Ultrasound Imaging for Diaphragm Function in a Population of Healthy Infants: A Short Observational Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
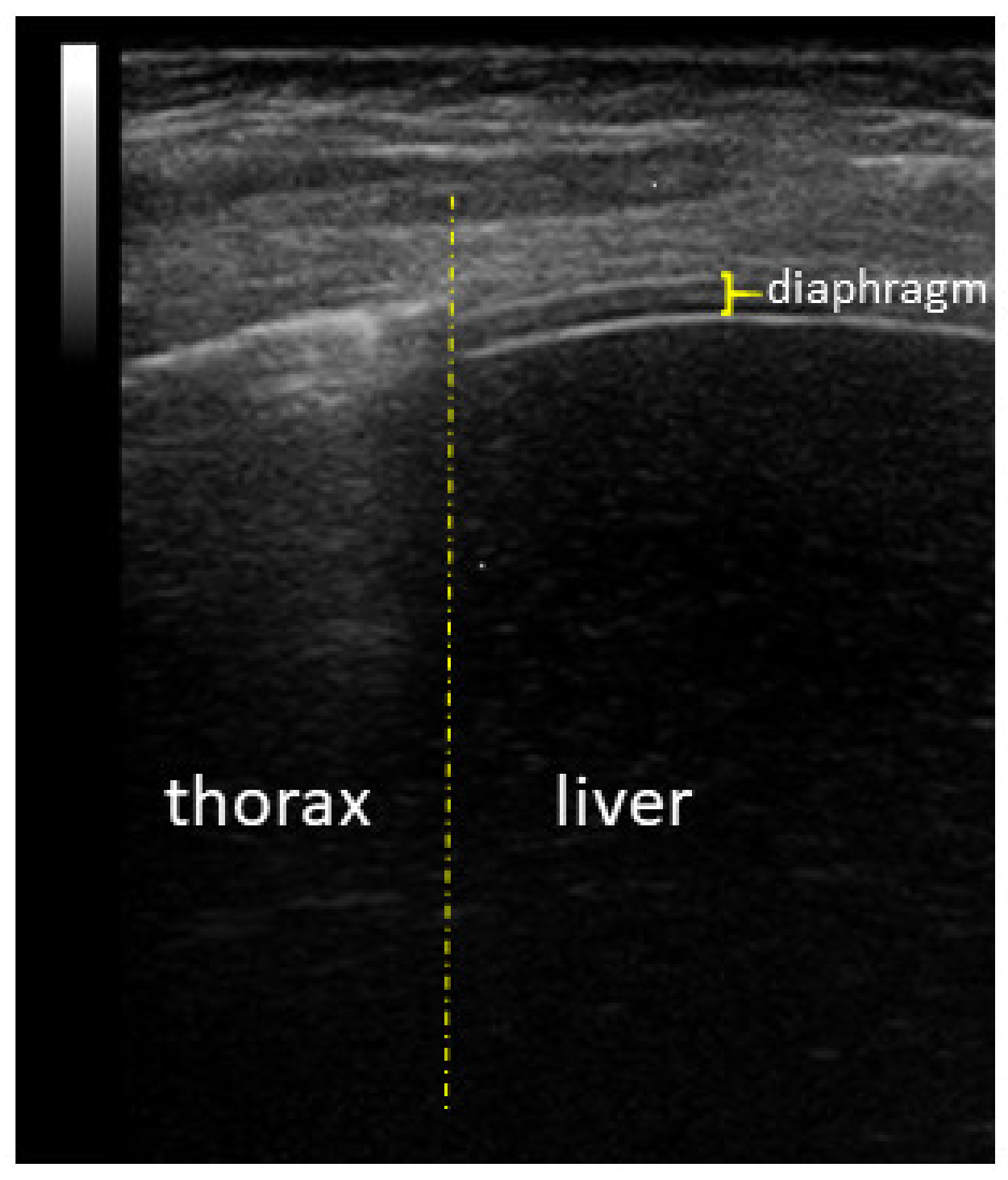
Diaphragm Ultrasound
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dassios, T.; Vervenioti, A.; Dimitriou, G. Respiratory muscle function in the newborn: A narrative review. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 91, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Physiology masterclass: Extremes of age: Newborn and infancy. Breathe 2016, 12, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.; Telias, I.; Beitler, J.R. Esophageal Manometry. Respir. Care 2020, 65, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.D.; Lim, J.K.B.; Glau, C.; Conlon, T.; James, R.; Lee, J.H. A narrative review of diaphragmatic ultrasound in pediatric critical care. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 2471–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, J.; De Bruin, P.F.; Pride, N.B. In vivo assessment of diaphragm contraction by ultrasound in normal subjects. Thorax 1995, 50, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, V.K.; McCool, F.D. Diaphragm dimensions of the healthy term infant. Acta Paediatr. 2003, 92, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.A.; Epelman, M.; Navarro, O.M. Ultrasound imaging of diaphragmatic motion. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Supino, M.C.; Giglioni, E.; Battaglia, M.; Mesturino, A.; Scateni, S.; Scialanga, B.; Reale, A.; Musolino, A.M.C. Point of care diaphragm ultrasound in infants with bronchiolitis: A prospective study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Ojembarrena, A.; Ruiz-González, E.; Estepa-Pedregosa, L.; Armenteros-López, A.I.; Segado-Arenas, A.; Lubián-López, S.P. Reproducibility and reference values of diaphragmatic shortening fraction for term and premature infants. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Halaby, H.; Abdel-Hady, H.; Alsawah, G.; Abdelrahman, A.; El-Tahan, H. Sonographic evaluation of diaphragmatic excursion and thickness in healthy infants and children. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Berti, B.; Palermo, C.; Leone, D.; Ferrantini, G.; De Sanctis, R.; Onesimo, R.; Curatola, A.; Fanelli, L.; Forcina, N.; et al. Ultrasound assessment of diaphragmatic function in type 1 spinal muscular atrophy. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, B.; Buonsenso, D.; De Rose, C.; Ferrantini, G.; De Sanctis, R.; Forcina, N.; Mercuri, E.; Pane, M. Point-of-care lung and diaphragm ultrasound in a patient with spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1. J. Ultrasound 2022, 25, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, M.; Greco, M.; Bocchino, S.; Cabrini, L.; Beccaria, P.F.; Zangrillo, A. Assessment of diaphragmatic dysfunction in the critically ill patient with ultrasound: A systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, M.; Hedenstierna, G.; Roneus, A.; Segelsjö, M.; Larsson, A.; Perchiazzi, G. The Diaphragm Acts as a Brake during Expiration to Prevent Lung Collapse. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Echography | Second Echography | Third Echography | Fourth Echography | Fifth Echography | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 22) | (N = 6) | (N = 25) | (N = 24) | (N = 8) | |
| Weight (Kg) | |||||
| median (IQR) | 3.23 (2.88–3.41) | 3.35 (3.03–3.70) | 3.89 (35.60–4.38) | 5.50 (5.04–5.92) § | 7.44 (6.79–8.11) |
| mean (SD) | 3.17 (0.47) | 3.38 (0.52) | 4 (0.63) | 5.52 (0.79) § | 7.51 (0.91) |
| Chest circumference (cm) | |||||
| median (IQR) | 33.30 (31.50–34.72) | 34.90 (31.12–35.70) | 35.50 (34.45–37.05) | 39.80 (39.00–41.10) § | 45.25 (42.30–46.67) |
| mean (SD) | 33.07 (1.63) | 33.78 (2.67) | 35.80 (2.37) | 40.00 (2.33) § | 45.14 (3.42) |
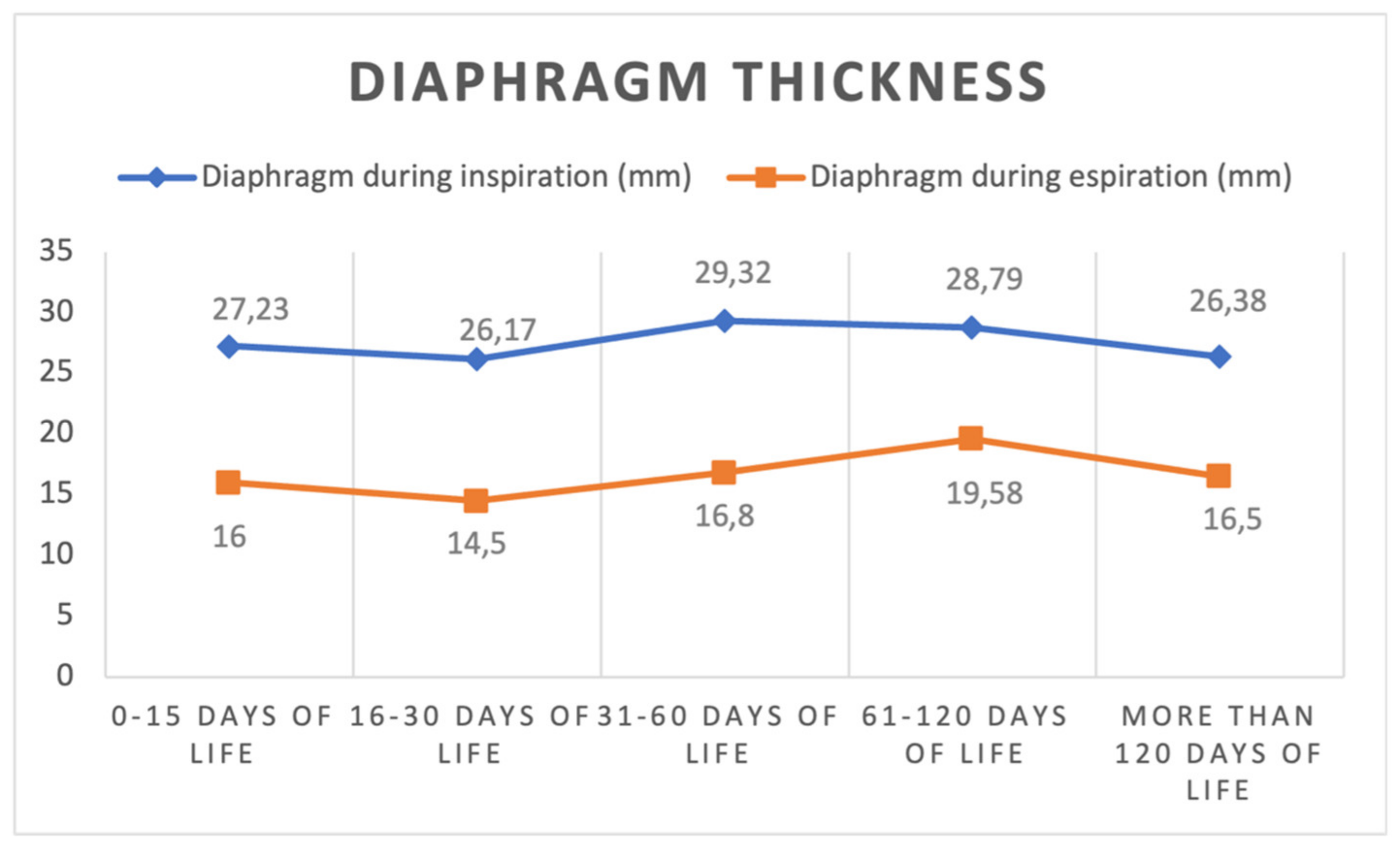
| Diaphragm thickness in inspiration (mm) | |||||
| median (IQR) | 27 (20.00–31.75) | 25 (23.00–29.25) | 30.00 (25.00–33.00) | 29.00 (23.50–34.00) | 26.00 (22.50–32.50) |
| mean (SD) | 27.23 (7.07) | 26.17 (7.11) | 29.32 (6.52) | 28.79 (5.94) | 26.38 (5.78) |
| Diaphragm thickness in expiration (mm) | |||||
| median (IQR) | 15 (14–17) | 15.50 (12.75–16.25) | 16 (13.50–20.00) | 19.50 (15.25–22.75) | 18 (14.25–18.75) |
| mean (SD) | 16 (4.83) | 14.50 (2.88) | 16.80 (4.90) | 19.58 (4.81) | 16.50 (2.88) |
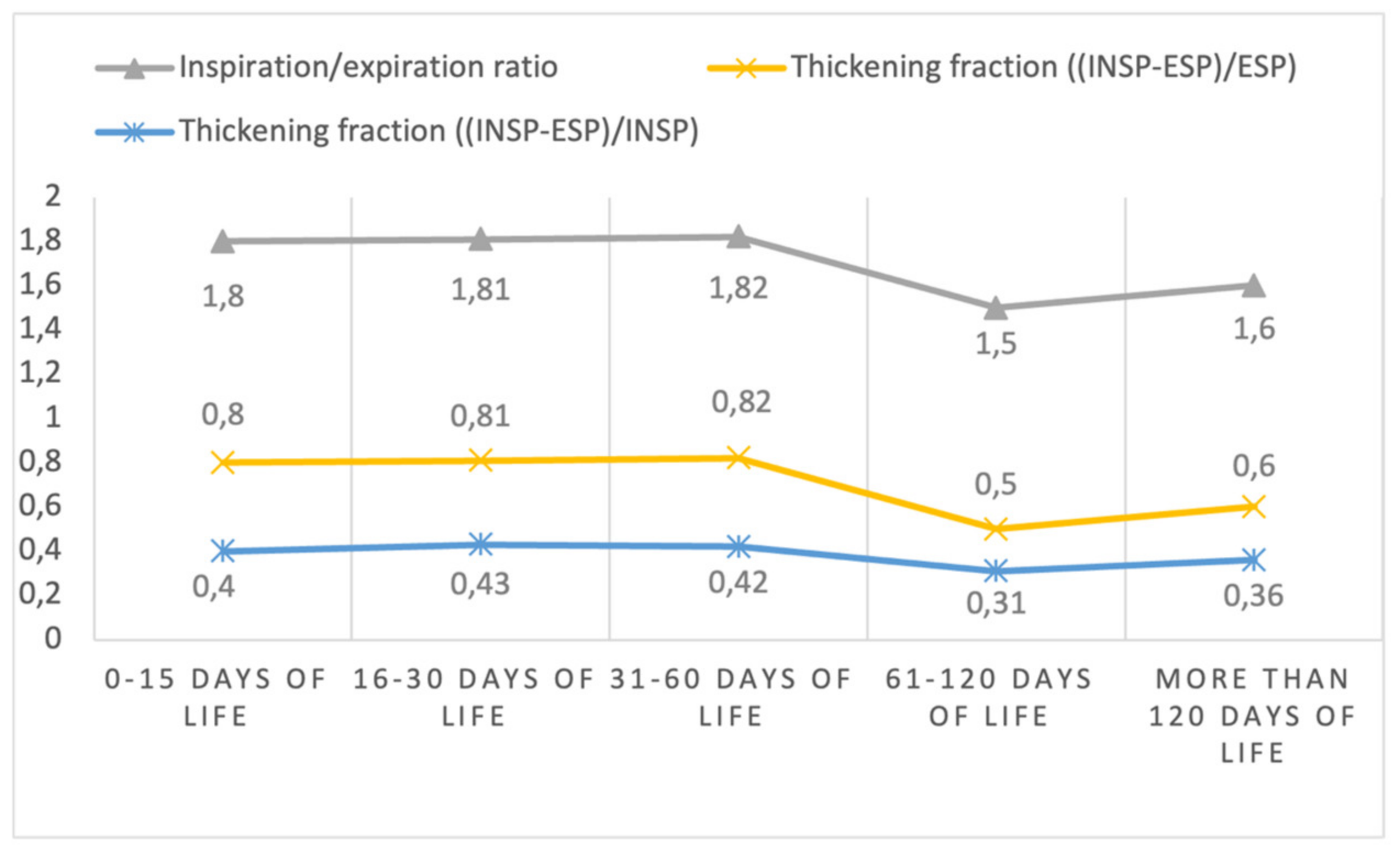
| Diaphragm Inspiration-expiration ratio | |||||
| median (IQR) | 1.68 (1.41–1.94) | 1.76 (1.54–2.03) | 1.69 (1.46–2.19) | 1.47 (1.26–1.70) | 1.56 (1.43–1.83) |
| mean (SD) | 1.80 (0.65) | 1.81 (0.35) | 1.82 (0.47) | 1.50 (0.30) | 1.60 (0.20) |
| Diaphragm thickening fraction * | |||||
| median (IQR) | 0.68 (0.41–0.94) | 0.76 (0.54–1.03) | 0.69 (0.46–1.19) | 0.47 (0.26–0.70) | 0.56 (0.43–0.83) |
| mean (SD) | 0.80 (0.65) | 0.81 (0.35) | 0.82 (0.47) | 0.50 (0.30) | 0.60 (0.20) |
| Diaphragm thickening fraction ** | |||||
| median (IQR) | 0.41 (0.29–0.48) | 0.43 (0.35–0.50) | 0.41 (0.31–0.54) | 0.32 (0.21–0.41) | 0.36 (0.30–0.45) |
| mean (SD) | 0.40 (0.15) | 0.43 (0.09) | 0.42 (0.14) | 0.31 (0.13) | 0.36 (0.08) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buonsenso, D.; Mariani, F.; Morello, R.; Cammarota, G.; De Rose, C.; Valentini, P.; Camporesi, A.; Vetrugno, L. Ultrasound Imaging for Diaphragm Function in a Population of Healthy Infants: A Short Observational Report. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061095
Buonsenso D, Mariani F, Morello R, Cammarota G, De Rose C, Valentini P, Camporesi A, Vetrugno L. Ultrasound Imaging for Diaphragm Function in a Population of Healthy Infants: A Short Observational Report. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(6):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061095
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuonsenso, Danilo, Francesco Mariani, Rosa Morello, Gianmaria Cammarota, Cristina De Rose, Piero Valentini, Anna Camporesi, and Luigi Vetrugno. 2023. "Ultrasound Imaging for Diaphragm Function in a Population of Healthy Infants: A Short Observational Report" Diagnostics 13, no. 6: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061095
APA StyleBuonsenso, D., Mariani, F., Morello, R., Cammarota, G., De Rose, C., Valentini, P., Camporesi, A., & Vetrugno, L. (2023). Ultrasound Imaging for Diaphragm Function in a Population of Healthy Infants: A Short Observational Report. Diagnostics, 13(6), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13061095








