A Two-Step Single Plex PCR Method for Evaluating Key Colonic Microbiota Markers in Young Mexicans with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Protocol and Pilot Epidemiological Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Biological Samples
2.4. DNA Extraction and Purification
2.5. Selection of CM Markers
2.6. Oligonucleotide Primers of 16S rRNA
2.7. Two-Step Single-Plex PCR (2S-PCR)
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Selection of CM Differential Markers
3.2. Primer Design and Analysis
3.3. 2S-PCR
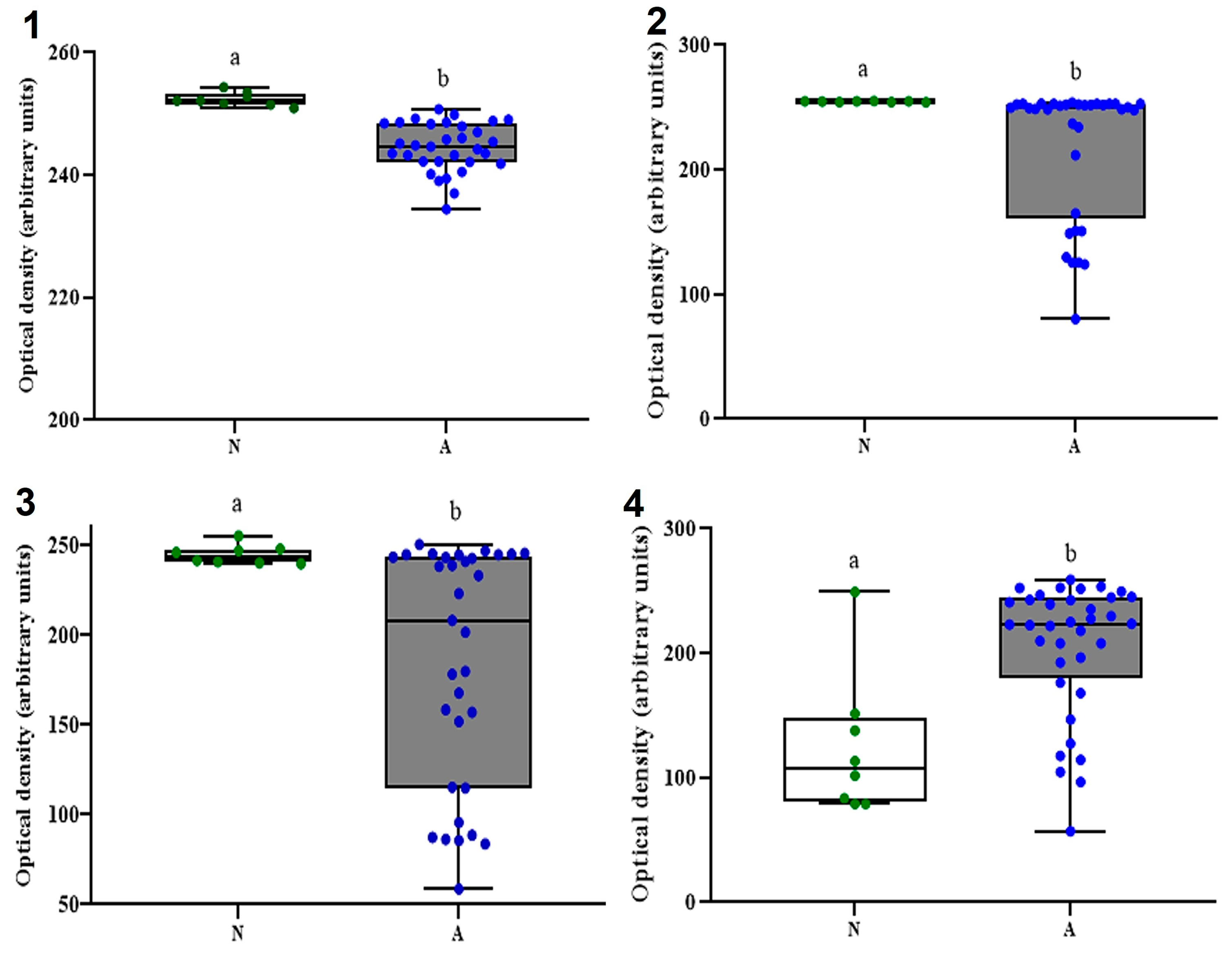
3.4. CM Commensal Biomarkers in ASD and NT Pediatric Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fida, M.; Khalil, S.; Abu Saleh, O.; Challener, D.W.; Sohail, M.R.; Yang, J.N.; Pritt, B.S.; Schuetz, A.N.; Patel, R. Diagnostic value of 16S ribosomal RNA gene polymerase chain reaction/Sanger sequencing in clinical practice. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhu, S.; Wang, B.; Duan, L. Alterations of gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome based on 16S rRNA-targeted sequencing: A systematic review. Clin. Translat. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. Gut microbiota profile in patients with type 1 diabetes based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing: A systematic review. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 3936247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.A.; Neoh, H.M.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chin, S.F.; Jamal, R. 16S rRNA gene sequencing for deciphering the colorectal cancer gut microbiome: Current protocols and workflows. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, K.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Zhu, T.; Yu, J.; Fang, S.; et al. Gut microbial profile is associated with the severity of social impairment and IQ performance in children with autism spectrum disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 789864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezawada, N.; Phang, T.H.; Hold, G.L.; Hansen, R. Autism spectrum disorder and the gut microbiota in children: A systematic review. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Zheng, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, H. Altered composition and function of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Trans. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Vázquez, L.; Van Ginkel Riba, G.; Arija, V.; Canals, J. Composition of gut microbiota in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-Martínez, P.; Rubio-Aparicio, M.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Veas, A.; Martínez-González, A.E. A meta-analysis of gut microbiota in children with autism. J. Autism Dev. Dis. 2022, 52, 1374–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, S.; Naik, B.; Ramachandra, N.B. Mucosa-associated specific bacterial species disrupt the intestinal epithelial barrier in the autism phenome. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 15, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, S.K.; Zarei, K.; Guseva, N.V.; Mangalam, A.K. Microbiota analysis using two-step PCR and next-generation 16S rRNA gene sequencing. JoVE 2019, 152, e59980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Bediwy, A.S.; El-Sawaf, Y.; Toema, O. Gut microbiota in various childhood disorders: Implication and indications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, V.; Yeasin, R.; Claud, E.C. Childhood development and the microbiome—The intestinal microbiota in maintenance of health and development of disease during childhood development. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, M.; Troisi, J. Gut reactions: How far are we from understanding and manipulating the microbiota complexity and the interaction with its host? Lessons from autism spectrum disorder studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Duan, G.; Song, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiota changes in patients with autism spectrum disorders. J. Psychiatric. Res. 2020, 129, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Yi, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Mou, W.W. Imbalance in the gut microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorders. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 572752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, H. Changes in the gut microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 1614–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Liang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, J. Altered gut microbiota in Chinese children with autism spectrum disorders. Front. Cell. Inf. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coretti, L.; Paparo, L.; Riccio, M.P.; Amato, F.; Cuomo, M.; Natale, A.; Borrelli, L.; Corrado, G.; de Caro, C.; Comegna, M.; et al. Gut microbiota features in young children with autism spectrum disorders. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanno, H.; Maeno, S.; Salminen, S.; Gueimonde, M.; Endo, A. 16S rRNA gene sequence diversity in Faecalibacterium prausnitzii-complex taxa has marked impacts on quantitative analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, fiac004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaei, M.; Sarafraz, N.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Leylabadlo, H.E. The importance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in human health and diseases. New Microbes New Infect. 2021, 43, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekani, M.; Baghi, H.B.; Naghili, B.; Vahed, S.Z.; Sóki, J.; Memar, M.Y. To resist and persist: Important factors in the pathogenesis of Bacteroides fragilis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikkert, O.P.; Ivanov, M.V.; Ukhova, A.; Zuysman, V.S.; Glukhova, L.B.; Avakyan, M.R.; Karnachuk, O.V. Desulfovibrio isolate from the microbiote of children with autistic spectrum disorders Immobilizes iron in poorly soluble crystalline sulfides. Microbiology 2021, 90, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Abbasi, A.; Somi, M.H.; Moaddab, S.Y.; Nikniaz, L.; Kafil, H.S.; Ebrahimzadeh Leylabadlo, H. Akkermansia muciniphila: From its critical role in human health to strategies for promoting its abundance in human gut microbiome. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Christophersen, C.T.; Sorich, M.J.; Gerber, J.P.; Angley, M.T.; Conlon, M.A. Low relative abundances of the mucolytic bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and Bifidobacterium spp. in feces of children with autism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6718–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltysova, M.; Tomova, A.; Ostatnikova, D. Gut microbiota profiles in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendraszak, M.; Gałęcka, M.; Kotwicka, M.; Regdos, A.; Pazgrat-Patan, M.; Andrusiewicz, M. Could selected gut microorganisms be diagnostic biomarkers for autism spectrum disorders? Study based on a commercial microbiota test. Res. Square 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pacheco, M.C.; Pimentel-Hernández, C.; Rivas-Mirelles, E.; Arredondo-García, J.L. Normatividad que rige la investigación clínica en seres humanos y requisitos que debe cumplir un centro de investigación para participar en un estudio clínico en México. Acta Pediatr. Mex. 2016, 37, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Chen, C.C.; Panyod, S.; Chen, R.A.; Wu, M.S.; Sheen, L.Y.; Chang, S.C. Optimization of fecal sample processing for microbiome study—The journey from bathroom to bench. J. Formosan Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K. Phenol-Chloroform Isoamyl Alcohol (PCI) DNA Extraction. In At the Bench: A Laboratory Navigator, 1st ed.; Barker, K., Tett, S., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.; McPherson, J.D.; McCombie, W.R. Coming of age: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nature Rev. Gen. 2016, 17, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapin, A.; Pattaroni, C.; Marsland, B.J.; Harris, N.L. Microbiota analysis using an Illumina MiSeq platform to sequence 16S rRNA genes. Curr. Protocols Mouse Biol. 2017, 7, 100–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.J.; Lee, E.S.; Nam, Y.D. Progress of analytical tools and techniques for human gut microbiome research. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Větrovský, T.; Baldrian, P. The variability of the 16S rRNA gene in bacterial genomes and its consequences for bacterial community analyses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Aladid, R.; Fernández-Barat, L.; Alcaraz-Serrano, V.; Bueno-Freire, L.; Vázquez, N.; Pastor-Ibáñez, R.; Palomeque, A.; Oscanoa, P.; Torres, A. Determining the most accurate 16S rRNA hypervariable region for taxonomic identification from respiratory samples. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkova, L.; Tomova, A.; Repiska, G.; Babinska, K.; Bokor, B.; Mikula, I.; Minarik, G.; Ostatnikova, D.; Soltys, K. Evaluation of 16S rRNA primer sets for characterisation of microbiota in paediatric patients with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.F.; Cao, W.W.; Cerniglia, C.E. PCR detection and quantitation of predominant anaerobic bacteria in human and animal fecal samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M. Mucin Utilisation and Host Interactions of the Novel Intestinal Microbe Akkermansia muciniphila. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2007. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing. p. 28238314. [Google Scholar]
- Bahena-Román, M.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, I.A.; Orbe-Orihuela, Y.C.; Díaz-Benítez, C.E.; Lagunas-Martínez, A.; Ayala-García, J.C.; Castañeda-Márquez, A.C.; Bermúdez-Morales, V.H.; Peralta-Romero, J.; Cruz, M.; et al. Low abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and low consumption of polyphenols associated with metabolic disorders in child population. Human Nutr. Metab. 2022, 30, 200167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T. Parameters for successful PCR primer design. In Quantitative Real-Time PCR: Methods and Protocols; Biassoni, R., Raso, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2065, pp. 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.; Singh, K.; Fern, A.; Kirton, E.S.; He, S.; Woyke, T.; Lee, J.; Chen, F.; Dangl, J.L.; Tringe, S.G. Primer and platform effects on 16S rRNA tag sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Castro Sangrador, J.; Dordević, D.; Rozehnalová, M.; Černý, M.; Fafula, R.; Vítězová, M.; Rittmann, S.K.-M.R. Evaluation of physiological parameters of intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria isolated from patients suffering from IBD and healthy people. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.; Schwab, C.; Milinovich, G.; Reichert, J.; Ben Mahfoudh, K.; Decker, T.; Engel, M.; Hai, B.; Hainzl, E.; Heider, S.; et al. Phylotype-level 16S rRNA analysis reveals new bacterial indicators of health state in acute murine colitis. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Harun, A.; Yean, C.Y.; Zaidah, A.R. A Nanoplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection of vancomycin-and linezolid-resistant genes in Enterococcus. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, S.J.; Musfeldt, M.; Ullmann, U.; Hampe, J.; Schreiber, S. Quantification of intestinal bacterial populations by real-time PCR with a universal primer set and minor groove binder probes: A global approach to the enteric flora. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srirungruang, S.; Mahajindawong, B.; Nimitpanya, P.; Bunkasem, U.; Ayuyoe, P.; Nuchprayoon, S.; Sanprasert, V. Comparative Study of DNA Extraction Methods for the PCR Detection of Intestinal Parasites in Human Stool Samples. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, A.E.; Andreo-Martínez, P. Autism and gut microbiota: A bibliometric study. Rev. J. Autism Develop. Dis. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Piccolo, M.; Vannini, L.; Siragusa, S.; De Giacomo, A.; Serrazzanetti, D.I.; Cristofori, F.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Gobbetti, M.; Francavilla, R. Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Ristori, M.V.; Guerrera, S.; Guarrasi, V.; Conte, F.; Russo, A.; Lupi, E.; Albitar-Nehme, S.; Gardini, S.; Paci, P.; et al. Gut microbiota ecology and inferred functions in children with ASD compared to neurotypical subjects. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 871086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; Cao, S.; Liang, G.; He, D.; Lv, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Q. Comparison of gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders and neurotypical boys in China: A case-control study. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2021, 6, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berding, K.; Donovan, S.M. Diet can impact microbiota composition in children with autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Fox, G.E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: The primary kingdoms. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5088–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.; Bonham, K.S.; Rowland, S.; Pattanayak, C.W.; RESONANCE Consortium; Klepac-Ceraj, V. Comparative analysis of 16S rRNA gene and metagenome sequencing in pediatric gut microbiomes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 670336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
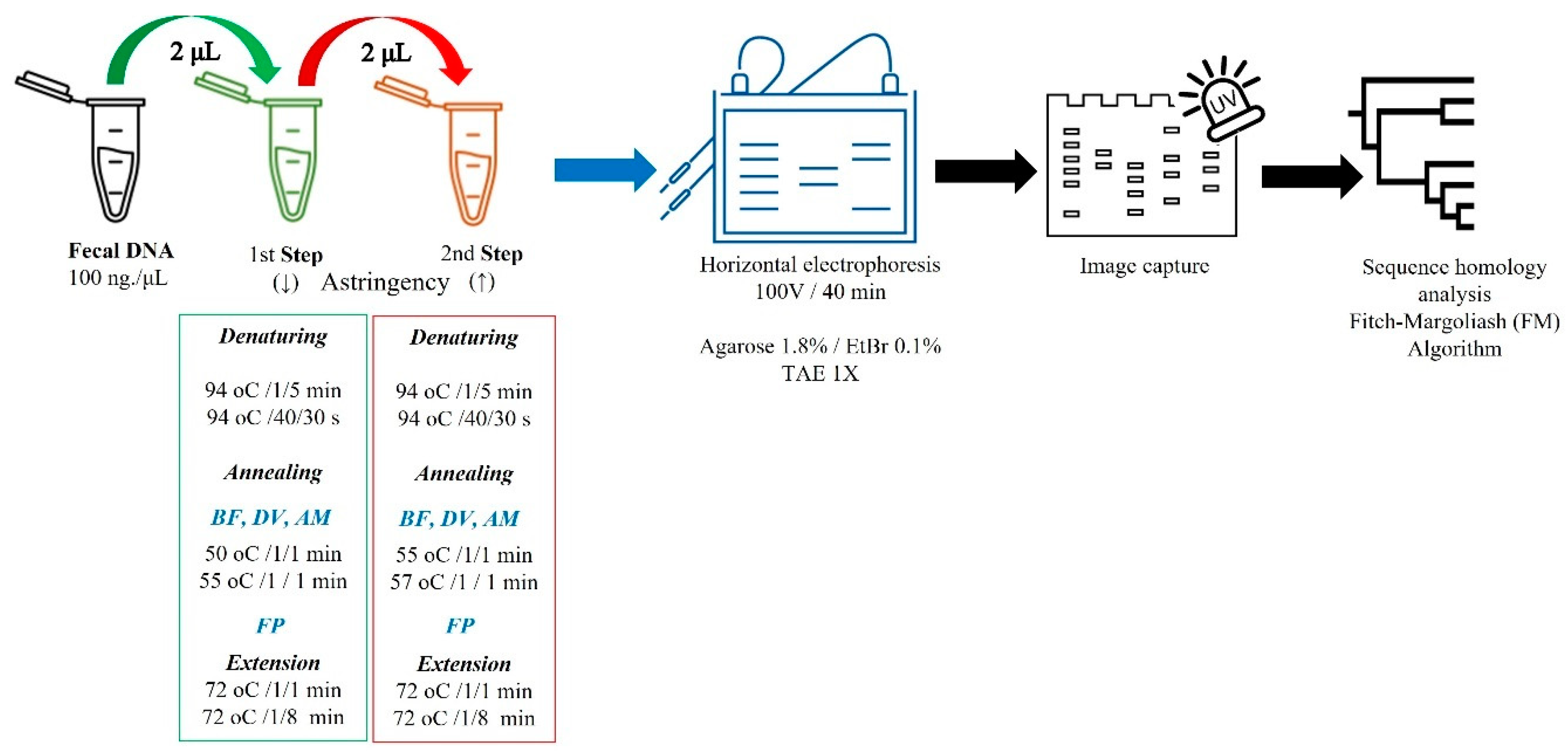

| Bacteria | Primer Sequences (3′-5′) | Length (bp) | Tm (°C) | GeneBank/Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF | F: CCCTTTACTCGGGGATAG R: CTTGGCTGGTTCAGGCTAG | 265 | 55 | NR_074784.2 * |
| FP | F: GATGGCCTCGCGTCCGATTAG R: CCGAAGACCTTCTTCCTCC | 198 | 57 | [19,20] |
| DV | F: GCGTGAAAGGACTTCGGT R: CCACCAACTAGCTAATGGGA | 196 | 55 | AB252583.1 * |
| AM | F: CAGCACGTGAAGGTGGGGAC R: CCTTGCGGTTGGCTTCAGAT | 327 | 60 | [25] |
| MeSH-Keyword, BOP, (Search Stage) 2 | 80–89 | 90–99 | 00–09 | 10–19 | 20–23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autism/autistic disorder/ASD (1) | 27,300 | 68,900 | 321,000 | 853,000 | 211,000 |
| (1) + Microbiota/GI microbiome (2) | 16 | 46 | 996 | 12,800 | 16,800 |
| (1 + 2) + Bacteroides fragilis (3a) | 4 | 1 | 38 | 1590 | 1670 |
| (1 + 2) + Akkermansia muciniphila (3b) | 0 | 1 | 8 | 922 | 1950 |
| (1 + 2) + Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (3c) | 0 | 0 | 17 | 1080 | 1670 |
| (1 + 2) + Desulfovibrio vulgaris (3d) | 0 | 0 | 6 | 105 | 117 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Mejía, J.; Campos-Vega, R.; Wall-Medrano, A.; Jiménez-Vega, F. A Two-Step Single Plex PCR Method for Evaluating Key Colonic Microbiota Markers in Young Mexicans with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Protocol and Pilot Epidemiological Application. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142387
Herrera-Mejía J, Campos-Vega R, Wall-Medrano A, Jiménez-Vega F. A Two-Step Single Plex PCR Method for Evaluating Key Colonic Microbiota Markers in Young Mexicans with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Protocol and Pilot Epidemiological Application. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(14):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142387
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Mejía, Julián, Rocío Campos-Vega, Abraham Wall-Medrano, and Florinda Jiménez-Vega. 2023. "A Two-Step Single Plex PCR Method for Evaluating Key Colonic Microbiota Markers in Young Mexicans with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Protocol and Pilot Epidemiological Application" Diagnostics 13, no. 14: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142387
APA StyleHerrera-Mejía, J., Campos-Vega, R., Wall-Medrano, A., & Jiménez-Vega, F. (2023). A Two-Step Single Plex PCR Method for Evaluating Key Colonic Microbiota Markers in Young Mexicans with Autism Spectrum Disorders: Protocol and Pilot Epidemiological Application. Diagnostics, 13(14), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142387








