Characteristic Chest Computed Tomography Findings for Birt–Hogg–Dube Syndrome Indicating Requirement for Genetic Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
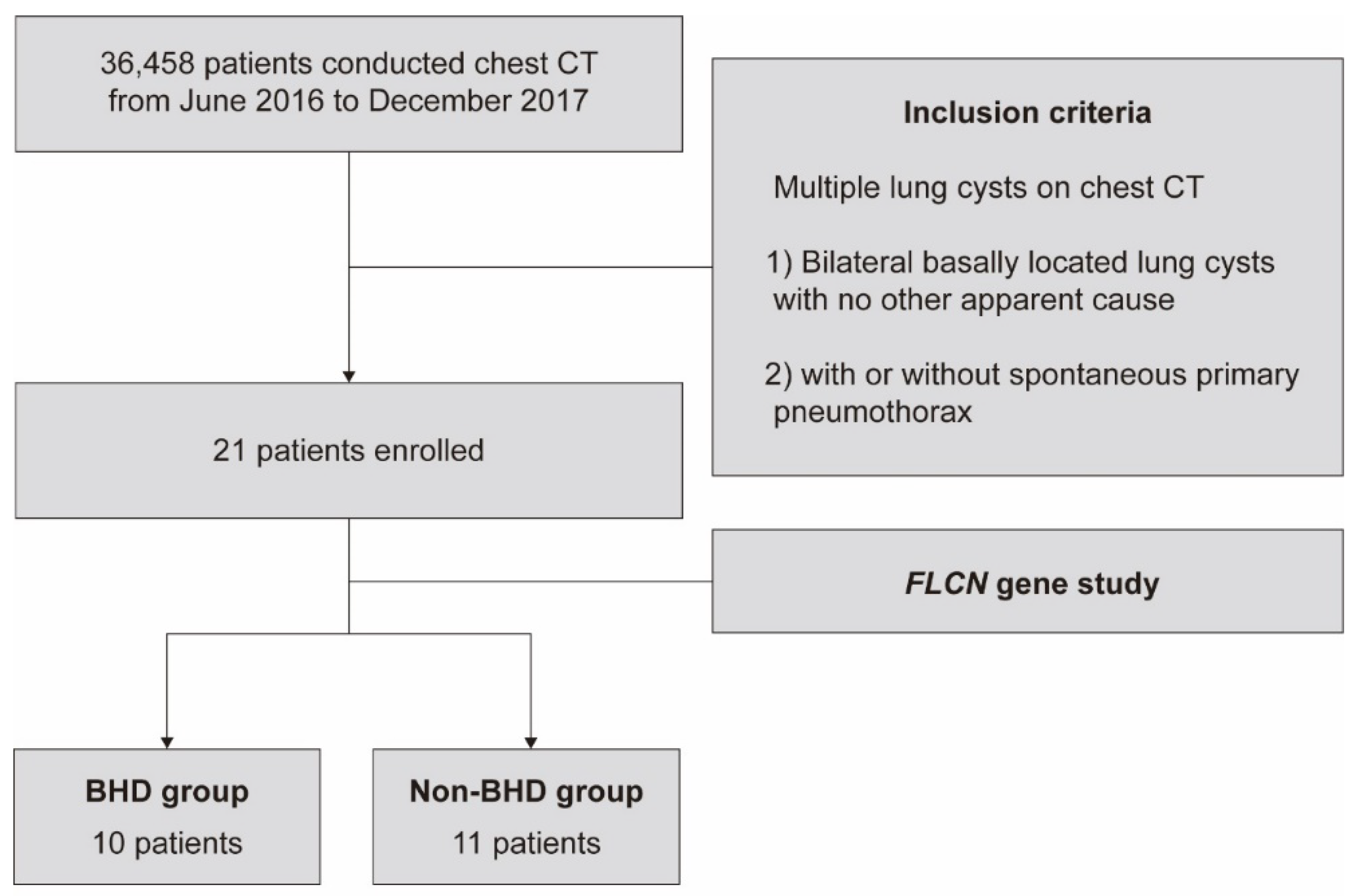
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CT protocol and Analysis
2.3. FLCN Gene Mutation Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Enrolled Patients
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of BHD
3.3. Characteristics of Lung Cysts in BHD Patients
3.4. Correlation between Cystic Features and FLCN Gene Mutations
3.5. ROC Analysis for BHD Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
References
- Birt, A.R.; Hogg, G.R.; Dubé, W.J. Hereditary multiple fibrofolliculomas with trichodiscomas and acrochordons. Arch. Dermatol. 1977, 113, 1674–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, M.L.; Warren, M.B.; Toro, J.R.; Matrosova, V.; Glenn, G.; Turner, M.L.; Duray, P.; Merino, M.; Choyke, P.; Pavlovich, C.P.; et al. Mutations in a novel gene lead to kidney tumors, lung wall defects, and benign tumors of the hair follicle in patients with the Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Cancer Cell. 2002, 2, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunogi, M.; Kurihara, M.; Ikegami, T.S.; Kobayashi, T.; Shindo, N.; Kumasaka, T.; Gunji, Y.; Kikkawa, M.; Iwakami, S.I.; Hino, O.; et al. Clinical and genetic spectrum of Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome patients in whom pneumothorax and/or multiple lung cysts are the presenting feature. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinlein, O.K.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Ruzicka, T.; Sattler, E.C. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: An underdiagnosed genetic tumor syndrome. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2018, 16, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näf, E.; Laubscher, D.; Hopfer, H.; Streit, M.; Matyas, G. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Novel FLCN frameshift deletion in daughter and father with renal cell carcinomas. Fam. Cancer 2016, 15, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Published BHD Families. January, 2017. Available online: https://www.bhdsyndrome.org/for-researchers/what-is-bhd/introduction/published-bhd-families/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Menko, F.H.; Van Steensel, M.A.; Giraud, S.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Richard, S.; Ungari, S.; Nordenskjöld, M.; vOHansen, T.; Solly, J.; Maher, E.R.; et al. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Diagnosis and management. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, J.R.; Wei, M.H.; Glenn, G.M.; Weinreich, M.; Toure, O.; Vocke, C.; Turner, M.; Choyke, P.; Merino, M.J.; Pinto, P.A.; et al. BHD mutations, clinical and molecular genetic investigations of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: A new series of 50 families and a review of published reports. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houweling, A.C.; Gijezen, L.M.; Jonker, M.A.; van Doorn, M.B.; Oldenburg, R.A.; van Spaendonck-Zwarts, K.Y.; Leter, E.M.; van Os, T.A.; van Grieken, N.C.; Jaspars, E.H.; et al. Renal cancer and pneumothorax risk in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome; an analysis of 115 FLCN mutation carriers from 35 BHD families. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesma, P.C.; van de Beek, I.; van der Wel, T.J.; Reinhard, R.; Rozendaal, L.; Starink, T.M.; van Waesberghe, J.H.T.; Horenblas, S.; Gille, H.J.; Jonker, M.A.; et al. Renal imaging in 199 Dutch patients with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Screening compliance and outcome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Park, C.H.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, G.D.; Byun, M.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.A.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, S.Y.; et al. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome prospectively detected by review of chest computed tomography scans. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Shen, Q.; Ouyang, R.; Song, M.; Zong, D.; Shi, Z.; Long, Y.; Chen, P.; Peng, H. The clinical characteristics of East Asian patients with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Seyama, K.; McCormack, F.X. Pulmonary manifestations of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Fam. Cancer 2013, 12, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.C.; Kang, E.Y.; Yong, H.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, K.Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Oh, Y.W. A Stepwise Diagnostic Approach to Cystic Lung Diseases for Radiologists. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins Neil, J.; Schisterman Enrique, F. The inconsistency of “optimal” cut-points using two ROC based criteria. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbar, B.; Alvord, W.G.; Glenn, G.; Turner, M.; Pavlovich, C.P.; Schmidt, L.; Walther, M.; Choyke, P.; Weirich, G.; Hewitt, S.M.; et al. Risk of renal and colonic neoplasms and spontaneous pneumothorax in the Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Furuya, M.; Tanaka, R.; Koga, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Gotoda, H.; Takagi, S.; Hsu, Y.H.; Fujii, T.; Okada, A.; Kuroda, N.; et al. Pulmonary cysts of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 9 families. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Vassallo, R.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A.; McCormack, F.X. Diffuse Cystic Lung Disease. Part II. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalon, J.G.; Richards, J.C.; Koelsch, T.; Downey, G.P.; Lynch, D.A. Isolated Cystic Lung Disease: An Algorithmic Approach to Distinguishing Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome, Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, and Lymphocytic Interstitial Pneumonia. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobino, K.; Hirai, T.; Johkoh, T. Differentiation between Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome and lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Quantitative analysis of pulmonary cysts on computed tomography of the chest in 66 females. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Chae, E.J.; Do, K.-H.; Lee, S.M.; Song, J.W. Differentiation between Lymphangioleiomyomatosis and Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome: Analysis of Pulmonary Cysts on CT Images. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.C.; Khabibullin, D.; Henske, E.P. Mechanisms of pulmonary cyst pathogenesis in Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome: The stretch hypothesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 52, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobino, K.; Gunji, Y.; Kurihara, M.; Kunogi, M.; Koike, K.; Tomiyama, N.; Johkoh, T.; Kodama, Y.; Iwakami, S.I.; Kikkawa, M.; et al. Characteristics of pulmonary cysts in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Thin-section CT findings of the chest in 12 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 77, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.P.; Gross, B.H.; Holloway, B.J.; Seely, J.; Stark, P.; Kazerooni, E.A. Thoracic CT findings in Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.S.; Nickerson, M.L.; Warren, M.B.; Glenn, G.M.; Toro, J.R.; Merino, M.J.; Turner, M.L.; Choyke, P.L.; Sharma, N.; Peterson, J.; et al. Germline BHD-mutation spectrum and phenotype analysis of a large cohort of families with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, M.; Nakatani, Y. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome: Clinicopathological features of the lung. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 66, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Wataya-Kaneda, M.; Tanaka, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tsujimura, A.; Inoue, K.; Nonomura, N.; Katayama, I. Two Japanese cases of birt-hogg-dubé syndrome with pulmonary cysts, fibrofolliculomas, and renal cell carcinomas. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2014, 6, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kang, H.C.; Ganeshan, D.M.; Bathala, T.K.; Kundra, V. Diagnostic Approach to Hereditary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kang, H.C.; Ganeshan, D.; Morani, A.; Gautam, R.; Choyke, P.L.; Kundra, V. The ABCs of BHD: An In-Depth Review of Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zou, W.; Ma, D.; Min, H.; Chen, B.; Ye, M.; Pan, Y.; Cao, L.; Wan, Y.; et al. FLCN intragenic deletions in Chinese familial primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167A, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensel, B.; Kühn, J.P.; Kracht, F.; Völzke, H.; Lieb, W.; Dabers, T.; Lorbeer, R. Prevalence of renal cysts and association with risk factors in a general population: An MRI-based study. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 3068–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesma, P.C.; Reinhard, R.; Kon, Y.; Sriram, J.D.; Smit, H.J.; van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Menko, F.H.; Postmus, P.E. Prevalence of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome in patients with apparently primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| BHD | Non-BHD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 10) | (N = 11) | ||
| Sex | 0.730 | ||
| Male | 2 (20.0%) | 4 (36.4%) | |
| Female | 8 (80.0%) | 7 (63.6%) | |
| Age (years; mean ± standard deviation) | 49.4 ± 16.2 | 50.4 ± 12.4 | 0.879 |
| Smoking status | 0.961 | ||
| Never smoker | 9 (90.0%) | 11 (100.0%) | |
| Current smoker | 1 (10.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 3 (30.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.181 |
| Diabetes | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (9.1%) | 1.000 |
| Tuberculosis | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Proteinuria | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Hematuria | 2 (28.6%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.732 |
| Pulmonary function test | |||
| FVC (%; mean ± standard deviation) | 94.8 ± 11.5 | 91.8 ± 10.1 | 0.603 |
| FEV1 (%; median [IQR]) | 91.0 [9] | 93.0 [17] | 0.796 |
| FEV1/FVC (%; mean ± standard deviation) | 72.8 ± 7.8 | 79.5 ± 16.7 | 0.384 |
| History of spontaneous pneumothorax | 7 (70.0%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0.051 |
| Family history of spontaneous pneumothorax | 3 (30.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.181 |
| Typical skin lesions † | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | NA |
| Typical renal lesions ‡ | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | NA |
| Renal cyst | 5 (50.0%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.240 |
| Patient | Age | Sex | Skin Lesion | Renal Lesion | Renal Function Impairment | Lung Function Impairment | History of Pneumothorax | FLCN Gene Mutation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal History | Family History ‡ | ||||||||
| A | 50 | M | None | Cortical single cyst †, 1.1 cm | None | None | Positive | Negative | c.1285dupC |
| B | 31 | F | None | None | None | None | Positive | Positive | c.1177-5_1177-3delCTC |
| C | 56 | F | Verruca † | Cortical multiple cyst †, tiny | None | None | Negative | Negative | c.1023_1024insTCTTC |
| D | 54 | F | None | Cortical single cyst †, 2.1 cm | None | None | Positive | Negative | c.1177-5_1177-3delCTC |
| E | 53 | F | None | Cortical multiple cyst †, tiny | None | N/A | Positive | Positive | c.507G>A |
| F | 70 | F | None | Medullary single cyst †, 0.9 cm | None | Obstructive | Negative | Negative | c.1128G>A |
| G | 35 | M | None | None | None | N/A | Positive | Negative | c.469_471delTTC |
| H | 24 | F | None | None | None | N/A | Positive | Negative | c.1285delC |
| I | 46 | F | None | None | None | None | Negative | Positive | c.1285dupC |
| J | 75 | F | None | None | None | N/A | Positive | Negative | c.469_471delTTC |
| Features of Lung Cysts | BHD | Non-BHD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 10) | (N = 11) | ||
| Number > 40 | 8 (80%) | 8 (72.7%) | 1.000 |
| Maximal diameter (Centimeters; mean ± standard deviation) | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 1.6 ± 0.9 | <0.001 ** |
| Diversity of size | 10 (100%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0.001 * |
| Diversity of morphology | 10 (100%) | 6 (54.5%) | 0.054 |
| Features of Lung Cysts | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis † | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value | |
| Number > 40 | 1.500 (0.195–13.860) | 0.697 | 1.306 (0.001–6.392) | 0.341 |
| Maximum diameter (cm) | 6.352 (2.112–53.223) | 0.014 | 6.884 (1.745–117.748) | 0.048 * |
| Diversity of size | 999.999 (0.000–999.999) | 0.995 | Omitted | |
| Diversity of morphology | 999.999 (0.000–999.999) | 0.995 | 999.999 (0.000–999.999) | 0.997 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.J.; Park, C.H.; Park, H.J.; Shin, J.M.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, K.-A.; Moon, D.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.E.; Byun, M.K. Characteristic Chest Computed Tomography Findings for Birt–Hogg–Dube Syndrome Indicating Requirement for Genetic Evaluation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020198
Choi YJ, Park CH, Park HJ, Shin JM, Kim TH, Lee K-A, Moon DH, Lee S, Lee SE, Byun MK. Characteristic Chest Computed Tomography Findings for Birt–Hogg–Dube Syndrome Indicating Requirement for Genetic Evaluation. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(2):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020198
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yong Jun, Chul Hwan Park, Hye Jung Park, Jae Min Shin, Tae Hoon Kim, Kyung-A Lee, Duk Hwan Moon, Sungsoo Lee, Sang Eun Lee, and Min Kwang Byun. 2023. "Characteristic Chest Computed Tomography Findings for Birt–Hogg–Dube Syndrome Indicating Requirement for Genetic Evaluation" Diagnostics 13, no. 2: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020198
APA StyleChoi, Y. J., Park, C. H., Park, H. J., Shin, J. M., Kim, T. H., Lee, K.-A., Moon, D. H., Lee, S., Lee, S. E., & Byun, M. K. (2023). Characteristic Chest Computed Tomography Findings for Birt–Hogg–Dube Syndrome Indicating Requirement for Genetic Evaluation. Diagnostics, 13(2), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13020198






