Acquisition and Analysis of Excised Neocortex from Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Mesoscale Diffusion MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Equipment
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. MR Imaging
2.3. Diffusion Image Processing
2.4. Tractography
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
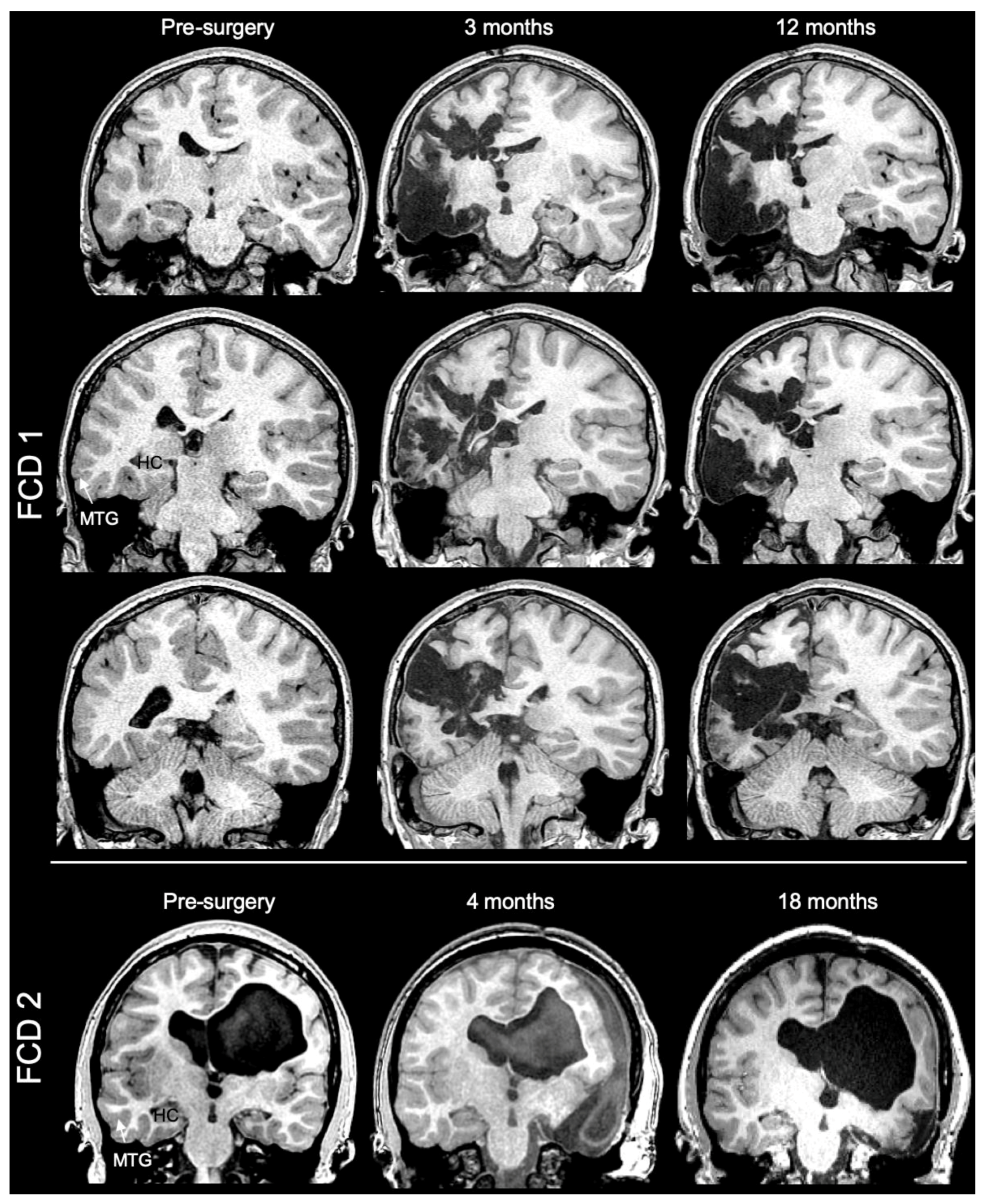
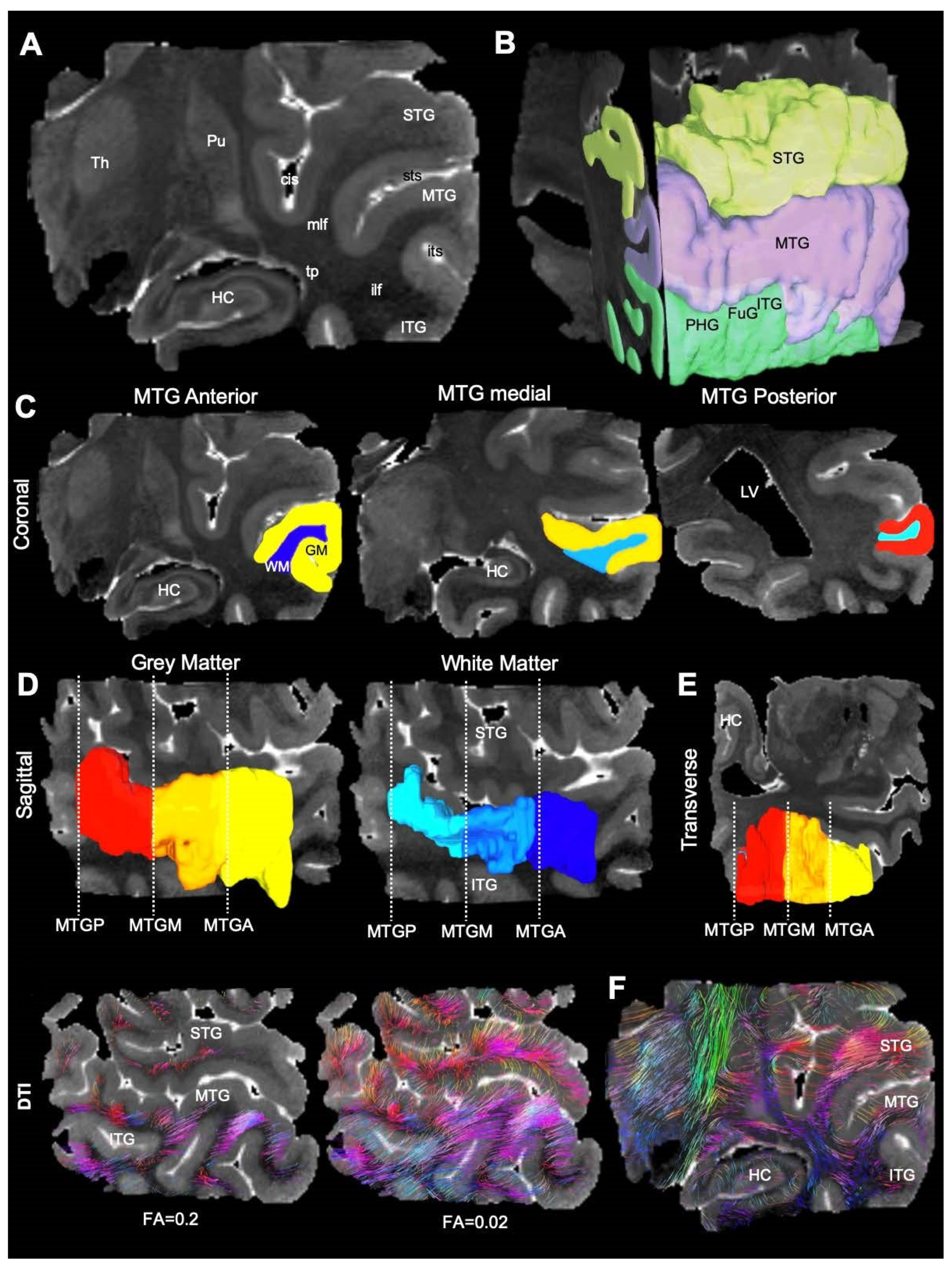
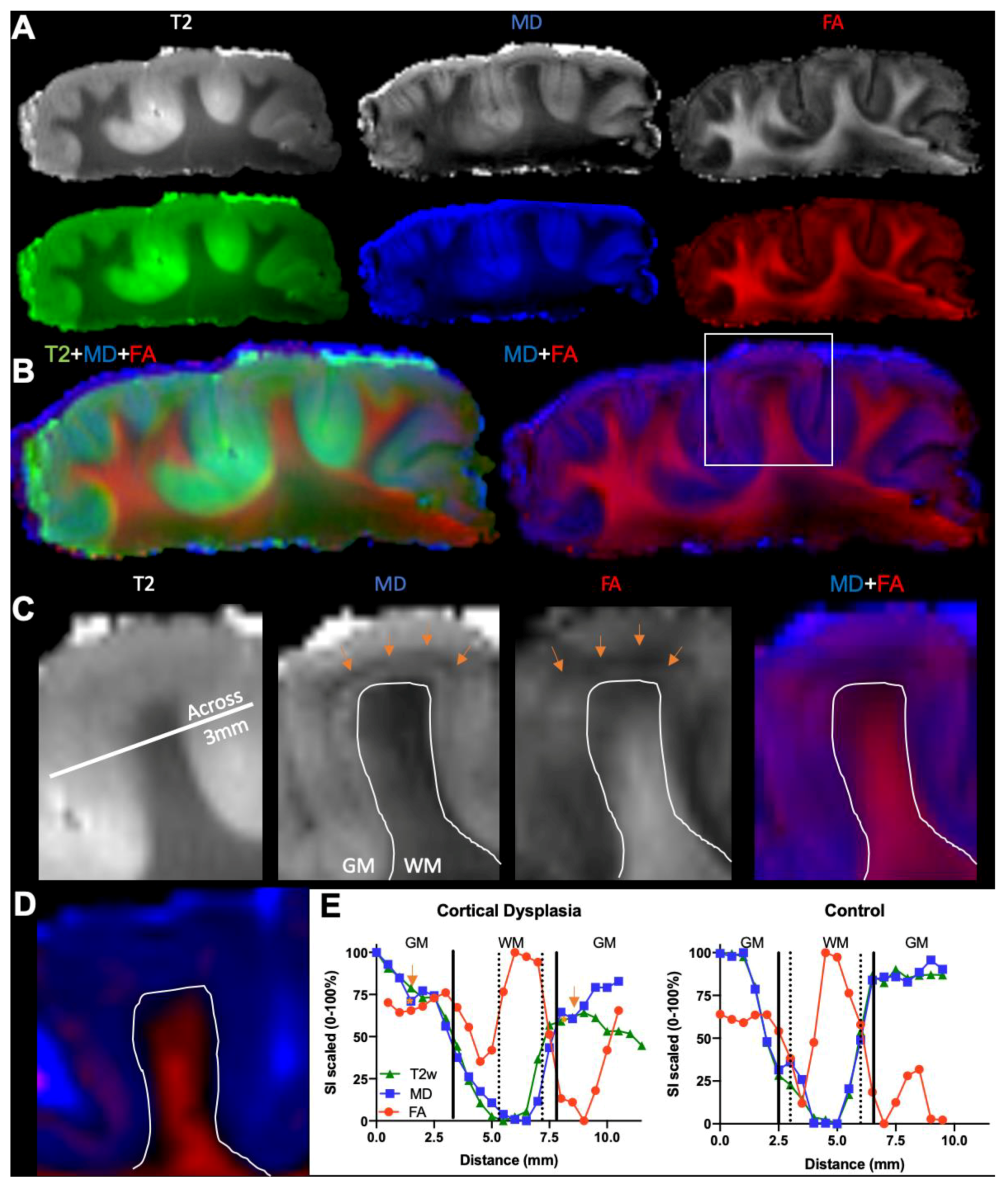
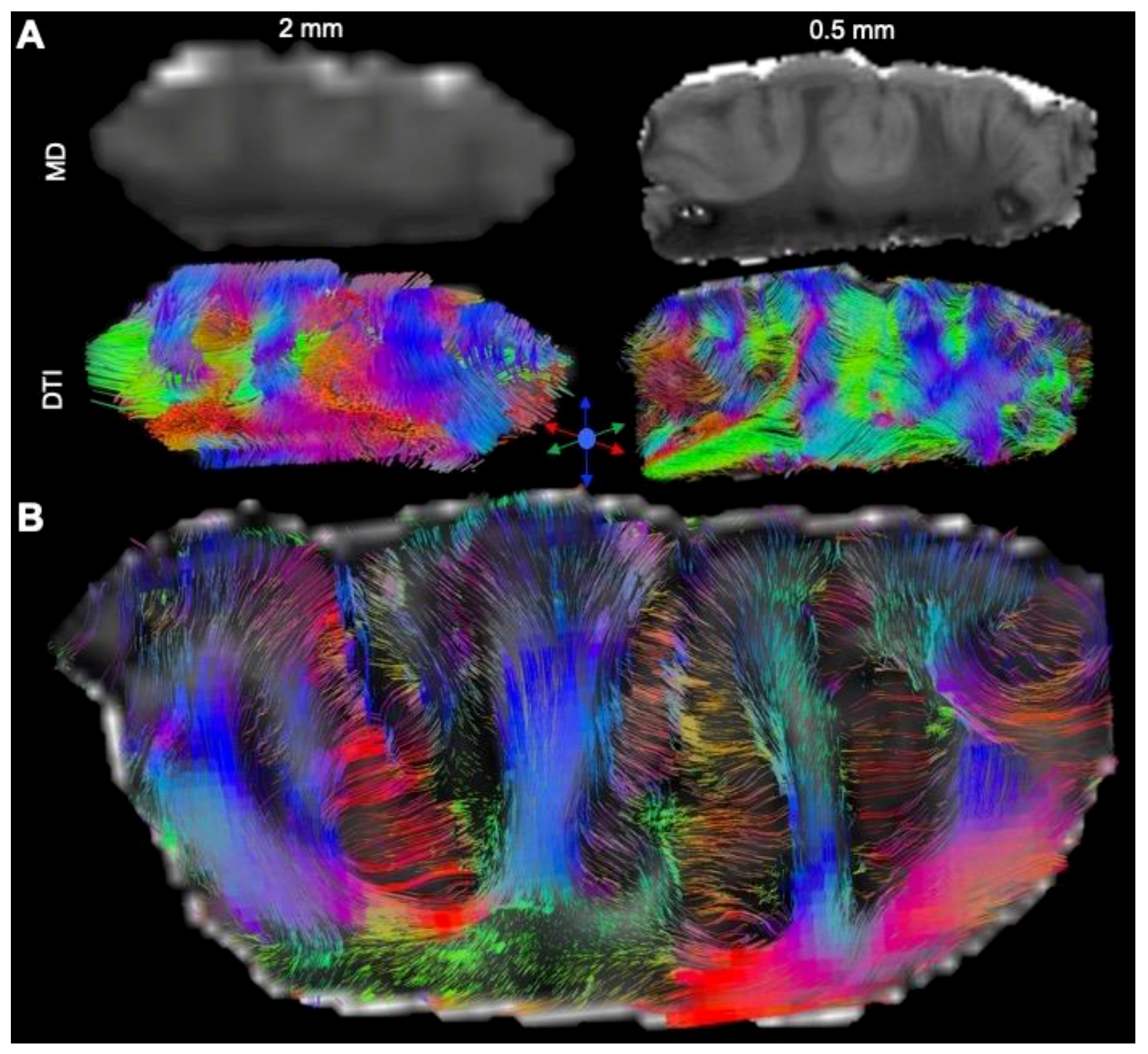
3.1. Magnetic Resonance (MR)-Histology of the Excised Human Cortex
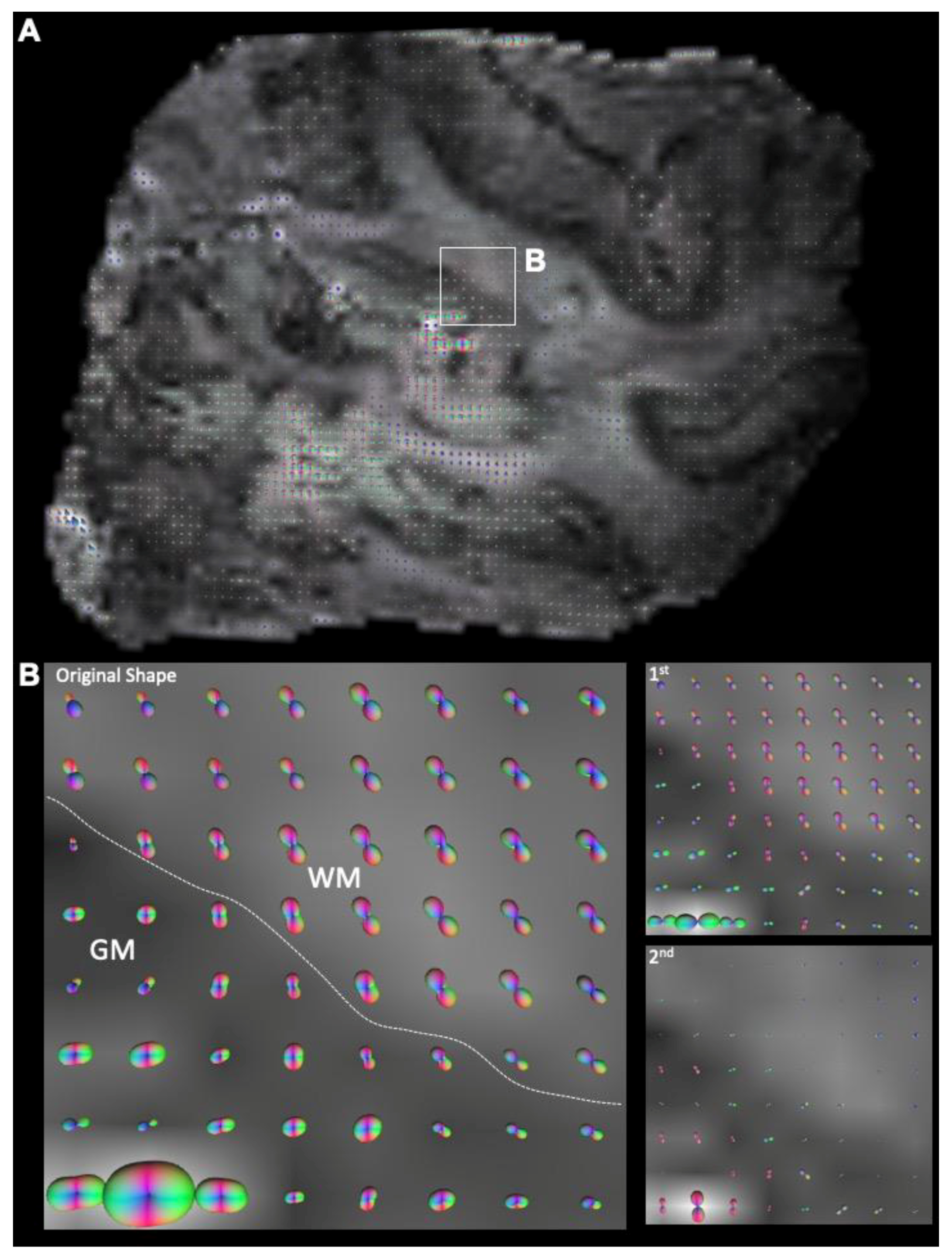
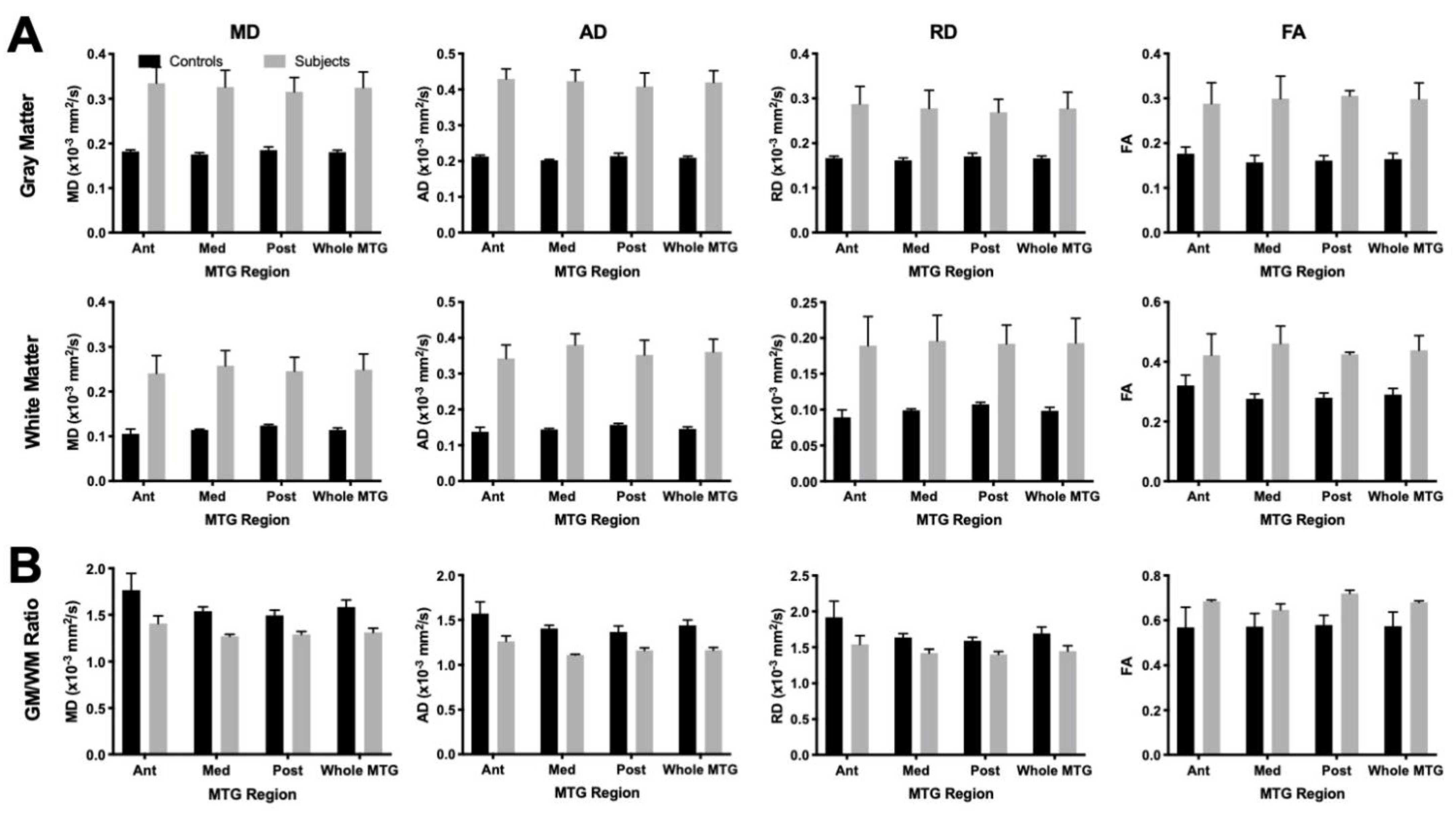
3.2. Mesoscale Diffusion Characteristics of Cortical Dysplasia
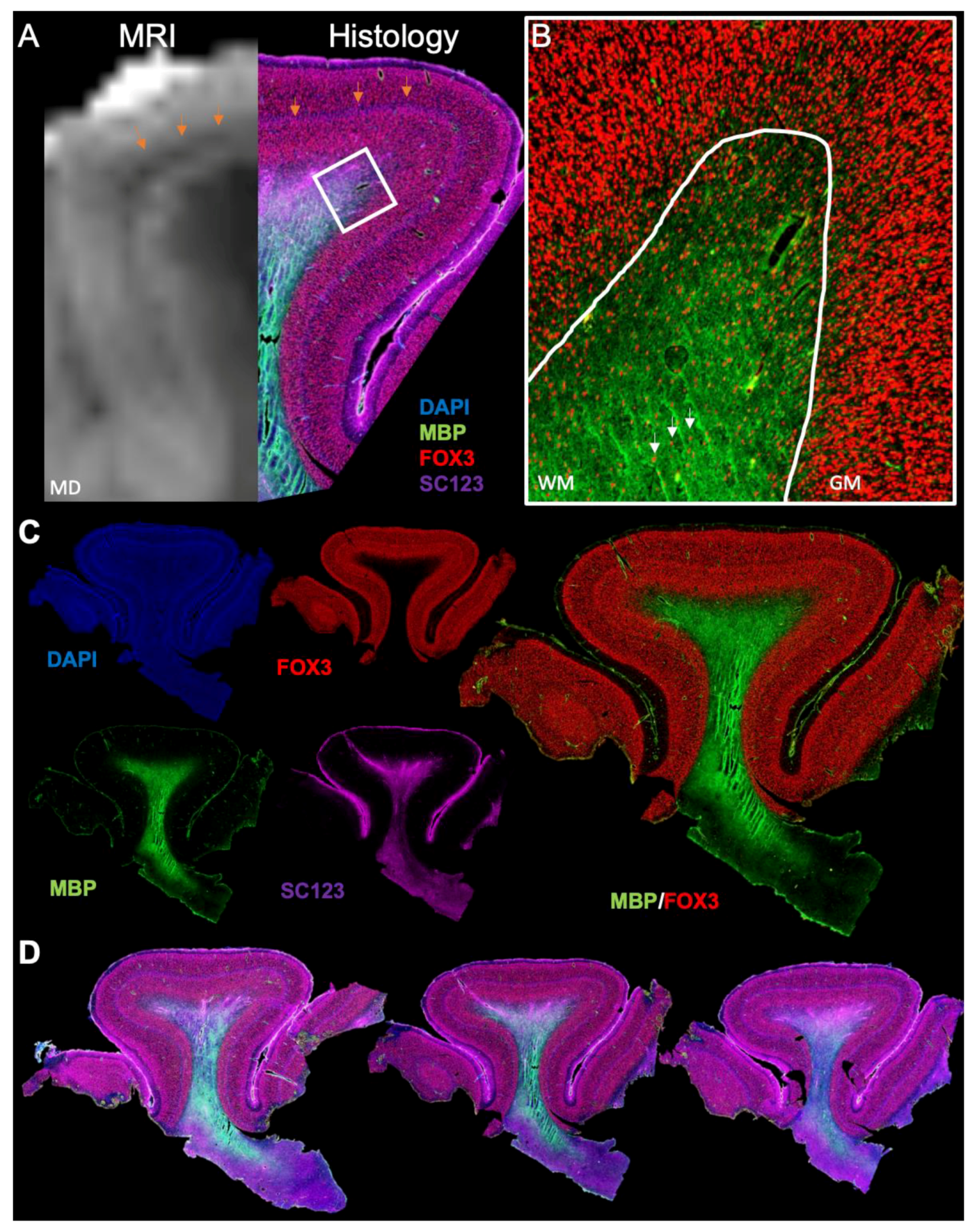
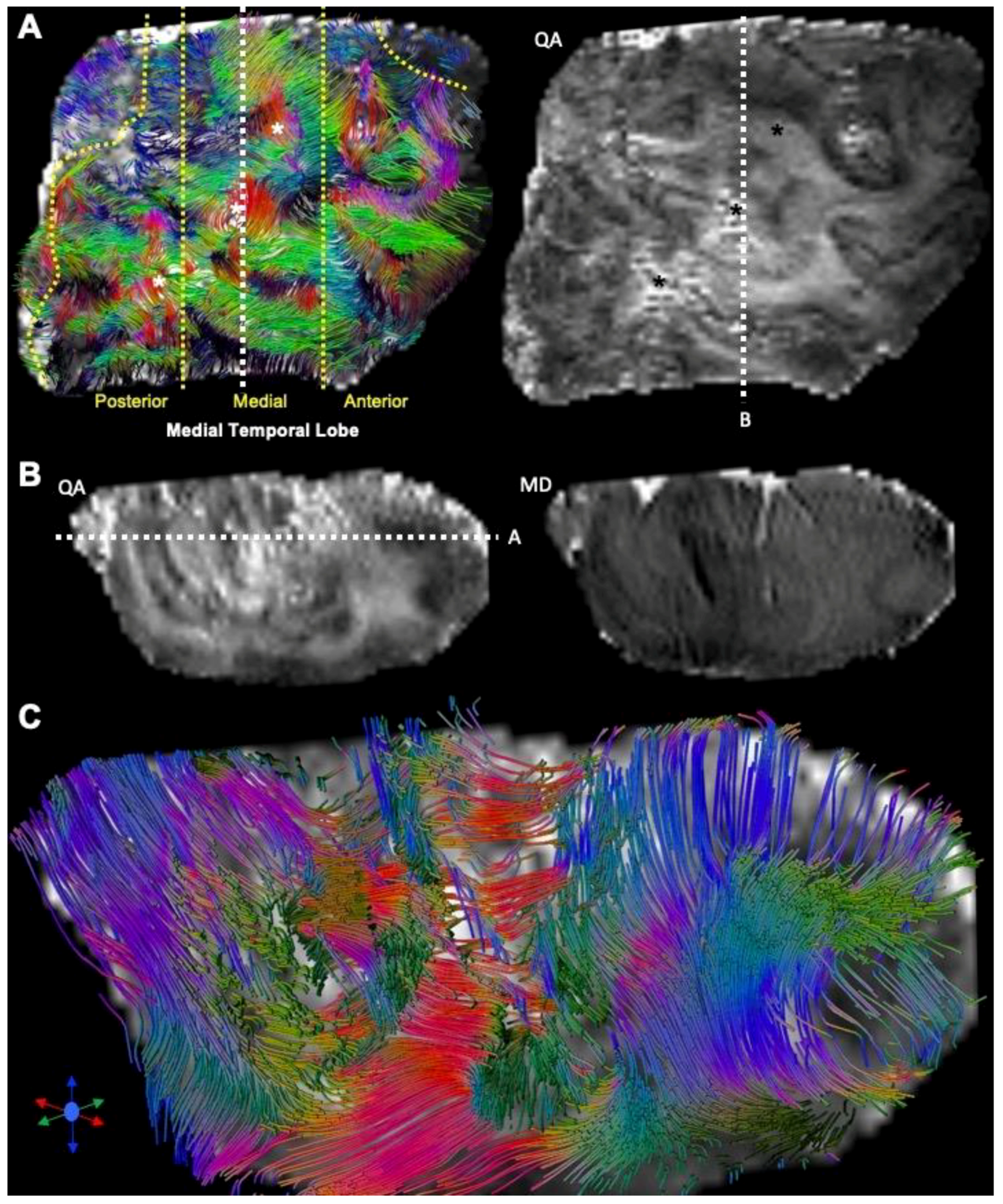
3.3. Histological Underpinnings of Grey Matter Abnormalities
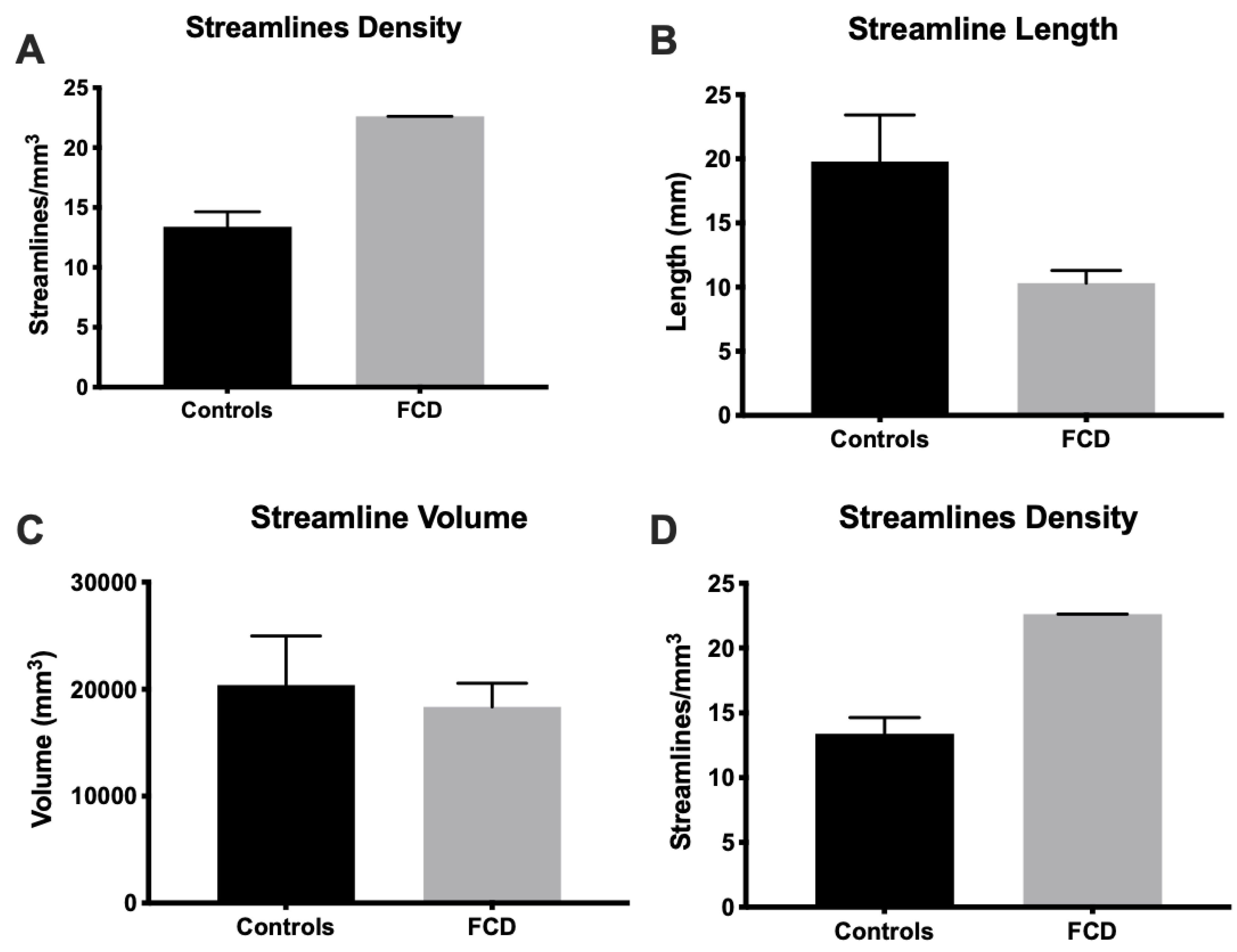
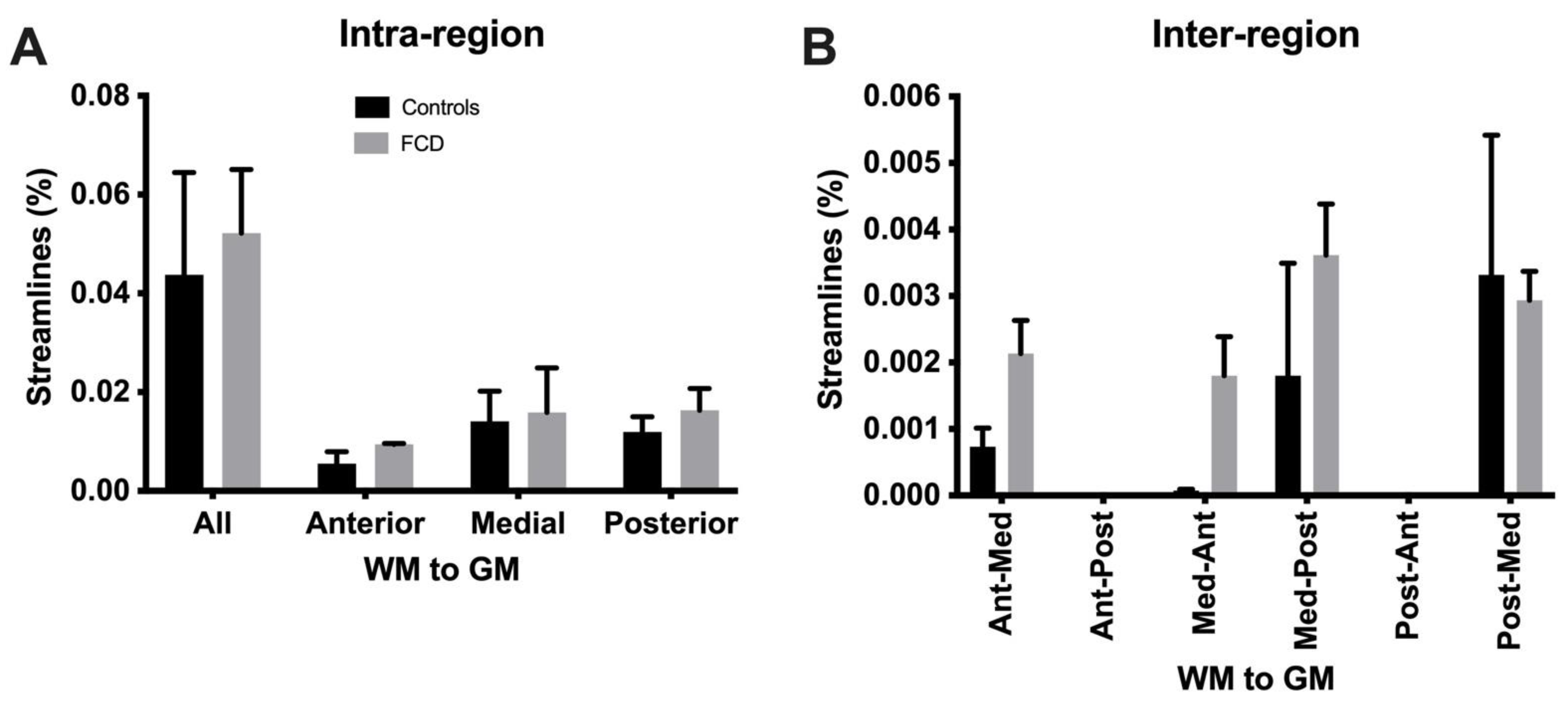
3.4. Tractography Reveals Connectivity Changes Associated with Cortical Dysplasia
4. Discussion
4.1. Ex Vivo MR Imaging as an Analytical Tool in Pediatric Epilepsy
4.2. Experimental and Interpretation Limitations Inherent to Ex Vivo Mesoscale MR Imaging and Surgical Tissue Samples
4.3. Mesoscale MR Imaging as a Frontier for Precision Medicine in Pediatric Epilepsy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crome, L. Infantile cerebral gliosis with giant nerve cells. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1957, 20, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.C.; Falconer, M.A.; Bruton, C.J.; Corsellis, J.A. Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1971, 34, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Vinters, H.V.; Palmini, A.; Jacques, T.S.; Avanzini, G.; Barkovich, A.J.; Battaglia, G.; et al. The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: A consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najm, I.M.; Sarnat, H.B.; Blumcke, I. Review: The international consensus classification of Focal Cortical Dysplasia-a critical update 2018. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisodiya, S.M.; Fauser, S.; Cross, J.H.; Thom, M. Focal cortical dysplasia type II: Biological features and clinical perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 830–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.; Lorio, S.; Jacques, T.S.; Benova, B.; Gunny, R.; Cross, J.H.; Baldeweg, T.; Carmichael, D.W. Towards in vivo focal cortical dysplasia phenotyping using quantitative MRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 15, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, J.; Krol, P. Focal cortical dysplasia-review. Pol. J. Radiol. 2012, 77, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Tassi, L.; Deleo, F.; Citterio, A.; Bramerio, M.; Mai, R.; Sartori, I.; Cardinale, F.; Lo Russo, G.; Spreafico, R. Focal cortical dysplasia type IIa and IIb: MRI aspects in 118 cases proven by histopathology. Neuroradiology 2012, 54, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, L.; Colombo, N.; Garbelli, R.; Francione, S.; Lo Russo, G.; Mai, R.; Cardinale, F.; Cossu, M.; Ferrario, A.; Galli, C.; et al. Focal cortical dysplasia: Neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain 2002, 125, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretti, A.; Meoded, A.; Rossi, A.; Raybaud, C.; Huisman, T.A. Diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography in brain malformations. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 28–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, E.; Zarei Mahmoodabadi, S.; Otsubo, H.; Snead, O.C.; Holowka, S.; Bells, S.; Raybaud, C. Subcortical alterations in tissue microstructure adjacent to focal cortical dysplasia: Detection at diffusion-tensor MR imaging by using magnetoencephalographic dipole cluster localization. Radiology 2009, 251, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, G.P. The potential role of novel diffusion imaging techniques in the understanding and treatment of epilepsy. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2015, 5, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, G.P.; Micallef, C.; Symms, M.R.; Alexander, D.C.; Duncan, J.S.; Zhang, H. Advanced diffusion imaging sequences could aid assessing patients with focal cortical dysplasia and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.K. Usefulness of diffusion tensor tractography in pediatric epilepsy surgery. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, D.I.; Mori, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.D.; Heo, K.; Lee, B.I. Diffusion tensor MRI visualizes decreased subcortical fiber connectivity in focal cortical dysplasia. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, R.M.; Jansen, J.F.; de Louw, A.J.; Vlooswijk, M.C.; Hoeberigs, M.C.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Backes, W.H.; Hofman, P.A. Abnormal Profiles of Local Functional Connectivity Proximal to Focal Cortical Dysplasias. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca Vde, C.; Yasuda, C.L.; Tedeschi, G.G.; Betting, L.E.; Cendes, F. White matter abnormalities in patients with focal cortical dysplasia revealed by diffusion tensor imaging analysis in a voxelwise approach. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Lee, H.M.; Gill, R.; Crane, J.; Sziklas, V.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A. A connectome-based mechanistic model of focal cortical dysplasia. Brain 2019, 142, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, C.; Tachrount, M.; Thomas, D.; Michalak, Z.; Liu, J.; Ellis, M.; Diehl, B.; Miserocchi, A.; McEvoy, A.W.; Eriksson, S.; et al. Combined Ex Vivo 9.4T MRI and Quantitative Histopathological Study in Normal and Pathological Neocortical Resections in Focal Epilepsy. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, I.; Milesi, G.; Medici, V.; Tassi, L.; Didato, G.; Cardinale, F.; Tringali, G.; Colombo, N.; Bramerio, M.; D’Incerti, L.; et al. Type II focal cortical dysplasia: Ex vivo 7T magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities and histopathological comparisons. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, M.; Foley, L.; Manivannan, A.; Hitchens, T.K.; Richardson, R.M.; Modo, M. Mesoscale diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of the ex vivo human hippocampus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 4200–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modo, M.; Hitchens, T.K.; Liu, J.R.; Richardson, R.M. Detection of aberrant hippocampal mossy fiber connections: Ex vivo mesoscale diffusion MRI and microtractography with histological validation in a patient with uncontrolled temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Ye, F.Q.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Modi, P.; Saleem, K.S.; Leopold, D.A.; Pierpaoli, C. Anatomical accuracy of brain connections derived from diffusion MRI tractography is inherently limited. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16574–16579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf von Keyserlingk, D.; Schramm, U. Diameter of axons and thickness of myelin sheaths of the pyramidal tract fibres in the adult human medullary pyramid. Anat. Anz. 1984, 157, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Verhaart, W.J. Anatomico-physiological considerations about a human cebocephalic monstrum. Monatsschr. Psychiatr. Neurol. 1947, 50, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, J.M.; Marques, P.; Alves, V.; Sousa, N. A hitchhiker’s guide to diffusion tensor imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Acqua, F.; Bodi, I.; Slater, D.; Catani, M.; Modo, M. MR diffusion histology and micro-tractography reveal mesoscale features of the human cerebellum. Cerebellum 2013, 12, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.K.; Knosche, T.R.; Turner, R. White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: The do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2013, 73, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Foley, L.M.; Hitchens, T.K.; Richardson, R.M.; Modo, M. Ex vivo mesoscopic diffusion MRI correlates with seizure frequency in patients with uncontrolled mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 4529–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebroeck, A.; Miller, K.L.; Aggarwal, M. Ex vivo diffusion MRI of the human brain: Technical challenges and recent advances. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.; Shi, Y. Fiber Orientation and Compartment Parameter Estimation From Multi-Shell Diffusion Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2320–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Alexander, A.L. Hybrid diffusion imaging. Neuroimage 2007, 36, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedeen, V.J.; Hagmann, P.; Tseng, W.Y.; Reese, T.G.; Weisskoff, R.M. Mapping complex tissue architecture with diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F.C.; Verstynen, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tseng, W.Y. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F.C.; Wedeen, V.J.; Tseng, W.Y. Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Watkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbelli, R.; Milesi, G.; Medici, V.; Villani, F.; Didato, G.; Deleo, F.; D’Incerti, L.; Morbin, M.; Mazzoleni, G.; Giovagnoli, A.R.; et al. Blurring in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: Clinical, high-field imaging and ultrastructural study. Brain 2012, 135, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Y. Imaging laminar structures in the gray matter with diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2019, 197, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinnijenhuis, M.; Zerbi, V.; Kusters, B.; Slump, C.H.; Barth, M.; van Cappellen van Walsum, A.M. Layer-specific diffusion weighted imaging in human primary visual cortex in vitro. Cortex 2013, 49, 2569–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampel, R.; Bazin, P.L.; Pine, K.; Weiskopf, N. In-vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of laminae in the human cortex. Neuroimage 2019, 197, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, P.D.; Sebire, N.J.; Siegel, M.J.; Olsen, O.E. Tumors in pediatric patients at diffusion-weighted MR imaging: Apparent diffusion coefficient and tumor cellularity. Radiology 2007, 245, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Iima, M. Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging: What Water Tells Us about Biological Tissues. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, E.B.; Schwerin, S.C.; Avram, A.V.; Juliano, S.L.; Pierpaoli, C. Diffusion MRI and the detection of alterations following traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.K.; Sun, S.W.; Ramsbottom, M.J.; Chang, C.; Russell, J.; Cross, A.H. Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, G.; Crooijmans, H.J.; Germann, M.; Scheffler, K.; Muller-Gerbl, M.; Muller, B. Three-dimensional strain fields in human brain resulting from formalin fixation. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 202, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelwall, P.E.; Shepherd, T.M.; Stanisz, G.J.; Blackband, S.J. Effects of temperature and aldehyde fixation on tissue water diffusion properties, studied in an erythrocyte ghost tissue model. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, L.E.M.; Adler, D.H.; Ittyerah, R.; Pluta, J.B.; Robinson, J.L.; Schuck, T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Grossman, M.; Detre, J.A.; Elliott, M.A.; et al. Comparison of In Vivo and Ex Vivo MRI of the Human Hippocampal Formation in the Same Subjects. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 5185–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamante, F. The Seven Deadly Sins of Measuring Brain Structural Connectivity Using Diffusion MRI Streamlines Fibre-Tracking. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.; Janve, V.; Gao, Y.; Stepniewska, I.; Landman, B.A.; Anderson, A.W. Comparison of 3D orientation distribution functions measured with confocal microscopy and diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2016, 129, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatil, A.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Matsuda, K.M.; Figley, C.R. Quantitative Ex Vivo MRI Changes due to Progressive Formalin Fixation in Whole Human Brain Specimens: Longitudinal Characterization of Diffusion, Relaxometry, and Myelin Water Fraction Measurements at 3T. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.M.; Thelwall, P.E.; Stanisz, G.J.; Blackband, S.J. Aldehyde fixative solutions alter the water relaxation and diffusion properties of nervous tissue. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.; Colenbier, N.; Almgren, H.; Dhollander, T.; Daparte, J.R.; Clauw, K.; Johri, A.; Meier, J.; Palmer, J.; Schirner, M.; et al. Pre- and post-surgery brain tumor multimodal magnetic resonance imaging data optimized for large scale computational modelling. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niesen, C.E.; Xu, J.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Wheeler, C.J.; Mamelak, A.N.; Wang, C. Transcriptomic profiling of human peritumoral neocortex tissues revealed genes possibly involved in tumor-induced epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawlani, V.; Patel, M.D.; Davies, N.; Flintham, R.; Wesolowski, R.; Ughratdar, I.; Pohl, U.; Nagaraju, S.; Petrik, V.; Kay, A.; et al. Multiparametric MRI: Practical approach and pictorial review of a useful tool in the evaluation of brain tumours and tumour-like lesions. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.J.; Kirilina, E.; Mohammadi, S.; Weiskopf, N. Microstructural imaging of human neocortex in vivo. Neuroimage 2018, 182, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganepola, T.; Nagy, Z.; Ghosh, A.; Papadopoulo, T.; Alexander, D.C.; Sereno, M.I. Using diffusion MRI to discriminate areas of cortical grey matter. Neuroimage 2018, 182, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuken, M.C.; Isaacs, B.R.; Trampel, R.; van der Zwaag, W.; Forstmann, B.U. Visualizing the Human Subcortex Using Ultra-high Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Brain Topogr. 2018, 31, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Poser, B.A.; Douaud, G.; Frost, R.; In, M.H.; Speck, O.; Koopmans, P.J.; Miller, K.L. High-resolution diffusion MRI at 7T using a three-dimensional multi-slab acquisition. Neuroimage 2016, 143, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Baba, H.; Ono, T.; Ono, K. The utility of diffusion tensor imaging tractography for post-operative evaluation of a patient with hemispherotomy performed for intractable epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K.; Alexander, D.C.; Bowtell, R.; Cercignani, M.; Dell’Acqua, F.; McHugh, D.J.; Miller, K.L.; Palombo, M.; Parker, G.J.M.; Rudrapatna, U.S.; et al. Microstructural imaging of the human brain with a ‘super-scanner’: 10 key advantages of ultra-strong gradients for diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2018, 182, 8–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Waldeck, S.; Mauer, U.M. Intraoperative image guidance in neurosurgery: Development, current indications, and future trends. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 197364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonutti, M.; Elson, D.S.; Yang, G.Z.; Darzi, A.W.; Sodergren, M.H. The role of technology in minimally invasive surgery: State of the art, recent developments and future directions. Postgrad. Med. J. 2017, 93, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.J.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Caldairou, B.; Hall, J.A.; Guiot, M.C.; Schrader, D.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A. Multimodal MRI profiling of focal cortical dysplasia type II. Neurology 2017, 88, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Kanner, A.M.; Friedman, A.; Blumcke, I.; Crocker, C.E.; Cendes, F.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Forstl, H.; Fenton, A.A.; Grace, A.A.; et al. Epilepsy as a Network Disorder (2): What can we learn from other network disorders such as dementia and schizophrenia, and what are the implications for translational research? Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 78, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
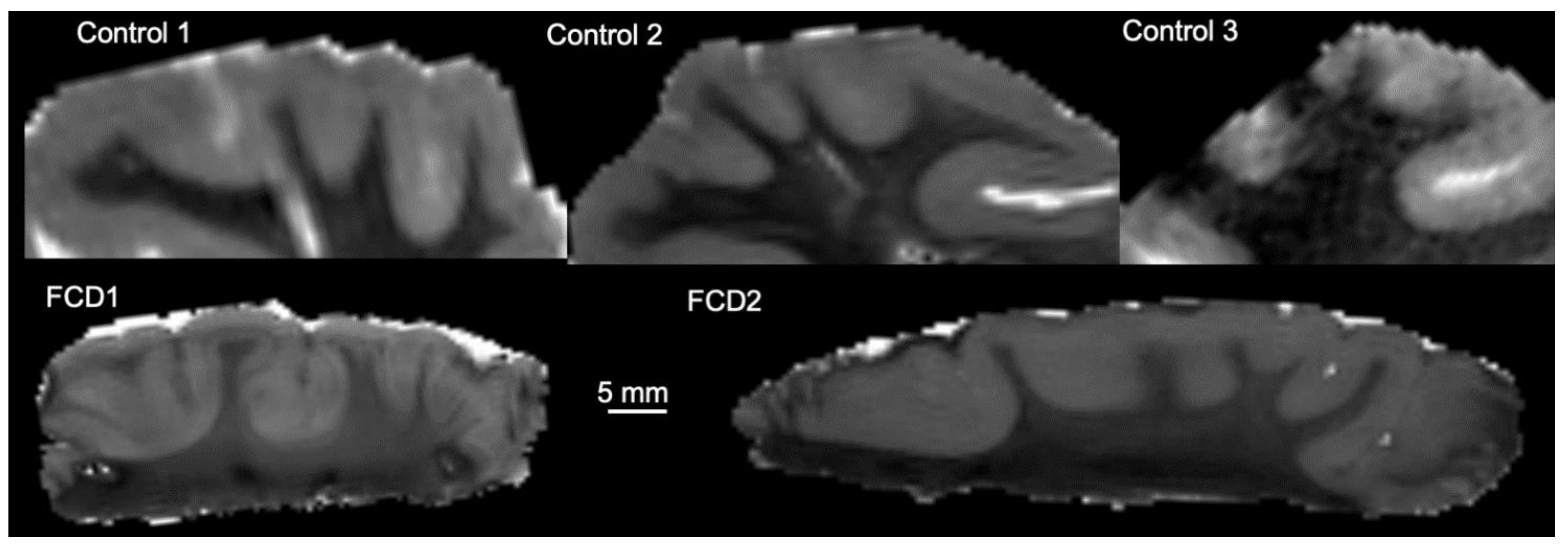
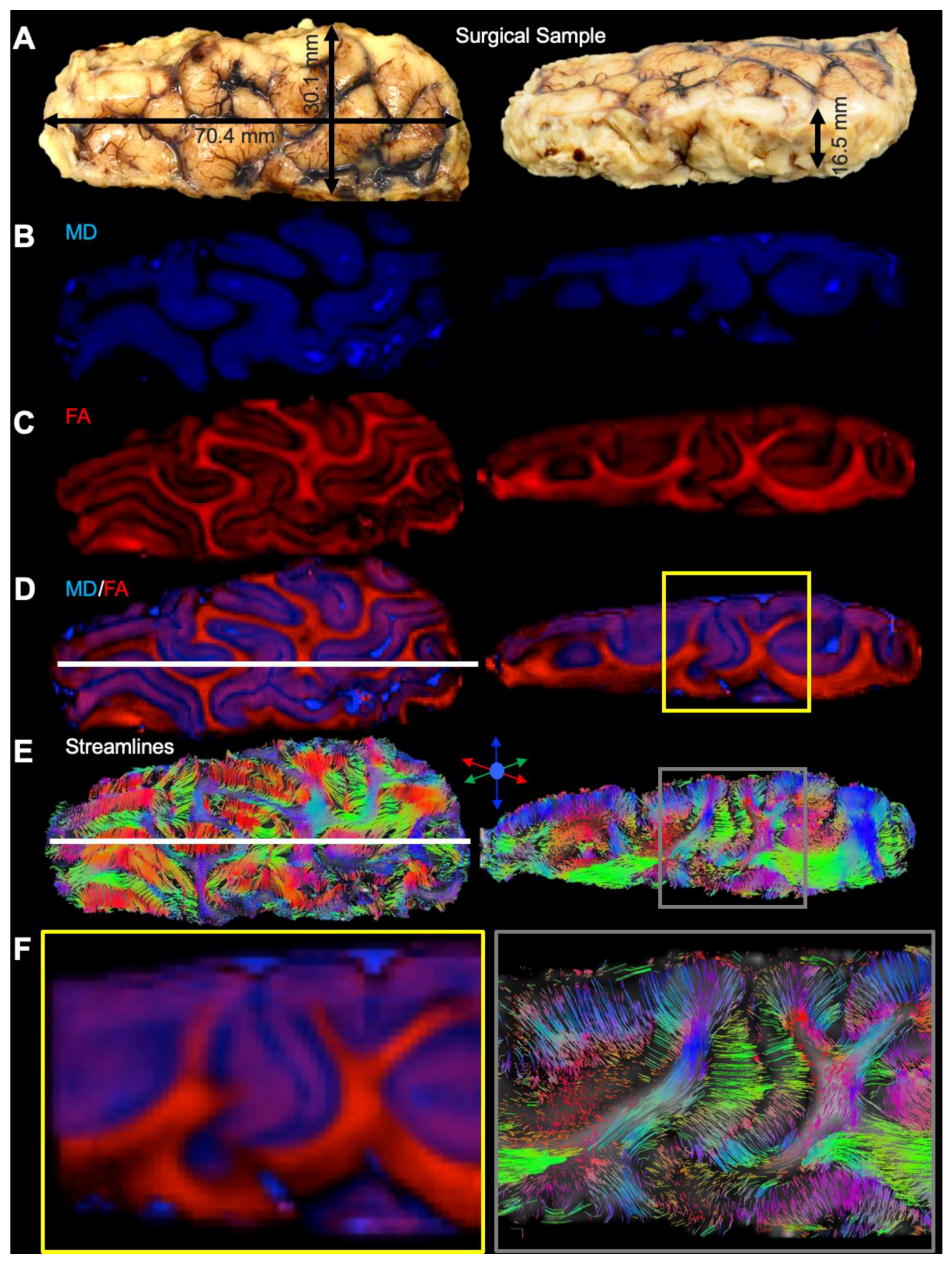
| Sample | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Volume (mm3) | Voxels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCD—A | 47.6 | 35.5 | 19.1 | 21,765 | 174,121 |
| FCD—B | 70.4 | 30.1 | 16.5 | 22,553 | 180,423 |
| Control—A | 58.6 | 50.8 | 60.9 | 143,365 | 1,146,920 |
| Control—B | 56.4 | 57.5 | 58.2 | 145,200 | 1,161,600 |
| Control—C | 62.9 | 42.6 | 64.3 | 123,095 | 984,759 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fountain, C.; Ghuman, H.; Paldino, M.; Tamber, M.; Panigrahy, A.; Modo, M. Acquisition and Analysis of Excised Neocortex from Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Mesoscale Diffusion MRI. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091529
Fountain C, Ghuman H, Paldino M, Tamber M, Panigrahy A, Modo M. Acquisition and Analysis of Excised Neocortex from Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Mesoscale Diffusion MRI. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(9):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091529
Chicago/Turabian StyleFountain, Chandler, Harmanvir Ghuman, Michael Paldino, Mandeep Tamber, Ashok Panigrahy, and Michel Modo. 2023. "Acquisition and Analysis of Excised Neocortex from Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Mesoscale Diffusion MRI" Diagnostics 13, no. 9: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091529
APA StyleFountain, C., Ghuman, H., Paldino, M., Tamber, M., Panigrahy, A., & Modo, M. (2023). Acquisition and Analysis of Excised Neocortex from Pediatric Patients with Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using Mesoscale Diffusion MRI. Diagnostics, 13(9), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13091529






