Diagnostic of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Using Passive Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.; Liu, T.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Lei, M.; Xu, W.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, B. Use of chest CT in combination with negative RT-PCR assay for the 2019 novel coronavirus but high clinical suspicion. Radiology 2020, 295, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, L.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Luong, Q.C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Le, H.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Cao, T.M.; Pham, Q.D. Importation and human-to-human transmission of a novel coronavirus in Vietnam. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report e 28. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200217-sitrep-28-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn¼a19cf2ad_2 (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- World Meter. Corona Virus Update (Live). Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Guarner, J. Three emerging coronaviruses in two decades: The story of SARS, MERS, and now COVID-19. Clin. Infect Dis. 2020, 153, 420.e1. [Google Scholar]
- Rajgor, D.; Lee, M.; Archuleta, S.; Bagdasarian, N.; Quek, S. The many estimates of the COVID-19 case fatality rate. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020, 20, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Qiu, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y. Lower mortality of COVID-19 by early recognition and intervention: Experience from Jiangsu Province. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2020, 10, 1.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Xu, D.; Gong, Q.; et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: A retrospective review of medical records. Lancet 2020, 395, 809.e15. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, D.S.; Azhar, E.I.; Madani, T.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Kock, R.; Dar, O.; Ippolito, G.; Mchugh, T.D.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; et al. The continuing 2019-nCOVID epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health-The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. J. Infect 2020, 91, 264.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 577.e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Jiang, F.; Su, W.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Mei, W.; Zhan, L.-Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients undergoing surgeries during the incubation period of COVID-19 infection. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 54, 2.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Axfors, C.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G. Population-level COVID-19 mortality risk for non-elderly individuals overall and for non-elderly individuals without underlying diseases in pandemic epicenters. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Chakraborty, C.; Giri, S.K.; Pani, S.K.; Frnda, J. BIFM: Big-Data Driven Intelligent Forecasting Model for COVID-19. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 97505–97517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascarella, G.; Strumia, A.; Piliego, C.; Bruno, F.; Del Buono, R.; Costa, F.; Scarlata, S.; Agrò, F.E. COVID-19 diagnosis and management: A comprehensive review. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of Coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of chest CT and RTPCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xing, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Laboratory Diagnosis and Monitoring the Viral Shedding of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Innovation 2020, 1, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanagreh, L.; Alzoughool, F.; Atoum, M. The human coronavirus disease COVID19: Its origin, characteristics, and insights into potential drugs and its mechanisms. Pathogens 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Government. The Diagnostic and Treatment Protocol of COVID-19. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-02/19/content_5480948.htm (accessed on 19 April 2020).
- Wu, D.; Wu, T.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: What we know. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Lin, R.; Han, K. Clinical feature of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e14–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, M.A. What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Johani, S.; Hajeer, A.H. MERS-CoV diagnosis: An update. J. Infect. Public Health 2016, 9, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Xia, L. CT features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in 62 patients in Wuhan, China. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 200230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. Chest CT for typical 2019-nCoV pneumonia: Relationship to negative RTPCR testing. Radiology 2020, 296, E41–E45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, H.K.; Chakraborty, C.; Shelke, Y.; Pani, S.K. COVID-19 diagnosis system by deep learning approaches. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Hsieh, B.; Xiong, Z.; Halsey, K.; Choi, J.W.; Tran, T.M.L.; Pan, I.; Shi, L.-B.; Wang, D.-C.; Mei, J.; et al. Performance of radiologists in differentiating COVID-19 from viral pneumonia on chest CT. Radiology 2020, 10, 8.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.-C.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.-J.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.-P.; Zhang, H.; Liang, L.-H.; Wu, X.-L.; Lei, Y.; et al. CT imaging and differential diagnosis of COVID-19. Can. Assoc. Radiol J. 2020, 71, 195.e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raptis, C.A.; Hammer, M.M.; Short, R.G.; Shah, A.; Bhalla, S.; Bierhals, A.J.; Filev, P.D.; Hope, M.D.; Jeudy, J.; Kligerman, S.J.; et al. Chest CT and coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A critical review of the literature to date. AJR 2020, 16, 1.e4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J. Relation between chest CT findings and clinical conditions of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia: A multicenter study. AJR 2020, 214, 1072.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Abedi, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. AJR 2020, 10, 1.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Zerunian, M.; Polici, M.; Pucciarelli, F.; Polidori, T.; Rucci, C.; Guido, G.; Bracci, B.; De Dominicis, C.; Laghi, A. Chest CT features of COVID-19 in Rome, Italy. Radiology 2020, 296, E79–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Xu, D.Y.; Guan, T.M.; Li, Z.P.; Kuang, J.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Feng, S.T. Clinical and CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19). J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 81, 147–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legua, P.; Forner-Giner, M.Á.; Nuncio-Jáuregui, N.; Hernández, F. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 296, E115–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryanin, I.; Karbainov, S.; Shevelev, O.; Tarakanov, A.; Redpath, K.; Vesnin, S.; Ivanov, Y. Passive microwave radiometry in biomedical studies. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiko, J.; Koskensalo, K.; Sainio, T. Imaging-based internal body temperature measurements: The journal Temperature toolbox. Temperature 2020, 7, 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manual MMWR2020 (RTM-01-RES). Available online: www.mmwr.co.uk (accessed on 26 January 2016).
- Laskari, K.; Siores, E.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Sfikakis, P.P. Microwave Radiometry for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Inflammatory Arthritis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmonov, B.; Ovchinnikov, L.; Galazis, C.; Emilov, B.; Karaibragimov, M.; Seitov, M.; Vesnin, S.; Losev, A.; Levshinskii, V.; Popov, I.; et al. Passive Microwave Radiometry for the Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Lung Complications in Kyrgyzstan. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesnin, S.G.; Sedankin, M.K.; Ovchinnikov, L.M.; Gudkov, A.G.; Leushin, V.Y.; Sidorov, I.A.; Goryanin, I.I. Portable microwave radiometer for wearable devices. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 318, 112506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogna, A.; Yogendra, P.; Lee, S.H.E.; Aziz, A.; Cheong, E.; Chan, L.P.; Venkatanarasimha, N. Diagnostic ultrasound services during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharashova, E.E.; Kholmatova, K.K.; Gorbatova, M.A.; Grjibovsky, A.M. Application of multiple logistic regression analysis in healthcare using the SPSS statistical software package. Sci. Healthc. 2017, 4, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, A.; Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Eber, C. Portable chest X-ray in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A pictorial review. Clin. Imaging 2020, 64, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, Y.H.; Patnaik, K.S. Application of Deep Learning Techniques in Diagnosis of COVID-19 (Coronavirus): A Systematic Review. Neural Process Lett. 2022, 55, 3551–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
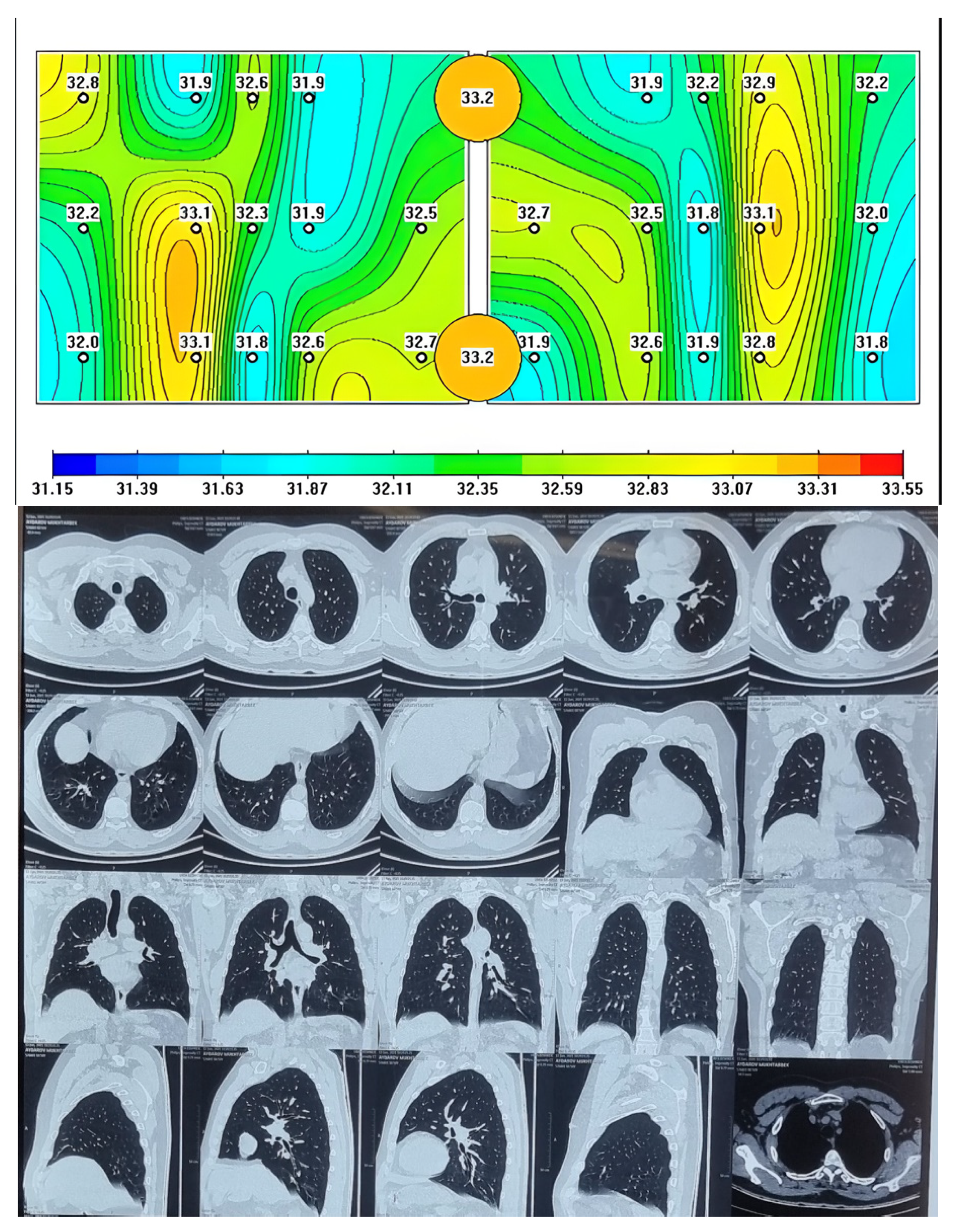
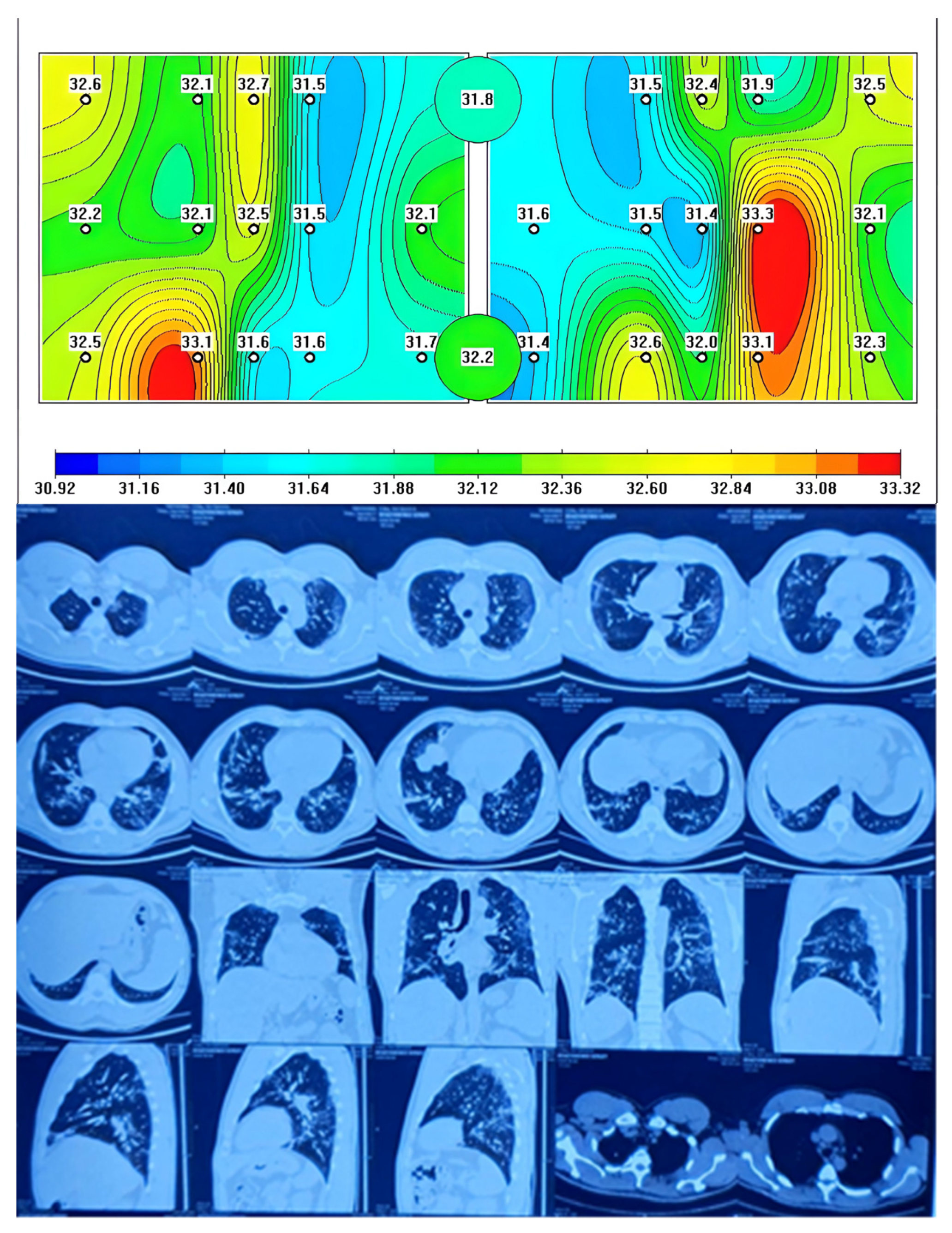
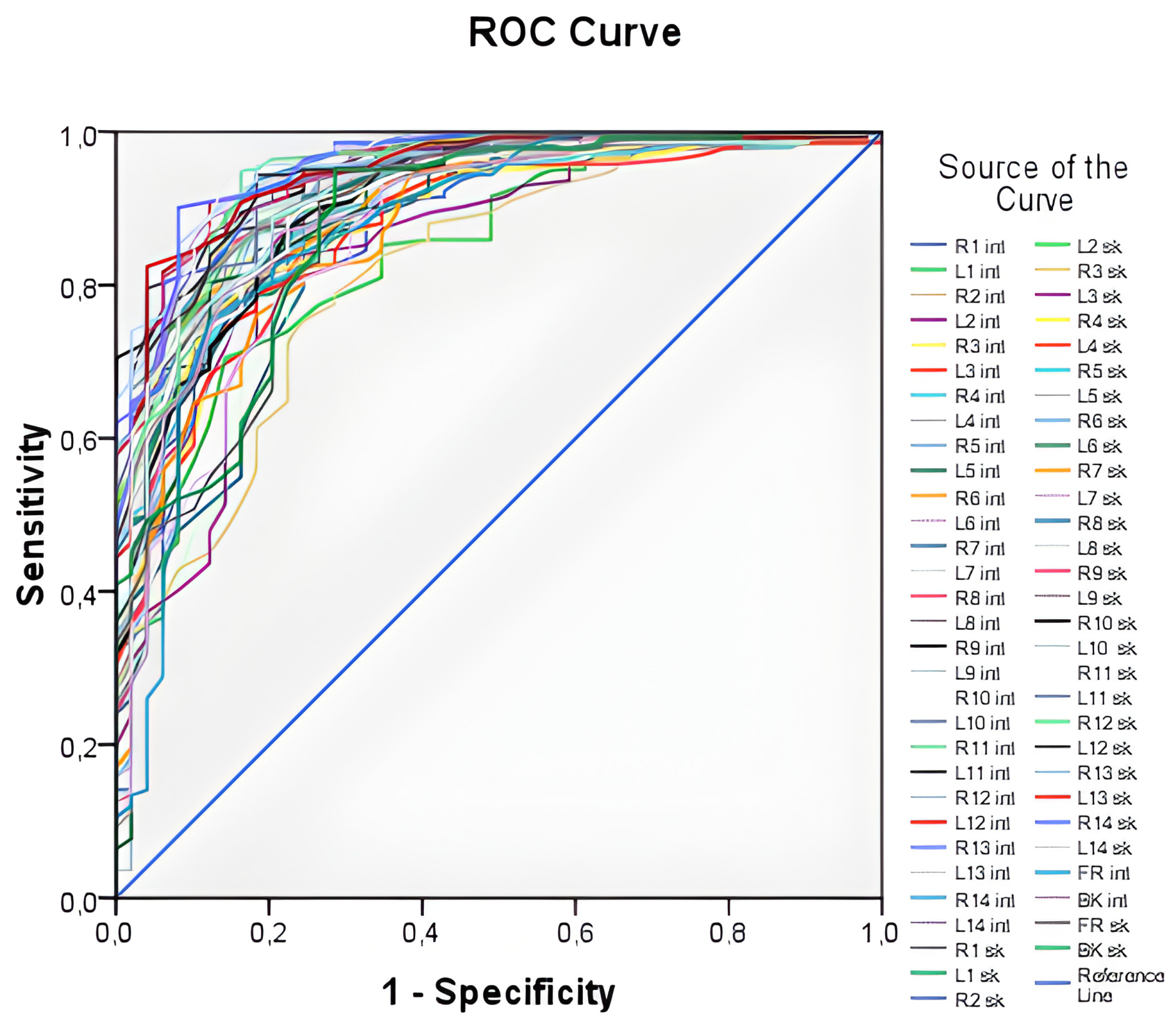
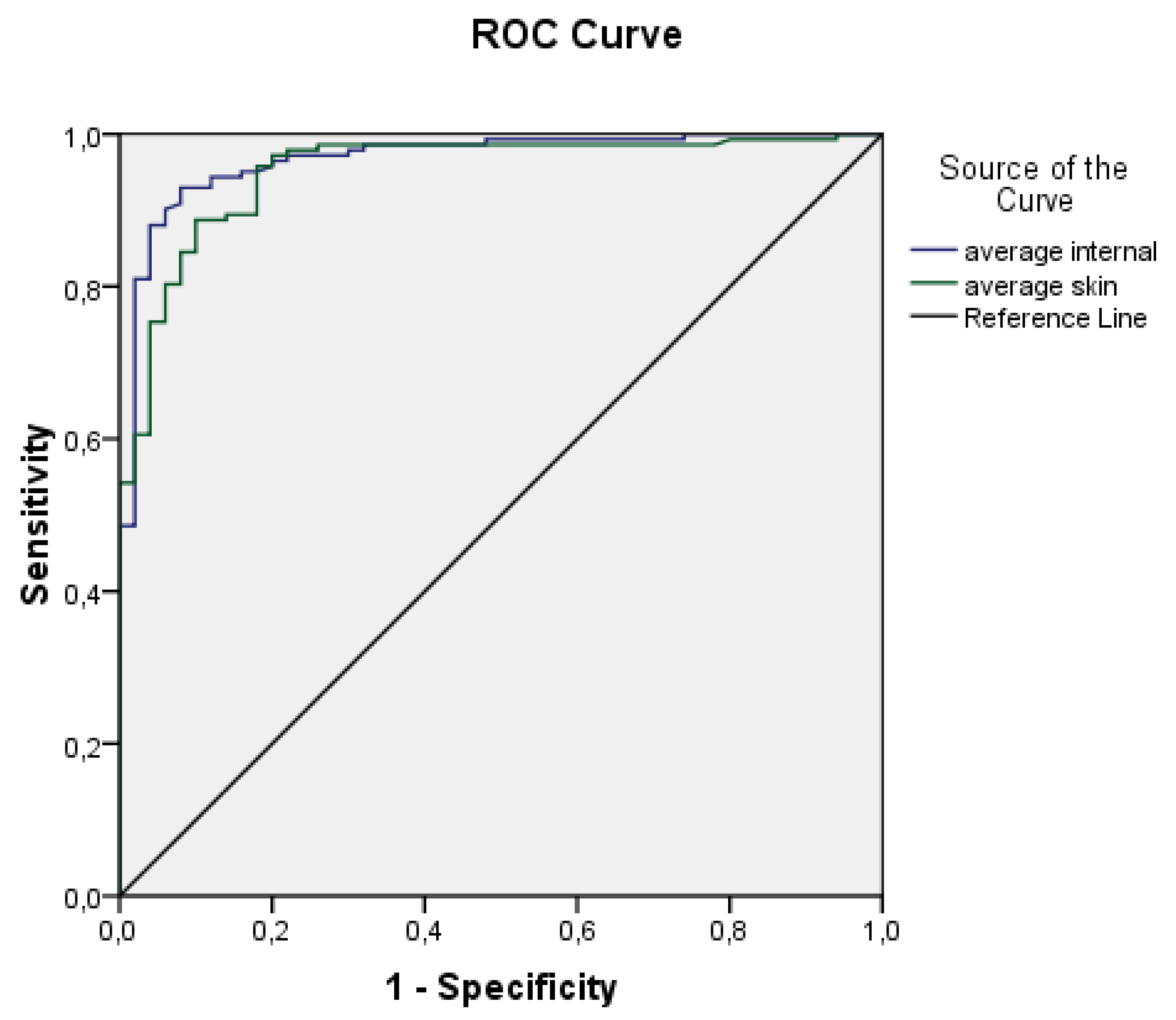
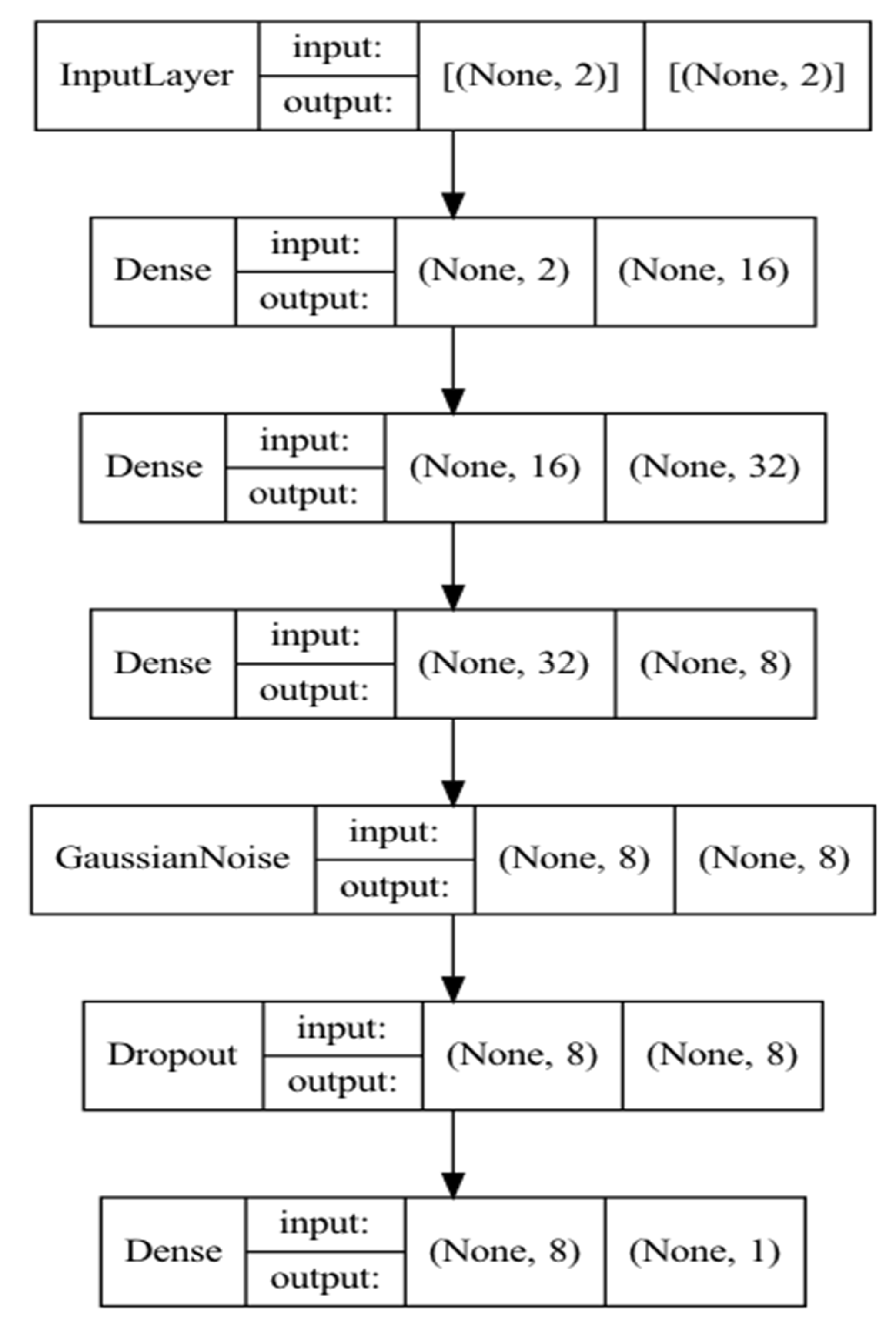
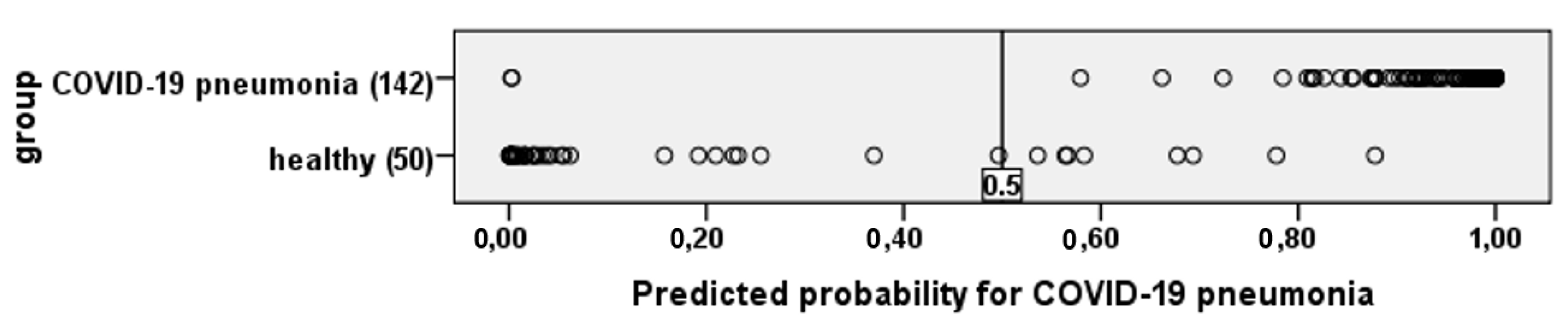
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| average internal (Tint) | 50 | 31.57 | 34.08 | 32.60 | 0.52 | 32.45 | 32.74 |
| average skin (Tsk) | 50 | 29.59 | 33.06 | 31.37 | 0.84 | 31.13 | 31.60 |
| difference | 50 | −0.27 | 3.16 | 1.2280 | 0.73 | 1.02 | 1.43 |
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Tint | 142 | 32.19 | 36.85 | 34.23 | 0.84 | 34.09 | 34.37 |
| Tsk | 142 | 30.06 | 36.07 | 33.21 | 0.78 | 33.08 | 33.34 |
| difference | 142 | −0.93 | 3.85 | 1.02 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 1.18 |
| Test Result Variable(s). | Area | Std. Error a | Asymptotic 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| average internal (Tint) | 0.967 | 0.013 | 0.941 | 0.993 |
| average skin (Tsk) | 0.951 | 0.016 | 0.919 | 0.983 |
| Observed | ROC Curve Best Thresholds | Predicted Correct | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | Deep Neural Network | |||
| group | control group | 88.8% | 92.7% | 99.7% |
| COVID-19 pneumonia | 95.2% | 97.6% | 98.6% | |
| Overall efficiency | 91.5% | 94.8% | 99.1% | |
| B | S.E. | Wald | df | Exp(B) | 95.0% CI for EXP(B) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Tint (b1) | 3.188 | 0.770 | 17.155 | 1 | 24.243 | 5.363 | 109.594 |
| Tsk (b2) | 1.677 | 0.524 | 10.236 | 1 | 5.351 | 1.915 | 14.951 |
| Const (b0) | −159,463 | 28,916 | 30,412 | 1 | 0.000 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emilov, B.; Sorokin, A.; Seiitov, M.; Kobayashi, B.T.; Chubakov, T.; Vesnin, S.; Popov, I.; Krylova, A.; Goryanin, I. Diagnostic of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Using Passive Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR). Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13152585
Emilov B, Sorokin A, Seiitov M, Kobayashi BT, Chubakov T, Vesnin S, Popov I, Krylova A, Goryanin I. Diagnostic of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Using Passive Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR). Diagnostics. 2023; 13(15):2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13152585
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmilov, Berik, Aleksander Sorokin, Meder Seiitov, Binsei Toshi Kobayashi, Tulegen Chubakov, Sergey Vesnin, Illarion Popov, Aleksandra Krylova, and Igor Goryanin. 2023. "Diagnostic of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Using Passive Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR)" Diagnostics 13, no. 15: 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13152585
APA StyleEmilov, B., Sorokin, A., Seiitov, M., Kobayashi, B. T., Chubakov, T., Vesnin, S., Popov, I., Krylova, A., & Goryanin, I. (2023). Diagnostic of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia Using Passive Medical Microwave Radiometry (MWR). Diagnostics, 13(15), 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13152585







