Synthetic Attenuation Correction Maps for SPECT Imaging Using Deep Learning: A Study on Myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preparation
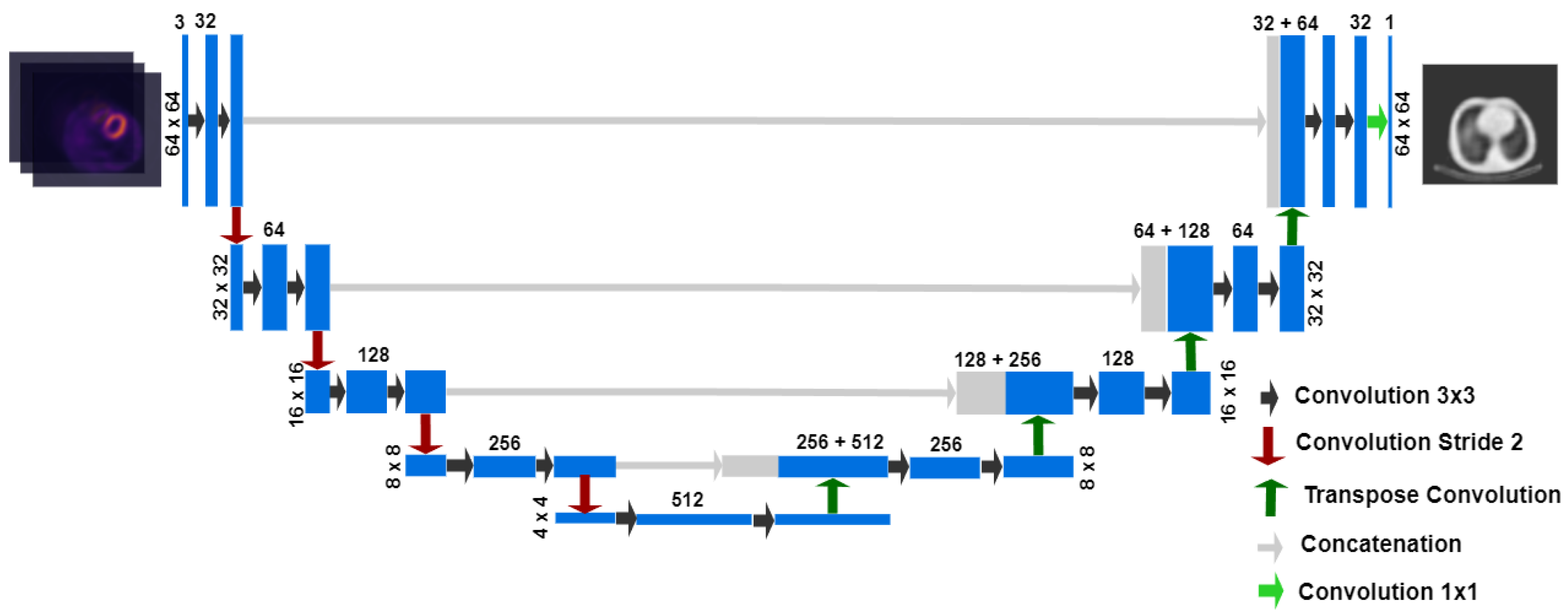
2.2. Network Architecture and Training
2.3. Image Reconstruction for Validation
2.4. Image Quality Metrics and Voxel-Level Quantitative Evaluation
2.5. Quantitative Evaluation of Myocardial Uptake
2.6. Semi-Quantitative Evaluation of Myocardial Perfusion
3. Results
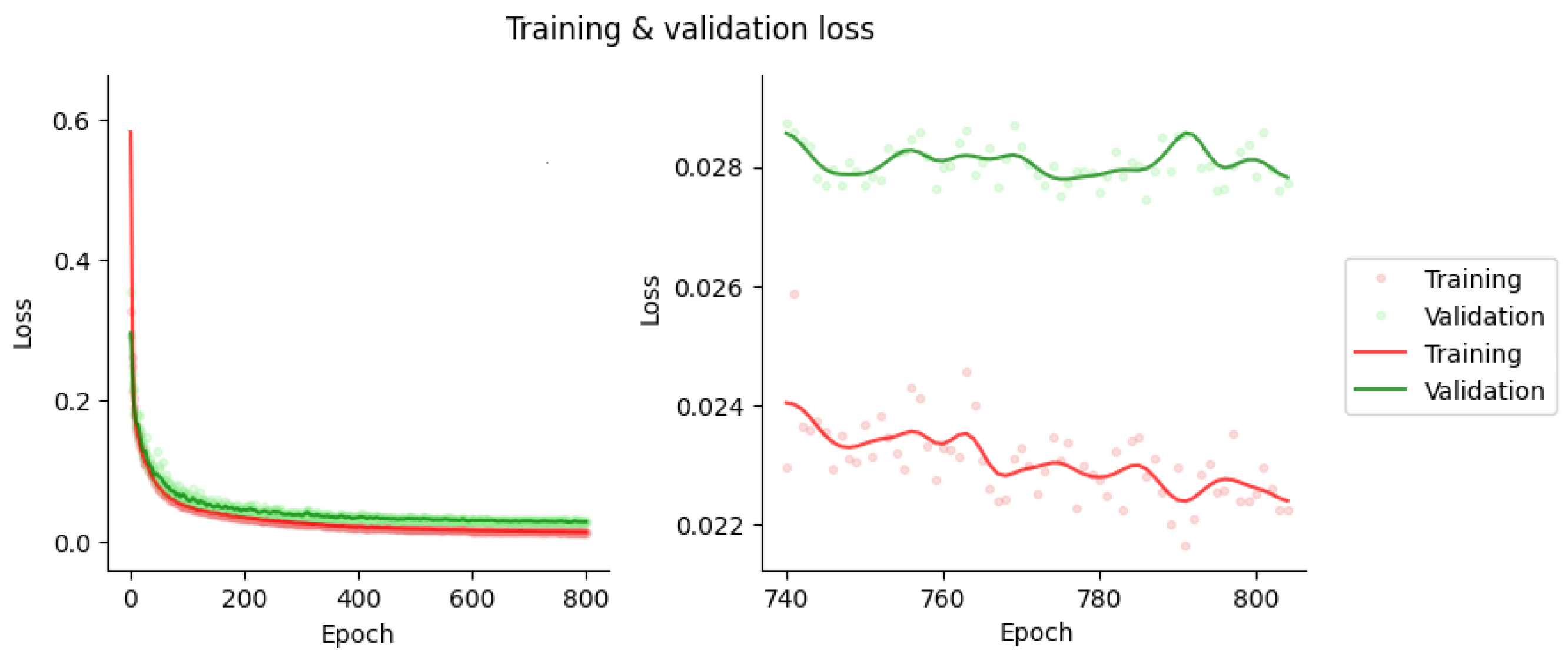
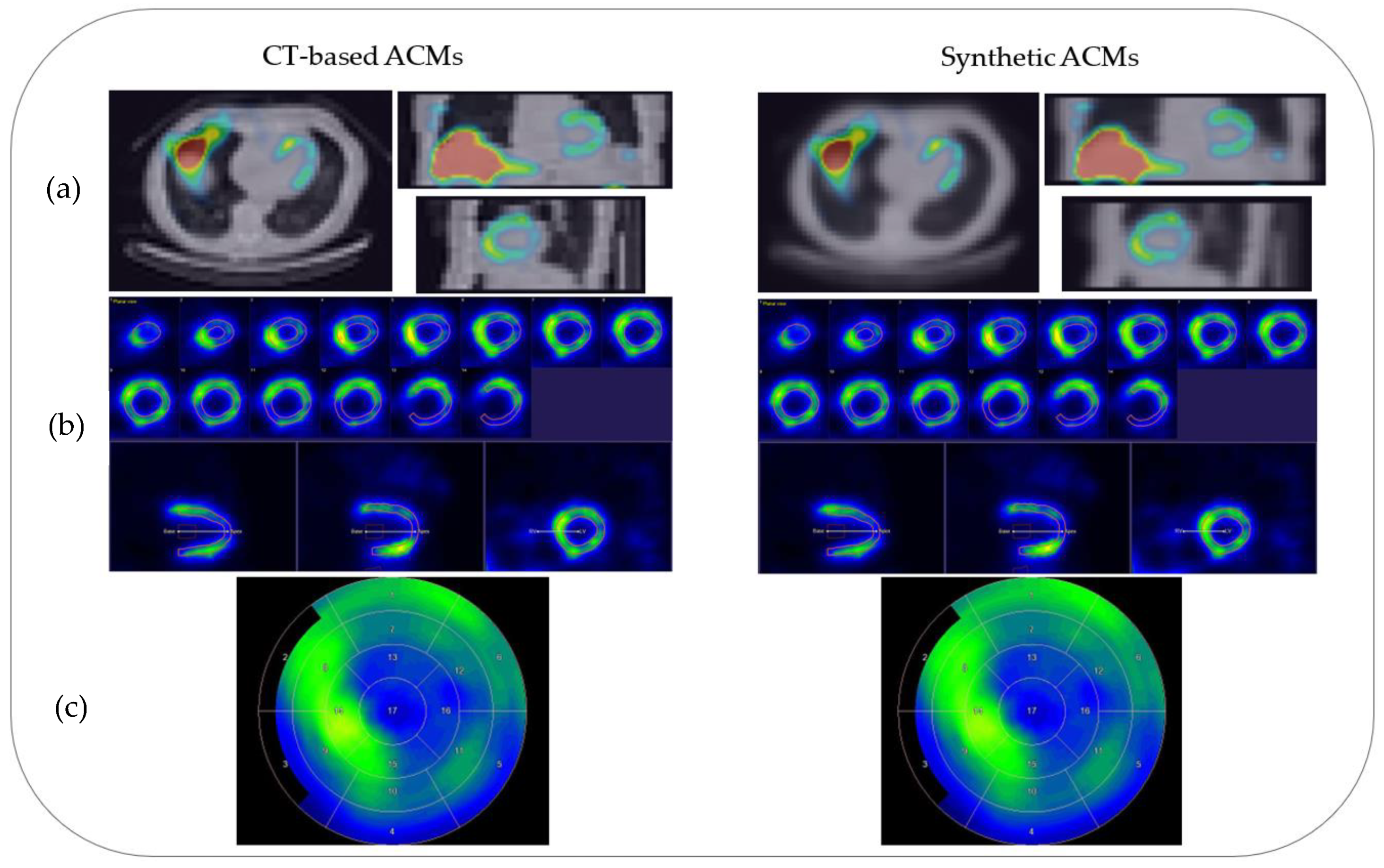
3.1. Network Training and Sample Results
3.2. Image Quality and Voxel-Level Evaluation
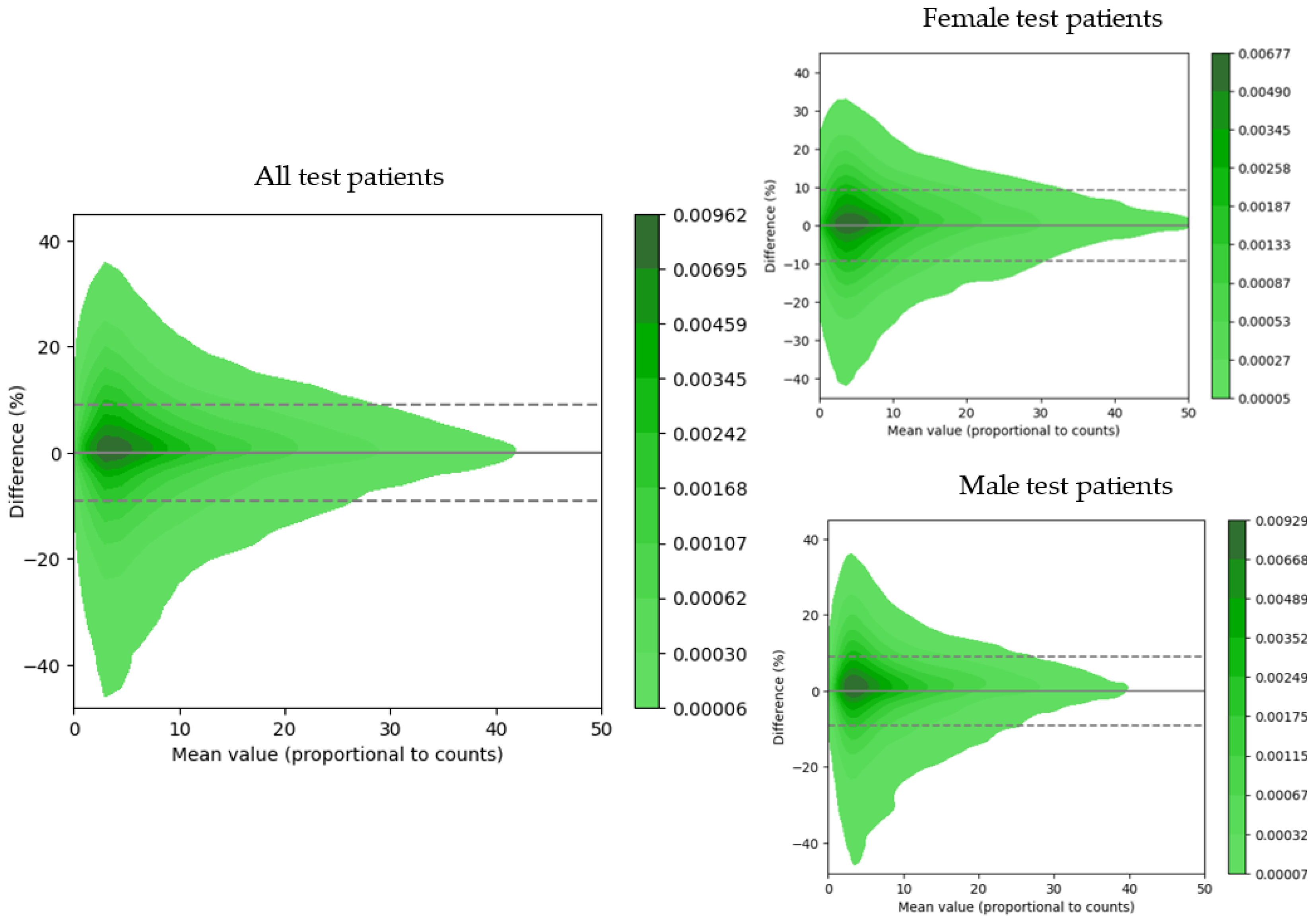
3.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Myocardial Uptake
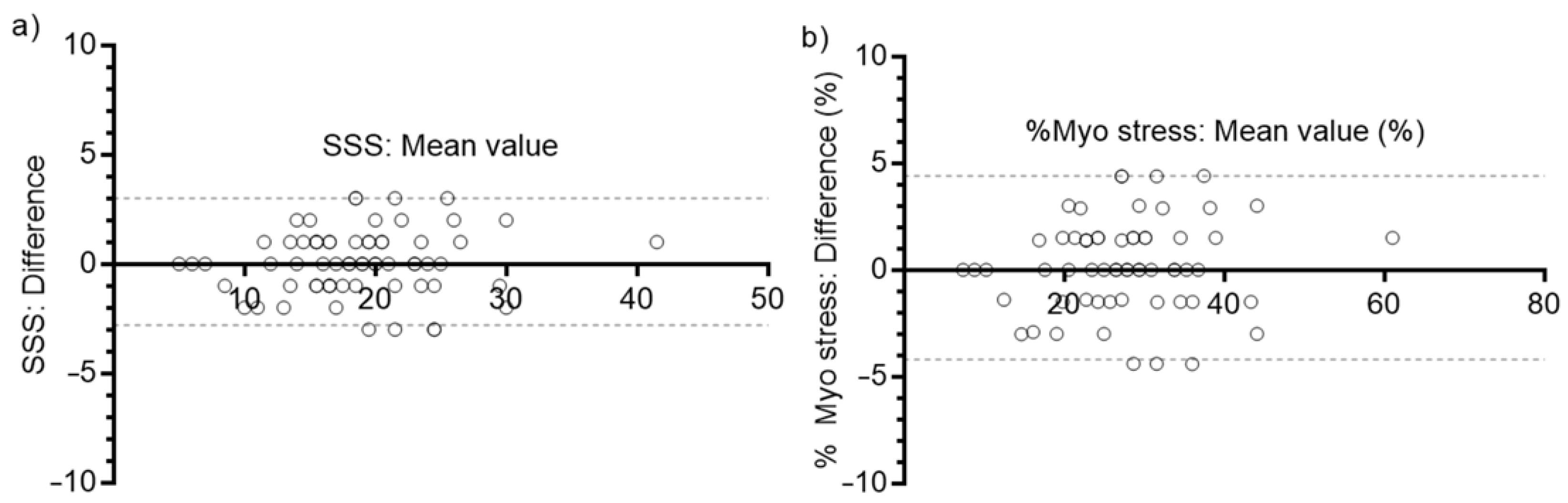
3.4. Semi-Quantitative Evaluation of Myocardial Perfusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klocke, F.J.; Baird, M.G.; Lorell, B.H.; Bateman, T.M.; Messer, J.V.; Berman, D.S.; O’gara, P.T.; Carabello, B.A.; Russell, R.O.; Cerqueira, M.D.; et al. ACC/AHA/ASNC Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Cardiac Radionuclide Imaging—Executive Summary. Circulation 2003, 108, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, J.D.; Mouden, M.; Ottervanger, J.P.; Van Dalen, J.A.; Knollema, S.; Slump, C.H.; Jager, P.L. Value of attenuation correction in stress-only myocardial perfusion imaging using CZT-SPECT. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2016, 24, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Bateman, T.M.; Case, J.A.; Heller, G. Attenuation artifact, attenuation correction, and the future of myocardial perfusion SPECT. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2007, 14, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, A.G.; Kalff, V.; Van Every, B.; Risa, B.; Barnden, L.R.; Kelly, M.J. Contributions of subdiaphragmatic activity, attenuation, and diaphragmatic motion to inferior wall artifact in attenuation-corrected Tc-99m myocardial perfusion SPECT. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2005, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, J.R.; Kritzman, J.N.; Ficaro, E.P. Attenuation correction for single photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2004, 6, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, V.; Green, R.; Cuocolo, A. Prone-only SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging: An alternative standard in clinical practice? J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 29, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawakol, A.E.; Tantawy, H.M.; Elashmawy, R.E.; Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Elsayed, Y.M. Added Value of CT Attenuation Correction and Prone Positioning in Improving Breast and Subdiaphragmatic Attenuation in Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2020, 49, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkerneker, D.; Brenner, R.; Martin, W.H.; Sampson, U.K.A.; Feurer, I.D.; Kronenberg, M.W.; Delbeke, D. CT-based attenuation correction versus prone imaging to decrease equivocal interpretations of rest/stress Tc-99m tetrofosmin SPECT MPI. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2007, 14, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCroix, K.; Tsui, B.; Hasegawa, B.; Brown, J. Investigation of the use of X-ray CT images for attenuation compensation in SPECT. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1994, 41, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Bailey, D.L.; Willowson, K.; Baldock, C. Investigation of the relationship between linear attenuation coefficients and CT Hounsfield units using radionuclides for SPECT. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, S.; Brown, T.L.; Lavely, W.C.; Zhang, Z.; Bengel, F.M. Attenuation Correction in Myocardial Perfusion SPECT/CT: Effects of Misregistration and Value of Reregistration. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, A.; Clack, R.; Natterer, F.; Gullberg, G. Toward accurate attenuation correction in SPECT without transmission measurements. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.; Ljungberg, M.; Wollmer, P.; Strand, S.-E.; Almquist, H.; Jonson, B. Quantitative SPECT by attenuation correction of the projection set using transmission data: Evaluation of a method. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1990, 16, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, M.; Strand, S.E. Attenuation correction in SPECT based on transmission studies and Monte Carlo simulations of build-up functions. J. Nucl. Med. 1990, 31, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mennessier, C.; Noo, F.; Clackdoyle, R.; Bal, G.; Desbat, L. Attenuation correction in SPECT using consistency conditions for the exponential ray transform. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 2483–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, H.M.; Larkin, R.S. Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1994, 13, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsui, B.; Hu, H.-B.; Gilland, D.; Gullberg, G. Implementation of simultaneous attenuation and detector response correction in SPECT. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1988, 35, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lei, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wynne, J.F.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. A review on medical imaging synthesis using deep learning and its clinical applications. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 22, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, H.; AkhavanAllaf, A.; Sanaat, A.; Shiri, I.; Zaidi, H. The promise of artificial intelligence and deep learning in PET and SPECT imaging. Phys. Medica 2021, 83, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C. Deep-learning-based methods of attenuation correction for SPECT and PET. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Park, D.; Gullberg, G.T.; Seo, Y. Joint correction of attenuation and scatter in image space using deep convolutional neural networks for dedicated brain 18F-FDG PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 075019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Miller, E.J.; Sinusas, A.J.; Liu, C.J.; Gullberg, G.T.; Seo, Y. Direct Attenuation Correction Using Deep Learning for Cardiac SPECT: A Feasibility Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, H.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, G.; Zaidi, H. Novel adversarial semantic structure deep learning for MRI-guided attenuation correction in brain PET/MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2746–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Miller, E.; Sinusas, A.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, C. Post-reconstruction attenuation correction for SPECT myocardium perfusion imaging facilitated by deep learning-based attenuation map generation. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 2881–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanious, K.; Jiang, C.; Fischer, M.; Küstner, T.; Hepp, T.; Nikolaou, K.; Gatidis, S.; Yang, B. MedGAN: Medical image translation using GANs. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2020, 79, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman, M.; Yang, J.; Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Miller, E.J.; Sinusas, A.J.; Liu, C.; Gullberg, G.T.; Seo, Y. Direct image-based attenuation correction using conditional generative adversarial network for SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging. In Medical Imaging 2021: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging; Gimi, B.S., Krol, A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, I.; Ghafarian, P.; Geramifar, P.; Leung, K.H.-Y.; Ghelichoghli, M.; Oveisi, M.; Rahmim, A.; Ay, M.R. Direct attenuation correction of brain PET images using only emission data via a deep convolutional encoder-decoder (Deep-DAC). Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6867–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladefoged, C.N.; Marner, L.; Hindsholm, A.; Law, I.; Højgaard, L.; Andersen, F.L. Deep Learning Based Attenuation Correction of PET/MRI in Pediatric Brain Tumor Patients: Evaluation in a Clinical Setting. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Yang, J.; Kim, K.; El Fakhri, G.; Seo, Y.; Li, Q. Attenuation correction for brain PET imaging using deep neural network based on Dixon and ZTE MR images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armanious, K.; Hepp, T.; Küstner, T.; Dittmann, H.; Nikolaou, K.; La Fougère, C.; Yang, B.; Gatidis, S. Independent attenuation correction of whole body [18F]FDG-PET using a deep learning approach with Generative Adversarial Networks. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Goorden, M.C.; Beekman, F.J. Convolutional neural network based attenuation correction for 123I-FP-CIT SPECT with focused striatum imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 195007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Onofrey, J.A.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, C. Deep learning-based attenuation map generation for myocardial perfusion SPECT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 47, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Kaida, H.; Yoshida, S.; Ishii, K. Attenuation correction using deep learning for brain perfusion SPECT images. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhag, A.D.; Miller, R.J.; Pieszko, K.; Lemley, M.; Kavanagh, P.; Feher, A.; Miller, E.J.; Sinusas, A.J.; Kaufmann, P.A.; Han, D.; et al. Deep Learning-Based Attenuation Correction Improves Diagnostic Accuracy of Cardiac SPECT. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namías, M.; Jeraj, R. A quantitative reconstruction software suite for SPECT imaging. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, San Andres Island, Colombia, 5–7 October 2017; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, R.; Lowekamp, B.; Yaniv, Z. Image Segmentation, Registration and Characterization in R with SimpleITK. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 86, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaniv, Z.; Lowekamp, B.C.; Johnson, H.J.; Beare, R. SimpleITK Image-Analysis Notebooks: A Collaborative Environment for Education and Reproducible Research. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 31, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onofrey, J.A.; Casetti-Dinescu, D.I.; Lauritzen, A.D.; Sarkar, S.; Venkataraman, R.; Fan, R.E.; Sonn, G.A.; Sprenkle, P.C.; Staib, L.H.; Papademetris, X. Generalizable Multi-Site Training and Testing Of Deep Neural Networks Using Image Normalization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2015, 1, 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerqueira, M.D.; Weissman, N.J.; Dilsizian, V.; Jacobs, A.K.; Kaul, S.; Laskey, W.K.; Pennell, D.J.; Rumberger, J.A.; Ryan, T.; Verani, M.S. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. Circulation 2002, 105, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, M.; Wygoda, Z.; Duszańska, A.; Szczerba, D.; Głowacki, J.; Gąsior, M.; Wasilewski, J.P. Interpreting myocardial perfusion scintigraphy using single-photon emission computed tomography. Part 1. Pol. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2017, 14, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berman, D.S.; Kang, X.; Gransar, H.; Gerlach, J.; Friedman, J.D.; Hayes, S.W.; Thomson, L.E.J.; Hachamovitch, R.; Shaw, L.J.; Slomka, P.J.; et al. Quantitative assessment of myocardial perfusion abnormality on SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging is more reproducible than expert visual analysis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2009, 16, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alom, Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| MSSIM | NMAE | MRE | MSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 3.08 ± 1.26 (%) | 9.15 ± 3.7 (%) | 1.2 × 10−4 ± 0.77 × 10−4 (cm−1) |
| Train | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 1.04 ± 0.19 (%) | 3.25 ± 0.98 (%) | 0.1 × 10−4 ± 0.05 × 10−4 (cm−1) |
| MSSIM | NMAE | MRE | MSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Test | 0.99 ± 0.003 | 0.23 ± 0.13 (%) | 5.9 ± 2.8 (%) | 0.18 ± 0.26 (PtoPC) |
| Male Test | 0.99 ± 0.002 | 0.26 ± 0.12 (%) | 6.2 ± 2.7 (%) | 0.16 ± 0.21 (PtoPC) |
| Female Test | 0.99 ± 0.003 | 0.21 ± 0.12 (%) | 5.9 ± 2.4 (%) | 0.24 ± 0.34 (PtoPC) |
| Segment | Global | LDAwa | LCX | RCA | Apex | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of values | 1122 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 | 66 |
| Minimum | −18 | −9.5 | −12.0 | −9.5 | −8.0 | −17.0 |
| 25% Percentile | −3.9 | −3.6 | −4.2 | −3.0 | −3.3 | −4.4 |
| Median | −0.65 | −1.0 | −1.1 | 0.17 | 0.38 | −0.95 |
| 75% Percentile | 2.4 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 1.8 | 3.2 |
| Maximum | 29 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 10.0 | 14 |
| Mean | −0.41 | −0.61 | −1.2 | 0.7 | −0.37 | −0.73 |
| Std. Deviation | 5.6 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 5.5 | 4.3 | 5.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prieto Canalejo, M.A.; Palau San Pedro, A.; Geronazzo, R.; Minsky, D.M.; Juárez-Orozco, L.E.; Namías, M. Synthetic Attenuation Correction Maps for SPECT Imaging Using Deep Learning: A Study on Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132214
Prieto Canalejo MA, Palau San Pedro A, Geronazzo R, Minsky DM, Juárez-Orozco LE, Namías M. Synthetic Attenuation Correction Maps for SPECT Imaging Using Deep Learning: A Study on Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132214
Chicago/Turabian StylePrieto Canalejo, Mariana Andrea, Aley Palau San Pedro, Ricardo Geronazzo, Daniel Mauricio Minsky, Luis Eduardo Juárez-Orozco, and Mauro Namías. 2023. "Synthetic Attenuation Correction Maps for SPECT Imaging Using Deep Learning: A Study on Myocardial Perfusion Imaging" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132214
APA StylePrieto Canalejo, M. A., Palau San Pedro, A., Geronazzo, R., Minsky, D. M., Juárez-Orozco, L. E., & Namías, M. (2023). Synthetic Attenuation Correction Maps for SPECT Imaging Using Deep Learning: A Study on Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2214. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132214









