[18F]FDG-PET/CT in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Retrospective Data from a Belgian Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
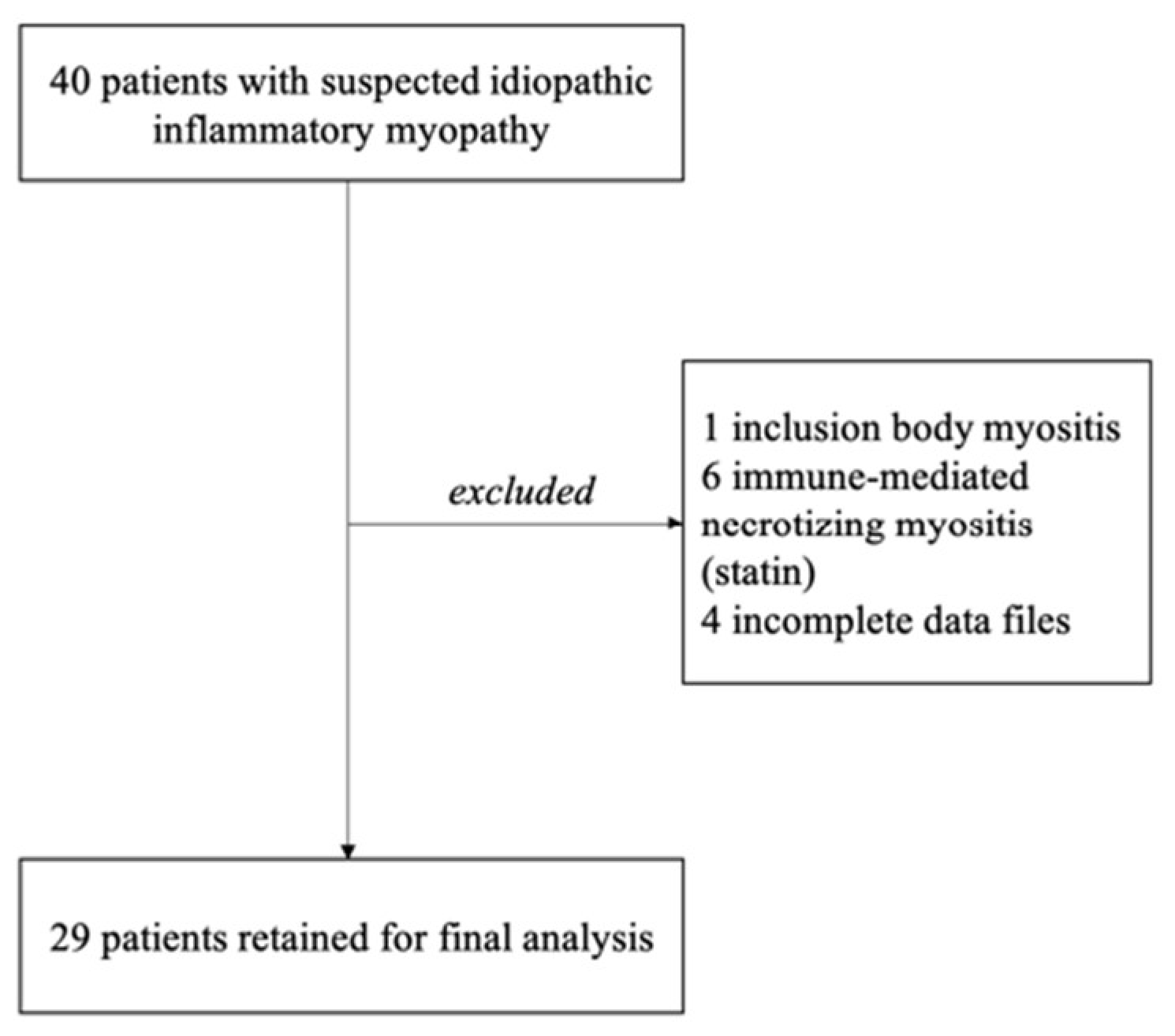
2. Materials and Methods
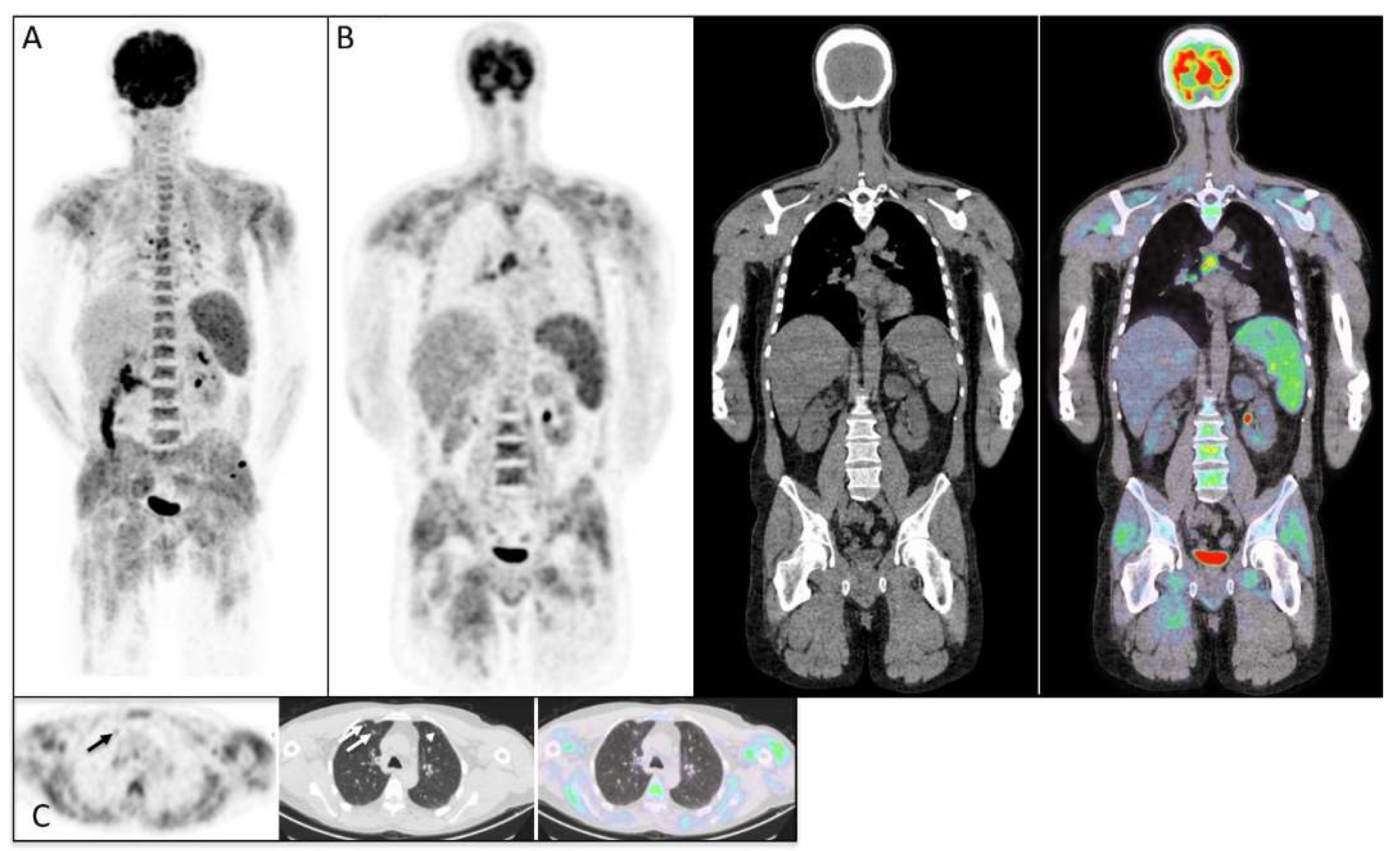
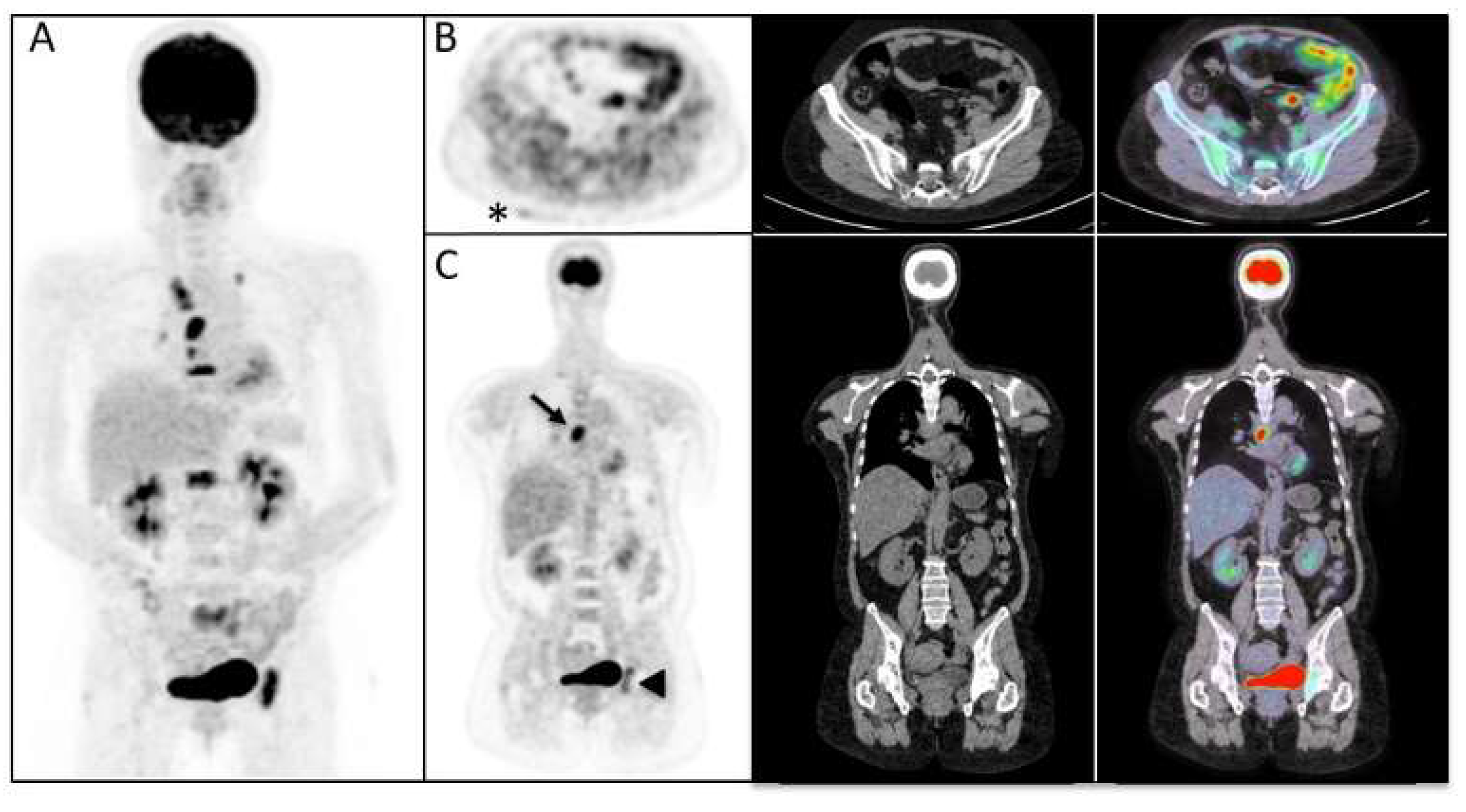
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yildiz, H.; D’Abadie, P.; Gheysens, O. The Role of Quantitative and Semi-quantitative [(18)F]FDG-PET/CT Indices for Evaluating Disease Activity and Management of Patients With Dermatomyositis and Polymyositis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 883727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohan, A.; Peter, J.B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betteridge, Z.; McHugh, N. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: An important tool to support diagnosis of myositis. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halilu, F.; Christopher-Stine, L. Myositis-specific Antibodies: Overview and Clinical Utilization. Rheumatol. Immunol. Res. 2022, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, C.; Paramalingam, S.; Stevenson, B.; Brusch, A.; Needham, M. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: A review. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 51, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammen, A.L.; Chung, T.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Rosen, P.; Rosen, A.; Doering, K.R.; Casciola-Rosen, L.A. Autoantibodies against 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in patients with statin-associated autoimmune myopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Trallero-Araguas, E.; Milisenda, J.C.; Grau-Junyent, J.M.; Mammen, A.L. Classification and management of adult inflammatory myopathies. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, I.E.; Tjarnlund, A.; Bottai, M.; Werth, V.P.; Pilkington, C.; de Visser, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Amato, A.A.; Barohn, R.J.; Liang, M.H.; et al. 2017 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Adult and Juvenile Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies and Their Major Subgroups. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, S.; Amato, A. Electrodiagnostic evaluation of myopathies. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 24, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malartre, S.; Bachasson, D.; Mercy, G.; Sarkis, E.; Anquetil, C.; Benveniste, O.; Allenbach, Y. MRI and muscle imaging for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Brain Pathol. 2021, 31, e12954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Casal-Dominguez, M.; Carrino, J.A.; Lahouti, A.H.; Basharat, P.; Albayda, J.; Paik, J.J.; Ahlawat, S.; Danoff, S.K.; Lloyd, T.E.; et al. Thigh muscle MRI in immune-mediated necrotising myopathy: Extensive oedema, early muscle damage and role of anti-SRP autoantibodies as a marker of severity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, G.; Monforte, M.; De Fino, C.; Kley, R.A.; Ricci, E.; Mirabella, M. Magnetic resonance imaging pattern recognition in sporadic inclusion-body myositis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariampillai, K.; Granger, B.; Amelin, D.; Guiguet, M.; Hachulla, E.; Maurier, F.; Meyer, A.; Tohme, A.; Charuel, J.L.; Musset, L.; et al. Development of a New Classification System for Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Based on Clinical Manifestations and Myositis-Specific Autoantibodies. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasova Studynkova, J.; Charvat, F.; Jarosova, K.; Vencovsky, J. The role of MRI in the assessment of polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmucci, S.; Di Mari, A.; Cancemi, G.; Pennisi, I.; Mauro, L.A.; Sambataro, G.; Sambataro, D.; Galioto, F.; Fazio, G.; Ferlito, A.; et al. Clinical and Radiological Features of Interstitial Lung Diseases Associated with Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis. Medicina 2022, 58, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. Inflammatory muscle diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendijk, J.E.; Amato, A.A.; Lecky, B.R.; Choy, E.H.; Lundberg, I.E.; Rose, M.R.; Vencovsky, J.; de Visser, M.; Hughes, R.A. 119th ENMC international workshop: Trial design in adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, with the exception of inclusion body myositis, 10–12 October 2003, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrick, A.; Kirby, J.; Ba, D.; Leslie, D.; Olsen, N.; Foulke, G. Positron emission tomography costs less to patients than conventional screening for malignancy in dermatomyositis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentick, G.; Fairley, J.; Nadesapillai, S.; Wicks, I.; Day, J. Defining the clinical utility of PET or PET-CT in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: A systematic literature review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 57, 152107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, T.; Maezawa, R.; Kurasawa, K.; Okada, H.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, T. Detection of inflammatory lesions by f-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, M.; Fujihara, K.; Misu, T.; Arai, A.; Kaneta, T.; Aoki, M. Clinical values of FDG PET in polymyositis and dermatomyositis syndromes: Imaging of skeletal muscle inflammation. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motegi, S.I.; Fujiwara, C.; Sekiguchi, A.; Hara, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Maeno, T.; Higuchi, T.; Hirasawa, H.; Kodaira, S.; Tomonaga, H.; et al. Clinical value of (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for interstitial lung disease and myositis in patients with dermatomyositis. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q. Multiple values of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai-Okuda, H.; Norikane, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mitamura, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Takami, Y.; Wakiya, R.; Nakashima, S.; Dobashi, H.; Nishiyama, Y. (18)F-FDG PET/CT in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis: Correlation with serum muscle enzymes. Eur. J. Hybrid Imaging 2020, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lv, X.; Chen, Q.; Wei, W. [(18)F]Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for diagnosing polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 5023–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszak, J.; Blondet, C.; Geny, B.; Namer, I.J.; Meyer, A. Comment on: Muscle fluorodeoxyglucose uptake assessed by positron emission tomography-computed tomography as a biomarker of inflammatory myopathies disease activity: Reply. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2345–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitone, N.; Versari, A.; Zuccoli, G.; Levrini, G.; Macchioni, P.; Bajocchi, G.; Salvarani, C. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for the assessment of myositis: A case series. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 570–573. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, S.; Ikeda, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Sanayama, Y.; Okubo, A.; Nakagomi, D.; Takahashi, K.; Yokota, M.; Suto, A.; et al. [18F]FDG uptake in proximal muscles assessed by PET/CT reflects both global and local muscular inflammation and provides useful information in the management of patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martis, N.; Viau, P.; Zenone, T.; Andry, F.; Grados, A.; Ebbo, M.; Castela, E.; Brihaye, B.; Denis, E.; Liguori, S.; et al. Clinical value of a [18F]-FDG PET-CT muscle-to-muscle SUV ratio for the diagnosis of active dermatomyositis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6708–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, H. Value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of occult malignancy in patients with dermatomyositis. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Cao, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, B.; Sun, Y.; Ke, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, B.; Lin, J. The lungs were on fire: A pilot study of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-related interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liang, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Lin, J. Radiological Characteristics of Patients With Anti-MDA5-Antibody-Positive Dermatomyositis in (18)F-FDG PET/CT: A Pilot Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 779272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.A.; Melzer, R.A.; Schindler, C.; Muller-Brand, J.; Tyndall, A.; Nitzsche, E.U. The value of [18F]FDG-PET in the diagnosis of large-vessel vasculitis and the assessment of activity and extent of disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Grau, J.M.; Gamez-Cenzano, C.; Vidaller-Palacin, A.; Martinez-Gomez, X.; Trallero-Araguas, E.; Andia-Navarro, E.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Conventional cancer screening versus PET/CT in dermatomyositis/polymyositis. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trallero-Araguas, E.; Gil-Vila, A.; Martinez-Gomez, X.; Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Alvarado-Cardenas, M.; Simo-Perdigo, M.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A. Cancer screening in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Ten years experience from a single center. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 53, 151940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girija, M.S.; Tiwari, R.; Vengalil, S.; Nashi, S.; Preethish-Kumar, V.; Polavarapu, K.; Kulanthaivelu, K.; Arbind, A.; Bardhan, M.; Huddar, A.; et al. PET-MRI in idiopathic inflammatory myositis: A comparative study of clinical and immunological markers with imaging findings. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2022, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliha, P.G.; Hudson, M.; Abikhzer, G.; Singerman, J.; Probst, S. 18F-FDG PET/CT versus conventional investigations for cancer screening in autoimmune inflammatory myopathy in the era of novel myopathy classifications. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2019, 40, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, Z.; Ye, S. Interstitial Lung Disease in Anti-MDA5 Positive Dermatomyositis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 60, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gono, T.; Masui, K.; Nishina, N.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Ikeda, K.; Kirino, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tanino, Y.; Nunokawa, T.; et al. Risk Prediction Modeling Based on a Combination of Initial Serum Biomarker Levels in Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Shao, C.; Huang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Zeng, X.; Xu, Z. Prognosis of adult idiopathic inflammatory myopathy-associated interstitial lung disease: A retrospective study of 679 adult cases. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, T.; Fort, R.; Cottin, V.; Provencher, S.; Durieu, I.; Jardel, S.; Hot, A.; Reynaud, Q.; Lega, J.C. Treatment of idiopathic inflammatory myositis associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Long, Y.; Zhang, B.; He, Q.; Tang, K.; Zhang, X. 18F-FDG PET/CT and HRCT: A combined tool for risk stratification in idiopathic inflammatory myopathy-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total number of patients | 29 |
| Mean age at diagnosis (years) | 48.7 |
| Sex (female) | 19 (65.5%) |
| Myositis subset | |
| Dermatomyositis | 22 (75.8%) |
| Polymyositis | 7 (24.1%) |
| Overlap syndrome | 0 (0.0%) |
| Symptoms | |
| Muscle weakness | 24 (82.7%) |
| Skin lesions | 22 (75.8%) |
| Cough | 5 (17.2%) |
| Dyspnea | 5 (17.2%) |
| Dysphagia | 9 (31%) |
| Arthralgia | 5 (17.2%) |
| Positive ANA | 21 (72.4%) |
| ANA, titer | |
| 1/80 | 8 (27.5%) |
| 1/160 | 4 (13.7%) |
| 1/320 | 4 (13.7%) |
| 1/640 | 2 (0.6%) |
| 1/1280 | 3 (10.3%) |
| Myositis-specific autoantibodies (17/29) | |
| SAE | 2 (0.6%) |
| SRP | 0 |
| MDA5 | 1 (0.3%) |
| MI-2 | 1 (0.3%) |
| Ro52 | 0 |
| NXP2 | 2 (0.6%) |
| TIF1-γ | 4 (13.7%) |
| PI12 | 1 (0.3%) |
| PI7 | 3 (10.3%) |
| JO-1 | 3 (10.3%) |
| CK level (U/L) at diagnosis (mean) [range] | 3125.14 [27–18,760] |
| CRP level (mg/L) at diagnosis (mean) | 30.3 |
| Positive electromyography | 17/27 (62.9%) |
| Positive whole-body muscle MRI | 10/19 (52.6%) |
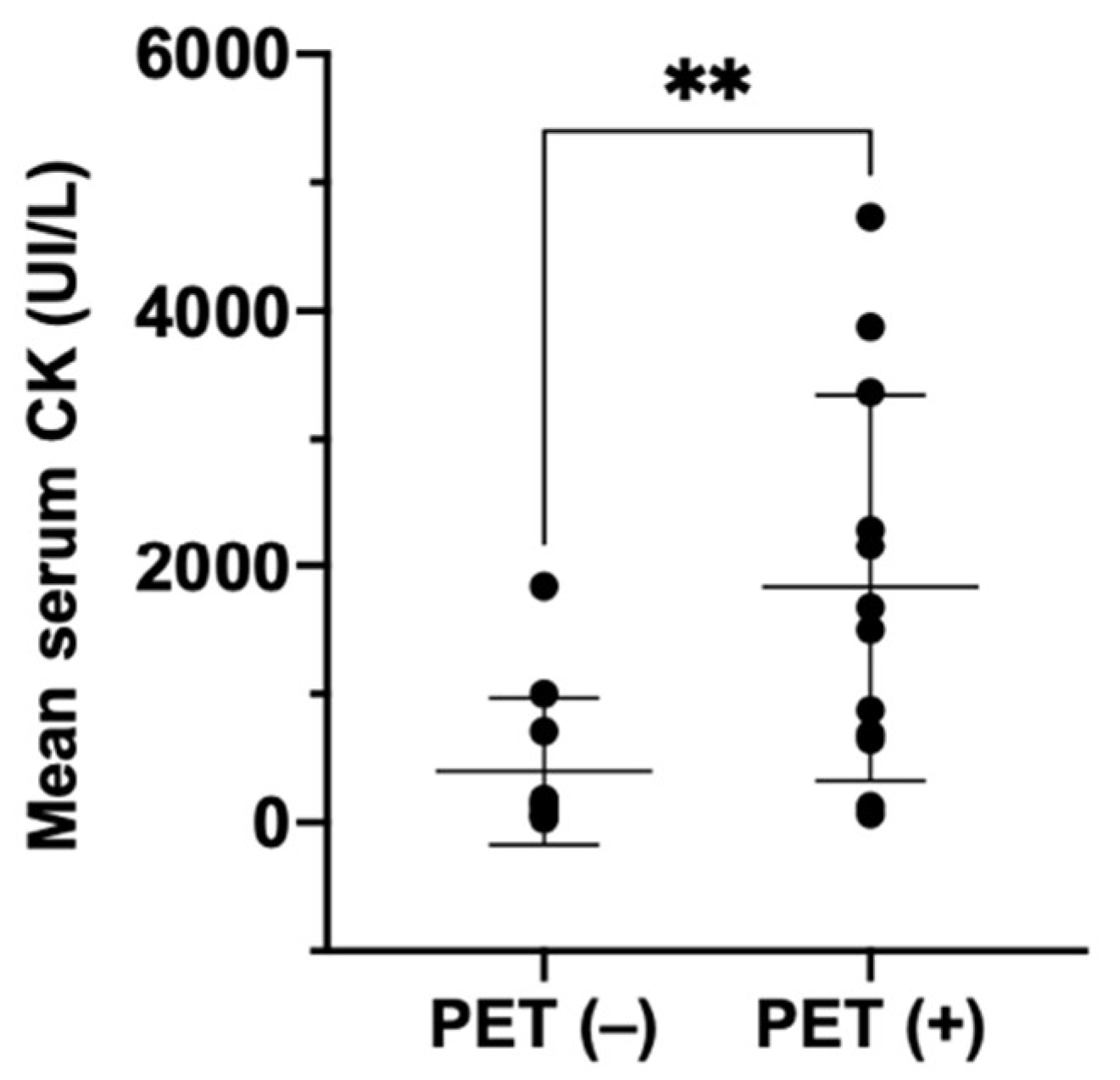
| Muscle activity on [18F]FDG-PET/CT | 13/27 (48.1%) |
| Positive skin biopsy | 11/17 (64.7%) |
| Positive muscle biopsy | 11/15 (73.3%) |
| Interstitial lung diseases | 8 (27.5%) |
| Cancer detected by [18F]FDG-PET/CT | 3/27 (11.1%) |
| Treatment | |
| Corticosteroids | 27 (93%) |
| Methotrexate | 18 (62%) |
| Azathioprine | 9 (31%) |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 1 (0.3%) |
| Rituximab | 2 (0.6%) |
| IVIG | 5 (17.2%) |
| Opportunistic infection | 3 (10.3%) |
| Death | 4 (13.7%) |
| PET/CT-Positive | PET/CT-Negative | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMG (+) | 12 | 4 | 0.0036 |
| EMG (−) | 1 | 9 | |
| MRI (+) | 8 | 3 | 0.0198 |
| MRI (−) | 1 | 7 |
| PET/CT-Positive | PET/CT-Negative | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dyspnea (+) | 4 | 0 | 0.002 |
| Dyspnea (−) | 3 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yildiz, H.; Lepere, C.; Zorzi, G.; Gheysens, O.; Roodhans, F.; Pothen, L. [18F]FDG-PET/CT in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Retrospective Data from a Belgian Cohort. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142316
Yildiz H, Lepere C, Zorzi G, Gheysens O, Roodhans F, Pothen L. [18F]FDG-PET/CT in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Retrospective Data from a Belgian Cohort. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(14):2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142316
Chicago/Turabian StyleYildiz, Halil, Charlotte Lepere, Giulia Zorzi, Olivier Gheysens, Fabien Roodhans, and Lucie Pothen. 2023. "[18F]FDG-PET/CT in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Retrospective Data from a Belgian Cohort" Diagnostics 13, no. 14: 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142316
APA StyleYildiz, H., Lepere, C., Zorzi, G., Gheysens, O., Roodhans, F., & Pothen, L. (2023). [18F]FDG-PET/CT in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Retrospective Data from a Belgian Cohort. Diagnostics, 13(14), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13142316






