Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Portosystemic Shunt
Abstract
1. Introduction
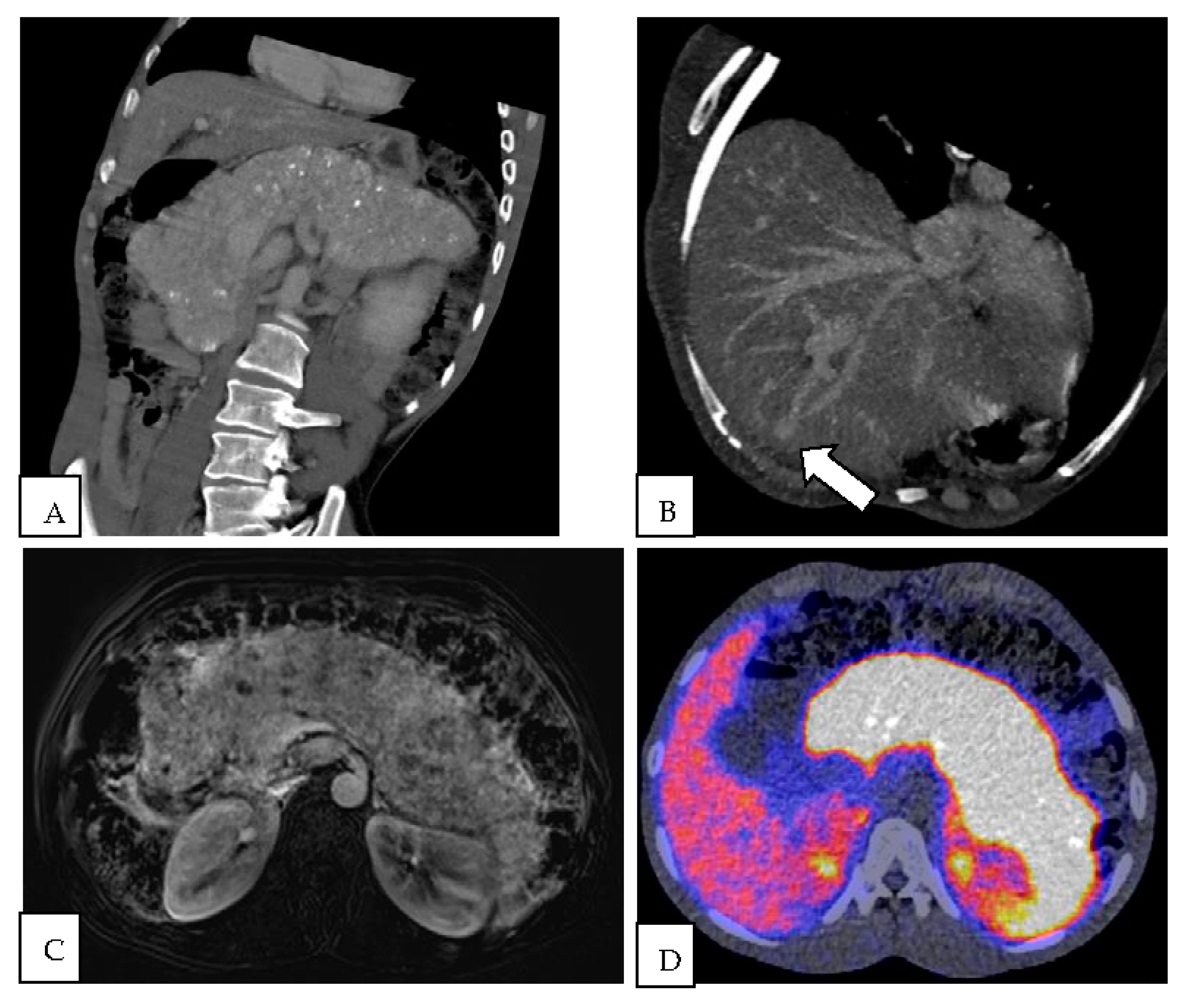
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsumoto, S.; Haberle, J.; Kido, J.; Mitsubuchi, H.; Endo, F.; Nakamura, K. Urea cycle disorders—Update. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, K.; Anderson, A.A.; Whitehead, M.T.; Gropman, A.L. Review of Multi-Modal Imaging in Urea Cycle Disorders: The Old, the New, the Borrowed, and the Blue. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 632307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monardo, A.S.; Marcus, A.J.; Berry, A.C. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor-Induced Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in the Absence of Hepatic Involvement. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbridge, V.; Townsend, A.; Pittman, K.; Kimber, R.; Patterson, W.; Sukumaran, S.; Price, T. Reversing Hyperammonemia in Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, e186–e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepatic encephalopathy in a 40-year-old woman. Am. J. Med. 1991, 90, 374–380. [CrossRef]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Deodhar, A.; Thornton, R.H.; Allen, P.J.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Brown, K.T.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Reidy, D.L. Resolution of Hepatic Encephalopathy Following Hepatic Artery Embolization in a Patient with Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumor Metastatic to the Liver. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türken, O.; Başekim, C.; Haholu, A.; Karagoz, B.; Bilgi, O.; Özgün, A.; Küçükardalı, Y.; Narin, Y.; Yazgan, Y.; Kandemir, E.G. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy in a patient with primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2009, 26, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Calhoun, S.; Shin, M.; Katz, R. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with Atypical Radiologic Presentation. Radiol. Case Rep. 2008, 3, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, A.; Philips, C.; Patidar, Y. Successful management of refractory hyperammonemia in metastatic neuroendocrine tumor. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2016, 3, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, T.; Kunnen, J.; Simoens, M. Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in Diffuse Liver Metastasis: Is This the End Stage? Gastroenterology 2012, 143, e9–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redant, S.; Empain, A.; Mugisha, A.; Kamgang, P.; Attou, R.; Honoré, P.M.; De Bels, D. Management of late onset urea cycle disorders—A remaining challenge for the intensivist? Ann. Intensiv. Care 2021, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Nagalli, S. Hyperammonemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557504/ (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, L.; Prasad, S.R.; Sunnapwar, A.; Kondapaneni, S.; Dasyam, A.; Tammisetti, V.S.; Salman, U.; Nazarullah, A.; Katabathina, V.S. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: 2020 Update on Pathologic and Imaging Findings and Classification. RadioGraphics 2020, 40, 1240–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Suz, P.; Reljic, T.; Are, A.C.; Kumar, A.; Powers, B.; Strosberg, J.; Denbo, J.W.; Fleming, J.B.; Anaya, D.A. Perioperative Carcinoid Crisis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naringrekar, H.; Vogel, A.; Prestipino, A.; Shahid, H. Imitators of chronic pancreatitis: Diffuse neuroendocrine tumour of the pancreas. BJR|Case Rep. 2017, 3, 20170015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santes, O.; Morales-Maza, J.; Domínguez-Rosado, I. Diffuse Enlargement of the Pancreas: An Unusual Radiologic Presentation of a Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, e165–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, P.; Haque, K.; Yang, Z.; Sangster, G. Diffuse Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor: A Rare Presentation. Indian J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 33, 364–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, N.-S.; Salahshour, F.; Taslimi, R.; Yazdi, N.A.; Esfandbod, M. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor presenting as a diffuse pancreatic enlargement, case report and review of literature. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, N.; Imaizumi, T.; Okada, K.-I.; Matsuyama, M.; Dowaki, S.; Tobita, K.; Ohtani, Y.; Ogoshi, K.; Hirabayashi, K.; Makuuchi, H. Nonfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumor with extension into the main pancreatic duct: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2011, 41, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Caplin, M.E.; Kunz, P.L.; Ruszniewski, P.B.; Bodei, L.; Hendifar, A.; Mittra, E.; Wolin, E.M.; Yao, J.C.; E Pavel, M.; et al. 177Lu-Dotatate plus long-acting octreotide versus high-dose long-acting octreotide in patients with midgut neuroendocrine tumours (NETTER-1): Final overall survival and long-term safety results from an open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cause | Mechanism or Examples |
|---|---|
| Extensive liver disease due to cirrhosis or metastases | Impaired urea cycle due to damaged hepatocytes and portosystemic shunting |
| Kidney failure | Excess of ammonia cannot be excreted as urea |
| Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth | Increased production of ammonia |
| Urease producing infection/sepsis | Increased production of ammonia, e.g., Proteus, H.Pylori, Nocardia, Klebsiella, Cryptococcus, Mycoplasma |
| Drugs | Valproic acid, carbamazepine, salicylate intoxication, f-fluorouracil, L-asparaginase |
| Reye syndrome | Impaired urea cycle, mitochondrial dysfunction |
| Reference | Differentiation | Grade NEN |
|---|---|---|
| Naringrekar et al., 2017 [16] | Unknown | Grade 2 (KI-67: 5%) |
| Singh et al., 2008 [8] | Well | Unknown |
| Santes et al., 2017 [17] | Well | Grade 1 (Ki-67: <1%) |
| Bhargava et al., 2018 [18] | Well | Grade 1 (Ki-67: <2%) |
| Salahshour et al., 2021 [19] | Well | Grade 1 (Ki-67: <1%) |
| Yazawa et al., 2011 [20] | Well | Grade 3 (Ki-67: 30–40%) |
| Reference | Pancreatic Involvement NET | Hepatic Involvement NET | Hepatic Vascular Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monardo et al., 2020 [3] | Yes | No | Possible portosystemic shunt. |
| Broadbridge et al., 2010 [4] | Yes | Yes | Portosystemic shunt due to portal vein thrombosis. |
| Clinicopathologic conference. 1991 [5] | Yes | Yes | Portosystemic shunt due to tumoral portal vein thrombosis. |
| Erinjeri et al., 2010 [6] | Yes | Yes | Portosystemic shunt due to arterioportal shunt. |
| Turken et al., 2009 [7] | No | Yes | No. |
| Singh et al., 2008 [8] | Yes | No | Atypical hemangioma. Signs of portal hypertension (splenomegaly, engorgement of portal vein and esophageal varices) but no cirrhosis. |
| Pande et al., 2016 [9] | No | Yes | No. |
| Vandamme et al., 2012 [10] | Yes | Yes | Mechanical compression of tumor on portal vein. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zorgdrager, M.; Cuperus, F.J.C.; de Haas, R.J. Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Portosystemic Shunt. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030572
Zorgdrager M, Cuperus FJC, de Haas RJ. Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Portosystemic Shunt. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030572
Chicago/Turabian StyleZorgdrager, Marcel, Frans J. C. Cuperus, and Robbert J. de Haas. 2023. "Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Portosystemic Shunt" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030572
APA StyleZorgdrager, M., Cuperus, F. J. C., & de Haas, R. J. (2023). Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy in a Patient with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Portosystemic Shunt. Diagnostics, 13(3), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030572







