Rapid Prediction of Retina Stress and Strain Patterns in Soccer-Related Ocular Injury: Integrating Finite Element Analysis with Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
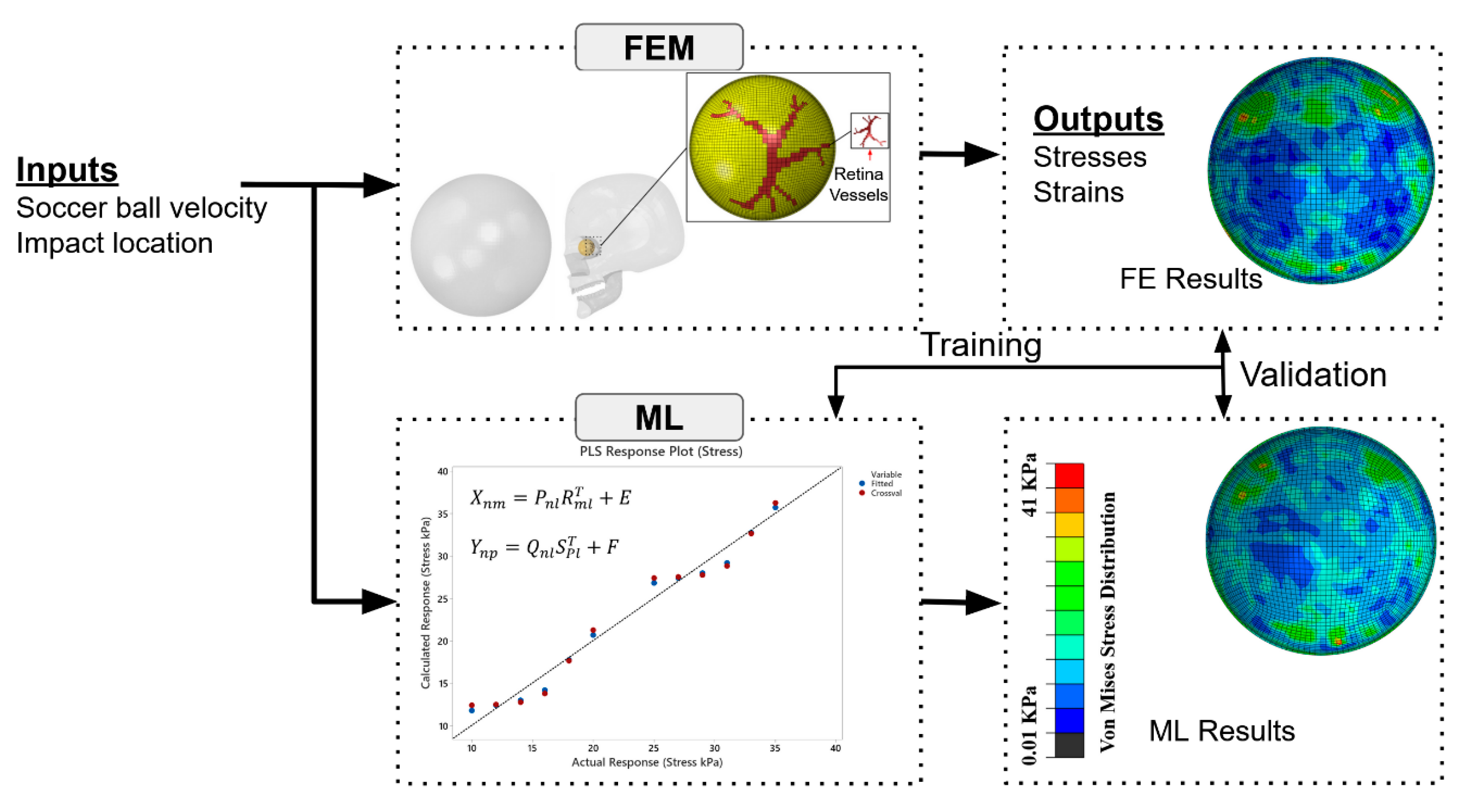
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FE Analysis
2.2. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) Model Training
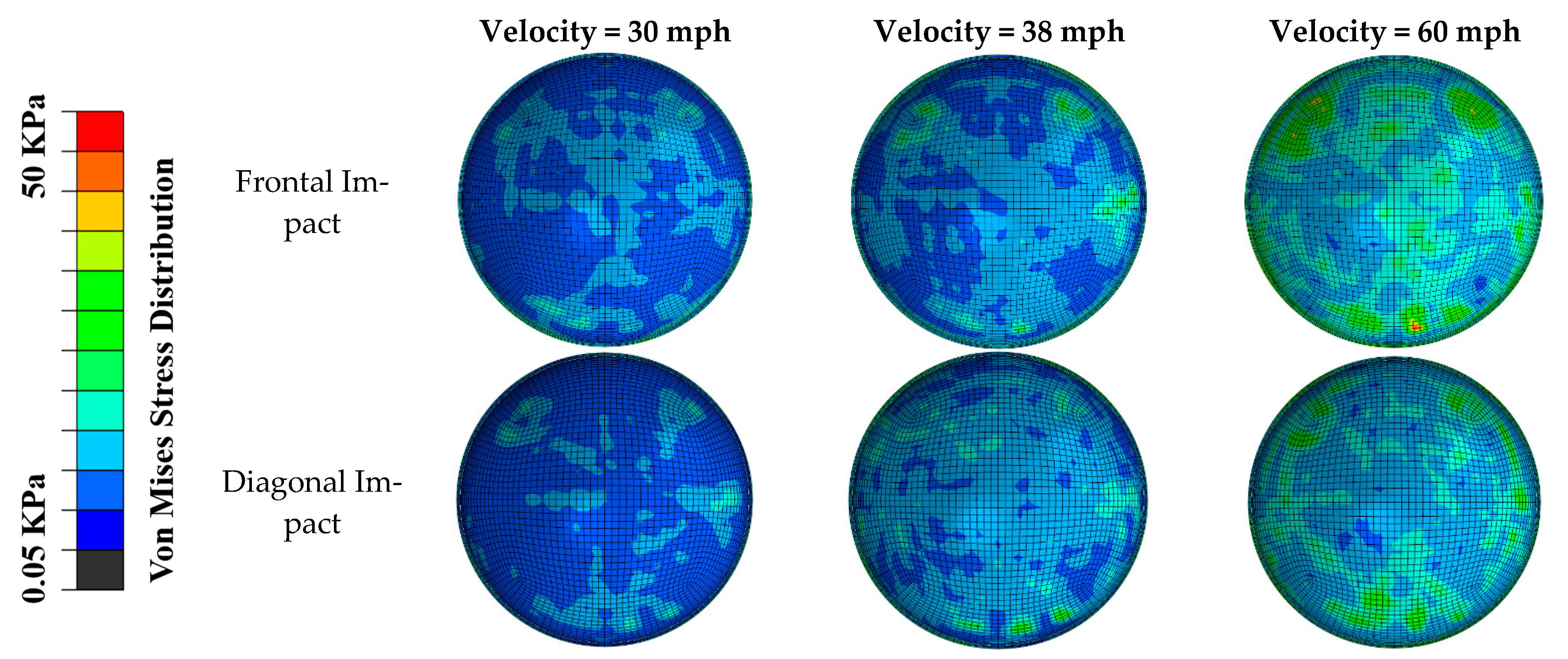
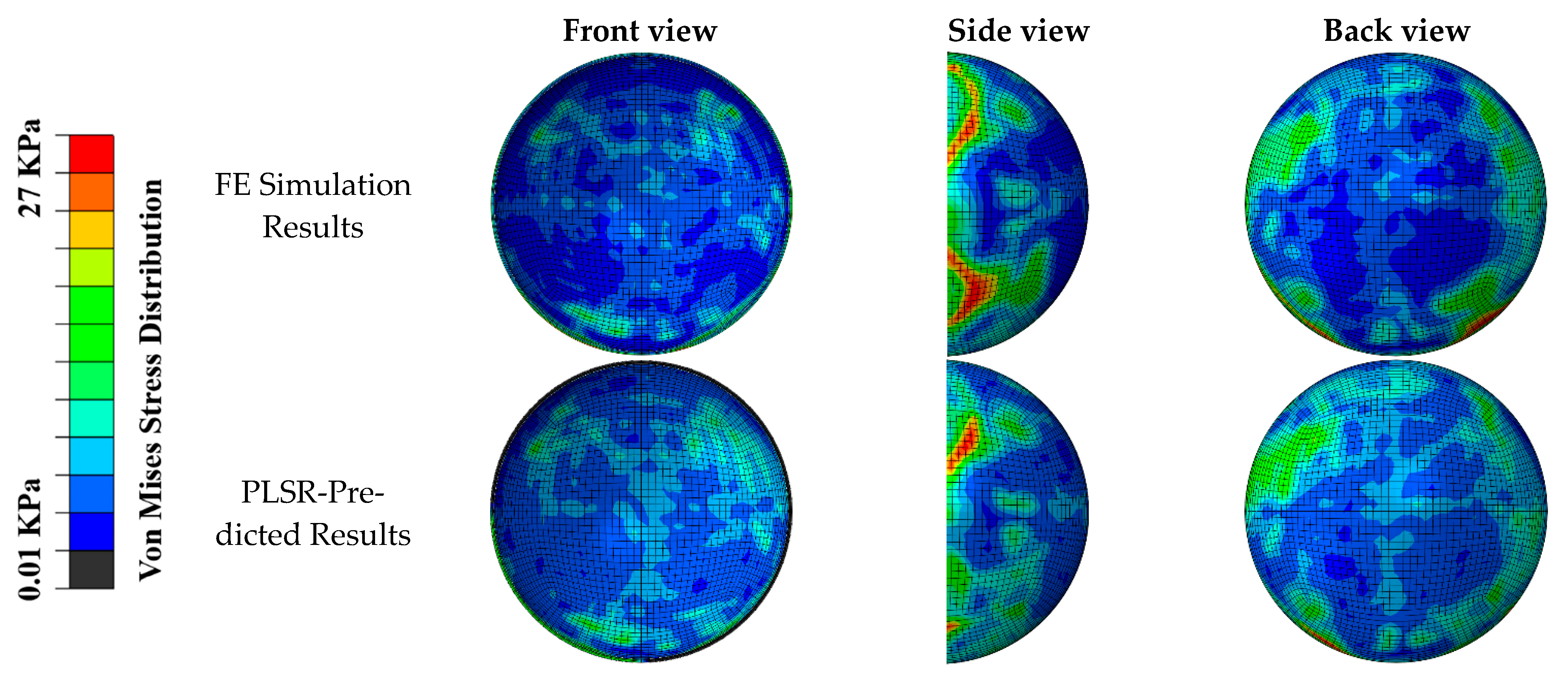
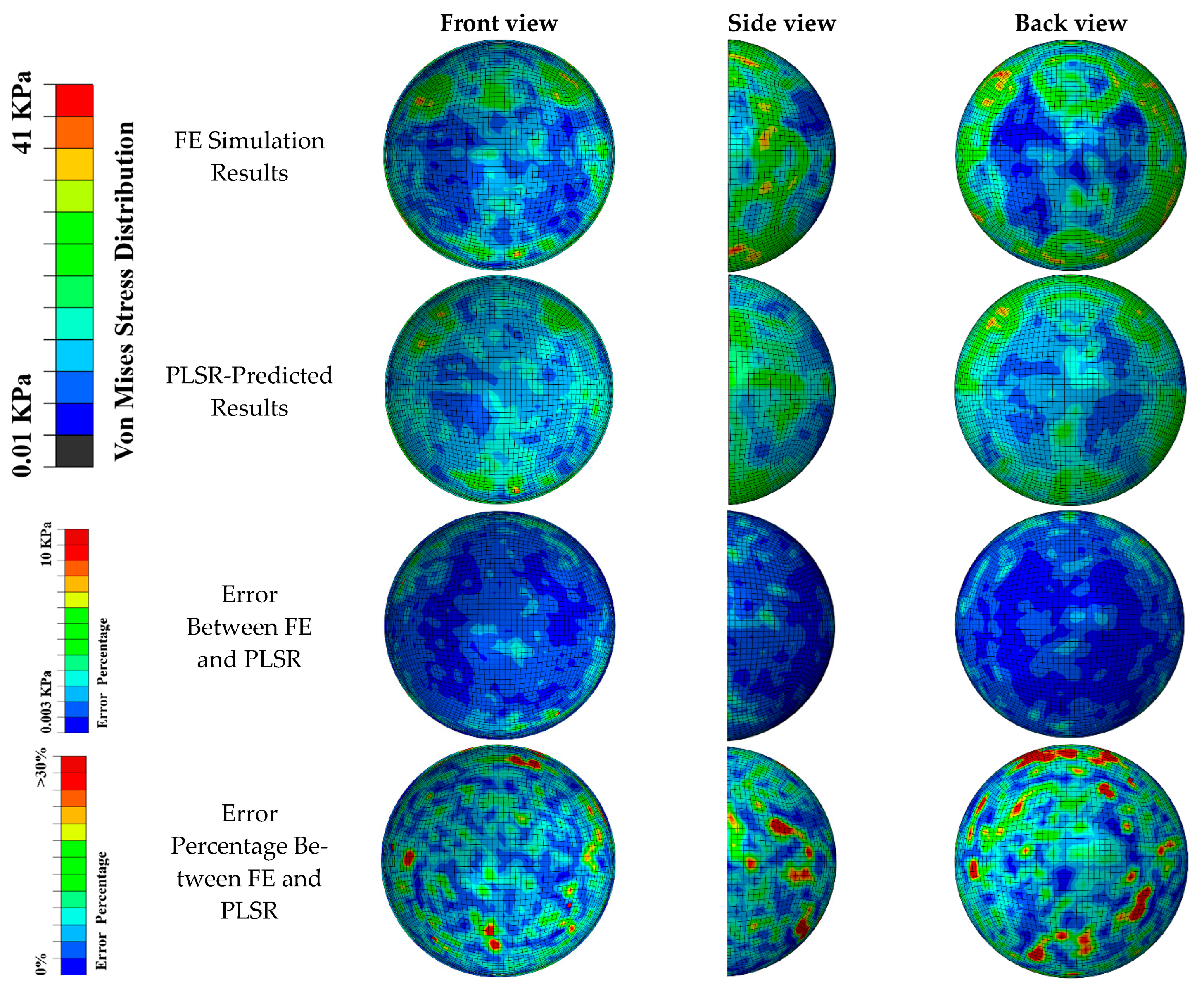
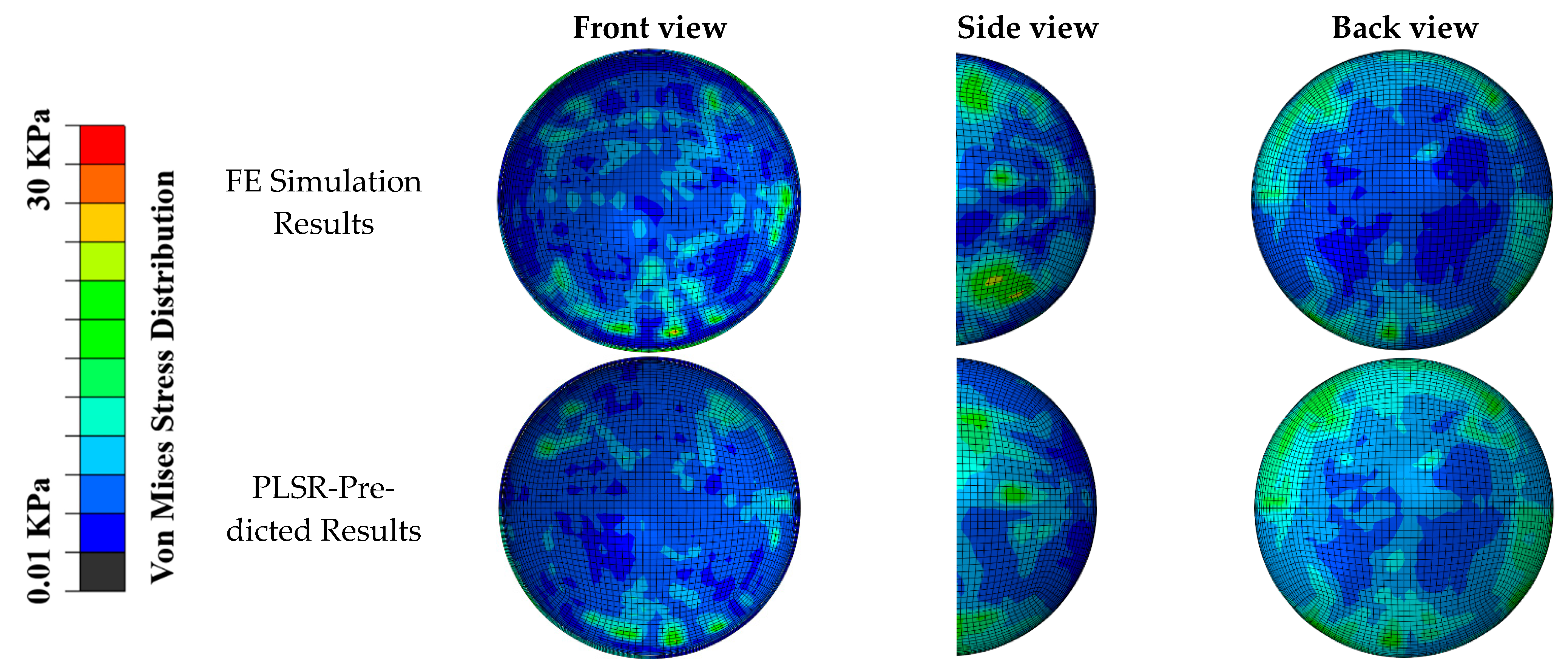
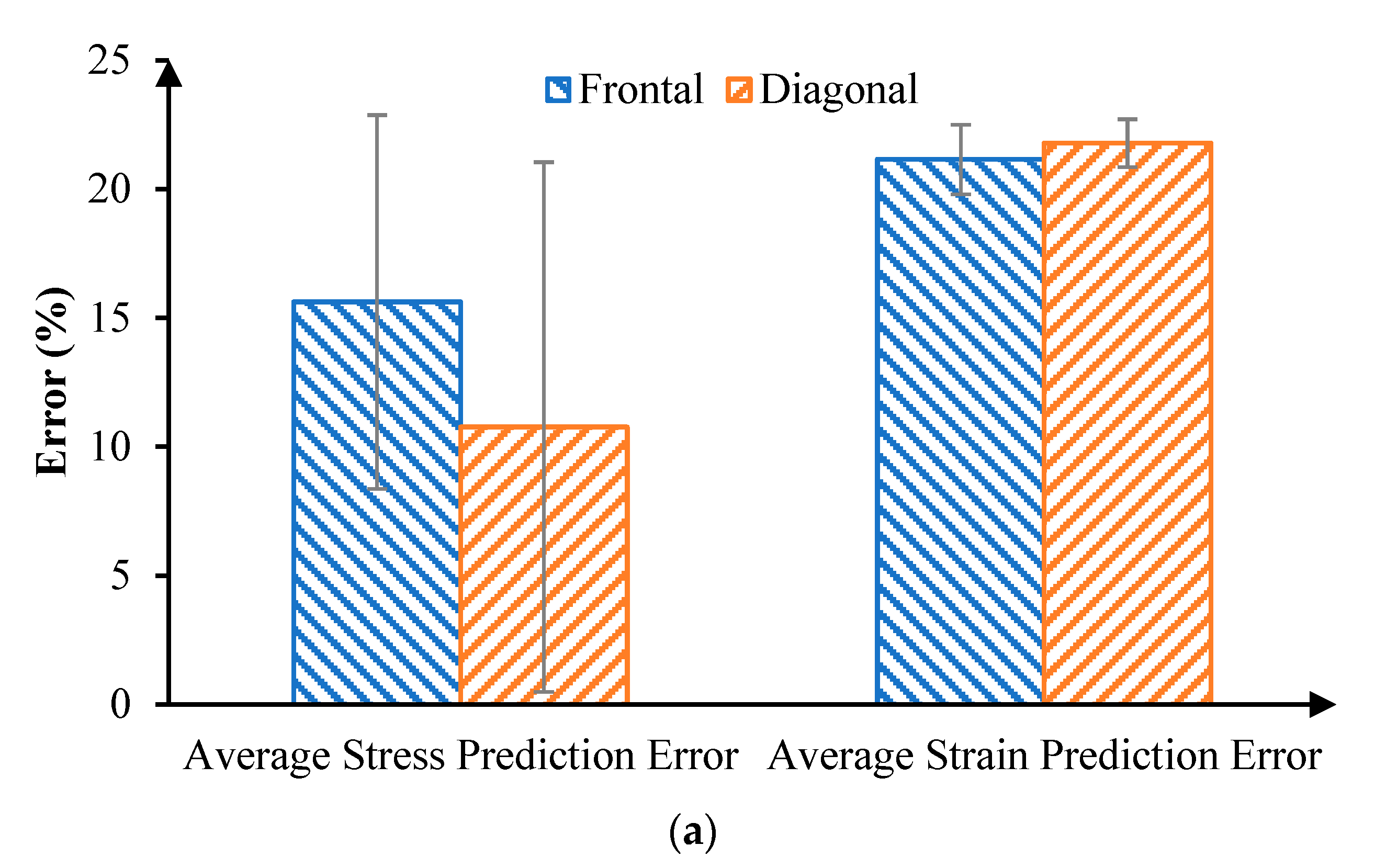
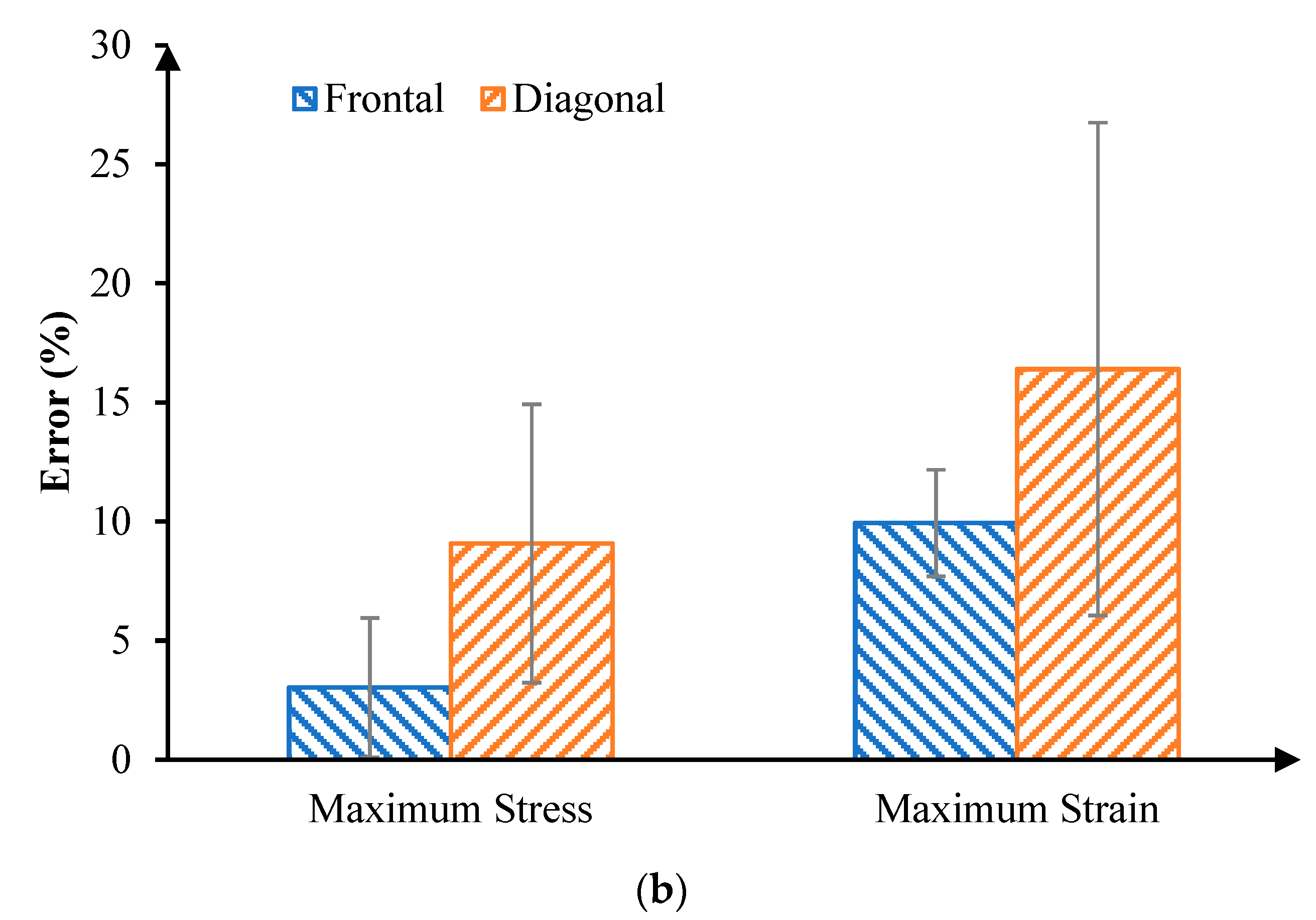
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, P.A.; Gopali, R.; Reddy, A.; Patel, K.K. Trends in soccer-related ocular injuries within the United States from 2010 through 2019. In Seminars in Ophthalmology; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, F.; Bauer, B. Sports-related eye injuries. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1995, 73, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacEwen, C.J. Eye injuries: A prospective survey of 5671 cases. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 73, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, W.F.; Feldman, K.W.; Weiss, A.H.; Tencer, A.F. Does soccer ball heading cause retinal bleeding? Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2002, 156, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipe, J.A.C.; Fernandes, V.L.; Barros, H.; Falcao-Reis, F.; Castro-Correia, J. Soccer-related ocular injuries. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, J.C.; Rocha-Sousa, A.; Falcão-Reis, F.; Castro-Correia, J. Modern sports eye injuries. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinger, P.F.; Filipe, J.C. The mechanism and prevention of soccer eye injuries. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Sports-Related Eye Injuries; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.S.; Eidsness, R.B.; Colleaux, K.M.; Romanchuk, K.G. Indoor soccer-related eye injuries: Should eye protection be mandatory? Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 42, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, G.; Ceylan, O.M.; Erdurman, F.C.; Durukan, A.H.; Sobacı, G. Soccer ball related posterior segment closed-globe injuries in outdoor amateur players. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2013, 19, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horn, E.P.; McDonald, H.R.; Johnson, R.N.; Ai, E.; Williams, G.A.; Lewis, J.M.; Rubsamen, P.E.; Sternberg, P., Jr.; Bhisitkul, R.B.; Mieler, W.F. Soccer ball-related retinal injuries: A report of 13 cases. Retina 2000, 20, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.A.; Taha, Z.; Hasanuddin, I.; Mokhtarudin, M.J.M. Mechanics of Soccer Heading and Protective Headgear; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshno, A.; Alhalel, A.; Fogel-Levin, M.; Zloto, O.; Moisseiev, J.; Vidne-Hay, O. Pediatric retinal damage due to soccer-ball-related injury: Results from the last decade. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, A.A.; Kennedy, E.A.; Duma, S.M.; Stitzel, J.D. Evaluation of different projectiles in matched experimental eye impact simulations. J. Biomech. Eng. 2011, 133, 031002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitzel, J.D.; Duma, S.M.; Cormier, J.M.; Herring, I.P. A nonlinear Finite Element Model of the Eye with Experimental Validation for the Prediction of Globe Rupture; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Kedar, S.; Ghate, D.; Gu, L. Indirect traumatic optic neuropathy induced by primary blast: A fluid–structure interaction study. J. Biomech. Eng. 2019, 141, 101011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffioti, J.M. Characterization of Pediatric Ocular; The University of Utah: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, J.; Yoshida, M.; Mizunuma, H. Experimental analyses of the retinal and subretinal haemorrhages accompanied by shaken baby syndrome/abusive head trauma using a dummy doll. Injury 2014, 45, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, D.W.; Song, H.H.; Mozafari, H.; Thoreson, W.B. Determining the Tractional Forces on Vitreoretinal Interface Using a Computer Simulation Model in Abusive Head Trauma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 223, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, N.; Kamalakkannan, S.B.; Hasija, V.; Shams, T.; Jenny, C.; Serbanescu, I.; Ho, J.; Rusinek, M.; Levin, A.V. Finite element model of ocular injury in abusive head trauma. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatric Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2009, 13, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, C.; Esposito, L.; Bonora, N.; Limido, J.; Lacome, J.-L.; Rossi, T. Traumatic eye injuries as a result of blunt impact: Computational issues. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 500, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Liu, S.; Fan, Y. Mechanism of traumatic retinal detachment in blunt impact: A finite element study. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.R.; Dong, P.; Shokrollahi, Y.; Gu, L.; Suh, D.W. Finite Element Analysis of Soccer Ball-Related Ocular and Retinal Trauma and Comparison with Abusive Head Trauma. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2022, 2, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaibeh, Y.; Dong, P.; Prabhu, D.; Kolluru, C.; Lee, J.; Zimin, V.; Mozafari, H.; Bizzera, H.; Gu, L.; Wilson, D. Deep learning segmentation of coronary calcified plaque from intravascular optical coherence tomography (IVOCT) images with application to finite element modeling of stent deployment. In Medical Imaging 2019: Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 340–349. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Sadeghipour, A.; Gerendas, B.S.; Waldstein, S.M.; Bogunović, H. Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 67, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoba, S.G.; Therese, A.B. Detection of glaucoma disease in fundus images based on morphological operation and finite element method. Biomed. Signal Processing Control 2020, 62, 101986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, S.; Luo, C.; Li, C.; Zhuang, Z. Predicting the effective mechanical property of heterogeneous materials by image based modeling and deep learning. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 347, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.-P.; Feng, X.-Q. Deep neural network method for predicting the mechanical properties of composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 161901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.; Maneparambil, K.; Rajan, S.; Neithalath, N. Machine learning-based accelerated property prediction of two-phase materials using microstructural descriptors and finite element analysis. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 191, 110328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Ye, G.; Kaya, M.; Gu, L. Simulation-Driven Machine Learning for Predicting Stent Expansion in Calcified Coronary Artery. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, M.; Martin, C.; Sun, W. A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: A fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, Y.; Dong, P.; Lam, M.; Suh, D.W.; Gu, L. Eye Protection for Mitigating Soccer Related Ocular Injuries: A Finite Element Approach. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2022, 5, 041003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.H.; Thoreson, W.B.; Dong, P.; Shokrollahi, Y.; Gu, L.; Suh, D.W. Exploring the Vitreoretinal Interface: A Key Instigator of Unique Retinal Hemorrhage Patterns in Pediatric Head Trauma. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 36, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GrabCad. Skull Model. 2018. Available online: https://grabcad.com/library/skull-43 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Pivonka, P. Multiscale Mechanobiology of Bone Remodeling and Adaptation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, C. Facial Approximation and Craniofacial Superimposition; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2721–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Wollensak, G.; Spoerl, E. Biomechanical characteristics of retina. Retina 2004, 24, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.; Jones, R.; Harland, A. Computational modelling of manually stitched soccer balls. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2006, 220, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Systèmes, D. Abaqus 6.13 Documentation Collection; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp.: Providence, RI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Razaghi, R.; Biglari, H.; Karimi, A. Finite element modeling of the eyeglass-related traumatic ocular injuries due to high explosive detonation. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, V.B.; Holdsworth, S.; Champagne, A.A.; Coverdale, N.S.; Cook, D.J.; Lee, T.-R.; Wang, A.D.; Li, S.; Fernandez, J.W. Rapid prediction of brain injury pattern in mTBI by combining FE analysis with a machine-learning based approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179457–179465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Razaghi, R.; Rahmati, S.M.; Sera, T.; Kudo, S. A nonlinear dynamic finite-element analyses of the basketball-related eye injuries. Sports Eng. 2018, 21, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Landsittel, D.; Benson, S.; Roberge, R.; Shaffer, R. Facial anthropometric differences among gender, ethnicity, and age groups. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
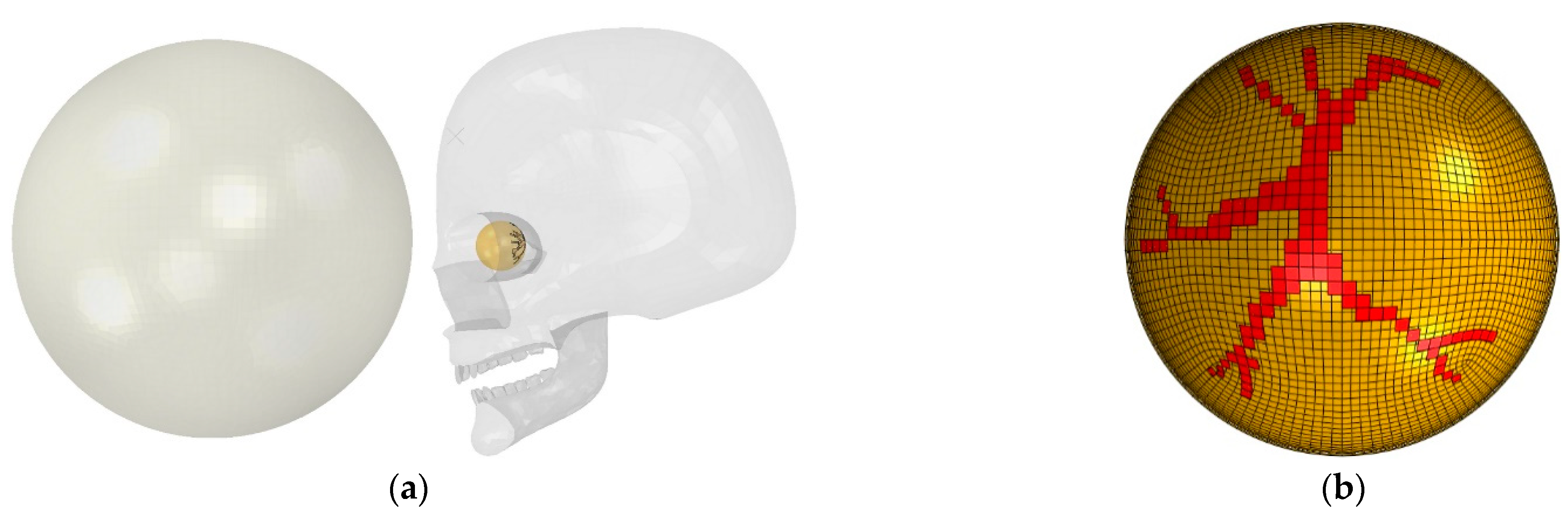


| Model Component | Element Type | Material Model | Number of Elements | Material Parameters | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skull | R3D3 | Rigid Body | 18,103 | - | - |
| Sclera | C3D8R | Hyperelastic | 28,032 | 1243 | [16] |
| Retina | C3D8R | Elastic | 17,856 (8322 located at the posterior retina) | 1000 | [37] |
| Vitreous | C3D8R | Viscoelastic | 103,968 | 1009 | = 0.07 [19] |
| Rubber soccer ball | S4R | Elastic shell (isotropy and homogeneity) | 5001 | 1160 | , C = 0.9 bar, T = 0.8 mm [38] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shokrollahi, Y.; Dong, P.; Kaya, M.; Suh, D.W.; Gu, L. Rapid Prediction of Retina Stress and Strain Patterns in Soccer-Related Ocular Injury: Integrating Finite Element Analysis with Machine Learning Approach. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071530
Shokrollahi Y, Dong P, Kaya M, Suh DW, Gu L. Rapid Prediction of Retina Stress and Strain Patterns in Soccer-Related Ocular Injury: Integrating Finite Element Analysis with Machine Learning Approach. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071530
Chicago/Turabian StyleShokrollahi, Yasin, Pengfei Dong, Mehmet Kaya, Donny W. Suh, and Linxia Gu. 2022. "Rapid Prediction of Retina Stress and Strain Patterns in Soccer-Related Ocular Injury: Integrating Finite Element Analysis with Machine Learning Approach" Diagnostics 12, no. 7: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071530
APA StyleShokrollahi, Y., Dong, P., Kaya, M., Suh, D. W., & Gu, L. (2022). Rapid Prediction of Retina Stress and Strain Patterns in Soccer-Related Ocular Injury: Integrating Finite Element Analysis with Machine Learning Approach. Diagnostics, 12(7), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12071530










