe, M.; Mayindi, N.; Chipungu, S.; Khoza, B.; Khambule, L.; Snyman, T.; Tollman, S.; Fabian, J.; George, J.; et al. Evaluating chronic kidney disease in rural South Africa: Comparing estimated glomerular filtration rate using point-of-care creatinine to iohexol measured GFR. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2021, 59, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, T.H.; Corso, O.; Ludlow, M.; Boyle, A.; Cass, A.; Chadban, S.J.; Joyner, B.; Shephard, M.; Usherwood, T. Screening for chronic kidney disease in Australia: A pilot study in the community and workplace. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horizon Scanning Research & Intelligence Centre. Point-of-Care Creatinine Testing for the Detection and Monitoring of Chronic Kidney Disease. Horizon Scan Report 0038, March 2014. Available online: https://www.community.healthcare.mic.nihr.ac.uk (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Komenda, P.; Lavallee, B.; Ferguson, T.W.; Tangri, N.; Chartrand, C.; McLeod, L.; Gordon, A.; Dart, A.; Rigatto, C. The Prevalence of CKD in Rural Canadian Indigenous Peoples: Results From the First Nations Community Based Screening to Improve Kidney Health and Prevent Dialysis (FINISHED) Screen, Triage, and Treat Program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairoun, A.A.; Al-Hemyari, S.S.; Shahwan, M.; Zyoud, S.H.; El-Dahiyat, F. Community pharmacist-led point-of-care eGFR screening: Early detection of chronic kidney disease in high-risk patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dart, A.; Lavallee, B.; Chartrand, C.; McLeod, L.; Ferguson, T.W.; Tangri, N.; Gordon, A.; Blydt-Hansen, T.; Rigatto, C.; Komenda, P. Screening for kidney disease in Indigenous Canadian children: The FINISHED screen, triage and treat program. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 23, e134–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, T.W.; Tangri, N.; Tan, Z.; James, M.T.; Lavallee, B.D.A.; Chartrand, C.D.; McLeod, L.L.; Dart, A.B.; Rigatto, C.; Komenda, P.V. Screening for chronic kidney disease in Canadian indigenous peoples is cost-effective. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, J.; Al Hamarneh, Y.N.; Bajorek, B.; Papastergiou, J.; Tsuyuki, R.T. Community pharmacist identification of chronic kidney disease using point-of-care technology: A pilot study. Can. Pharm. J./Rev. Pharm. Can. 2020, 153, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefansson, B.V.; Chertow, G.M.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Lindberg, M.; McMurray, J.; Rossing, P.; Toto, R.; et al. Rationale and protocol of the Dapagliflozin and Prevention of Adverse outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease (DAPA-CKD) randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The EMPA Kidney Collaborative Group. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraz-Muñoz, A.Y.; Weinstein, J.; Wald, R. eGFR Decline after SGLT2 Inhibitor Initiation: The Tortoise and the Hare Reimagined. Kidney360 2021, 2, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guidelines. Top 10 Takeaways for Nephrologists on the Management of People with CKD from the KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. 2024. Available online: https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/KDIGO-2024-CKD-Guideline-Top-10-Takeaways-for-Nephrologists-Management.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Curtis, S.; Martin, H.; DiNella, M.; Lavallee, B.; Chartrand, C.; McLeod, L.; Woods, C.; Dart, A.; Tangri, N.; Rigatto, C.; et al. Kidney Check Point-of-Care Testing—Furthering Patient Engagement and Patient-Centered Care in Canada’s Rural and Remote Indigenous Communities: Program Report. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2021, 8, 205435812110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General Pharmaceutical Council. Survey of Registered Pharmacy Professionals 2019: Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Report; General Pharmaceutical Council: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geerts, A.F.J.; De Koning, F.H.P.; De Vooght, K.M.K.; Egberts, A.C.G.; De Smet, P.A.G.M.; van Solinge, W.W. Feasibility of point-of-care creatinine testing in community pharmacy to monitor drug therapy in ambulatory elderly patients. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cámara Ramos, I.; Escribá Martí, G.; Escudero Quesada, V.; Salar Ibáñez, L.; Climent, M. MO378: The Importance of Community Pharmacy in Chronic Kidney Disease Patient Management. Drug Dosage Adjustment and Nephrotoxicity Detection. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37 (Suppl. S3), gfac069-011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lint, C.; van der Boog, P.; Wang, W.; Brinkman, W.P.; Rövekamp, T.; Neerincx, M.; Rabelink, T.; van Dijk, S. Patient experiences with self-monitoring renal function after renal transplantation: Results from a single-center prospective pilot study. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2015, 9, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, N.; Davids, M.; Blankvoort, N.; Pai, N.P.; Dheda, K.; Pai, M. Compounding diagnostic delays: A qualitative study of point-of-care testing in South Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2015, 20, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, G.; Dixon, S.; Garland, S.; Glogowska, M.; Hunt, H.; Lasserson, D. Point-of-care blood tests during home visits by out-of-hours primary care clinicians; a mixed methods evaluation of a service improvement. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingervelder, D.; Koffijberg, H.; Kusters, R.; IJzerman, M.J. Point-of-care testing in primary care: A systematic review on implementation aspects addressed in test evaluations. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 73, e13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.J.; Van den Bruel, A.; Jones, C.H.D.; Plüddemann, A.; Heneghan, C.; Thompson, M.J.; Price, C.P.; Howick, J. Point-of-care testing in UK primary care: A survey to establish clinical needs. Fam. Pract. 2016, 33, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Analyte | Organisation | Limits of Acceptable Performance/Analytical Total Error (ATE) |
|---|---|---|
| Creatinine | CLIA, AAB | 0.3 mg/dL (26.5 μmol/L) or 30% |
| NKDEP | 7.6% (desirable) 11.4% (minimum) | |
| BV | 8.87% | |
| RCPA | 10% | |
| Potassium | CLIA, AAB | 0.5 mmol/L |
| BV | 5.61% | |
| RCPA | ≤4.0 mmol/L = ±0.2 mmol/L >4.0 mmol/L = 5% | |
| eGFR | NKDEP | 10% |
| Device Name | Manufacturer * | Device Cost (£) ** | Size | Testing Unit | Testing Unit Cost (£) | Creatinine Method | Sample Type (s) | Sample Volume | Analysis Time | Cr/eGFR Only | Storage Conditions (D = Device; T = Testing Unit) | Recommended Operating Temperature | Detection Range (umol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nova Statsenor | Nova Biomedical | 1000–1500 | Portable, Handheld | Strip | 2.00–3.00 | Amperometric/enzymatic | Whole blood | 1.2 μL | 30 s | Yes | D = Room temp. T = Refrigerated (2–8 °C) | 15–40 °C | 27–1056 |
| Nova Max Creatinine | Nova Biomedical | 2000–3000 | Portable, Handheld | Strip | 2.00–5.00 | Amperometric/enzymatic | Whole blood | 1.2 μL | 30 s | Yes | D = Room Temp T = Refrigerated (2–8 °C) | 15–40 °C 10–90% humidity | 27–619 |
| i-STAT Alinity | Abbott, Zoetis | 5100–9000 | Portable, Handheld | Cartridge | 10.00–13.00 | Amperometric/enzymatic | Whole blood, Plasma, Serum | 65 μL | 2 min | No–includes full renal profile | D = Room Temp T = Room Temp | 16–30 °C | 18–1768 |
| Epoc Blood Analysis System | Siemens Healthineers | 6600–9000 | Portable, Handheld | Card | 5.50–13.00 | Amperometric/enzymatic | Whole blood, Plasma, Serum | 90 μL (92 μL = Syringe) | 40 s (165 s to calibrate) | No–includes full renal profile | D = Room Temp T = Room Temp | 15–30 °C <80% humidity | 27–1326 |
| Piccolo Xpress | Abaxis | 10,000–15,000 | Table-top | Disc | 10.00–20.00 | Indicator Absorbance | Whole blood, Plasma, Serum | 100 μL | 12 min | No–includes full renal profile | D = Room Temp T = Refrigerated | 15–32 °C 8–80% humidity | 18–1768 |
| ABL800 Flex | Radiometer | 15,000–30,000 | Table-top | Sensor Cassette | N/A *** | Amperometric/Enzymatic | Whole blood, Plasma, Serum | 65–100 μL | 1 min | Creatinine/Sodium/Potassium | D = 2–32 °C T = Room Temp | 15–32 °C | 10–2000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gama, R.M.; Nebres, D.; Bramham, K. Community Point of Care Testing in Diagnosing and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141542
Gama RM, Nebres D, Bramham K. Community Point of Care Testing in Diagnosing and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141542
Chicago/Turabian StyleGama, Rouvick Mariano, Danilo Nebres, and Kate Bramham. 2024. "Community Point of Care Testing in Diagnosing and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141542
APA StyleGama, R. M., Nebres, D., & Bramham, K. (2024). Community Point of Care Testing in Diagnosing and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141542






