Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound as an Innovative Imaging Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Nasolabial Folds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
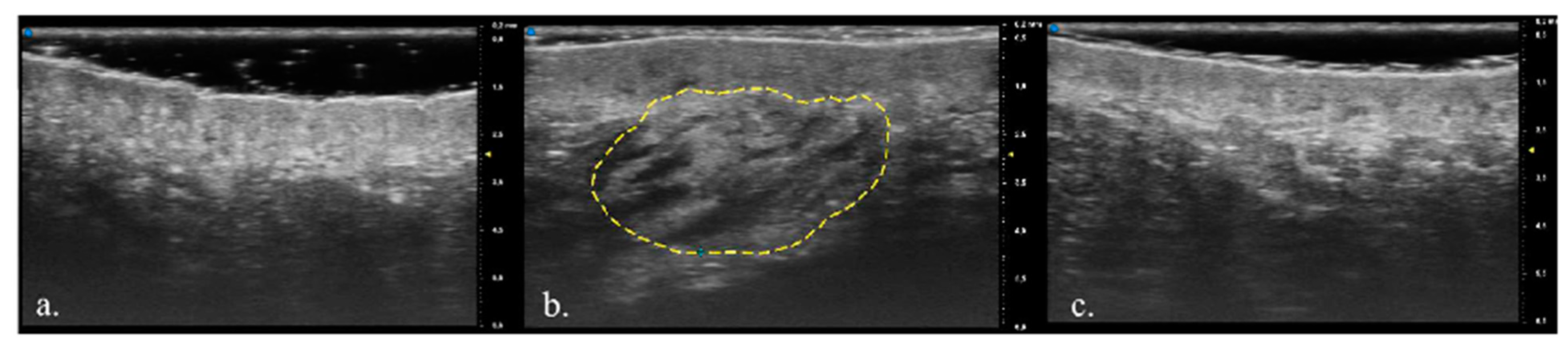
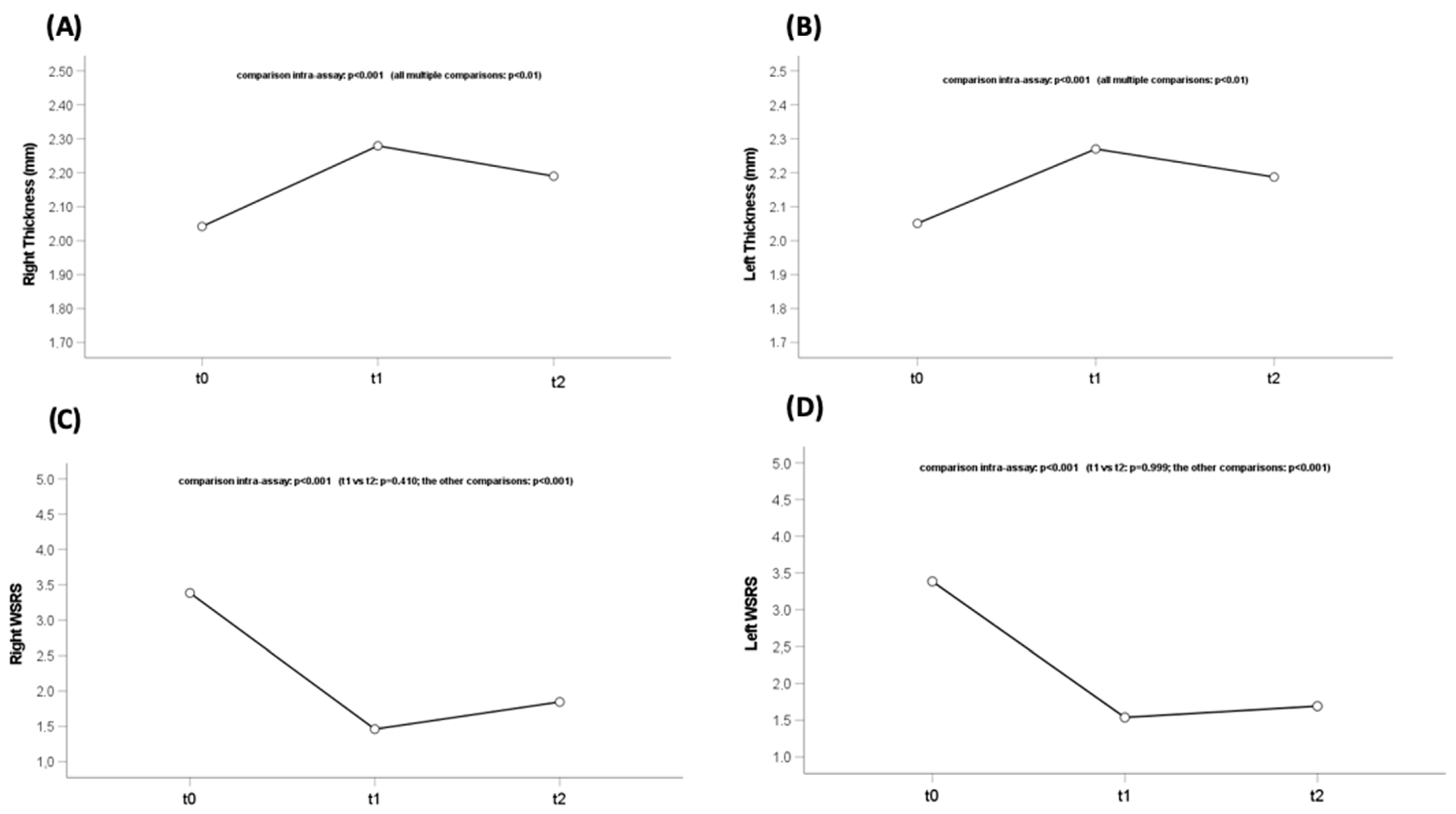
3. Results
Population Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAIS | Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| MHz | Megahertz |
| UHFUS | Ultra-high-frequency ultrasound |
| WSRS | Wrinkle Severity Rating Scale |
References
- Brandt, F.S.; Cazzaniga, A. Hyaluronic acid gel fillers in the management of facial aging. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wongprasert, P.; Dreiss, C.A.; Murray, G. Evaluating hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: A critique of current characterization methods. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurano, R.; Boffito, M.; Cassino, C.; Liberti, F.; Ciardelli, G.; Chiono, V. Design of Injectable Bioartificial Hydrogels by Green Chemistry for Mini-Invasive Applications in the Biomedical or Aesthetic Medicine Fields. Gels 2023, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maytin, E.V. Hyaluronan: More than just a wrinkle filler. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, T.; Swift, A.; Cotofana, S.; Nikolis, A. Evaluating safety in hyaluronic acid lip injections. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdiales-Gálvez, F.; Barres-Caballer, J.; Carrasco-Sánchez, S. Ultrasound assessment of tissue integration of the crosslinked hyaluronic acid filler VYC-25L in facial lower-third aesthetic treat-ment: A prospective multicenter study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 20, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jia, Q.N.; Jin, H.Z.; Li, F.; He, C.-X.; Yang, J.; Zuo, Y.-G.; Fu, L.-Q. Long-Term Follow-Up of Longevity and Diffusion Pattern of Hyaluronic Acid in Nasolabial Fold Correction through High-Frequency Ultrasound. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 189e–196e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granieri, G.; Oranges, T.; Morganti, R.; Janowska, A.; Romanelli, M.; Manni, E.; Dini, V. Ultra-high frequency ultrasound detection of the dermo-epidermal junction: Its potential role in dermatology. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidanzi, C.; D’Erme, A.M.; Janowska, A.; Dini, V.; Romanelli, M.; Margiotta, F.M.; Viacava, P.; Bagnoni, G. Epidemiology of melanoma: The importance of correctly reporting to the cancer registries. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 31, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oranges, T.; Janowska, A.; Scatena, C.; Faita, F.; Di Lascio, N.; Izzetti, R.; Fidanzi, C.; Romanelli, M.; Dini, V. Ultra-High Frequency Ultrasound in Melanoma Management: A New Combined Ultrasonographic-Histopathological Approach. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzetti, R.; Oranges, T.; Janowska, A.; Gabriele, M.; Graziani, F.; Romanelli, M. The Application of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in Dermatology and Wound Management. Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 2020, 19, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowska, A.; Oranges, T.; Granieri, G.; Romanelli, M.; Fidanzi, C.; Iannone, M.; Dini, V. Non-invasive imaging techniques in presurgical margin assessment of basal cell carcinoma: Current evidence. Skin Res. Technol. 2023, 29, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, J.L.; Hoffmann, R.K.; Ward, C.E.; Schulman, J.M.; Grekin, R.C. Biochemistry, Physiology, and Tissue Interactions of Contemporary Biodegradable Injectable Dermal Fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44 (Suppl. S1), S19–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortsman, X. Common Applications of Ultrasound in Cosmetic and Plastic Surgery. In Atlas of Dermatologic Ultrasound, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as a therapeutic target in human diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Convery, C.; Davies, E. This month’s guideline: The Use of Hyaluronidase in Aesthetic Practice (v2.4). J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2018, 11, E61–E68. [Google Scholar]
- Kalmanson, O.A.; Misch, E.S.; Terella, A. Hyaluronic acid fillers may be longer-lasting than previously described: A case report of delayed filler-associated facial cellulitis. JPRAS Open 2022, 33, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, G.; Haftek, M.; Gensanne, D.; Turlier, V.; Mas, A.; Lagarde, J.; Schmitt, A. Follow up study of dermal hyaluronic acid injection by high frequency ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 57, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.L.; Kohli, I.; Hamzavi, I.H.; Council, M.L.; Rossi, A.M.; Ozog, D.M. Emerging imaging technologies in dermatology: Part II: Applications and limitations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortsman, X. Practical applications of ultrasound in dermatology. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdiales-Gálvez, F.; De Cabo-Francés, F.M.; Bové, I. Ultrasound patterns of different dermal filler materials used in aesthetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Hu, J.; Chai, H. High-Frequency Ultrasound of Facial Filler Materials in the Nasolabial Groove. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.M.; Grönros, J.; Hägg, U.; Wikström, J.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Friberg, P.; Fritsche-Danielson, R. Non-invasive real-time imaging of atherosclerosis in mice using ultrasound biomicroscopy. Atherosclerosis 2007, 190, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Gaón, N.; Wortsman, X. Ultrasound-guided hyaluronidase injection in cosmetic complications. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, e39–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzetti, R.; Vitali, S.; Aringhieri, G.; Nisi, M.; Oranges, T.; Dini, V.; Ferro, F.; Baldini, C.; Romanelli, M.; Caramella, D.; et al. Ultra-High Frequency Ultrasound, A Promising Diagnostic Technique: Review of the Literature and Single-Center Experience. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021, 72, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fino, P.; Toscani, M.; Grippaudo, F.R.; Giordan, N.; Scuderi, N. Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Study on the Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Injectable Cross-linked Hyaluronic Gel for the Correction of Moderate-to-Severe Nasolabial Wrinkles. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, D.J.; Littler, C.M.; Swift, R.W.; Gottlieb, S. The wrinkle severity rating scale: A validation study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2004, 5, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefura, T.; Kacprzyk, A.; Droś, J.; Krzysztofik, M.; Skomarovska, O.; Fijałkowska, M.; Koziej, M. Tissue Fillers for the Nasolabial Fold Area: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 2300–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Delta Fullness | Mean | Sd | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Between T1 and T0 dx | 0.59 | 0.34 | <0.001 |
| Between T24w and T1 dx | −0.47 | 0.41 | |
| Between T1 and T0 sx | 0.79 | 0.39 | <0.001 |
| Between T24w and T1 sx | −0.38 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvia, G.; Zerbinati, N.; Manzo Margiotta, F.; Michelucci, A.; Granieri, G.; Fidanzi, C.; Morganti, R.; Romanelli, M.; Dini, V. Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound as an Innovative Imaging Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Nasolabial Folds. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172761
Salvia G, Zerbinati N, Manzo Margiotta F, Michelucci A, Granieri G, Fidanzi C, Morganti R, Romanelli M, Dini V. Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound as an Innovative Imaging Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Nasolabial Folds. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(17):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172761
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvia, Giorgia, Nicola Zerbinati, Flavia Manzo Margiotta, Alessandra Michelucci, Giammarco Granieri, Cristian Fidanzi, Riccardo Morganti, Marco Romanelli, and Valentina Dini. 2023. "Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound as an Innovative Imaging Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Nasolabial Folds" Diagnostics 13, no. 17: 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172761
APA StyleSalvia, G., Zerbinati, N., Manzo Margiotta, F., Michelucci, A., Granieri, G., Fidanzi, C., Morganti, R., Romanelli, M., & Dini, V. (2023). Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound as an Innovative Imaging Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Nasolabial Folds. Diagnostics, 13(17), 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13172761







