Evaluation of the BD Phoenix Carbapenemase-Producing Organism Panels for the Detection of Carbapenemase Producers in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
1. Introduction
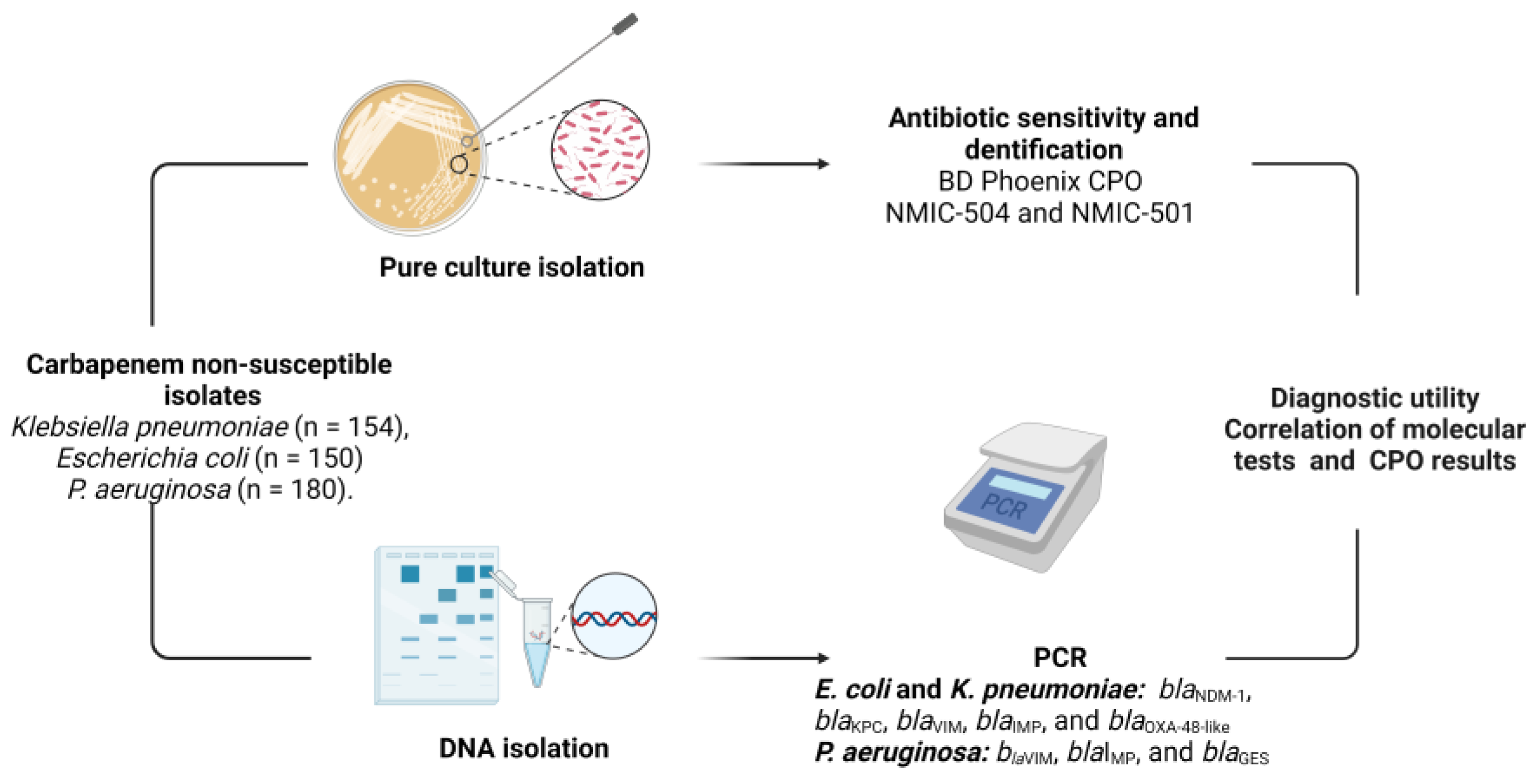
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Assay Using Phoenix CPO Panels
2.3. Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemases in Gram-Negatives
2.4. Diagnostic Utility
3. Results
3.1. Detected Carbapenemase-Encoding Genes
3.2. Performance of NMIC-501 CPO Panels
3.3. Clinical Isolates with At Least One Carbapenem Intermediate Result
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, L.K.; Weinstein, R.A. The Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: The Impact and Evolution of a Global Menace. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215 (Suppl. S1), S28–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambler, R.P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1980, 289, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The versatile beta-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Nicolau, D.P.; Hopkins, K.L.; Meunier, D. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales, Carbapenem Resistant Organisms, Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales, and Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms: Terminology Past its “Sell-By Date” in an Era of New Antibiotics and Regional Carbapenemase Epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Rapidec Carba NP Test for Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase Producers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3003–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Zwaluw, K.; de Haan, A.; Pluister, G.N.; Bootsma, H.J.; de Neeling, A.J.; Schouls, L.M. The carbapenem inactivation method (CIM), a simple and low-cost alternative for the Carba NP test to assess phenotypic carbapenemase activity in gram-negative rods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Simner, P.J. Phenotypic Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms from Clinical Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01140-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamma, P.D.; Opene, B.N.; Gluck, A.; Chambers, K.K.; Carroll, K.C.; Simner, P.J. Comparison of 11 Phenotypic Assays for Accurate Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, S.; Stefani, S.; Verhoef, J.; Van Belkum, A.; Vandamme, P.; Goessens, W. Comparative evaluation of the BD Phoenix and VITEK 2 automated instruments for identification of isolates of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahr, A.M.; Eigner, U.; Armbrust, M.; Caganic, A.; Dettori, G.; Chezzi, C.; Bertoncini, L.; Benecchi, M.; Menozzi, M.G. Two-center collaborative evaluation of the performance of the BD Phoenix automated microbiology system for identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Enterococcus spp. and Staphylococcus spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomson, G.; Turner, D.; Brasso, W.; Kircher, S.; Guillet, T.; Thomson, K. High-Stringency Evaluation of the Automated BD Phoenix CPO Detect and Rapidec Carba NP Tests for Detection and Classification of Carbapenemases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.H.; Ratnayake, L.; Ang, M.L.T.; Lin, R.T.P.; Chan, D.S.G. Diagnostic Accuracy of BD Phoenix CPO Detect for Carbapenemase Production in 190 Enterobacteriaceae Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Kosai, K.; Akamatsu, N.; Matsuyama, Y.; Oda, M.; Wakamatsu, A.; Izumikawa, K.; Mukae, H.; Yanagihara, K. Diagnostic Performance of BD Phoenix CPO Detect Panels for Detection and Classification of Carbapenemase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0089723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxatto, A.; Coste, A.T.; Pillonel, T.; Bertelli, C.; Greub, G.; Prod’hom, G. Evaluation of the BD Phoenix™ CPO Detect Test for the detection of carbapenemase producers. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 644.e9–644.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.; Koestler, J.; Reischl, U.; Gessner, A.; Jantsch, J. Detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales and the BD Phoenix CPO Detect panel. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.Y.; Mourad, D.; Hong, J.S.; Yoon, E.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, H.; Jeong, S.H. Performance Evaluation of the Newly Developed BD Phoenix NMIC-500 Panel Using Clinical Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacilli. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Gatermann, S.; Pfeifer, Y.; Reischl, U.; Gessner, A.; Jantsch, J. Evaluation of the automated BD Phoenix CPO Detect panel in combination with the β-CARBA assay for detection and classification of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 156, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, V.; Kircher, S.; Gill, T.; Hindler, J.A.; O’Rourke, S.; Cooper, C.; Tulpule, A.; Denys, G.A. Multicenter Evaluation of the BD Phoenix CPO Detect Test for Detection and Classification of Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms in Clinical Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M100-S30; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Second Informational Supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- Fernando, D.M.; Tun, H.M.; Poole, J.; Patidar, R.; Li, R.; Mi, R.; Amarawansha, G.E.A.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Khafipour, E.; Farenhorst, A.; et al. Detection of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Source and Drinking Water Samples from a First Nations Community in Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4767–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, J.; Widen, R.H.; Pignatari, A.C.; Kubasek, C.; Silbert, S. Rapid detection of carbapenemase genes by multiplex real-time PCR. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-González, E.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Bobadilla-Del-Valle, M.; Ponce-de-León-Garduño, L.A.; Esteban-Kenel, V.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Barrios-Camacho, H.; López-Jácome, L.E.; Colin-Castro, C.A.; et al. Drug resistance phenotypes and genotypes in Mexico in representative gram-negative species: Results from the infivar network. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Ramos, U.; Silva-Sánchez, J.; López-Jácome, L.E.; Hernández-Durán, M.; Colín-Castro, C.A.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Rodríguez-Santiago, J.; Morfín-Otero, R.; Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; Velázquez-Acosta, M.D.; et al. Carbapenemase-Encoding Genes and Colistin Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Mexico: Results from the Invifar Network. Microb. Drug Resist. 2023, 29, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.Y.; Bernal, J.F.; Montilla-Escudero, E.; Arévalo, S.A.; Prada, D.A.; Valencia, M.F.; Moreno, J.; Hidalgo, A.M.; García-Vega, Á.; Abrudan, M.; et al. Complexity of Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in Colombia Urges the Reinforcement of Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Surveillance Programs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73 (Suppl. S4), S290–S299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.T. Continuous Evolution: Perspective on the Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Resistance Among Enterobacterales and Other Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avakh, A.; Grant, G.D.; Cheesman, M.J.; Kalkundri, T.; Hall, S. The Art of War with. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.; Neidig, N.; Campbell, A.; Thornsberry, T.; Truex, T.; Fortney, T.; Zhang, Y.; Bush, K. Activity of imipenem/relebactam against carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae with high colistin resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3260–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, M.A.; Lomovskaya, O.; Dudley, M.N.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Sahm, D.F. Activity of Meropenem-Vaborbactam against Clinical Isolates of KPC-Positive Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak, K.M.; Karlowsky, J.A.; de Jonge, B.L.M.; Stone, G.G.; Sahm, D.F. Epidemiology of Carbapenem Resistance Determinants Identified in Meropenem-Nonsusceptible. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0200020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutal, H.; Vogel, A.; Bernabeu, S.; Devilliers, K.; Creton, E.; Cotellon, G.; Plaisance, M.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Jousset, A.; et al. A multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid identification of NDM-, KPC-, IMP- and VIM-type and OXA-48-like carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G.; Exindari, M.; Vavatsi, N.; Sofianou, D.; Diza, E. Mechanisms responsible for the emergence of carbapenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hippokratia 2012, 16, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| N | CPO Report | blaNDM | blaKPC | blaVIM | blaIMP | blaGES | blaOXA48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Class A | + | + | − | − | − | |
| 49 | Class B | + | − | − | − | − | |
| 25 | Class B | + | − | − | − | + | |
| 4 | Class B | + | − | + | − | + | |
| 4 | Class B | + | − | + | − | − | |
| 4 | Class B | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 1 | Class B | + | − | − | + | + | |
| 1 | Class B | − | + | − | − | + | |
| 1 | Class B | − | − | + | − | + | |
| 2 | Class D | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 1 | Class D | − | − | − | − | + | |
| 1 | Carbapenemase producer | − | − | − | − | + | |
| 1 | Carbapenemase producer | + | − | − | − | + | |
| 17 | No recommendation | + | − | − | − | + | |
| 16 | No recommendation | + | − | − | − | − | |
| 16 | No recommendation | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 5 | No recommendation | − | − | − | − | + | |
| 1 | No recommendation | + | − | + | − | + |
| N | CPO Report | blaNDM | blaKPC | blaVIM | blaIMP | blaGES | blaOXA48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | Class A | − | + | − | − | − | |
| 3 | Class A | + | + | − | − | + | |
| 3 | Class A | − | + | − | − | + | |
| 1 | Class A | − | + | − | + | + | |
| 33 | Class B | + | − | − | − | − | |
| 29 | Class B | + | − | − | − | + | |
| 5 | Class B | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 2 | Class B | + | − | + | − | + | |
| 1 | Class B | − | + | − | − | − | |
| 1 | Class B | + | − | + | − | − | |
| 1 | Class B | − | − | + | − | − | |
| 1 | Class D | − | − | − | − | + | |
| 1 | Class D | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 1 | Carbapenemase producer | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 1 | Carbapenemase producer | + | − | + | − | − | |
| 20 | No recommendation | + | − | − | − | + | |
| 18 | No recommendation | + | − | − | − | − | |
| 11 | No recommendation | − | − | − | − | − | |
| 3-1 | No recommendation | − | − | + | − | + | |
| 2 | No recommendation | + | − | + | − | + | |
| 2 | No recommendation | − | + | − | − | + | |
| 1 | No recommendation | − | + | − | − | − | |
| 1 | No recommendation | − | + | + | − | + | |
| 1 | No recommendation | − | + | + | − | − | |
| 1 | No recommendation | − | − | − | + | − |
| N | CPO Report | blaNDM | blaKPC | blaVIM | blaIMP | blaGES | blaOXA48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Class A | − | − | + | |||
| 6 | Class A | − | − | − | |||
| 2 | Class A | − | + | + | |||
| 1 | Class A | + | − | − | |||
| 27 | Class B | + | − | − | |||
| 6 | Class B | − | − | − | |||
| 2 | Class B | − | + | + | |||
| 1 | Class B | + | + | − | |||
| 2 | Class B | − | + | − | |||
| 20 | Class D | − | − | − | |||
| 5 | Class D | − | − | + | |||
| 1 | Class D | + | − | − | |||
| 18 | Carbapenemase producer | − | − | + | |||
| 6 | Carbapenemase producer | − | − | − | |||
| 9 | Carbapenemase producer | − | + | − | |||
| 3 | Carbapenemase producer | − | + | + | |||
| 4 | Carbapenemase producer | + | − | − | |||
| 2 | Carbapenemase producer | + | − | + | |||
| 39 | No recommendation | − | − | − | |||
| 4 | No recommendation | + | − | − | |||
| 6 | No recommendation | − | − | + | |||
| 3 | No recommendation | − | + | − | |||
| E. coli, Class B Value (95% CI) | K. pneumoniae, Class A Value (95% CI) | E. coli and K. pneumoniae, Class B Value (95% CI) | P. aeruginosa, No Recommendation Value (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 70.00 (60.96–78.02) | 75.00 (53.29–90.23) | 63.14 (56.63–69.30) | 23.35 (17.16–30.51) |
| Specificity | 83.33 (65.28–94.36) | 100.00 (97.20–100.00) | 82.35 (71.20–90.53) | 74.51 (60.37–85.67) |
| PLR | 4.20 (1.87–9.43) | NA | 3.58 (2.12–6.03) | 0.92 (0.53–1.58) |
| NLR | 0.36 (0.26–0.49) | 0.25 (0.13–0.50) | 0.45 (0.37–0.55) | 1.03 (0.86–1.23) |
| Prevalence | 80.00 (72.70–86.08) | 15.58 (10.25–22.30) | 77.63 (72.52–82.19) | 76.61 (70.41–82.06) |
| PPV | 94.38 (88.21–97.42) | 100.00 (0.00–0.00) | 92.55 (88.04–95.44) | 75.00 (63.53–83.79) |
| NPV | 40.98 (33.60–48.80) | 95.59 (91.55–97.74) | 39.16 (34.51–44.01) | 22.89 (19.85–26.24) |
| Accuracy | 72.67 (64.80–79.62) | 96.10 (91.71–98.56) | 67.43 (61.85–72.67) | 35.32 (28.99–42.06) |
| ID | CPO Report | blaNDM | blaKPC | blaVIM | blaIMP | blaOXA-48 | blaGES | ETP | IPM | MEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | ||||||||||
| 21-0100 | NR | - | - | - | - | - | ND | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.5 |
| 22-1191 | NR | - | - | - | - | - | ND | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.5 |
| 22-1782 | NR | - | - | - | - | - | ND | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.5 |
| 22-2012 | NR | - | - | - | - | - | ND | 1 | 1 | ≤0.5 |
| P. aeruginosa | ||||||||||
| 21-700 | NR | ND | ND | - | - | ND | - | ND | 4 | ≤0.5 |
| 21-0280 | NR | ND | ND | - | - | ND | - | ND | 4 | 4 |
| 21-0788 | Class D | ND | ND | - | - | ND | - | ND | 2 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correa-León, Y.P.; Pérez-Hernández, J.M.; Martinez-Guerra, B.A.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; Mena-Ramírez, J.P.; López-Gutiérrez, E.; López-Jácome, L.E.; Monroy-Colin, V.A.; Mireles-Davalos, C.D.; Padilla-Ibarra, C.; et al. Evaluation of the BD Phoenix Carbapenemase-Producing Organism Panels for the Detection of Carbapenemase Producers in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13223417
Correa-León YP, Pérez-Hernández JM, Martinez-Guerra BA, Rodríguez-Noriega E, Mena-Ramírez JP, López-Gutiérrez E, López-Jácome LE, Monroy-Colin VA, Mireles-Davalos CD, Padilla-Ibarra C, et al. Evaluation of the BD Phoenix Carbapenemase-Producing Organism Panels for the Detection of Carbapenemase Producers in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(22):3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13223417
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrea-León, Yoselin Paola, José Miguel Pérez-Hernández, Bernardo Alfonso Martinez-Guerra, Eduardo Rodríguez-Noriega, Juan Pablo Mena-Ramírez, Eduardo López-Gutiérrez, Luis Esaú López-Jácome, Víctor Antonio Monroy-Colin, Christian Daniel Mireles-Davalos, Cecilia Padilla-Ibarra, and et al. 2023. "Evaluation of the BD Phoenix Carbapenemase-Producing Organism Panels for the Detection of Carbapenemase Producers in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Diagnostics 13, no. 22: 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13223417
APA StyleCorrea-León, Y. P., Pérez-Hernández, J. M., Martinez-Guerra, B. A., Rodríguez-Noriega, E., Mena-Ramírez, J. P., López-Gutiérrez, E., López-Jácome, L. E., Monroy-Colin, V. A., Mireles-Davalos, C. D., Padilla-Ibarra, C., Quevedo-Ramos, M. A., Feliciano-Guzmán, J. M., Pérez-Vicelis, T., Velázquez-Acosta, M. d. C., Hernández-Durán, M., & Garza-González, E. (2023). Evaluation of the BD Phoenix Carbapenemase-Producing Organism Panels for the Detection of Carbapenemase Producers in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Diagnostics, 13(22), 3417. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13223417








