MiR-155 Dysregulation Is Associated with the Augmentation of ROS/p53 Axis of Fibrosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Is Protected by Resveratrol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Histological Examination
2.3. Immunohistochemistry of p53 and α-Smooth Muscle Actin (α-SMA)
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) of TIMP-1 and MiR-155
2.5. Evaluation of Biomarkers for Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants, and Hepatic Damage in the Liver Tissue and Blood
2.6. Statistical and Morphometric Analysis
3. Results
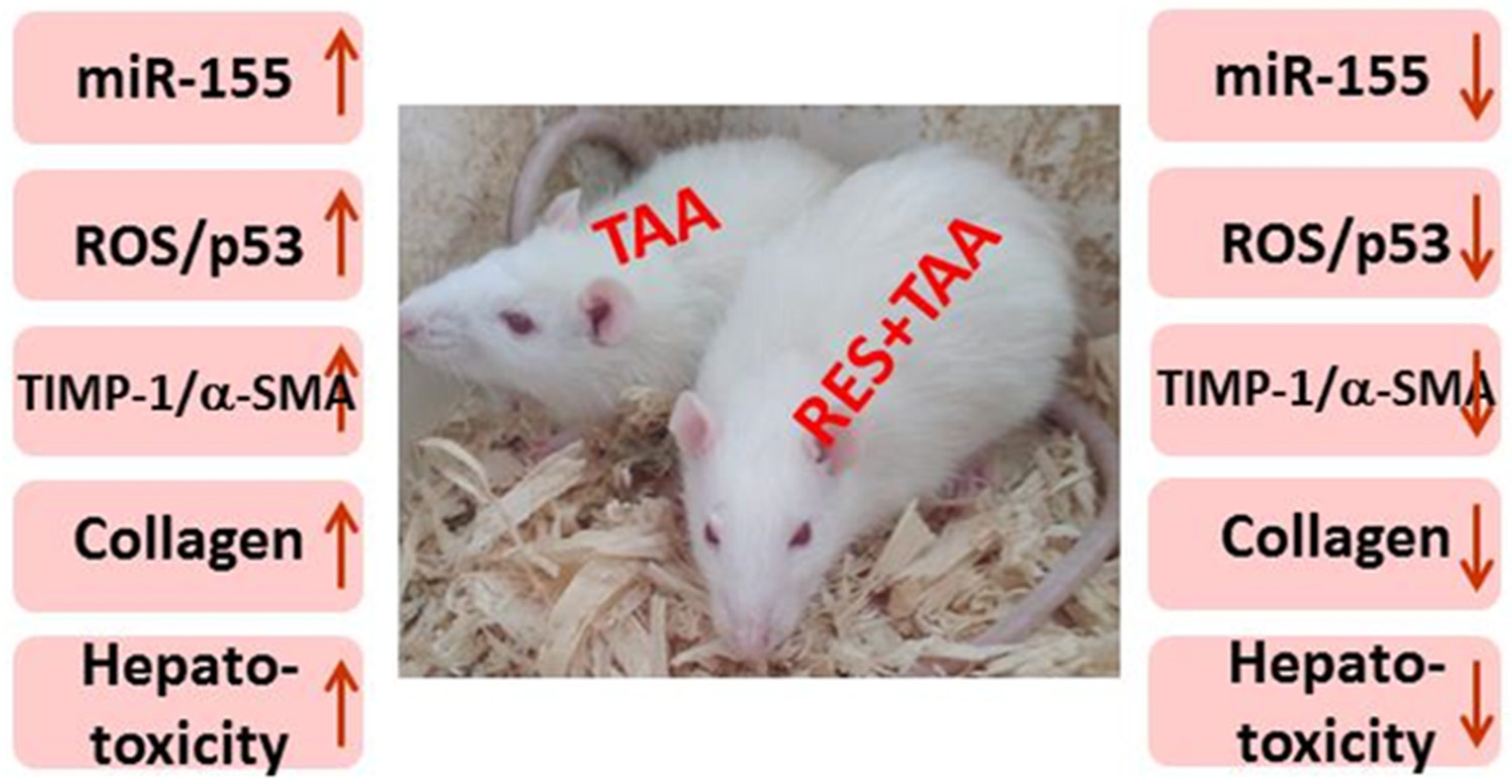
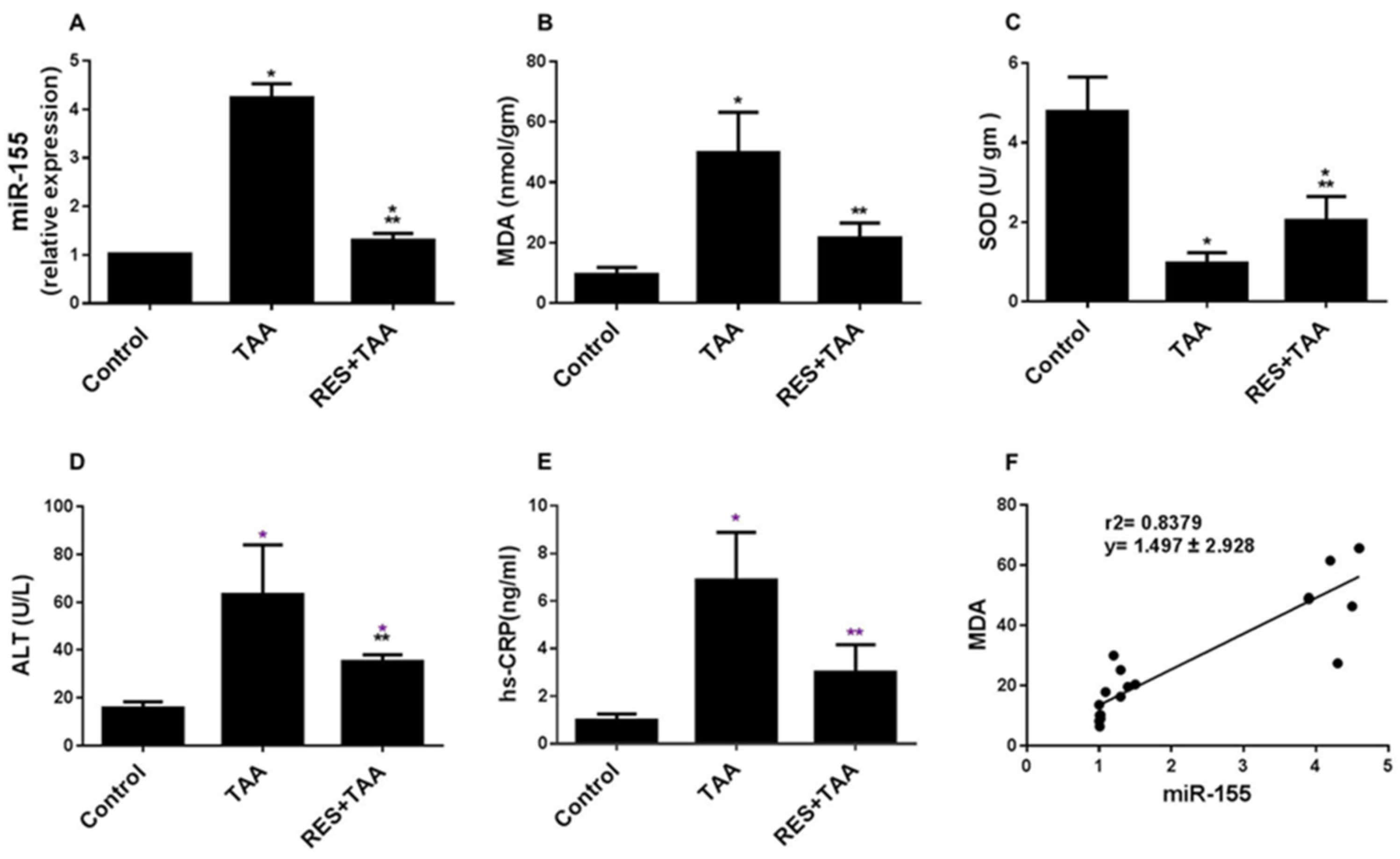
3.1. Induction of MiR-155 and Oxidative Stress by TAA Intoxication Is Inhibited by Resveratrol
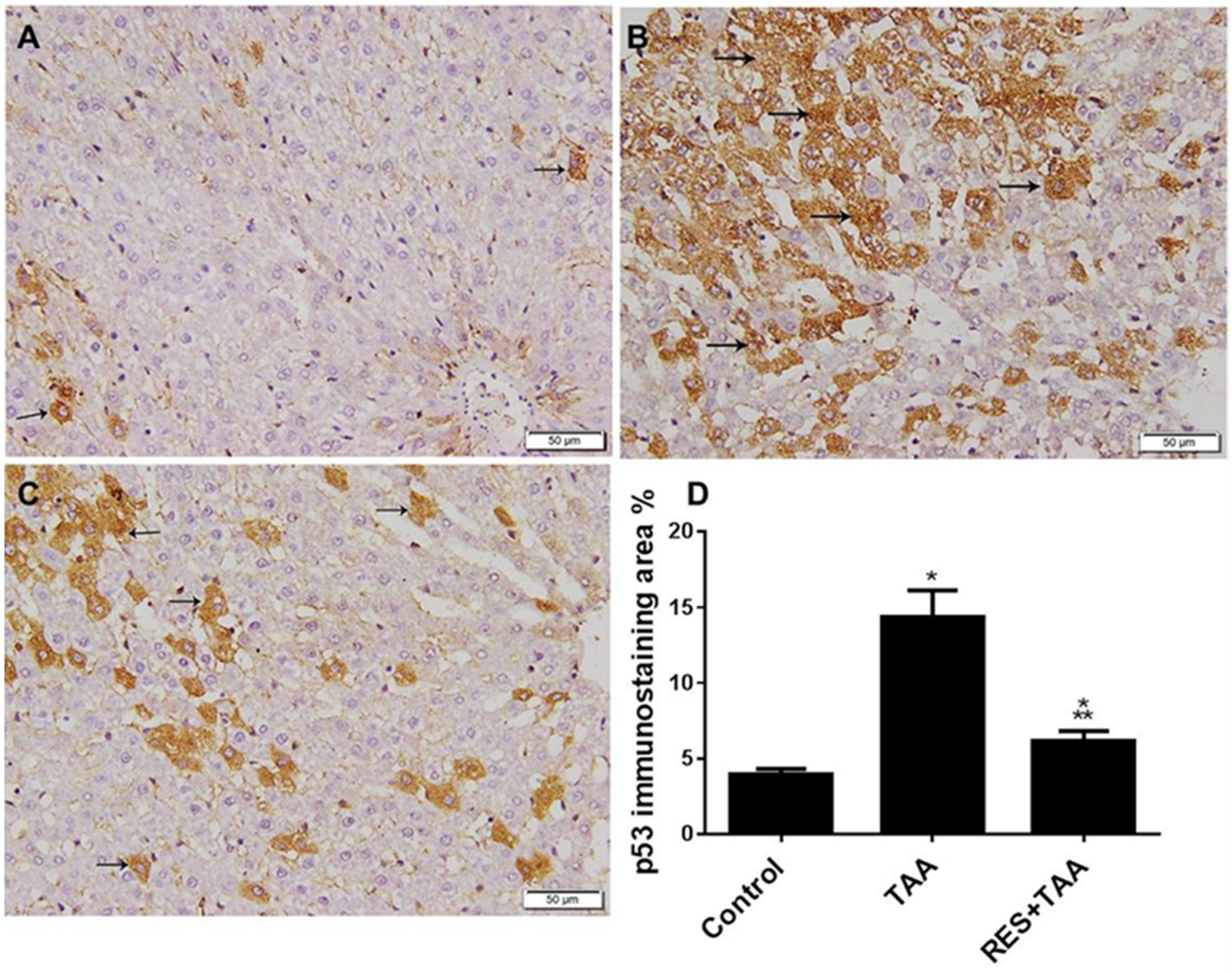
3.2. Resveratrol Inhibits TAA-Induced Biomarker of Apoptosis p53 in Liver Tissues
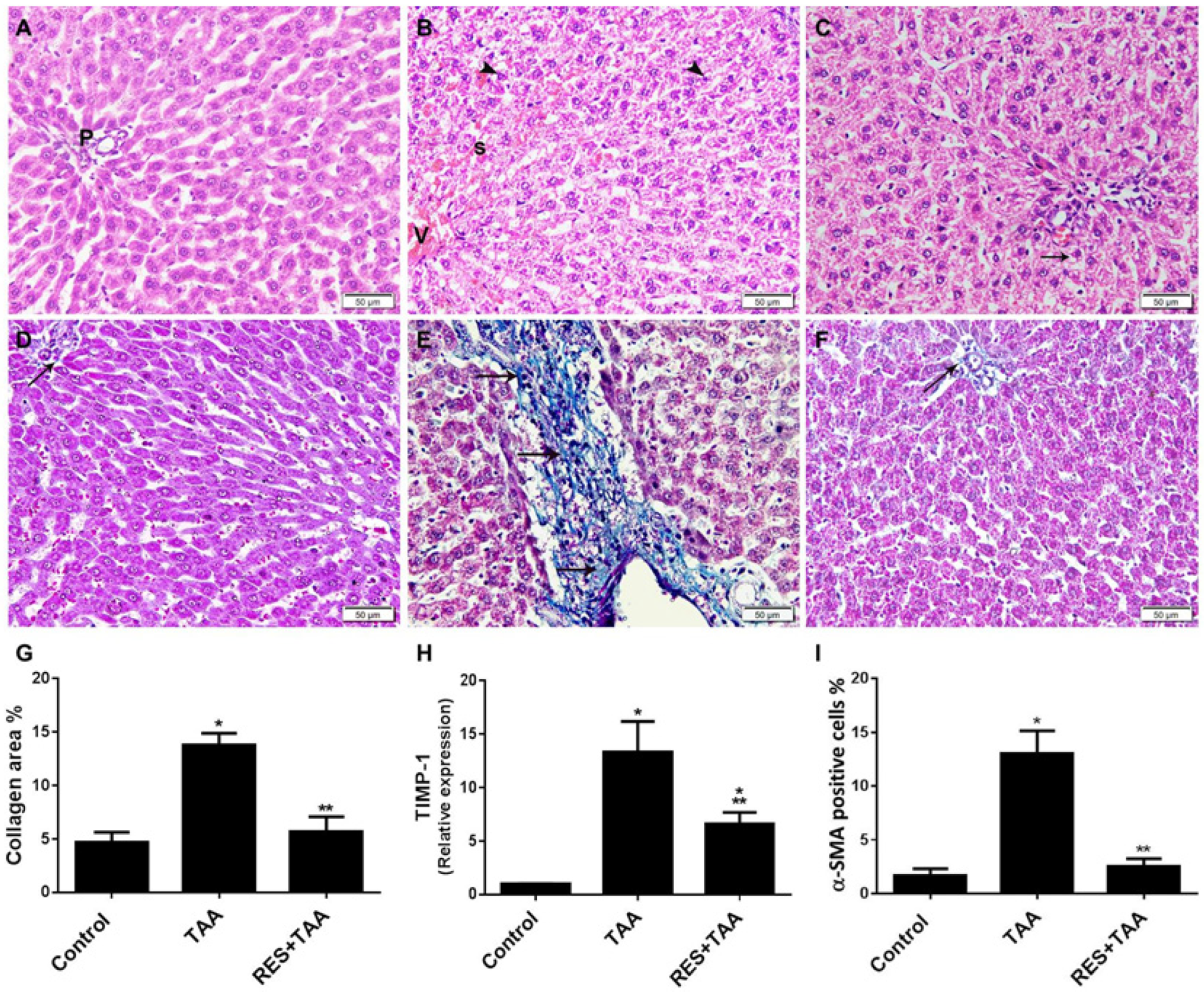
3.3. Resveratrol Is Associated with the Inhibition of Liver Injury and Fibrosis Induced by TAA
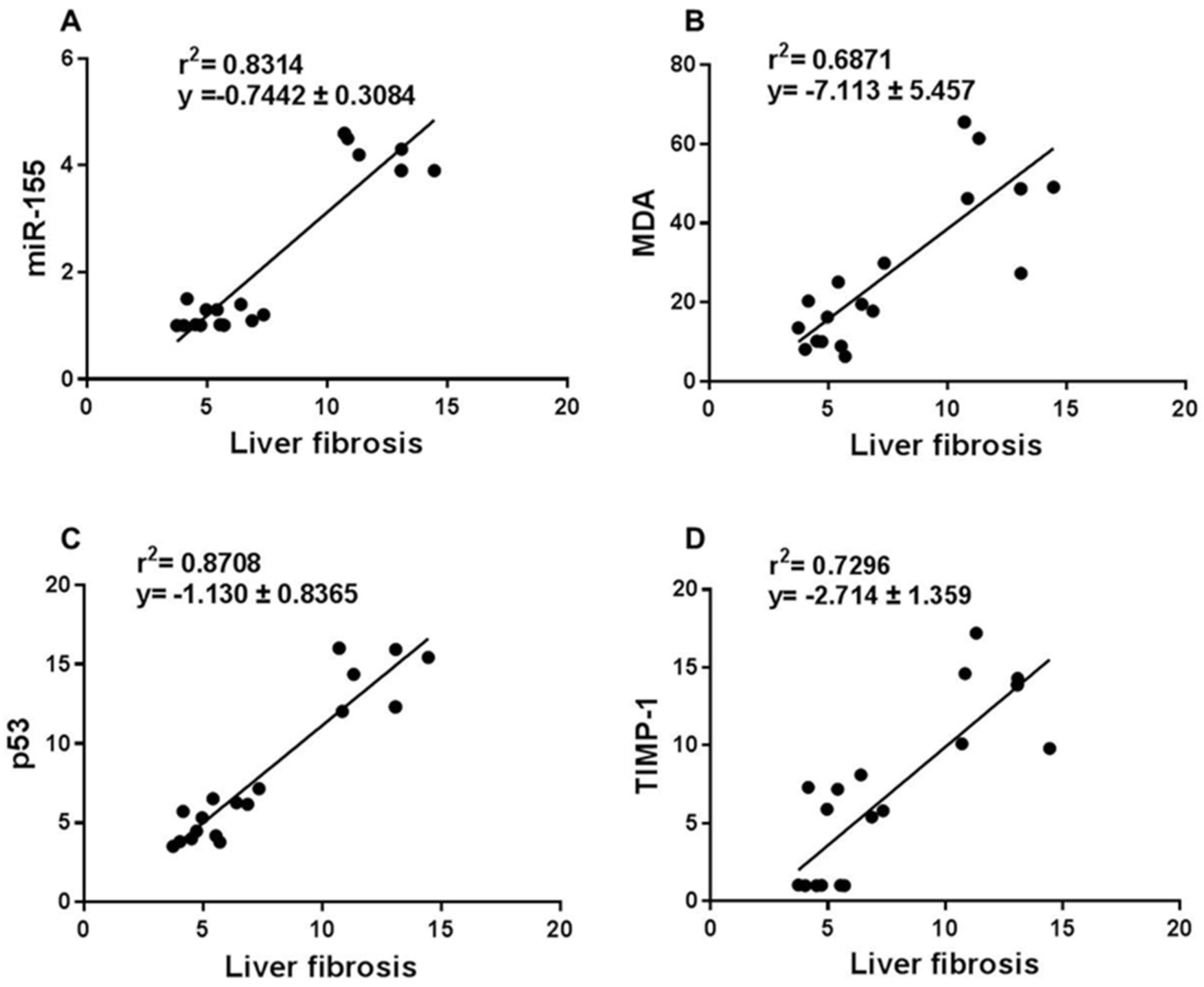
3.4. Correlation between Liver Fibrosis Score and miR-155, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hashem, F.; Al-Humayed, S.; Amin, S.N. Metformin inhibits mTOR-HIF-1α axis and profibrogenic and inflammatory biomarkers in thioacetamide-induced hepatic tissue alterations. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9328–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.; Hamesch, K.; Lunova, M.; Kim, Y.; Weiskirchen, R.; Strnad, P.; Friedman, S. Standard operating procedures in experimental liver research: Thioacetamide model in mice and rats. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49 (Suppl. S1), 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neff, G.W.; Duncan, C.W.; Schiff, E.R. The current economic burden of cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 661–671. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, S.L. Liver fibrosis—From bench to bedside. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, S38–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.J. Hepatic inflammation and progressive liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2515–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaisako, K.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. What’s new in liver fibrosis? The origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27 (Suppl. S2), 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gressner, A.M.; Weiskirchen, R. Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Trevijano, E.R.; Iraburu, M.J.; Fontana, L.; Domínguez-Rosales, J.A.; Auster, A.; Covarrubias-Pinedo, A.; Rojkind, M. Transforming growth factor beta1 induces the expression of alpha1(I) procollagen mRNA by a hydrogen peroxide-C/EBPbeta-dependent mechanism in rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 1999, 29, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Robino, G. Oxidative stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2001, 35, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casas-Grajales, S.; Muriel, P. Antioxidants in liver health. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 6, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodama, T.; Takehara, T.; Hikita, H.; Shimizu, S.; Shigekawa, M.; Tsunematsu, H.; Li, W.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; et al. Increases in p53 expression induce CTGF synthesis by mouse and human hepatocytes and result in liver fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3343–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ani, B. Resveratrol inhibits proteinase-activated receptor-2-induced release of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 from human endothelial cells. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hemmann, S.; Graf, J.; Roderfeld, M.; Roeb, E. Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis—A systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 955–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, P.; Tacke, F. Tiny RNA with great effects: miR-155 in alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1214–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Saha, B.; Zatsiorsky, J.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Satishchandran, A.; Szabo, G. The pro-inflammatory effects of miR-155 promote liver fibrosis and alcohol-induced steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onodera, Y.; Teramura, T.; Takehara, T.; Obora, K.; Mori, T.; Fukuda, K. miR-155 induces ROS generation through downregulation of antioxidation-related genes in mesenchymal stem cells. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zou, L.-X.; Lin, Q.-Y.; Yan, X.; Bi, H.-L.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.-S.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, H.-H. Resveratrol as a new inhibitor of immunoproteasome prevents PTEN degradation and attenuates cardiac hypertrophy after pressure overload. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tang, H.; Zeng, X.; Ye, D.; Liu, J. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion via Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in renal cell carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayev, A.; Sun, Y.; Snyder, R.B.; Berger, S.M.; Yu, J.J.; Holz, M.K. Resveratrol prevents rapamycin-induced upregulation of autophagy and selectively induces apoptosis in TSC2-deficient cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cudmore, M.J.; Ramma, W.; Cai, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Ahmad, S.; Al-Ani, B.; Ahmed, A. Resveratrol inhibits the release of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1) from human placenta. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 206, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepiana, J.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; Gómez-Zorita, S.; Eseberri, I.; González, M.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Portillo, M.P. Involvement of 5’-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) in the Effects of Resveratrol on Liver Steatosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawada, N.; Seki, S.; Inoue, M.; Kuroki, T. Effect of antioxidants, resveratrol, quercetin, and N-acetylcysteine, on the functions of cultured rat hepatic stellate cells and Kupffer cells. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Humayed, S.; Al-Hashem, F.; Haidara, M.A.; El Karib, A.O.; Kamar, S.; Amin, S.; Al-Ani, B. Resveratrol Pretreatment Ameliorates p53-Bax Axis and Augments the Survival Biomarker B-Cell Lymphoma 2 Modulated by Paracetamol Overdose in a Rat Model of Acute Liver Injury. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessoku, T.; Imajo, K.; Honda, Y.; Kato, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Kato, S.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Resveratrol ameliorates fibrosis and inflammation in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ShamsEldeen, A.M.; Al-Ani, B.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Rashed, L.; Badr, A.M.; Attia, A.; Farag, A.M.; Kamar, S.S.; Haidara, M.A.; Al Humayed, S.; et al. Resveratrol suppresses cholestasis-induced liver injury and fibrosis in rats associated with the inhibition of TGFβ1-Smad3-miR21 axis and profibrogenic and hepatic injury biomarkers. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, K.; Huang, T.; Wan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yan, D.; Li, G.; Gao, Y.; et al. Resveratrol Ameliorates Cardiac Hypertrophy by Down-regulation of miR-155 Through Activation of Breast Cancer Type 1 Susceptibility Protein. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawood, A.F.; Alzamil, N.M.; Hewett, P.W.; Momenah, M.A.; Dallak, M.; Kamar, S.S.; Kader, D.H.A.; Yassin, H.; Haidara, M.A.; Maarouf, A.; et al. Metformin Protects against Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: An Association between Desmin-Sarcomere Injury and the iNOS/mTOR/TIMP-1 Fibrosis Axis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, B.; Alzamil, N.M.; Hewett, P.W.; Al-Hashem, F.; Bin-Jaliah, I. Metformin ameliorates ROS-p53-collagen axis of fibrosis and dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus-induced left ventricular injury. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Simon, H.U. A novel link between p53 and ROS. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogiraju, R.; Xu, X.; Bochenek, M.L.; Steinbrecher, J.H.; Lehnart, S.E.; Wenzel, P.; Kessel, M.; Zeisberg, E.M.; Dobbelstein, M.; Schäfer, K. Endothelial p53 deletion improves angiogenesis and prevents cardiac fibrosis and heart failure induced by pressure overload in mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e001770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, X.F.; Ji, F.J.; Zang, H.L.; Cao, H. Activation of the miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 Signaling Pathway Contributes to the Progress of Liver Fibrosis via Inducing Apoptosis in Hepatocytes but Not in HSCs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csak, T.; Bala, S.; Lippai, D.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Szabo, G. MicroRNA-155 Deficiency Attenuates Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis without Reducing Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, J.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, W. ROS, P53, and ischemic acute kidney injury in diabetic models. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Shi, Y.; Shao, C. The tango of ROS and p53 in tissue stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, C.; Bi, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X. MicroRNA-155 Regulates ROS Production, NO Generation, Apoptosis and Multiple Functions of Human Brain Microvessel Endothelial Cells Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2870–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangmonkong, T.; Suriguga, S.; Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Groothuis, G.M.M.; Olinga, P.; Boersema, M. Targeting Oxidative Stress for the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 71–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Shang, X.; Shi, S.; et al. TIMP-1 promotes age-related renal fibrosis through upregulating ICAM-1 in human TIMP-1 transgenic mice. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Qin, S.Y.; Hu, B.L.; Qin, Q.Y.; Jiang, H.X.; Luo, W. Resveratrol improves CCL4-induced liver fibrosis in mouse by upregulating endogenous IL-10 to reprogramme macrophages phenotype from M(LPS) to M(IL-4). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dawood, A.F.; Al Humayed, S.; Momenah, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Ashour, H.; Kamar, S.S.; ShamsEldeen, A.M.; Haidara, M.A.; Al-Ani, B.; Ebrahim, H.A. MiR-155 Dysregulation Is Associated with the Augmentation of ROS/p53 Axis of Fibrosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Is Protected by Resveratrol. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071762
Dawood AF, Al Humayed S, Momenah MA, El-Sherbiny M, Ashour H, Kamar SS, ShamsEldeen AM, Haidara MA, Al-Ani B, Ebrahim HA. MiR-155 Dysregulation Is Associated with the Augmentation of ROS/p53 Axis of Fibrosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Is Protected by Resveratrol. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071762
Chicago/Turabian StyleDawood, Amal F., Suliman Al Humayed, Maha A. Momenah, Mohamed El-Sherbiny, Hend Ashour, Samaa S. Kamar, Asmaa M. ShamsEldeen, Mohamed A. Haidara, Bahjat Al-Ani, and Hasnaa A. Ebrahim. 2022. "MiR-155 Dysregulation Is Associated with the Augmentation of ROS/p53 Axis of Fibrosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Is Protected by Resveratrol" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071762
APA StyleDawood, A. F., Al Humayed, S., Momenah, M. A., El-Sherbiny, M., Ashour, H., Kamar, S. S., ShamsEldeen, A. M., Haidara, M. A., Al-Ani, B., & Ebrahim, H. A. (2022). MiR-155 Dysregulation Is Associated with the Augmentation of ROS/p53 Axis of Fibrosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Is Protected by Resveratrol. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071762





