Diagnostic Value of Whole-Blood and Plasma Samples in Epstein–Barr Virus Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Nucleic Acid Amplification Test
2.4. Data Interpretation and Statistical Analysis
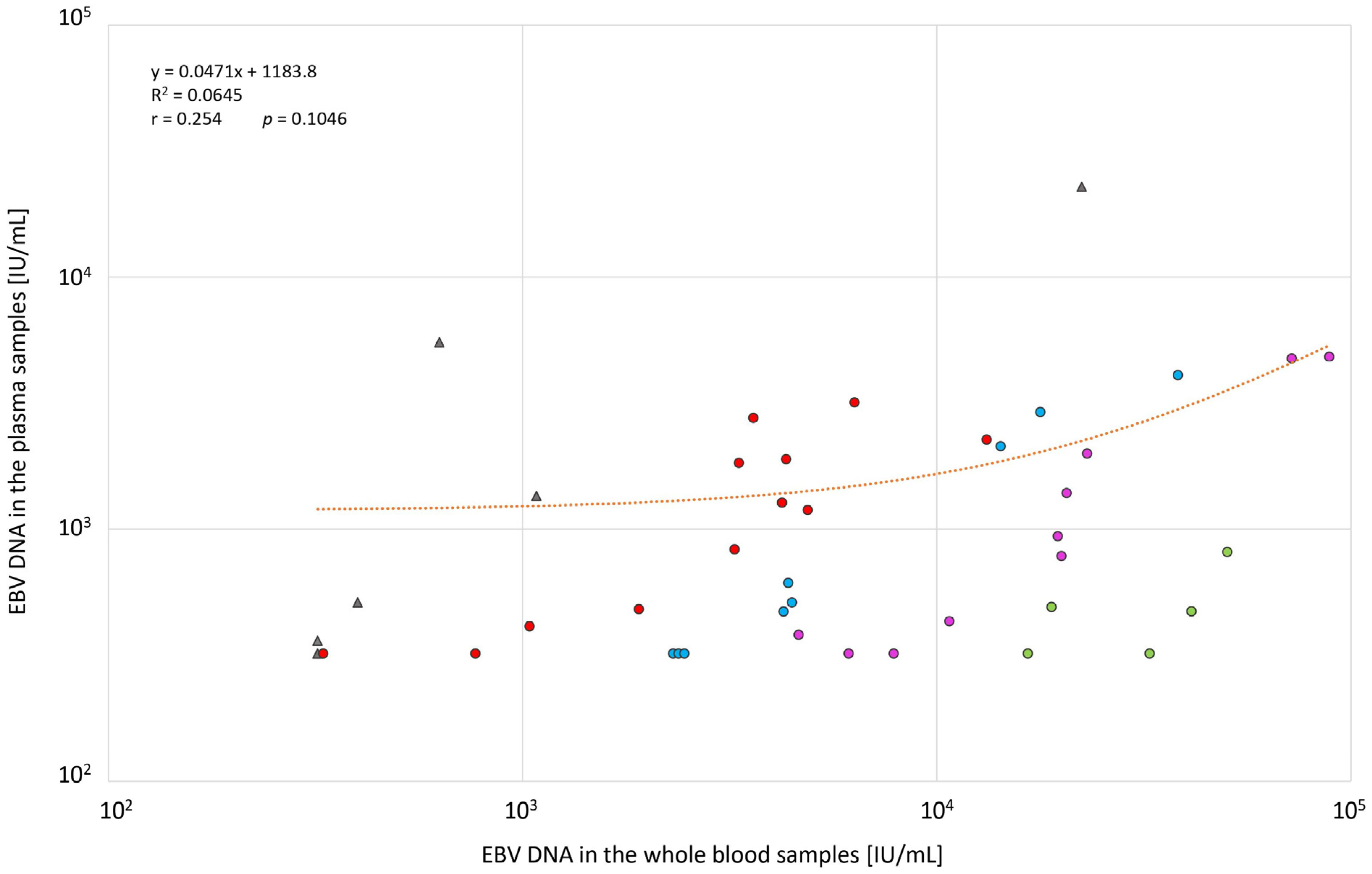
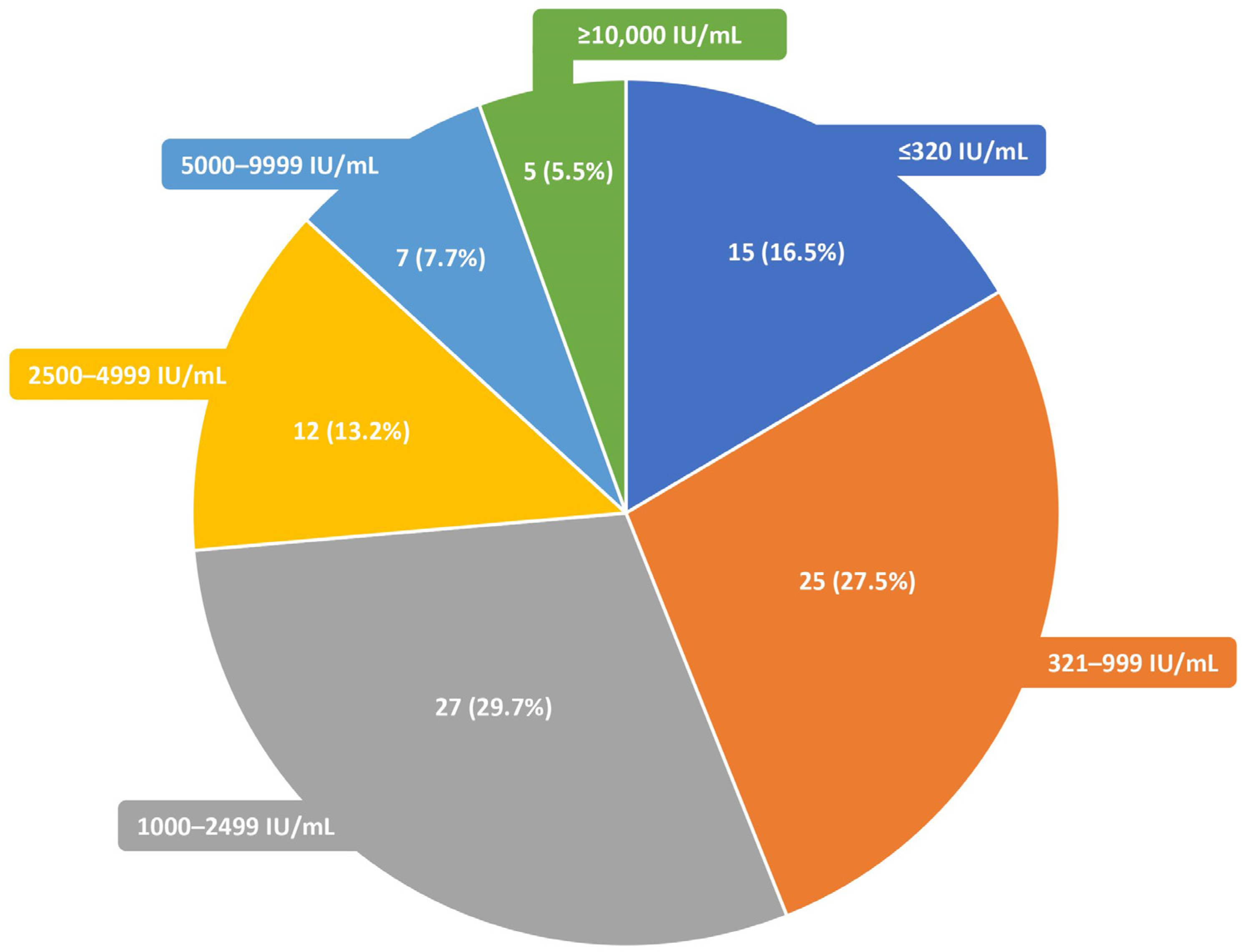
3. Results
- Up to 5 times; 12 (32.4%) samples;
- 6–10 times; 9 (24.3%) samples;
- 11–25 times; 10 (27.0%) samples;
- >25 times; 6 (16.2%) samples.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naughton, P.; Healy, M.; Enright, F.; Lucey, B. Infectious Mononucleosis: Diagnosis and Clinical Interpretation. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 78, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Biological Agents. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100, 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- Münz, C. Latency and Lytic Replication in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Oncogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowalk, A.; Green, M. Epstein-Barr Virus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 4.3.47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Fauci, A.S.; Varmus, H.; Nabel, G.J. Epstein-Barr Virus: An Important Vaccine Target for Cancer Prevention. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 107fs7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur-Melewska, K.; Breńska, I.; Jończyk-Potoczna, K.; Kemnitz, P.; Pieczonka-Ruszkowska, I.; Mania, A.; Służewski, W.; Figlerowicz, M. Neurologic Complications Caused by Epstein-Barr Virus in Pediatric Patients. J. Child. Neurol. 2016, 31, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.K.D.; Sato, D.K. Viral Encephalitis: A Practical Review on Diagnostic Approach and Treatment. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayee, R.; Ofori, M.E.; Wright, E.; Quaye, O. Epstein Barr Virus Associated Lymphomas and Epithelia Cancers in Humans. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Si, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, Z.; Nuermaimaiti, R.; Qian, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; You, M.J.; Zhang, H.; et al. A Retrospective Analysis of EBV-DNA Status with the Prognosis of Lymphoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5195–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; van der Velden, W.; Fox, C.P.; Engelhard, D.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ljungman, P.; on behalf of the Sixth European Conference on Infections in Leukemia, a joint venture of the Infectious Diseases Working Party of the European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT-IDWP), the Infectious Diseases Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC-IDG), the International Immunocompromised Host Society (ICHS) and the European Leukemia Net (ELN). Management of Epstein-Barr Virus Infections and Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Patients after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Sixth European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL-6) Guidelines. Haematologica 2016, 101, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, R.E.; Travis, L.B.; Rowlings, P.A.; Socié, G.; Kingma, D.W.; Banks, P.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Sale, G.E.; Horowitz, M.M.; Witherspoon, R.P.; et al. Risk of Lymphoproliferative Disorders after Bone Marrow Transplantation: A Multi-Institutional Study. Blood 1999, 94, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patriarca, F.; Medeot, M.; Isola, M.; Battista, M.L.; Sperotto, A.; Pipan, C.; Toffoletti, E.; Dozzo, M.; Michelutti, A.; Gregoraci, G.; et al. Prognostic Factors and Outcome of Epstein-Barr Virus DNAemia in High-Risk Recipients of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Treated with Preemptive Rituximab. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferla, V.; Rossi, F.G.; Goldaniga, M.C.; Baldini, L. Biological Difference Between Epstein–Barr Virus Positive and Negative Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Their Clinical Impact. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styczynski, J.; Reusser, P.; Einsele, H.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ward, K.N.; Ljungman, P.; Engelhard, D.; for the European Conference on Infections in Leukemia. Management of HSV, VZV and EBV Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies and after SCT: Guidelines from the Second European Conference on Infections in Leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2009, 43, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M. (Eds.) Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4511-0563-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hislop, A.D.; Taylor, G.S.; Sauce, D.; Rickinson, A.B. Cellular Responses to Viral Infection in Humans: Lessons from Epstein-Barr Virus. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 587–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, M.L.; Kersten, M.J.; Pals, S.T.; Bemelman, F.J.; ten Berge, I.J.M. Epstein-Barr Virus–Positive Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disease After Solid Organ Transplantation: Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Management. Transplant. Direct. 2016, 2, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Juan, R.; Comoli, P.; Caillard, S.; Moulin, B.; Hirsch, H.H.; Meylan, P. Epstein-Barr Virus-Related Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Kwong, Y.-L. EBV Viral Loads in Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Response Assessment. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakry, J.; Ambinder, R. The Biology and Clinical Utility of EBV Monitoring in Blood. In Epstein Barr Virus; Münz, C., Ed.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 475–499. ISBN 978-3-319-22833-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Woo, J.K.S.; King, A.; Zee, B.C.Y.; Lam, W.K.J.; Chan, S.L.; Chu, S.W.I.; Mak, C.; Tse, I.O.L.; Leung, S.Y.M.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA to Screen for Nasopharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, J.F.; Heath, A.B.; Minor, P.D.; Collaborative Study Group. A Collaborative Study to Establish the 1st WHO International Standard for Human Cytomegalovirus for Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology. Biologicals 2016, 44, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerbach, A.; Wutzler, P.; Häfer, R.; Zintl, F.; Gruhn, B. Monitoring of Epstein-Barr Virus Load after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Early Intervention in Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disease. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.E.; Douglas, L.; Andreadis, C.; Vogl, D.T.; Arnoldi, S.; Kotloff, R.; Svoboda, J.; Bloom, R.D.; Olthoff, K.M.; Brozena, S.C.; et al. EBV PCR in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder: Results of a Two-Arm Prospective Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Esser, J.W.J.; van der Holt, B.; Meijer, E.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Trenschel, R.; Thijsen, S.F.T.; van Loon, A.M.; Frassoni, F.; Bacigalupo, A.; Schaefer, U.W.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation Is a Frequent Event after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) and Quantitatively Predicts EBV-Lymphoproliferative Disease Following T-Cell–Depleted SCT. Blood 2001, 98, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, S.; Behnke-Hall, K.; Gruhn, B.; Bauer, J.; Horn, M.; Beck, J.; Reiter, A.; Wagner, H.J. Comparison of Six Different Specimen Types for Epstein-Barr Viral Load Quantification in Peripheral Blood of Pediatric Patients after Heart Transplantation or after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarotto, T.; Chiereghin, A.; Piralla, A.; Gibertoni, D.; Piccirilli, G.; Turello, G.; Campanini, G.; Gabrielli, L.; Costa, C.; Comai, G.; et al. Kinetics of Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Whole Blood and Plasma of Kidney Transplant Recipients: Implications on Management Strategies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarotto, T.; Chiereghin, A.; Piralla, A.; Piccirilli, G.; Girello, A.; Campanini, G.; Gabrielli, L.; Costa, C.; Prete, A.; Bonifazi, F.; et al. Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Kinetics in Whole Blood and Plasma of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakry, J.A.; Hegde, A.M.; Durand, C.M.; Massie, A.B.; Greer, A.E.; Ambinder, R.F.; Valsamakis, A. The Clinical Significance of EBV DNA in the Plasma and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with or without EBV Diseases. Blood 2016, 127, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. When Kissing (Disease) Counts. Blood 2016, 127, 1947–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadowsky, R.M.; Laus, S.; Green, M.; Webber, S.A.; Rowe, D. Measurement of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Loads in Whole Blood and Plasma by TaqMan PCR and in Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes by Competitive PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5245–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, D.E.; Bollore, K.; Viljoen, J.; Foulongne, V.; Reynes, J.; Cartron, G.; Vendrell, J.-P.; Van de Perre, P.; Tuaillon, E. Comparison of EBV DNA Viral Load in Whole Blood, Plasma, B-Cells and B-Cell Culture Supernatant: EBV DNA Load in Various Blood Specimens. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepka, M.; Depka, D.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Bogiel, T. Whole Blood versus Plasma Samples—How Does the Type of Specimen Collected for Testing Affect the Monitoring of Cytomegalovirus Viremia? Pathogens 2022, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, Q.-F.; Wang, H.; Jin, J.; Wang, W.-H.; Wang, S.-L.; Song, Y.-W.; Liu, Y.-P.; Fang, H.; Ren, H.; et al. Clinical Implications of Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Early-Stage Extranodal Nasal-Type NK/T-Cell Lymphoma Patients Receiving Primary Radiotherapy. Blood 2012, 120, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-X.; Li, P.-F.; Bai, B.; Gao, Y.; Rong, Q.-X.; Cai, Q.-Q.; Lin, S.-X.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, Z.-M.; Jiang, W.-Q.; et al. Differential Clinical Significance of Pre-, Interim-, and Post-Treatment Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Load in NK/T-Cell Lymphoma Treated with P-GEMOX Protocol. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, K.H.; Chang, M.H.; Ji, S.H.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.J.; Ko, Y.; Ki, C.-S.; et al. Whole Blood Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Load as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Surrogate: Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Cho, H.; Sung, H.; Jung, A.R.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.-W.; Ryu, J.-S.; Chae, E.J.; Kim, K.W.; Huh, J.; et al. Superiority of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in the Plasma Over Whole Blood for Prognostication of Extranodal NK/T Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 594692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, H.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Bai, B.; Chu, J.; Zhao, S.; Luo, X.; et al. Plasma EBV-DNA and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell EBV-DNA Have Disparate Clinical Relevance in Patients with Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 157, 105320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Kimura, H.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, C.; Ishida, F.; Izutsu, K.; Fukushima, N.; Isobe, Y.; Takizawa, J.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Pretreatment EBV-DNA Copy Number Is Predictive of Response and Toxicities to SMILE Chemotherapy for Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.S.; Park, C.; Sung, H.; Lee, S.-W.; Huh, J.; Suh, C. Pretreatment Whole Blood Epstein-Barr Virus-DNA Is a Significant Prognostic Marker in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.C.; Cupelli, E.; Santangelo, R.; Maiolo, E.; Alma, E.; Giachelia, M.; Martini, M.; Bellesi, S.; D’Alò, F.; Voso, M.T.; et al. Whole Blood EBV-DNA Predicts Outcome in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Huang, L.; Tian, J. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr Viral DNA among Children at a Single Hospital in Suzhou, China. J. Pediatr. 2022, 98, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age Group | Sex | n | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Female | 12 | 23.5% |
| Male | 12 | 23.5% | |
| Adults | Female | 12 | 23.5% |
| Male | 15 | 29.4% |
| Whole Blood | Plasma | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive EBV DNA | Positive EBV DNA | Negative EBV DNA | |
| n | 134 | 43 | 91 |
| Percentage | 100% | 32.1% | 67.9% |
| Sample No. | EBV DNA (IU/mL) Level | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Whole Blood | In Plasma | ||
| 15,729 | 1080 | 1350 | 270 |
| 15,679 | 22,400 | 22,800 | 400 |
| 18,216 | 320 | 360 | 40 |
| 17,343 | 630 | 5500 | 4870 |
| 15,407 | 400 | 510 | 110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rzepka, M.; Depka, D.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Bogiel, T. Diagnostic Value of Whole-Blood and Plasma Samples in Epstein–Barr Virus Infections. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030476
Rzepka M, Depka D, Gospodarek-Komkowska E, Bogiel T. Diagnostic Value of Whole-Blood and Plasma Samples in Epstein–Barr Virus Infections. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(3):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030476
Chicago/Turabian StyleRzepka, Mateusz, Dagmara Depka, Eugenia Gospodarek-Komkowska, and Tomasz Bogiel. 2023. "Diagnostic Value of Whole-Blood and Plasma Samples in Epstein–Barr Virus Infections" Diagnostics 13, no. 3: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030476
APA StyleRzepka, M., Depka, D., Gospodarek-Komkowska, E., & Bogiel, T. (2023). Diagnostic Value of Whole-Blood and Plasma Samples in Epstein–Barr Virus Infections. Diagnostics, 13(3), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13030476







