Six-Degree-of-Freedom Freehand 3D Ultrasound: A Low-Cost Computer Vision-Based Approach for Orthopedic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
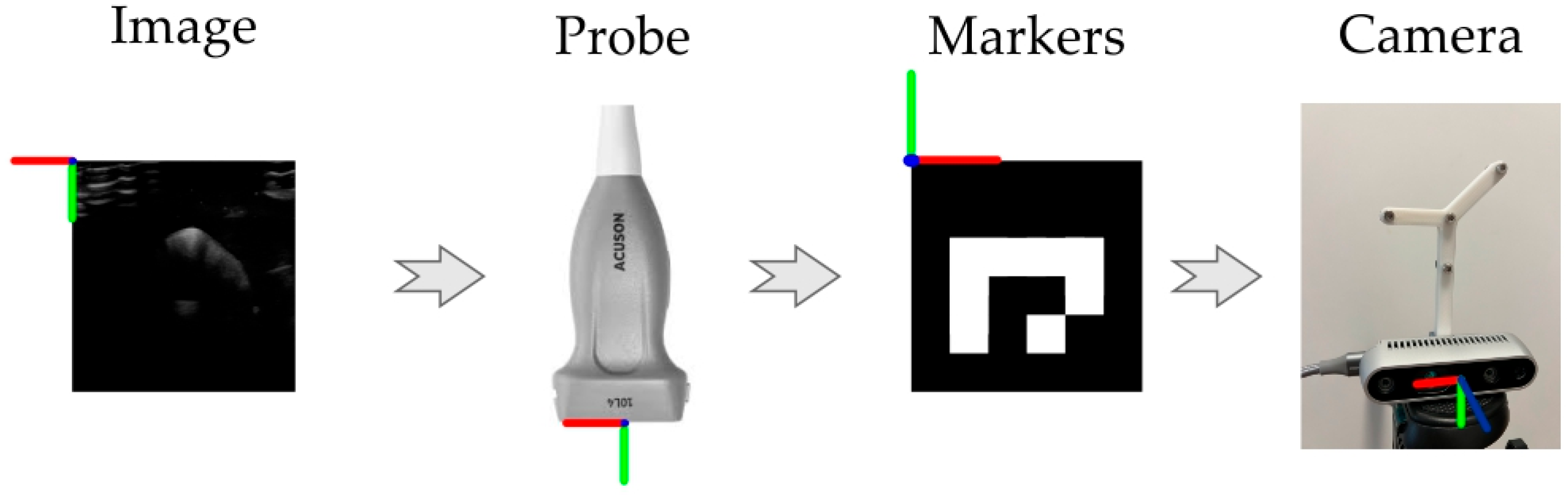
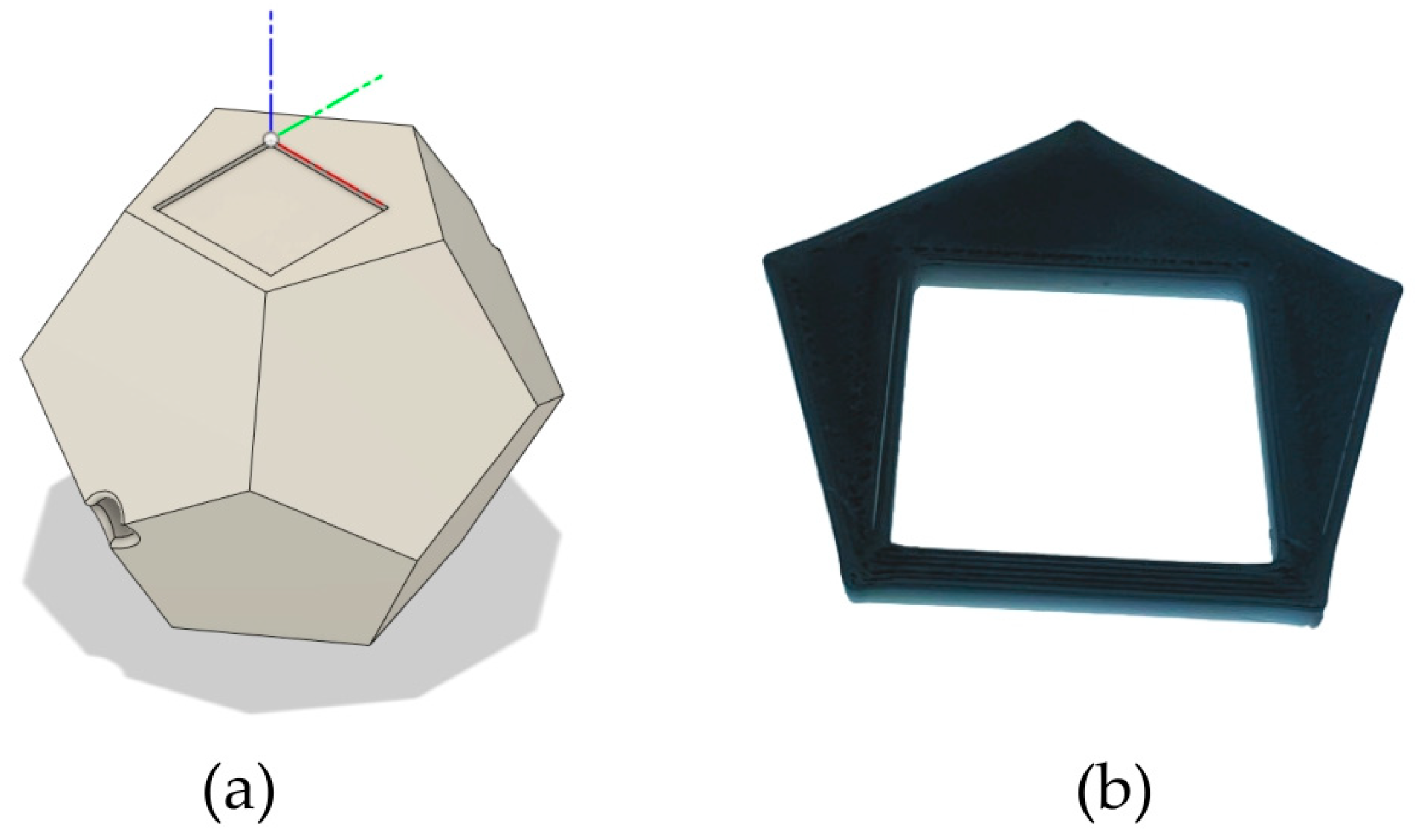
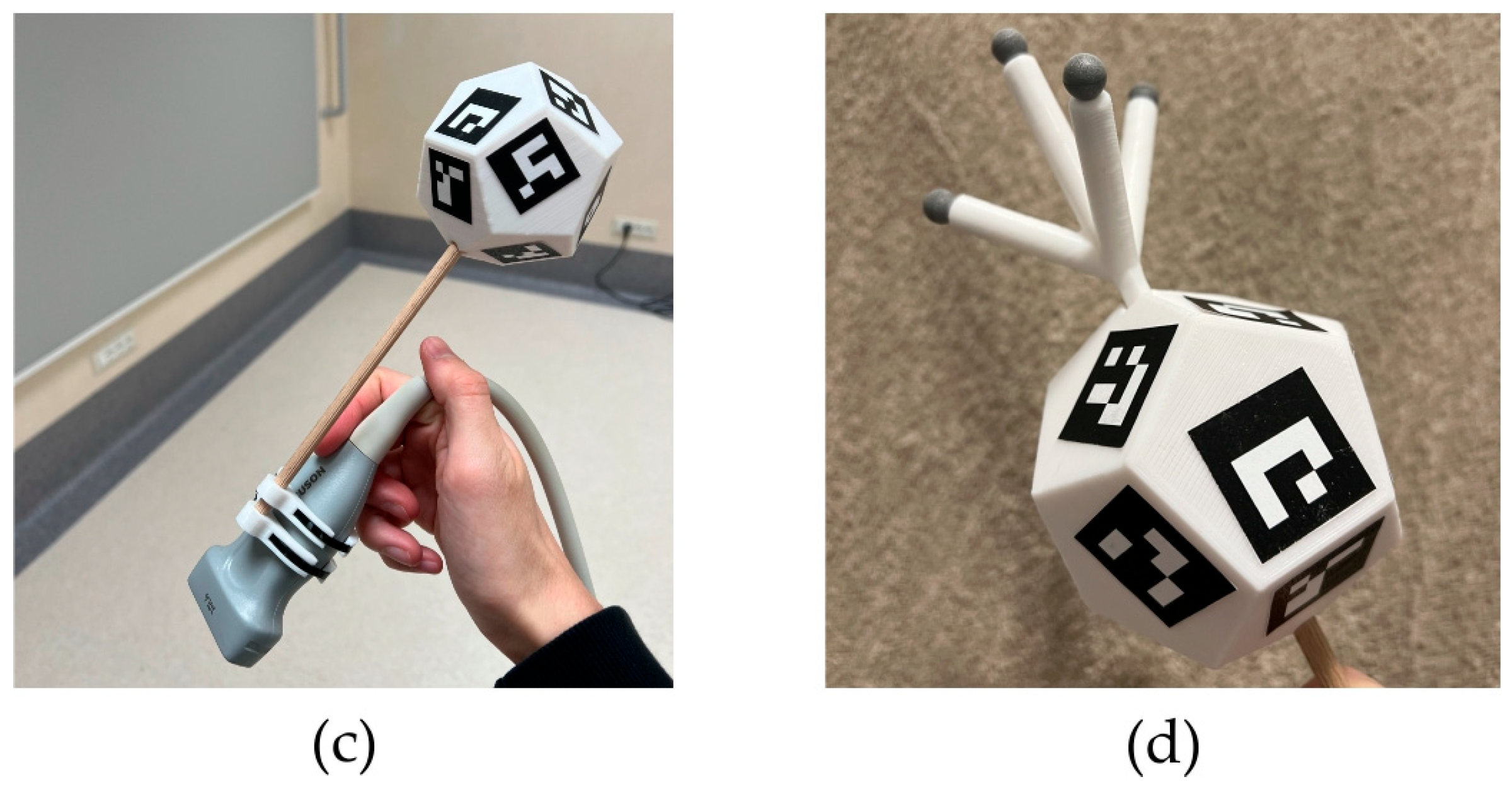
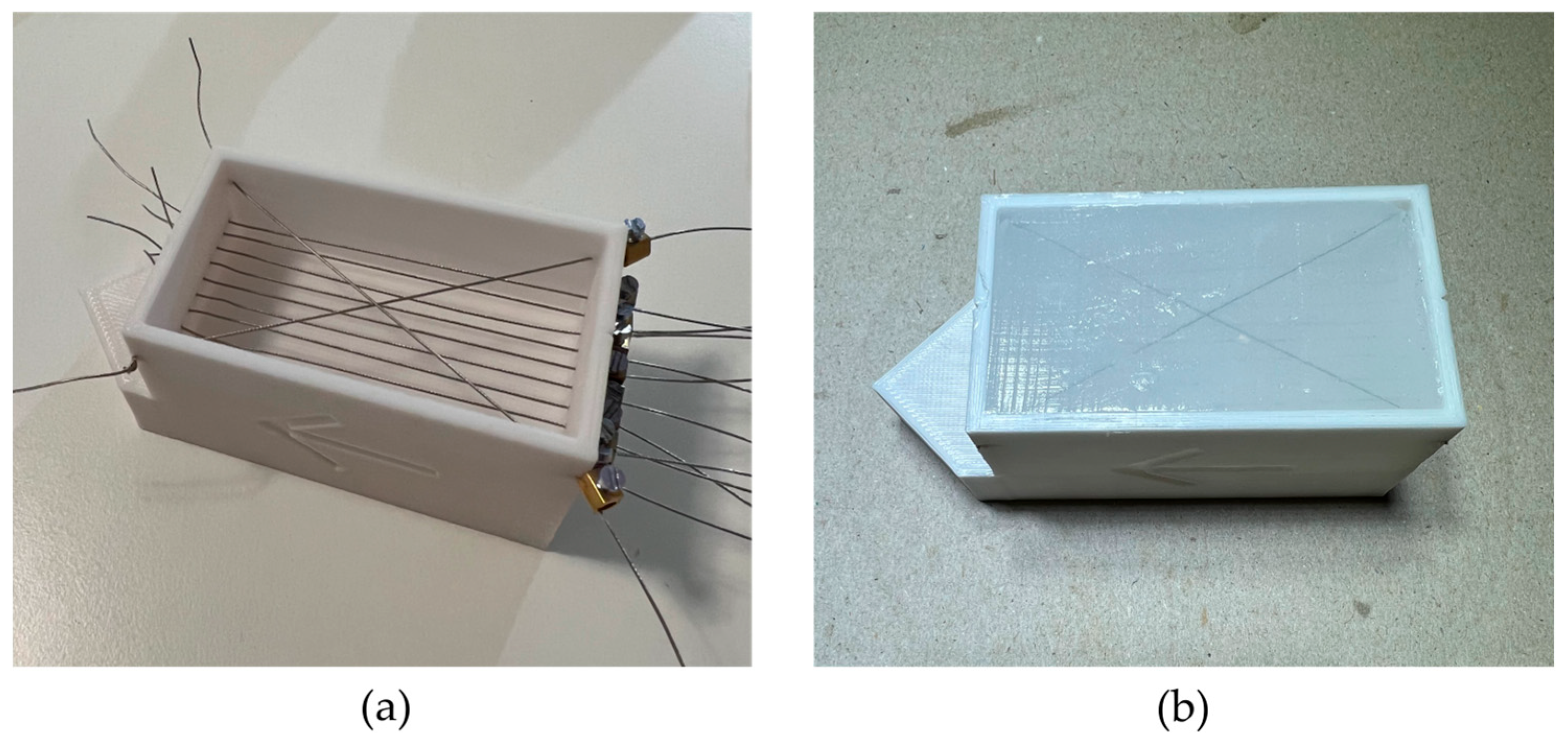
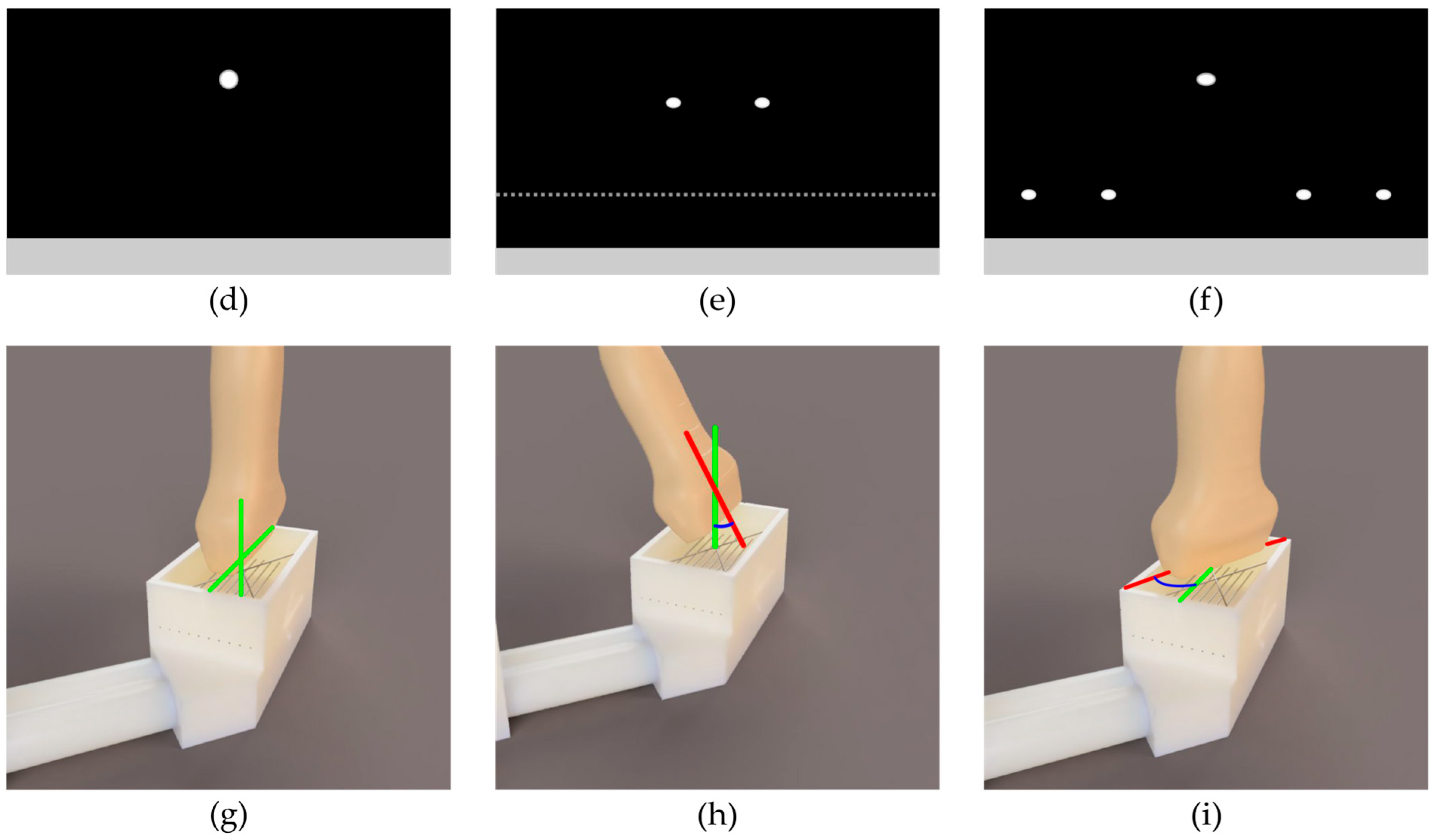
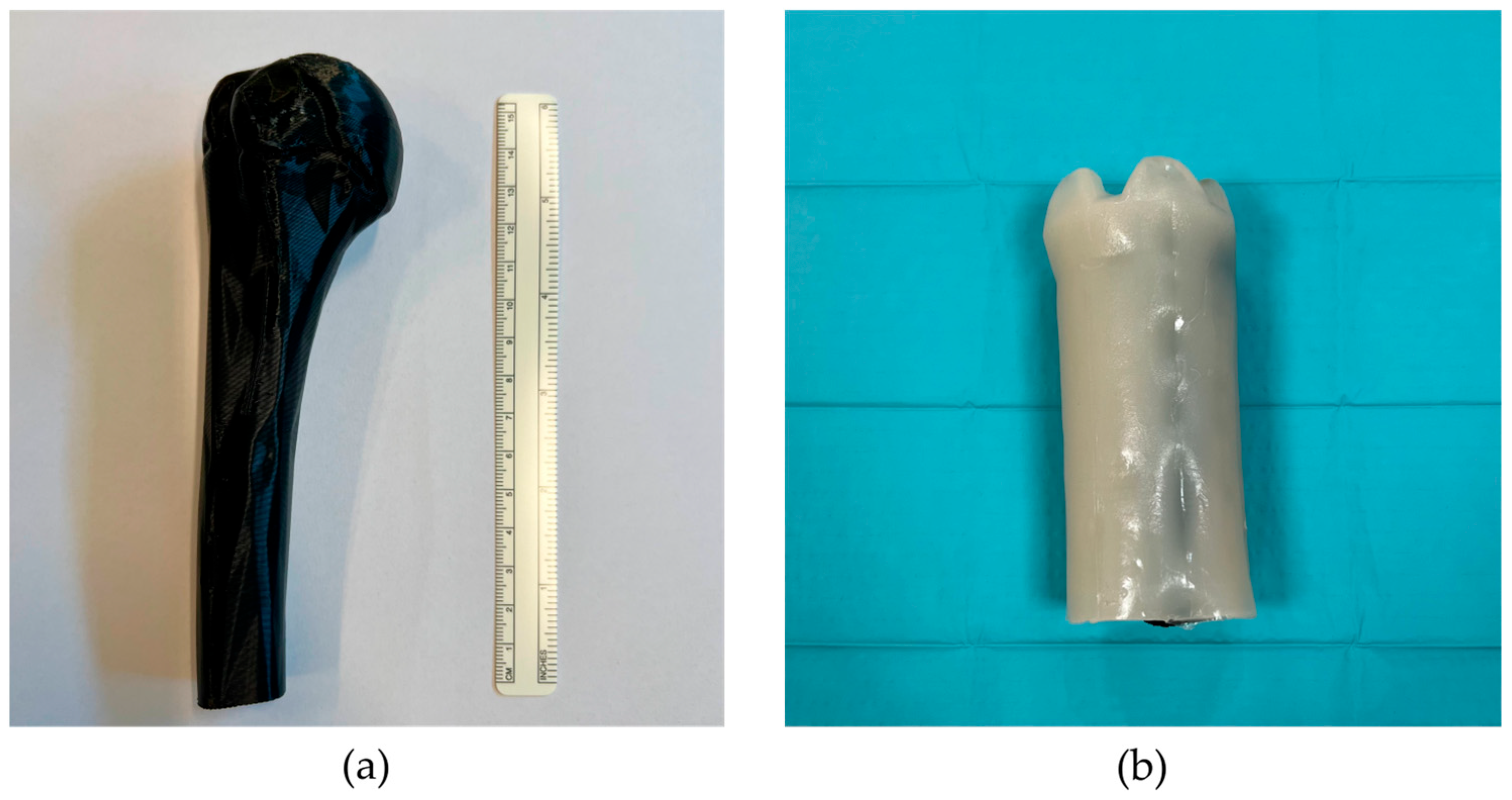
2. Materials and Methods
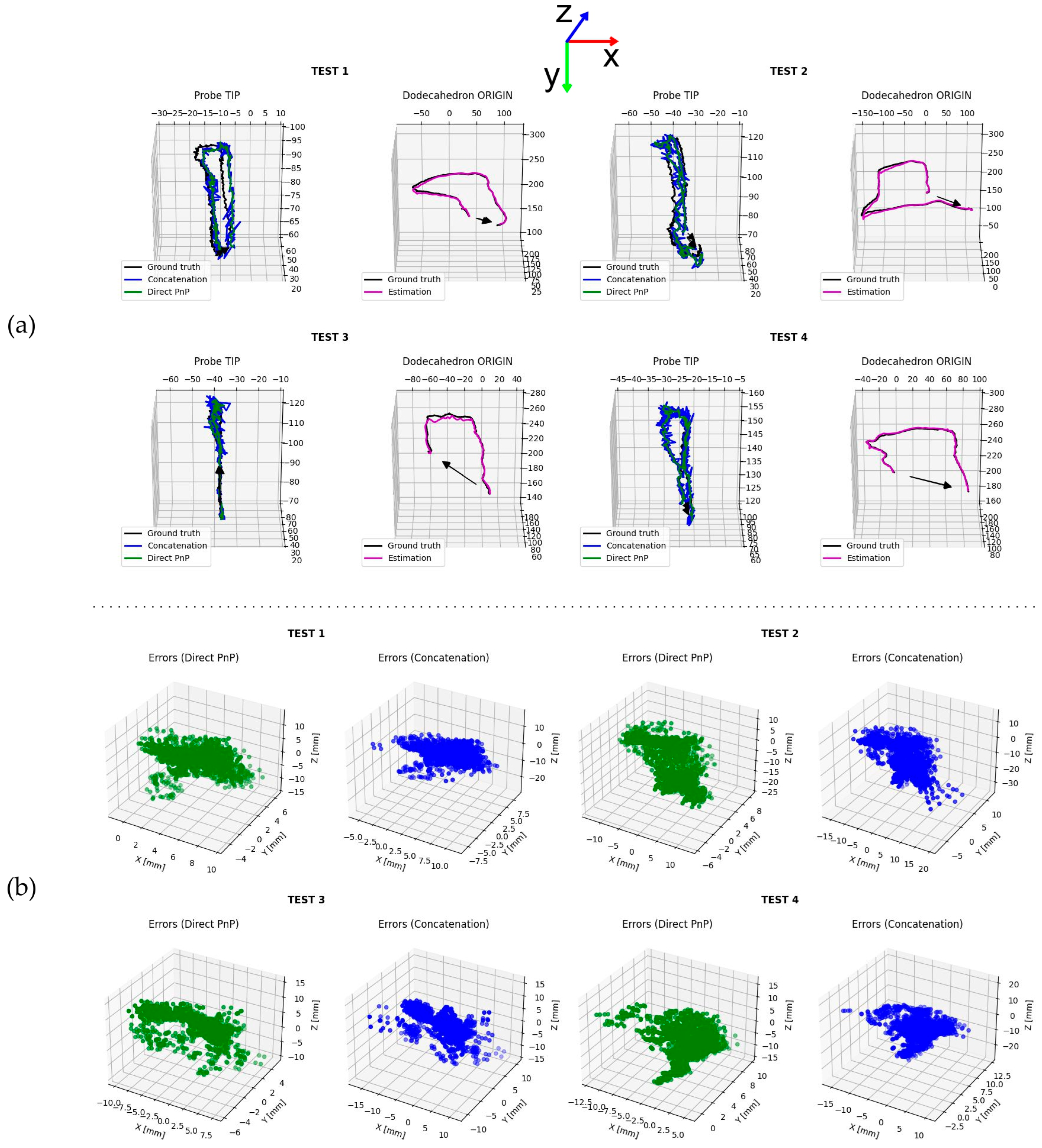
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Combes, D.; Lancigu, R.; de Cepoy, P.; Caporilli-Razza, F.; Hubert, L.; Rony, L.; Aubé, C. Imaging of Shoulder Arthroplasties and Their Complications: A Pictorial Review. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffulli, N.; Longo, U.G.; Berton, A.; Loppini, M.; Denaro, V. Biological Factors in the Pathogenesis of Rotator Cuff Tears. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2011, 19, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolk, A.; Henseler, J.F.; de Witte, P.B.; van Zwet, E.W.; van der Zwaal, P.; Visser, C.P.J.; Nagels, J.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; de Groot, J.H. The Effect of a Rotator Cuff Tear and Its Size on Three-Dimensional Shoulder Motion. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 45, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neer, C.S.; Craig, E.V.; Fukuda, H. Cuff-Tear Arthropathy. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1983, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, U.G.; Facchinetti, G.; Marchetti, A.; Candela, V.; Risi Ambrogioni, L.; Faldetta, A.; De Marinis, M.G.; Denaro, V. Sleep Disturbance and Rotator Cuff Tears: A Systematic Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, T.; Bloem, J.L.; Morrison, W.B.; Wilson, D.J.; White, L. Musculoskeletal Imaging; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-57376-8. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, A.; Beltran, J. Orthopaedic Imaging: A Practical Approach; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 1975136497. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, J. 2. How High Are the Doses? Ann. ICRP 2000, 30, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.J. Radiation Shielding for Diagnostic Radiology. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 165, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammet, S. Magnetic Resonance Safety. Abdom. Radiol. 2016, 41, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.E. Basic Physics of Ultrasound Imaging. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, S131–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Haar, G. Ultrasound Bioeffects and Safety. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H 2009, 224, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K. Introduction to B-Mode Imaging. In Diagnostic Ultrasound, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. ISBN 9781138893603. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, A.; Prager, R.; Treece, G.; Berman, L. Engineering a Freehand 3D Ultrasound System. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 757–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.H.; Fuchs, H. 3D Ultrasound Display Using Optical Tracking. In Proceedings of the First Conference on Visualization in Biomedical Computing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–25 May 1990; pp. 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lin, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lao, Y.; Huang, J. An Accurate Recognition of Infrared Retro-Reflective Markers in Surgical Navigation. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, U.G.; De Salvatore, S.; Carnevale, A.; Tecce, S.M.; Bandini, B.; Lalli, A.; Schena, E.; Denaro, V. Optical Motion Capture Systems for 3D Kinematic Analysis in Patients with Shoulder Disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.H.; Lee, W.-S. Freehand 3-D Ultrasound Imaging: A Systematic Review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2099–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zeng, Z. A Review on Real-Time 3D Ultrasound Imaging Technology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6027029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xie, B.; Ye, P.; Chen, Z. Correspondence-3-D Ultrasonic Strain Imaging Based on a Linear Scanning System. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2015, 62, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, W.; Jin, L.-W.; Wei, G.; Li, X. Linear Tracking for 3-D Medical Ultrasound Imaging. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Cai, Q.; Chen, M.; Jiang, X. Recent Advances in Tracking Devices for Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Applications. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, É.; Gueziri, H.E.; Collins, D.L.; Popa, T.; Kersten-Oertel, M. Evaluation of Low-Cost Hardware Alternatives for 3D Freehand Ultrasound Reconstruction in Image-Guided Neurosurgery. In Proceedings of the Simplifying Medical Ultrasound, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 2021; Noble, J.A., Aylward, S., Grimwood, A., Min, Z., Lee, S.-L., Hu, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaitzakis, M.; Cain, B.; Carroll, S.; Ambrosi, A.; Whitehead, C.; Vitzilaios, N. Fiducial Markers for Pose Estimation. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 101, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Wang, R.; Kin, K.; Twigg, C.; Han, S.; Yang, M.-H.; Chien, S.-Y. DodecaPen: Accurate 6DoF Tracking of a Passive Stylus. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Quebec, QC, Canada, 22–25 October 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 365–374. [Google Scholar]
- Eade, E. Lie Groups for 2d and 3d Transformations. 2013; Volume 117. Available online: http://ethaneade.com/lie.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Siciliano, B.; Khatib, O.; Kröger, T. Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springe: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 200. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, R.W.; Rohling, R.N.; Gee, A.H.; Berman, L. Rapid Calibration for 3-D Freehand Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998, 24, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, K.; Machireddy, R.R.; Seshadri, S. Characterization of Biomechanical Properties of Agar Based Tissue Mimicking Phantoms for Ultrasound Stiffness Imaging Techniques. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 35, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchel Piovesan Pereira, B.; Tagkopoulos, I. Benzalkonium Chlorides: Uses, Regulatory Status, and Microbial Resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00377-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.M.; Santos, T.Q.; Oliveira, D.P.; Alvarenga, A.V.; Costa-Felix, R.P.B. Standard Operating Procedure to Prepare Agar Phantoms. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 733, 12044. [Google Scholar]
- de Assis, M.K.M.; Souza, R.M.; Costa-Félix, R.P.B.; Alvarenga, A.V. Assessment of Ultrasonic Properties of an Agarose Phantom at the Frequency Range 2.25 MHz to 10 MHz. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1826, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, E.L.; Sathoff, H.J.; Zagzebski, J.A. Ultrasonic Shear Wave Properties of Soft Tissues and Tissuelike Materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1983, 74, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1588–2008 (Revision of IEEE Std 1588–2002); IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–269.
- Scheiterer, R.L.; Na, C.; Obradovic, D.; Steindl, G. Synchronization Performance of the Precision Time Protocol in Industrial Automation Networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, E.; Uchiyama, H.; Spindler, F. Pose Estimation for Augmented Reality: A Hands-On Survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 22, 2633–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzakis George and Lourakis, M. A Consistently Fast and Globally Optimal Solution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Online, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 478–494. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eade, E. Gauss-Newton/Levenberg-Marquardt Optimization. Tech. Rep. 2013. Available online: https://www.ethaneade.org/optimization.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Madsen, K.; Nielsen, H.B.; Tingleff, O. Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems; Technical University of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gorry, P.A. General Least-Squares Smoothing and Differentiation by the Convolution (Savitzky-Golay) Method. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. A Solution for the Best Rotation to Relate Two Sets of Vectors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeyama, S. Least-Squares Estimation of Transformation Parameters between Two Point Patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemake, K. Animating Rotation with Quaternion Curves. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1985, 19, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, H.J.; Weijers, G.; de Wild, M.; Korsten, H.H.M.; de Korte, C.L.; Bouwman, R.A. Differences in Ultrasound Elevational Beam Width (Slice Thickness) between Popular Handheld Devices. WFUMB Ultrasound Open 2023, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A. Slice Thickness Measurements. J. Ultrasound Med. 1988, 7, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Grosso, V.A.; Mader, C.W. Speed of Sound in Pure Water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 52, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, K.; Sperl, J.I.; Vogel, M.W.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. Acoustical Properties of Selected Tissue Phantom Materials for Ultrasound Imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, N475–N484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.M.; Russell, L.; Khan, S.N. Osteoporosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000, 372, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Chi, Z. Speckle Suppression and Contrast Enhancement in Reconstruction of Freehand 3D Ultrasound Images Using an Adaptive Distance-Weighted Method. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Gao, B.; Wang, M. Robot-Assisted Autonomous Ultrasound Imaging for Carotid Artery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, R.; Salehi, M.; Jagoda, S.; Kumar, N.; Sprung, J.; Ladikos, A.; Bauer, R.; Zettinig, O.; Wein, W. 3D Freehand Ultrasound without External Tracking Using Deep Learning. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 48, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Test # | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | [mm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | x | y | z | ||||
| Origin 1 | 1 | 0.197 | 0.663 | −0.045 | 0.693 | 2.655 | 2.686 | 3.312 | 5.024 |
| 2 | −0.135 | 1.734 | −3.149 | 3.597 | 4.352 | 2.184 | 7.550 | 8.241 | |
| 3 | −0.181 | 1.765 | 1.464 | 2.301 | 1.110 | 1.219 | 4.206 | 4.518 | |
| 4 | −1.712 | 0.611 | 4.020 | 4.414 | 2.992 | 2.216 | 3.427 | 5.061 | |
| Direct | 1 | 3.947 | 0.895 | 0.792 | 4.124 | 1.899 | 2.020 | 5.005 | 5.722 |
| 2 | 0.928 | 0.599 | −2.934 | 3.135 | 4.352 | 2.184 | 7.550 | 8.984 | |
| 3 | −0.857 | 0.453 | 2.689 | 2.858 | 2.908 | 1.920 | 4.299 | 5.534 | |
| 4 | 0.675 | 3.860 | 0.373 | 3.937 | 2.206 | 1.773 | 5.817 | 6.469 | |
| Concatenation | 1 | 3.893 | 0.928 | 0.629 | 4.051 | 2.578 | 2.478 | 5.965 | 6.954 |
| 2 | 0.964 | 0.589 | −2.797 | 3.017 | 4.860 | 2.678 | 7.643 | 9.445 | |
| 3 | −0.846 | 0.505 | 2.596 | 2.777 | 3.539 | 2.496 | 4.561 | 6.290 | |
| 4 | 0.884 | 3.581 | 1.348 | 3.927 | 3.296 | 2.342 | 6.792 | 7.905 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Sanctis, L.; Carnevale, A.; Antonacci, C.; Faiella, E.; Schena, E.; Longo, U.G. Six-Degree-of-Freedom Freehand 3D Ultrasound: A Low-Cost Computer Vision-Based Approach for Orthopedic Applications. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141501
De Sanctis L, Carnevale A, Antonacci C, Faiella E, Schena E, Longo UG. Six-Degree-of-Freedom Freehand 3D Ultrasound: A Low-Cost Computer Vision-Based Approach for Orthopedic Applications. Diagnostics. 2024; 14(14):1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141501
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Sanctis, Lorenzo, Arianna Carnevale, Carla Antonacci, Eliodoro Faiella, Emiliano Schena, and Umile Giuseppe Longo. 2024. "Six-Degree-of-Freedom Freehand 3D Ultrasound: A Low-Cost Computer Vision-Based Approach for Orthopedic Applications" Diagnostics 14, no. 14: 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141501
APA StyleDe Sanctis, L., Carnevale, A., Antonacci, C., Faiella, E., Schena, E., & Longo, U. G. (2024). Six-Degree-of-Freedom Freehand 3D Ultrasound: A Low-Cost Computer Vision-Based Approach for Orthopedic Applications. Diagnostics, 14(14), 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14141501








