Can Low-Iodine, Low-Radiation-Dose CT Aortogram Reliably Detect Endoleak after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of the Aorta?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
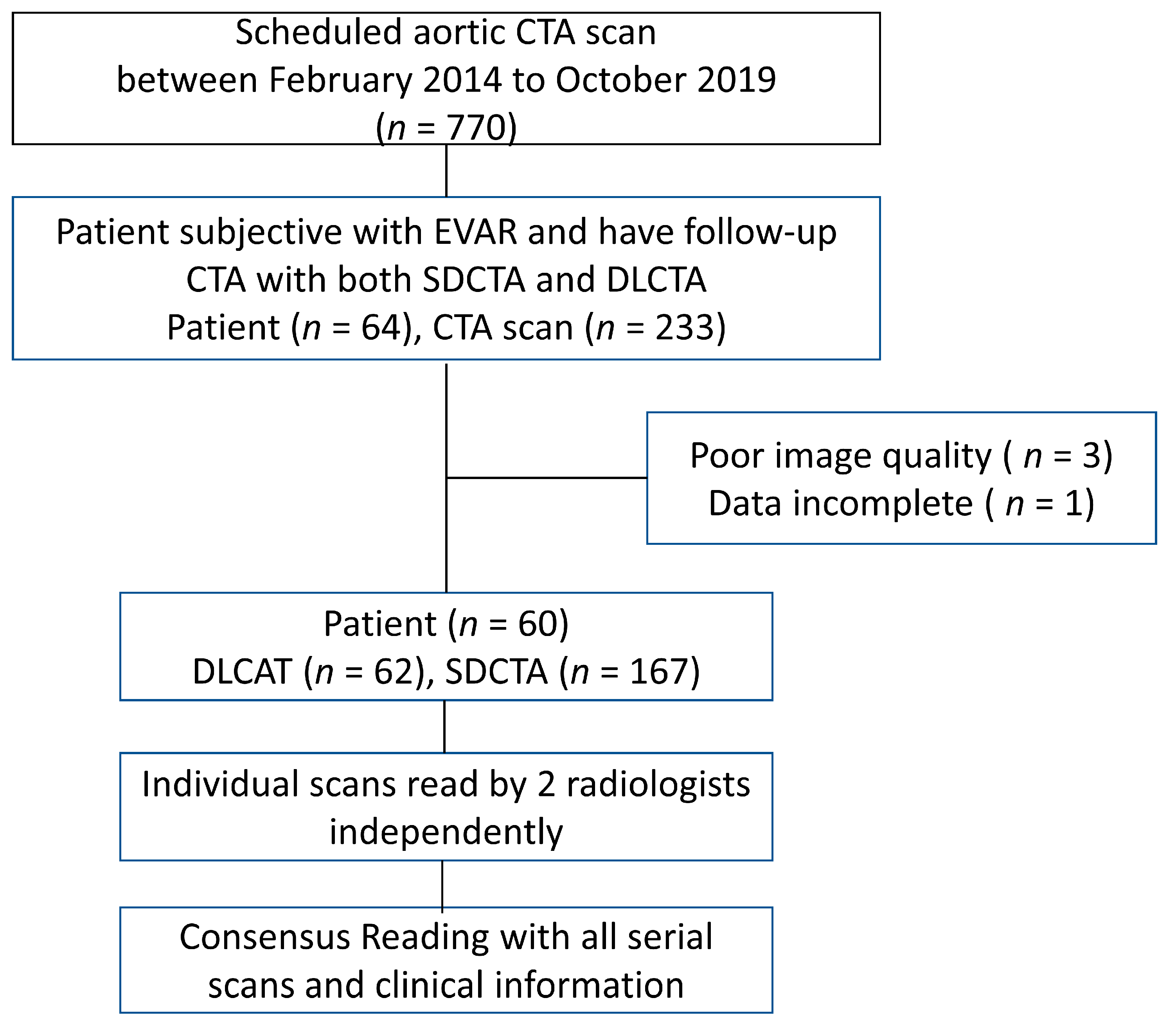
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. CT Technique and Acquisition Protocol
2.3. Image Reconstruction and Analysis
2.4. Radiation Dose Estimation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
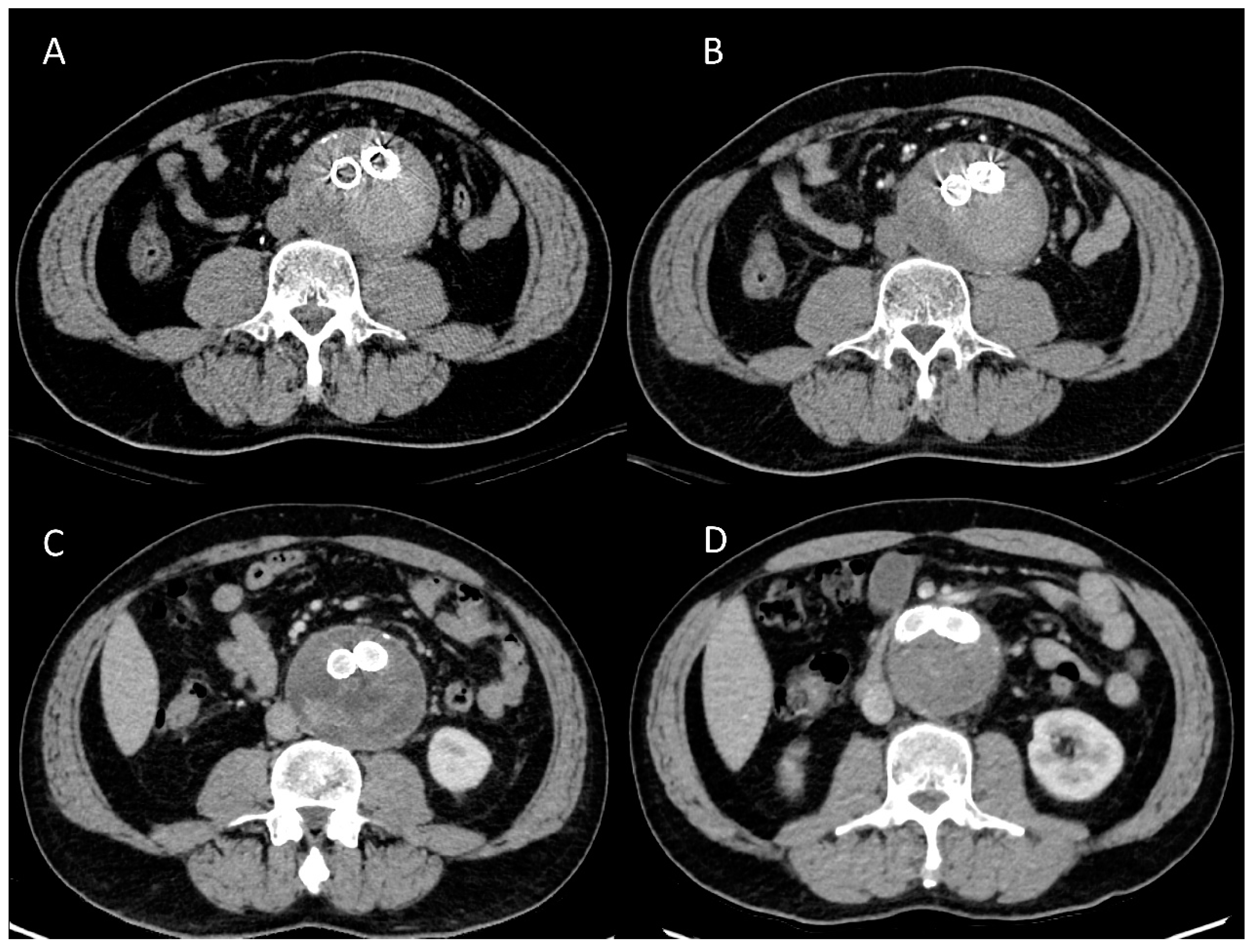
3.2. Endoleak Analysis

| Endoleak Detection by Standard-Dose CTA and DLCTA | ||||||||
| SDCTA | ||||||||
| Endoleak | Positive | Negative | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | |
| DLCTA | Positive | 12 | 2 | 85.7% | 95.7% | 85.7% | 95.7% | 93.3% |
| Negative | 2 | 44 | ||||||
| Endoleak Detection by Standard-Dose CTA and DLCTA (Revised Version) | ||||||||
| SDCTA | ||||||||
| Endoleak | Positive | Negative | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Sccuracy | |
| DLCTA | Positive | 14 | 0 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Negative | 0 | 46 | ||||||
3.3. Radiation and Contrast Medium Dose
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLCTA | double-low computed tomography angiography |
| SDCTA | standard-dose computed tomography angiography |
| EVAR | endovascular aneurysm repair |
| TEVAR | thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| CM | contrast medium |
| ROI | region of interest |
| CTDIvol | volume CT dose index |
| DLP | dose–length product |
| ED | effective dose |
References
- Schermerhorn, M.L.; O’Malley, A.J.; Jhaveri, A.; Cotterill, P.; Pomposelli, F.; Landon, B.E. Endovascular vs. open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms in the Medicare population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Kingdom, E.T.I.; Greenhalgh, R.M.; Brown, L.C.; Powell, J.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Epstein, D.; Sculpher, M.J. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L.; et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiratzka, L.F.; Bakris, G.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Bersin, R.M.; Carr, V.F.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Eagle, K.A.; Hermann, L.K.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Kazerooni, E.A.; et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with Thoracic Aortic Disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation 2010, 121, e266–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golzarian, J.; Struyven, J. Imaging of complications after endoluminal treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobo, R.; Buth, J.; EUROSTAR Collaborators. Secondary interventions following endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair using current endografts. A EUROSTAR report. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 43, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, M.K.; Ouriel, K.; Greenberg, R.; McCann, R.; Murphy, M.; Fillinger, M.; Wyers, M.; Carpenter, J.; Fairman, R.; Makaroun, M.S. Are type II endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair endograft dependent? J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 43, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picel, A.C.; Kansal, N. Essentials of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair imaging: Postprocedure surveillance and complications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W358–W372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, M.; Cerini, P.; Lizio, D.; Vigna, L.; Carriero, A.; Fossaceca, R. Cumulative radiation dose and radiation risk from medical imaging in patients subjected to endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Radiol. Med. 2015, 120, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacul, F.; van der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Webb, J.A.; Thomsen, H.S.; Morcos, S.K.; Almen, T.; Aspelin, P.; Bellin, M.F.; Clement, O.; et al. Contrast induced nephropathy: Updated ESUR Contrast Media Safety Committee guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Cohan, R.H.; Ellis, J.H. Contrast media controversies in 2015: Imaging patients with renal impairment or risk of contrast reaction. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederle, F.A.; Freischlag, J.A.; Kyriakides, T.C.; Matsumura, J.S.; Padberg, F.T., Jr.; Kohler, T.R.; Kougias, P.; Jean-Claude, J.M.; Cikrit, D.F.; Swanson, K.M.; et al. Long-term comparison of endovascular and open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ippolito, D.; Talei Franzesi, C.; Fior, D.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Minutolo, O.; Sironi, S. Low kV settings CT angiography (CTA) with low dose contrast medium volume protocol in the assessment of thoracic and abdominal aorta disease: A feasibility study. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20140140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seehofnerova, A.; Kok, M.; Mihl, C.; Douwes, D.; Sailer, A.; Nijssen, E.; de Haan, M.J.; Wildberger, J.E.; Das, M. Feasibility of low contrast media volume in CT angiography of the aorta. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2015, 2, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higashigaito, K.; Schmid, T.; Puippe, G.; Morsbach, F.; Lachat, M.; Seifert, B.; Pfammatter, T.; Alkadhi, H.; Husarik, D.B. CT Angiography of the Aorta: Prospective Evaluation of Individualized Low-Volume Contrast Media Protocols. Radiology 2016, 280, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X. Use of low tube voltage and low contrast agent concentration yields good image quality for aortic CT angiography. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 1313.e5–1313.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.A.; Huang, E.P.; Chen, K.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Chuo, C.C.; Wu, F.Z.; Wu, M.T. Comparison of four contrast medium delivery protocols in low-iodine and low-radiation dose CT angiography of the aorta. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 797.e9–797.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.A.; Stoll, S.; Melzig, C.; Steuwe, A.; Partovi, S.; Bockler, D.; Kauczor, H.U.; Rengier, F. Prospective Study of Low-Radiation and Low-Iodine Dose Aortic CT Angiography in Obese and Non-Obese Patients: Image Quality and Impact of Patient Characteristics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, S.W.; Charagundla, S.R. Imaging techniques for detection and management of endoleaks after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Radiology 2007, 243, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Wichmann, J.L.; Weyer, H.; Scholtz, J.E.; Leithner, D.; Spandorfer, A.; Bodelle, B.; Jacobi, V.; Vogl, T.J.; Albrecht, M.H. Endoleaks after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair: Improved detection with noise-optimized virtual monoenergetic dual-energy CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 94, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs-Farkas, Z.; Semadeni, M.; Bensler, S.; Patak, M.A.; von Allmen, G.; Vock, P.; Schindera, S.T. Endoleak detection with CT angiography in an abdominal aortic aneurysm phantom: Effect of tube energy, simulated patient size, and physical properties of endoleaks. Radiology 2009, 251, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deak, Z.; Grimm, J.M.; Mueck, F.; Geyer, L.L.; Treitl, M.; Reiser, M.F.; Wirth, S. Endoleak and in-stent thrombus detection with CT angiography in a thoracic aortic aneurysm phantom at different tube energies using filtered back projection and iterative algorithms. Radiology 2014, 271, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, N.J.; Kaza, R.K.; Maturen, K.E.; Liu, P.S.; Platt, J.F. Evaluation of low-dose CT angiography with model-based iterative reconstruction after endovascular aneurysm repair of a thoracic or abdominal aortic aneurysm. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.G.; Kriegshauser, J.S.; Paden, R.G.; He, M.; Wu, Q.; Hara, A.K. Ultra-low-dose computed tomographic angiography with model-based iterative reconstruction compared with standard-dose imaging after endovascular aneurysm repair: A prospective pilot study. Abdom. Imaging 2014, 39, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffa, V.; Solazzo, A.; D’Auria, V.; Del Prete, A.; Vallone, A.; Luzietti, M.; Madau, M.; Grassi, R.; Miele, V. Dual-source dual-energy CT: Dose reduction after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. La Radiol. Med. 2014, 119, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patino, M.; Parakh, A.; Lo, G.C.; Agrawal, M.; Kambadakone, A.R.; Oliveira, G.R.; Sahani, D.V. Virtual Monochromatic Dual-Energy Aortoiliac CT Angiography With Reduced Iodine Dose: A Prospective Randomized Study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Donato, G.; Pasqui, E.; Panzano, C.; Galzerano, G.; Cappelli, A.; Palasciano, G. Early Experience with the New Ovation Alto Stent Graft in Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. EJVES Vasc. Forum 2022, 54, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Value | SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Total no. of patients | 60 | |
| Males | 53 | |
| Females | 7 | |
| Age | 64.9 | 11.3 |
| BMI | 26.8 | 3.8 |
| Body weight (kg) | 74.8 | 12.9 |
| Body Height (cm) | 166.7 | 7.6 |
| CTDIvol (mGy) | 2.85 | 1.6 |
| Iodine load (mg/kg) | 199.7 | 11.2 |
| Type of stent | ||
| TEVAR | 36 | |
| EVAR | 24 | |
| Interval of CTA follow-up (days) | 306.7 | 99.5 |
| Number of CTA studies | 5.2 | 1.9 |
| DLCTA | SDCTA | |
|---|---|---|
| Arterial-phase endoleak (total) | 12 | 12 |
| Certain absence | 2 | 2 |
| Probable absence | 0 | 0 |
| Possible presence | 3 | 3 |
| Probable presence | 9 | 9 |
| Delay-phase endoleak (total) | 14 | 14 |
| Certain absence | 0 | 0 |
| Probable absence | 0 | 0 |
| Possible presence | 1 | 1 |
| Probable presence | 12 | 11 |
| Certain presence | 1 | 2 |
| Noise level | ||
| Good | 11 | 13 |
| Intermediate | 3 | 1 |
| Poor | 0 | 0 |
| Aneurysm Size (cm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial CTA | Midterm CTA | Last CTA | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | |
| All (n = 60) | 4.09 | 0.68 | 4.01 | 1.24 | 4.03 | 1.02 | 0.908 |
| Presence of endoleak (n = 14) | 4.88 | 0.65 | 4.88 | 1.11 | 4.94 | 0.99 | 0.987 |
| Absence of endoleak (n = 46) | 3.83 | 0.71 | 3.63 | 0.85 | 3.70 | 0.88 | 0.572 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.-A.; Huang, E.P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chuo, C.-C.; Huang, S.-T.; Wu, M.-T. Can Low-Iodine, Low-Radiation-Dose CT Aortogram Reliably Detect Endoleak after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of the Aorta? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132228
Chen P-A, Huang EP, Chen Y-C, Chuo C-C, Huang S-T, Wu M-T. Can Low-Iodine, Low-Radiation-Dose CT Aortogram Reliably Detect Endoleak after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of the Aorta? Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132228
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Po-An, Eric P. Huang, Yi-Chun Chen, Chiung-Chen Chuo, Shu-Tin Huang, and Ming-Ting Wu. 2023. "Can Low-Iodine, Low-Radiation-Dose CT Aortogram Reliably Detect Endoleak after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of the Aorta?" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132228
APA StyleChen, P.-A., Huang, E. P., Chen, Y.-C., Chuo, C.-C., Huang, S.-T., & Wu, M.-T. (2023). Can Low-Iodine, Low-Radiation-Dose CT Aortogram Reliably Detect Endoleak after Endovascular Aneurysm Repair of the Aorta? Diagnostics, 13(13), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132228






