Ensemble Learning for Hormone Binding Protein Prediction: A Promising Approach for Early Diagnosis of Thyroid Hormone Disorders in Serum
Abstract
1. Introduction
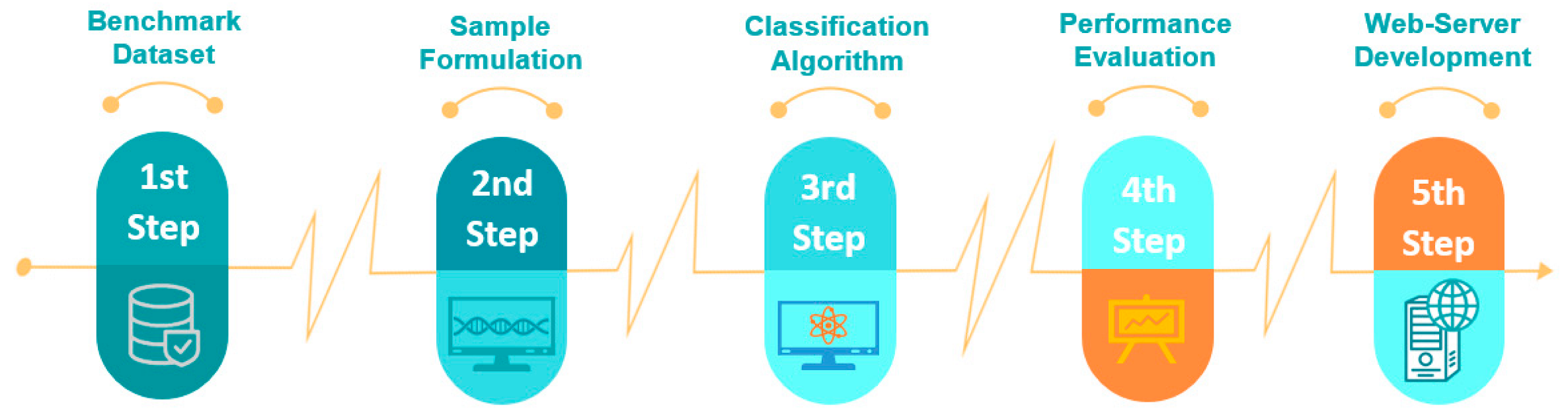
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Benchmark Dataset
2.2. Feature Formulation
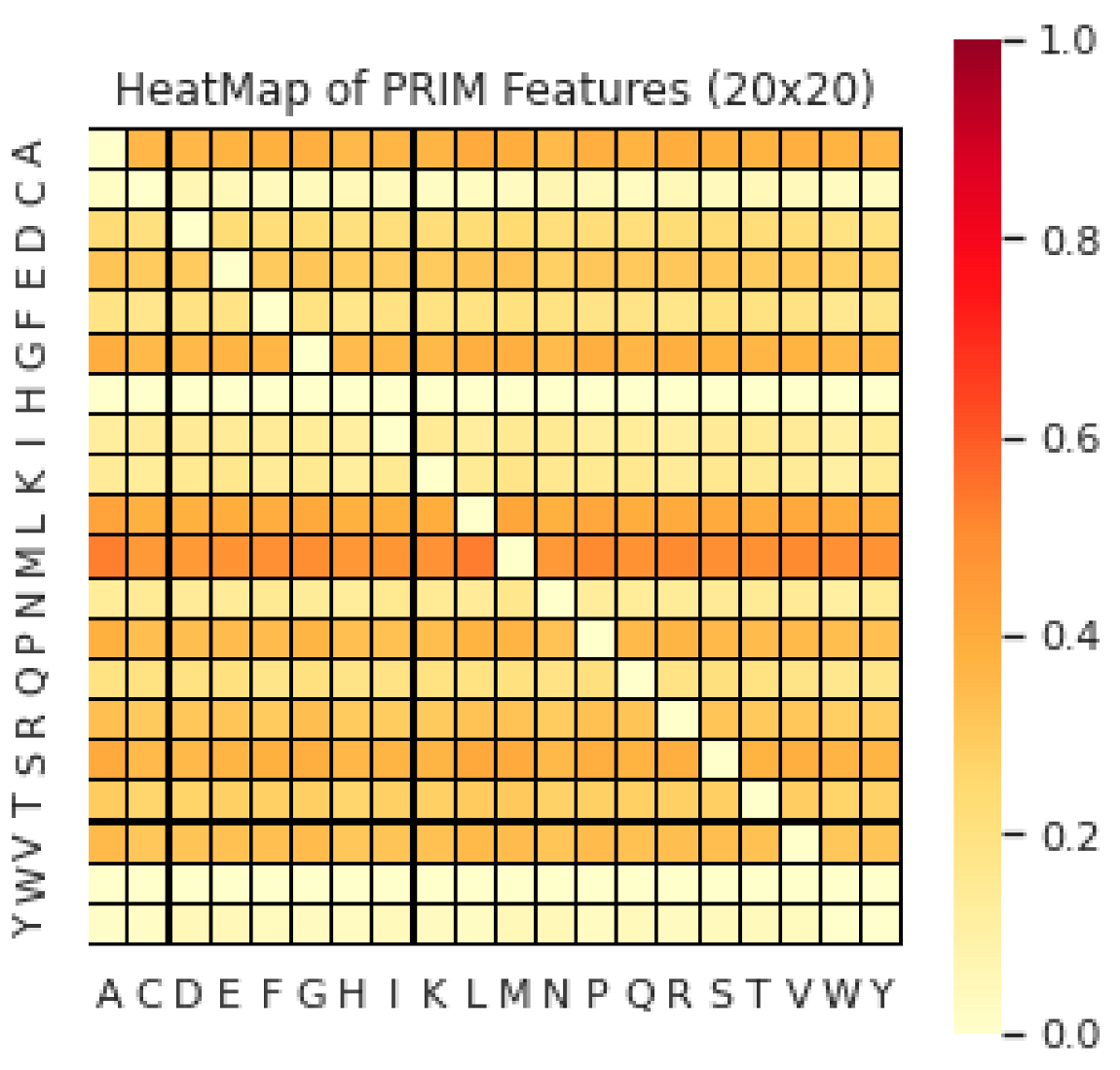
Position Relative Features
2.3. Statistical Moments
2.4. Classification Algorithm
2.4.1. Boosted Random Forest
2.4.2. AdaBoost Classifier
2.4.3. Hyper-Parameter Optimization
2.5. Performance Evaluation
2.5.1. Accuracy
2.5.2. Precision, Recall and F-Score
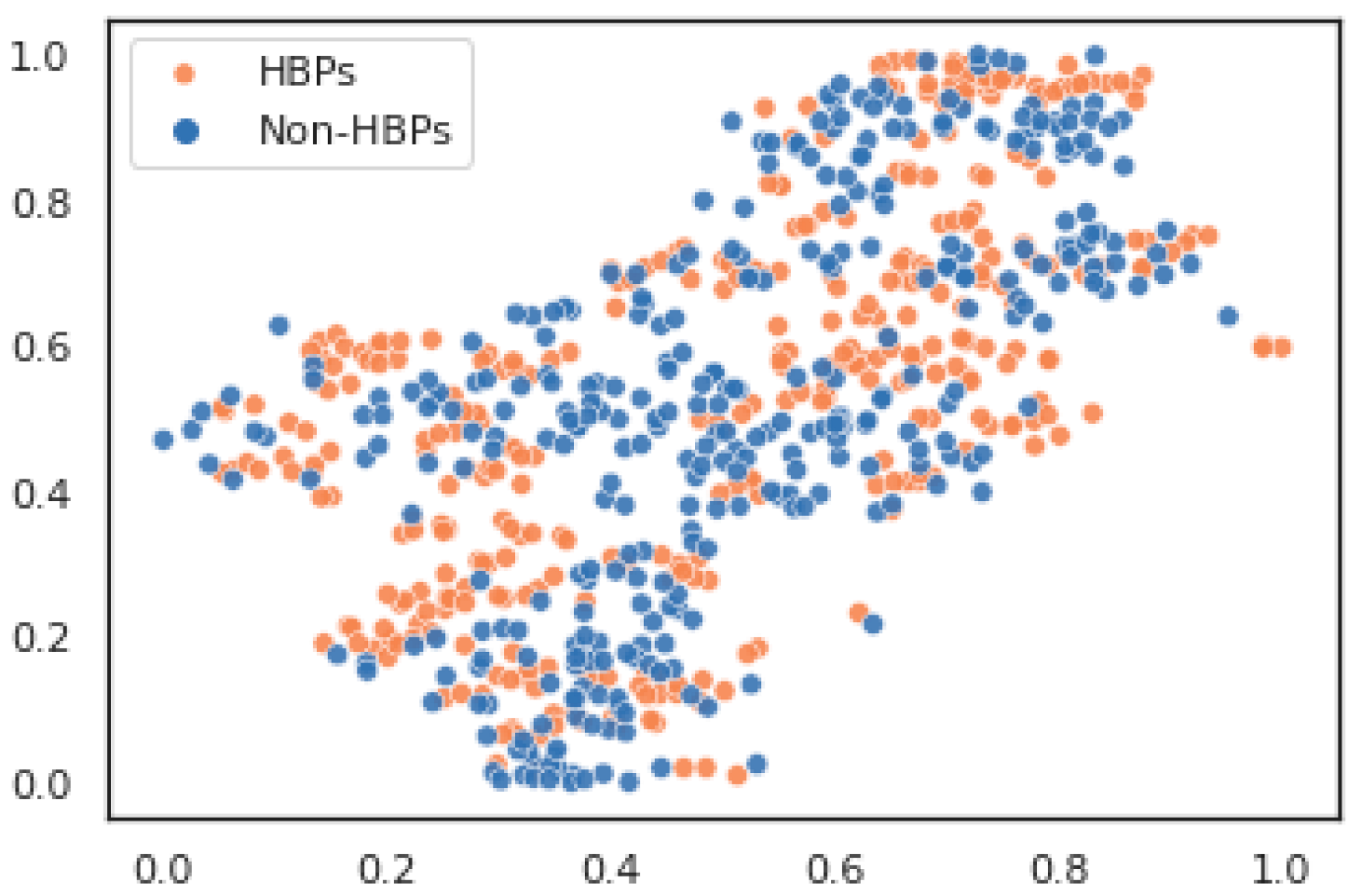
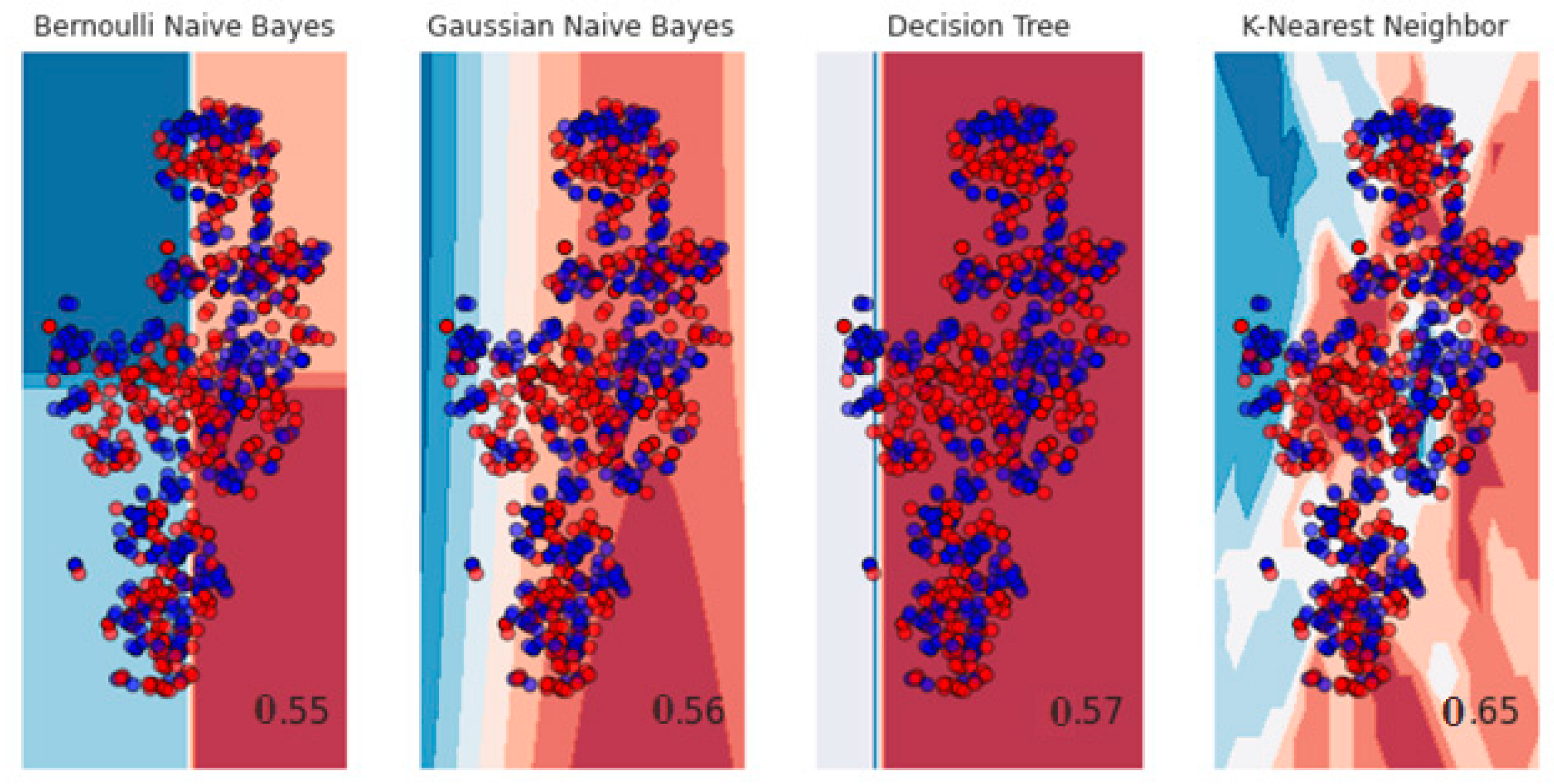
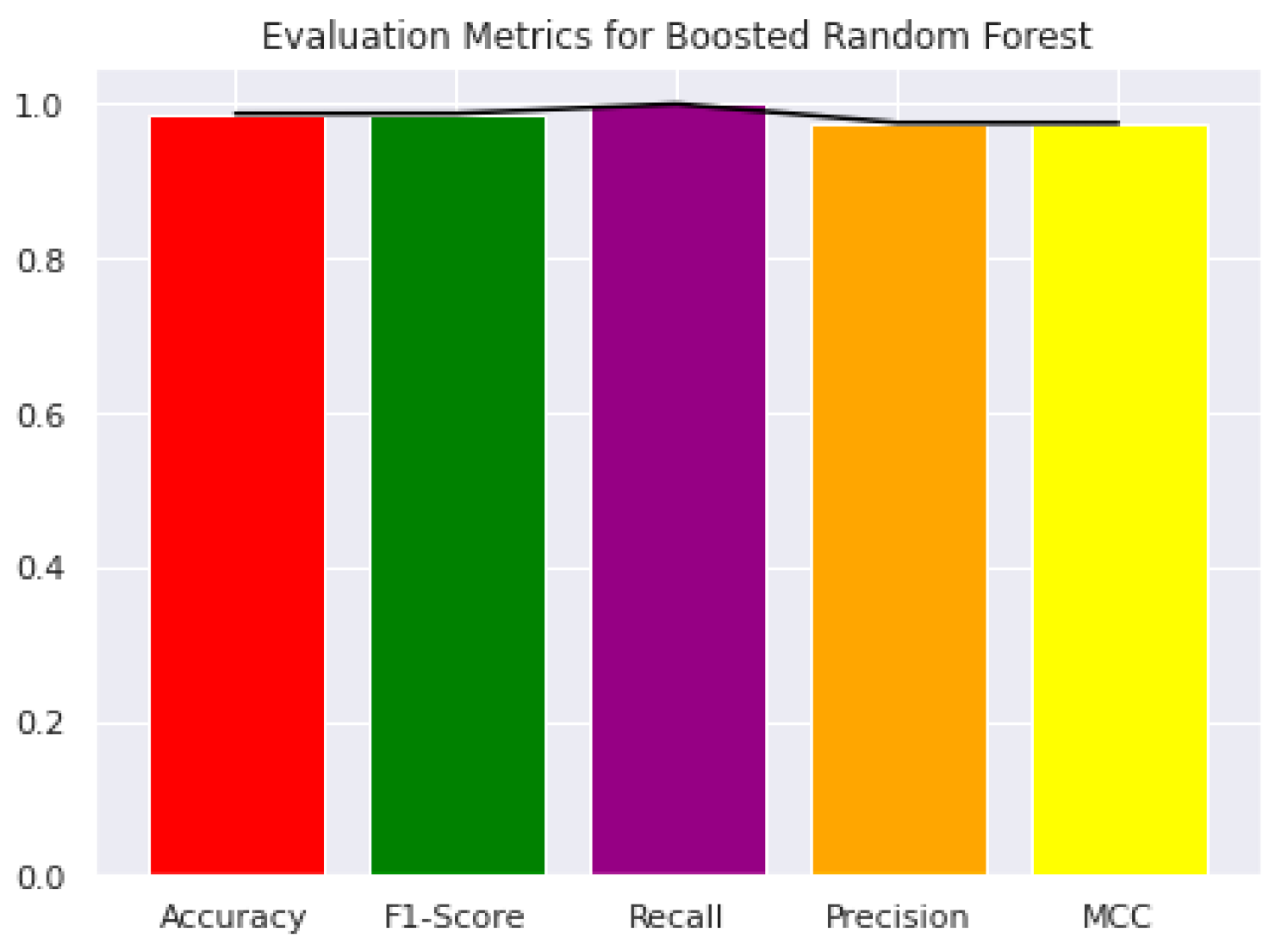
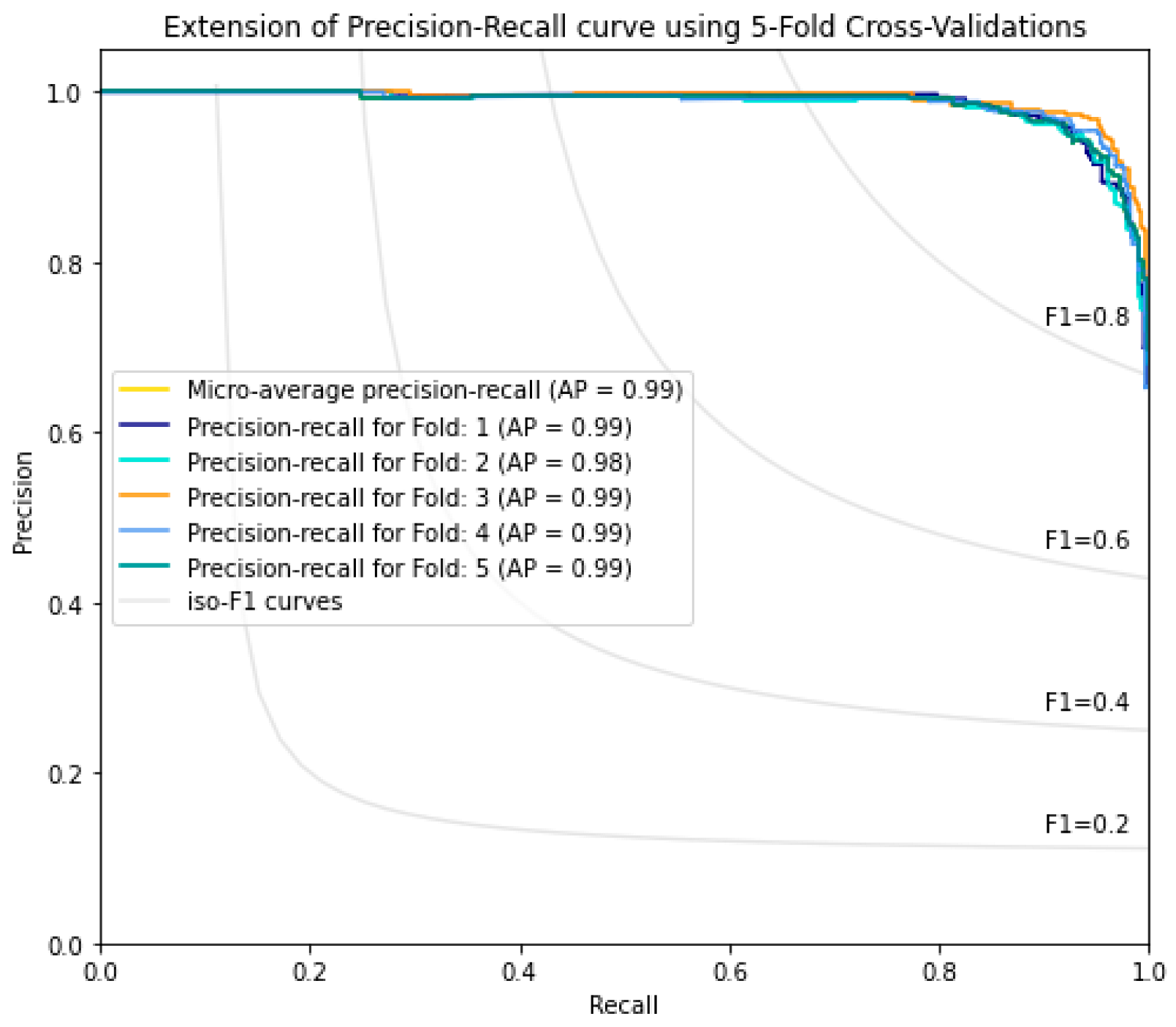
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Genetic Variation: Associations with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3683392/ (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Adverse Effects of the Metabolic Acidosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-C. Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 273, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. Predicting Membrane Protein Types by the LLDA Algorithm. Protein Pept. Lett. 2008, 15, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.D.; Zhou, G.P.; Chou, K.C. Support vector machines for predicting membrane protein types by using functional domain composition. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yan, X. BS-KNN: An effective algorithm for predicting protein subchloroplast localization. Evol. Bioinform. 2011, 2011, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awais, M.; Hussain, W.; Khan, Y.D.; Rasool, N.; Khan, S.A.; Chou, K.C. iPhosH-PseAAC: Identify phosphohistidine sites in proteins by blending statistical moments and position relative features according to the Chou’s 5-step rule and general pseudo amino acid composition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2019, 18, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandaswamy, K.K.; Chou, K.-C.; Martinetz, T.; Möller, S.; Suganthan, P.; Sridharan, S.; Pugalenthi, G. AFP-Pred: A random forest approach for predicting antifreeze proteins from sequence-derived properties. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 270, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.S.; Yu, Z.G.; Anh, V.; Krishnajith, A.P.D.; Tian, Y.C. An Ensemble Method for Predicting Subnuclear Localizations from Primary Protein Structures. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Khan, S.; Ali, F.; Hayat, M.; Qasim, M.; Gul, S. iHBP-DeepPSSM: Identifying hormone binding proteins using PsePSSM based evolutionary features and deep learning approach. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 204, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kumar, H.; Patil, S.; Ahmad, A.; Babour, A.; Daud, A. Deep-GHBP: Improving prediction of Growth Hormone-binding proteins using deep learning model. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 78, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Sahu, R.; Nath, A. A representation transfer learning approach for enhanced prediction of growth hormone binding proteins. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 87, 107274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Zou, P.; Zhang, C.-M.; Chen, R.; Huang, P.; Lin, H. HBPred: A tool to identify growth hormone-binding proteins. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libbrecht, M.W.; Noble, W.S. Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga, P.; Calvo, B.; Santana, R.; Bielza, C.; Galdiano, J.; Inza, I.; Lozano, J.A.; Armañanzas, R.; Santafé, G.; Pérez, A.; et al. Machine learning in bioinformatics. Brief. Bioinform. 2006, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.Y.; Fasman, G.D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1978, 47, 45–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Khan, Y.D. Identification of 4-carboxyglutamate residue sites based on position based statistical feature and multiple classification. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, S.; Ashraf, A.; Hussain, W.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. Identification of Lysine Carboxylation Sites in Proteins by Integrating Statistical Moments and Position Relative Features via General PseAAC. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, S.; Hussain, W.; Khan, Y.D.; Rasool, N. NPalmitoylDeep-PseAAC: A Predictor of N-Palmitoylation Sites in Proteins Using Deep Representations of Proteins and PseAAC via Modified 5-Steps Rule. Curr. Bioinform. 2021, 16, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barukab, O.; Khan, Y.D.; Khan, S.A.; Chou, K.-C. iSulfoTyr-PseAAC: Identify Tyrosine Sulfation Sites by Incorporating Statistical Moments via Chou’s 5-steps Rule and Pseudo Components. Curr. Genom. 2019, 20, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, S.; Hussain, W.; Khan, Y.D.; Rasool, N. Optimization of serine phosphorylation prediction in proteins by comparing human engineered features and deep representations. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 615, 114069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, S.; Hussain, W.; Khan, Y.D.; Rasool, N. iPhosS(Deep)-PseAAC: Identification of Phosphoserine Sites in Proteins Using Deep Learning on General Pseudo Amino Acid Compositions. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 19, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.H.; Khan, Y.D. CanLect-Pred: A cancer therapeutics tool for prediction of target cancerlectins using experiential annotated proteomic sequences. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 9520–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malebary, S.J.; Khan, Y.D. Evaluating machine learning methodologies for identification of cancer driver genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.D.; Alzahrani, E.; Alghamdi, W.; Ullah, M.Z. Sequence-based Identification of Allergen Proteins Developed by Integration of PseAAC and Statistical Moments via 5-Step Rule. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.K.; Ehsan, A.; Khan, Y.D.; Chou, K.-C. iHyd-LysSite (EPSV): Identifying Hydroxylysine Sites in Protein Using Statistical Formulation by Extracting Enhanced Position and Sequence Variant Feature Technique. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. A Sequence-Based Predictor of Zika Virus Proteins Developed by Integration of PseAAC and Statistical Moments. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2020, 23, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Hussain, W.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. iTSP-PseAAC: Identifying Tumor Suppressor Proteins by Using Fully Connected Neural Network and PseAAC. Curr. Bioinform. 2021, 16, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malebary, S.J.; Khan, R.; Khan, Y.D. ProtoPred: Advancing Oncological Research Through Identification of Proto-Oncogene Proteins. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68788–68797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, S.; Ali, R.F.; Khan, Y.D.; Dominic, P.D.D. iGluK-Deep: Computational identification of lysine glutarylation sites using deep neural networks with general pseudo amino acid compositions. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 40, 11691–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.D.; Khan, N.S.; Naseer, S.; Butt, A.H. iSUMOK-PseAAC: Prediction of lysine sumoylation sites using statistical moments and Chou’s PseAAC. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malebary, S.; Khan, Y. Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides Using Chou’s 5 Step Rule. CMC 2021, 67, 2863–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.H.; Khan, S.A.; Jamil, H.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. A Prediction Model for Membrane Proteins Using Moments Based Features. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8370132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.H.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. A Treatise to Computational Approaches towards Prediction of Membrane Protein and Its Subtypes. J. Membr. Biol. 2017, 250, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.H.; Mahmood, M.K.; Khan, Y.D. An Exposition Analysis of Facial Expression Recognition Techniques. Pak. J. Sci. 2016, 68, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, P.T.; Paramesran, R.; Ong, S.H. Image analysis using Hahn moments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 2057–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.H.; Khan, Y.D. Prediction of S-Sulfenylation Sites Using Statistical Moments Based Features via CHOU’S 5-Step Rule. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 26, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.H.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. Prediction of antioxidant proteins by incorporating statistical moments based features into Chou’s PseAAC. J. Theor. Biol. 2019, 473, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.H.; Rasool, N.; Khan, Y.D. Predicting membrane proteins and their types by extracting various sequence features into Chou’s general PseAAC. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, H.-A.; Chong, C.-W.; Besar, R.; Abas, F.S.; Sim, K.-S. Translation and Scale Invariants of Hahn Moments. Int. J. Image Graph. 2009, 9, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H. BioSeq-Analysis2.0: An updated platform for analyzing DNA, RNA and protein sequences at sequence level and residue level based on machine learning approaches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. BioSeq-Analysis: A platform for DNA, RNA and protein sequence analysis based on machine learning approaches. Brief Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1280–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A desicion-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. In Computational Learning Theory; Vitányi, P., Ed.; In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1201.0490 (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- Identification of Hormone-Binding Proteins Using a Novel Ensemble Classifier|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00607-018-0682-x (accessed on 30 October 2022).
- iGHBP: Computational Identification of Growth Hormone Binding Proteins from Sequences Using Extremely Randomised Tree—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2001037018301168 (accessed on 30 October 2022).



| Protein Sequences | Benchmark Dataset | Independent Dataset | Overall Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBPs | 358 | 50 | 408 |
| Non-HBPs | 358 | 50 | 408 |
| Overall | 716 | 100 | 816 |
| Method | SN (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | MCC | F-Score | AUC | AUPRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [45] | 92.7 | 87.9 | 90.7 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| HBPred [13] | 88.6 | 81.3 | 84.9 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| BioSeq-SVM [41] | 70.7 | 63.4 | 67.1 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| BioSeq-RF [42] | 70.7 | 74.8 | 72.8 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Proposed Method | 94.9 | 93.8 | 94.4 | 0.8875 | 0.9438 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| Method | SN (%) | SP (%) | ACC (%) | MCC | F-Score | AUC | AUPRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBPred [13] | 80.43 | 56.52 | 68.48 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| iGHBP [46] | 80.71 | 83.90 | 82.31 | 0.650 | -- | -- | -- |
| HBPred_2.0 [13] | 89.18 | 80.43 | 84.78 | 0.698 | -- | -- | -- |
| Proposed Method | 93.8 | 95.6 | 94.6 | 0.8929 | 0.9472 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butt, A.H.; Alkhalifah, T.; Alturise, F.; Khan, Y.D. Ensemble Learning for Hormone Binding Protein Prediction: A Promising Approach for Early Diagnosis of Thyroid Hormone Disorders in Serum. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111940
Butt AH, Alkhalifah T, Alturise F, Khan YD. Ensemble Learning for Hormone Binding Protein Prediction: A Promising Approach for Early Diagnosis of Thyroid Hormone Disorders in Serum. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(11):1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111940
Chicago/Turabian StyleButt, Ahmad Hassan, Tamim Alkhalifah, Fahad Alturise, and Yaser Daanial Khan. 2023. "Ensemble Learning for Hormone Binding Protein Prediction: A Promising Approach for Early Diagnosis of Thyroid Hormone Disorders in Serum" Diagnostics 13, no. 11: 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111940
APA StyleButt, A. H., Alkhalifah, T., Alturise, F., & Khan, Y. D. (2023). Ensemble Learning for Hormone Binding Protein Prediction: A Promising Approach for Early Diagnosis of Thyroid Hormone Disorders in Serum. Diagnostics, 13(11), 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13111940







