Antiretroviral Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid: The Effect of Inflammation and Genetic Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Biomarkers
2.3. Pharmacokinetic Analyses
2.4. Pharmacogenetic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Description
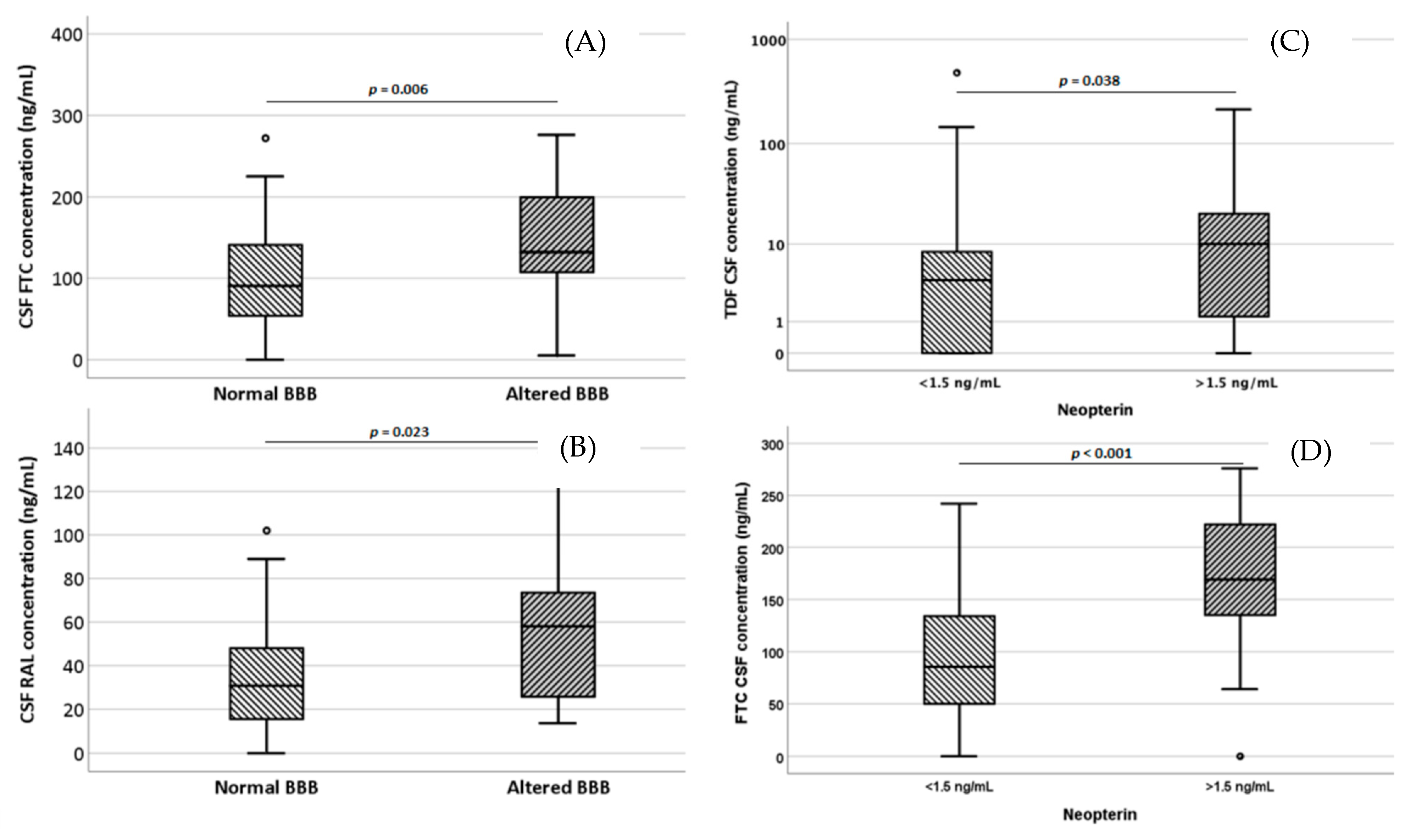
3.2. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
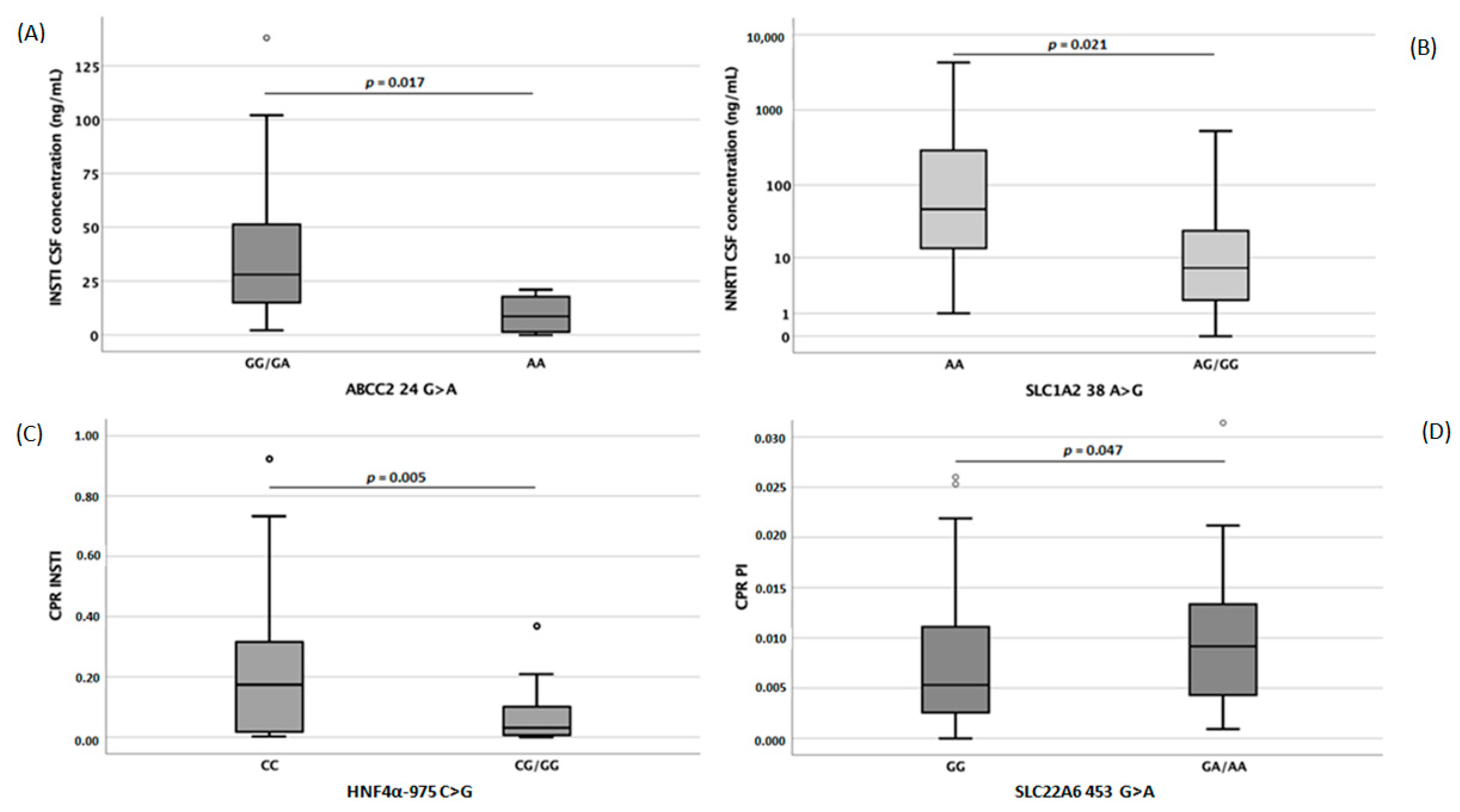
3.3. Pharmacogenetic Evaluation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistics, G. Global Statistics. HIV.gov. Available online: https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/data-and-trends/global-statistics (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Nightingale, S.; Winston, A.; Letendre, S.; Michael, B.D.; McArthur, J.C.; Khoo, S.; Solomon, T. Controversies in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Lu, Q.; Farrell, M.; Lappin, J.M.; Shi, J.; Lu, L.; Bao, Y. Global prevalence and burden of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2020, 95, e2610–e2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Samani, D.; Nambiar, N.; Ghate, M.V.; Gangakhedkar, R.R. Prevalence of MMP-8 gene polymorphisms in HIV-infected individuals and its association with HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder. Gene 2018, 646, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, I.; Trunfio, M.; Guastamacchia, G.; Bonora, S.; Calcagno, A. A review of the potential mechanisms of neuronal toxicity associated with antiretroviral drugs. J. Neurovirol. 2020, 26, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M. HIV and viral protein effects on the blood brain barrier. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1143543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, N.; Rosen, E.P.; Gilliland, W.M.; Kovarova, M.; Remling-Mulder, L.; De La Cruz, G.; White, N.; Adamson, L.; Schauer, A.P.; Sykes, C.; et al. Antiretroviral concentrations and surrogate measures of efficacy in the brain tissue and CSF of preclinical species. Xenobiotica 2019, 49, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H. External quality assessment in clinical neurochemistry: Survey of analysis for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteins based on CSF/serum quotients. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempestilli, M.; Premaschi, S.; Goffredo, B.; Cusato, J. Indicazioni per l’armonizzazione e l’intervallo Terapeutico nel Monitoraggio Plasmatico dei Farmaci Antiretrovirali. Available online: https://bc.sibioc.it/bc/autore/cognome/Tempestilli/qualeautore/3044 (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Simiele, M.; Ariaudo, A.; De Nicolò, A.; Favata, F.; Ferrante, M.; Carcieri, C.; Bonora, S.; Di Perri, G.; De Avolio, A. UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of three new antiretroviral drugs, dolutegravir, elvitegravir and rilpivirine, and other thirteen antiretroviral agents plus cobicistat and ritonavir boosters in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 138, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Simiele, M.; Alberione, M.C.; Bracchi, M.; Marinaro, L.; Ecclesia, S.; Di Perri, G.; D’Avolio, A.; Bonora, S. Cerebrospinal fluid inhibitory quotients of antiretroviral drugs in HIV-infected patients are associated with compartmental viral control. Clin. Infect. Dis 2015, 60, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Cusato, J.; Simiele, M.; Motta, I.; Audagnotto, S.; Bracchi, M.; D’Avolio, A.; Di Perri, G.; Bonora, S. High interpatient variability of raltegravir CSF concentrations in HIV-positive patients: A pharmacogenetic analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Yilmaz, A.; Cusato, J.; Simiele, M.; Bertucci, R.; Siccardi, M.; Marinaro, L.; D’Avolio, A.; Di Perri, G.; Bonora, S. Determinants of darunavir cerebrospinal fluid concentrations: Impact of once-daily dosing and pharmacogenetics. AIDS 2012, 26, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA, C.f.M.P.f.H.U. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Cusato, J.; Allegra, S.; Nicolo, A.; Calcagno, A.; D’Avolio, A. Precision medicine for HIV: Where are we? Pharmacogenomics 2018, 19, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siccardi, M.; Almond, L.; Schipani, A.; Csajka, C.; Marzolini, C.; Wyen, C.; Brockmeyer, N.H.; Boffito, M.; Owen, A.; Back, D. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of efavirenz dose reduction using an in vitro-in vivo extrapolation model. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siccardi, M.; Marzolini, C.; Seden, K.; Almond, L.; Kirov, A.; Khoo, S.; Owen, A.; Back, D. Prediction of drug-drug interactions between various antidepressants and efavirenz or boosted protease inhibitors using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling approach. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 52, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene, L.; Duiculescu, D.; Ruta, S.M. How much do antiretroviral drugs penetrate into the central nervous system? J. Med. Life 2011, 4, 432–439. [Google Scholar]
- Strazielle, N.; Ghersi-Egea, J.F. Factors affecting delivery of antiviral drugs to the brain. Rev. Med. Virol. 2005, 15, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coisne, C.; Engelhardt, B. Tight junctions in brain barriers during central nervous system inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A.A.; Uppada, S.; Achkar, I.W.; Hashem, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H.A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S. Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke-Labesque, F.; Gautier-Veyret, E.; Chhun, S.; Guilhaumou, R. Inflammation is a major regulator of drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters: Consequences for the personalization of drug treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 215, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Jackson, S.H. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: Basic principles and practical applications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirl-Carrillo, M.; McDonagh, E.M.; Hebert, J.M.; Gong, L.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Pharmacogenomics knowledge for personalized medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.; Marsot, A.; Villard, E.; Choquet, S.; Khe, H.X.; Zahr, N.; Lechat, P.; Leblond, V.; Hulot, J.S. Impact of ABCC2 polymorphisms on high-dose methotrexate pharmacokinetics in patients with lymphoid malignancy. Pharm. J. 2013, 13, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xing, X.; Shan, F.; Li, S.; Xiao, A.; Xing, Z.; Xue, K.; Hu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Miao, R.; et al. ABCC2-24C>T polymorphism is associated with the response to platinum/5-Fu-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy and better clinical outcomes in advanced gastric cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55449–55457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rocha, I.M.; Gasparotto, A.S.; Lazzaretti, R.K.; Notti, R.K.; Sprinz, E.; Mattevi, V.S. Polymorphisms associated with renal adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy in a Southern Brazilian HIV cohort. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungtivasuwan, K.; Avihingsanon, A.; Thammajaruk, N.; Mitruk, S.; Burger, D.M.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Punyawudho, B.; Pengsuparp, T. Influence of ABCC2 and ABCC4 polymorphisms on tenofovir plasma concentrations in Thai HIV-infected patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3240–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusato, J.; Tomasello, C.; Simiele, M.; Calcagno, A.; Bonora, S.; Marinaro, L.; Leggieri, A.; Allegra, S.; Di Perri, G.; D’Avolio, A. Efavirenz pharmacogenetics in a cohort of Italian patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, R.M.; Scherkenbach, L.A.; Sparreboom, A. Pharmacogenetics of the organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2. Pharmacogenomics 2009, 10, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

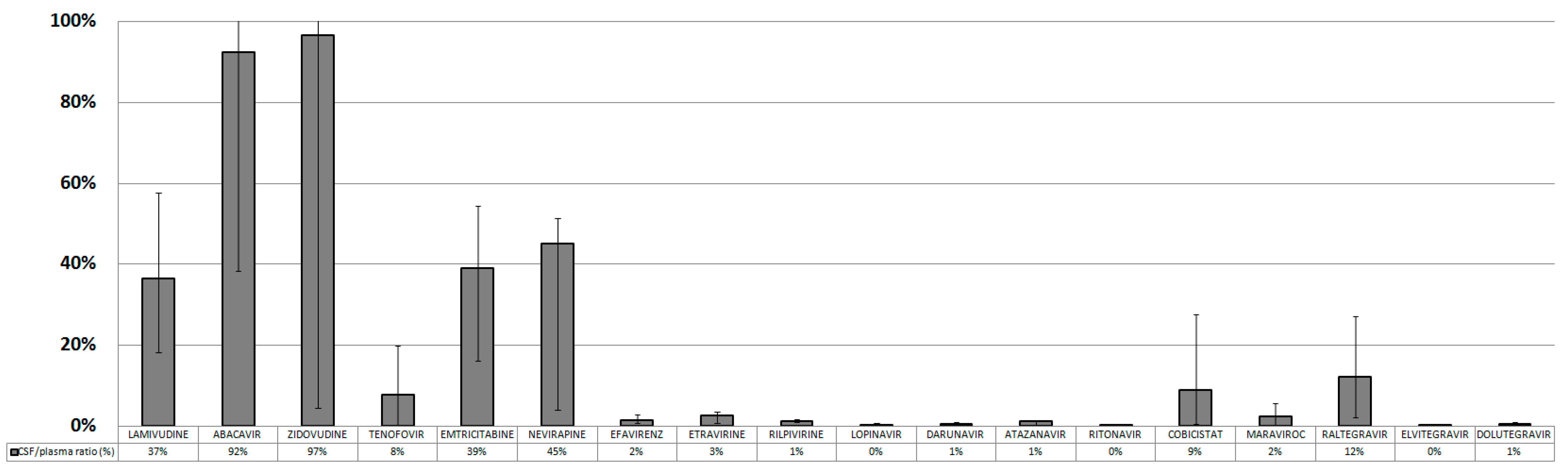
| 3TC | ABV | AZT | TDF | FTC | NVP | EFV | ETV | RPV | LPV | DRV | ATV | RTV | COBI | MVC | RAL | ELV | DTG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 57 | 34 | 12 | 107 | 104 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 6 | 28 | 78 | 31 | 116 | 4 | 21 | 80 | 4 | 12 |
| Median CSF conc. (ng/mL) | 122.0 | 87.5 | 15.0 | 5.0 | 102.5 | 1062.0 | 40.5 | 16.5 | 2.0 | 25.0 | 29.4 | 7.2 | 0.36 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 30.4 | 3.9 | 6.5 |
| IQR | 74.5–162 | 17.5–234 | 6.7–34.7 | 0–10 | 57.2–155 | 268.5–3050.5 | 24.6–81.7 | 5.4–23.4 | 1–3 | 13–49 | 14–47.2 | 1.9–21.7 | 0–0.9 | 2.2–8.1 | 0.4–5.4 | 18.7–56.5 | 2.5–5.7 | 3.3–11 |
| Percentage of patients with CSF conc. < LOQ | 0 | 14.7 | 33.3 | 31.8 | 8.7 | 11.1 | 14.3 | 28.6 | 0 | 60.7 | 37.2 | 61.3 | 94.8 | 25 | 71.4 | 5 | 75 | 83.3 |
| Percentage of patients with CSF conc. < LOD | 0 | 11.8 | 16.7 | 31.8 | 6.7 | 11.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.1 | 2.6 | 12.9 | 28.4 | 0 | 14.3 | 1.3 | 0 | 8.3 |
| Correlation with plasma (Spearman’s ρ) | ρ = 0.47; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.86; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.34; p = 0.278 | ρ = 0.54; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.59; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.32; p = 0.406 | ρ = 0.63; p = 0.021 | ρ = 0.21; p = 0.473 | ρ = 0.84; p = 0.038 | ρ = 0.04; p = 0.857 | ρ = 0.49; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.79; p < 0.001 | ρ = 0.36; p = n.c. | ρ = 0.80; p = 0.2 | ρ = 0.12; p = 0.623 | ρ = 0.47; p < 0.001 | ρ = 1; p = n.c. | ρ = −0.1; p = 0.749 |
| 3TC | ABV | AZT | TDF | FTC | NVP | EFV | ETV | RPV | LPV | DRV | ATV | RTV | COBI | MVC | RAL | ELV | DTG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | rs1045642 | ||||||||||||||||||
| rs1128503 | PL 0.022 | CSF 0.028 PL 0.035 | |||||||||||||||||
| rs2032582 | PL 0.041 | CSF 0.036 | CSF 0.044 | CSF 0.031 PL 0.029 | |||||||||||||||
| ABCC2 | rs717620 | CSF 0.041 PL 0.047 | CSF 0.030 | ||||||||||||||||
| SLC22A6 | rs4149170 | ||||||||||||||||||
| SLCO1A2 | rs10841795 | ||||||||||||||||||
| rs11568563 | CSF 0.032 | ||||||||||||||||||
| ABCG2 | rs2231142 | PL 0.009 | |||||||||||||||||
| rs13120400 | CSF 0.017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| HNF4α | rs1884613 | ||||||||||||||||||
| ABCC10 | rs9349256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cusato, J.; Avataneo, V.; Antonucci, M.; Trunfio, M.; Marinaro, L.; Palermiti, A.; Manca, A.; Di Perri, G.; Mula, J.; Bonora, S.; et al. Antiretroviral Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid: The Effect of Inflammation and Genetic Variants. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020295
Cusato J, Avataneo V, Antonucci M, Trunfio M, Marinaro L, Palermiti A, Manca A, Di Perri G, Mula J, Bonora S, et al. Antiretroviral Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid: The Effect of Inflammation and Genetic Variants. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(2):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020295
Chicago/Turabian StyleCusato, Jessica, Valeria Avataneo, Miriam Antonucci, Mattia Trunfio, Letizia Marinaro, Alice Palermiti, Alessandra Manca, Giovanni Di Perri, Jacopo Mula, Stefano Bonora, and et al. 2023. "Antiretroviral Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid: The Effect of Inflammation and Genetic Variants" Diagnostics 13, no. 2: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020295
APA StyleCusato, J., Avataneo, V., Antonucci, M., Trunfio, M., Marinaro, L., Palermiti, A., Manca, A., Di Perri, G., Mula, J., Bonora, S., D’Avolio, A., & Calcagno, A. (2023). Antiretroviral Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid: The Effect of Inflammation and Genetic Variants. Diagnostics, 13(2), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020295









