Airflow Obstruction in Adults with Williams Syndrome and Mice with Elastin Insufficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Human Subjects’ Characteristics
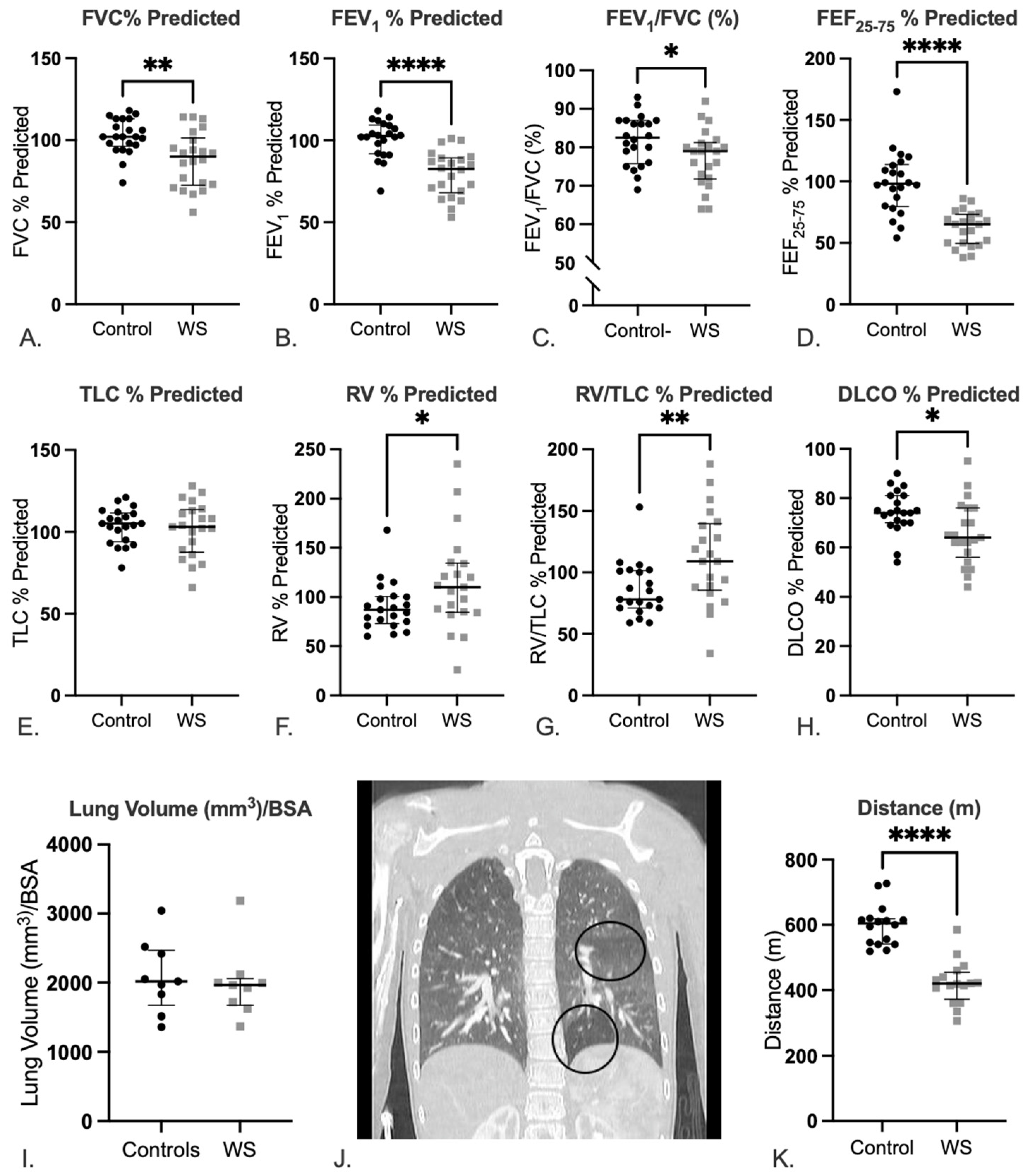
2.2. Lungs of Patients with WS Show Evidence of Abnormal Lung Function with a Predominantly Obstructive Pattern
2.3. Patients with WS Show Decreased Exercise Tolerance
2.4. Lungs from Elastin-Insufficient Mice Exhibit Biomechanical Differences
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Subjects’ Protections and Enrollment
4.2. Pulmonary Function Testing
4.3. CT Analysis of Lung Volume and Air trapping
4.4. Animal Studies
4.5. Ex Vivo Processing and microCT Imaging and Analysis
4.6. In Vivo Murine Pulmonary microCT Imaging and Analysis
4.7. Histological Analysis of Lung Airspaces
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duque Lasio, M.L.; Kozel, B.A. Elastin-driven genetic diseases. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozel, B.A.; Mecham, R.P. Elastic fiber ultrastructure and assembly. Matrix Biol. 2019, 84, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecham, R.P. Elastin in lung development and disease pathogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2018, 73, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D.; Endicott, S.K.; Province, M.A.; Pierce, J.A.; Campbell, E.J. Marked longevity of human lung parenchymal elastic fibers deduced from prevalence of D-aspartate and nuclear weapons-related radiocarbon. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Revenga, L.; Badenas, C.; Carrio, A.; Mila, M. Elastin mutation screening in a group of patients affected by vascular abnormalities. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2005, 26, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, Z.; Gao, J.; Pope, F.M.; Davis, E.C. Autosomal dominant cutis laxa with severe lung disease: Synthesis and matrix deposition of mutant tropoelastin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.H.; Ciulla, D.M.; Klanderman, B.J.; Hersh, C.P.; Litonjua, A.A.; Sparrow, D.; Raby, B.A.; Silverman, E.K. Analysis of exonic elastin variants in severe, early-onset chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, C.M.; Silverman, E.K.; Broekelmann, T.; Litonjua, A.A.; Hernandez, M.; Sylvia, J.S.; Stoler, J.; Reilly, J.J.; Chapman, H.A.; Speizer, F.E.; et al. A functional mutation in the terminal exon of elastin in severe, early-onset chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, J.J.; Verleden, G.; Gewillig, M.; Devriendt, K. Haploinsufficiency of elastin gene may lead to familial cardiopathy and pulmonary emphysema. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 2053–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozel, B.A.; Barak, B.; Kim, C.A.; Mervis, C.B.; Osborne, L.R.; Porter, M.; Pober, B.R. Williams syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromme, P.; Bjornstad, P.G.; Ramstad, K. Prevalence estimation of Williams syndrome. J. Child. Neurol. 2002, 17, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuren, A.J.; Apitz, J.; Harmjanz, D. Supravalvular aortic stenosis in association with mental retardation and a certain facial appearance. Circulation 1962, 26, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.T., 2nd. Cardiovascular disease in Williams syndrome. Circulation 2013, 127, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozel, B.A.; Bayliss, S.J.; Berk, D.R.; Waxler, J.L.; Knutsen, R.H.; Danback, J.R.; Pober, B.R. Skin findings in Williams syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2014, 164, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.A.; Gopagondanahalli, K.R.; Malhotra, A. Williams-Beuren Syndrome and Congenital Lobar Emphysema: Uncommon Association with Common Pathology? Case Rep. Pediatr. 2017, 2017, 3480980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.; Fiorino, E. A Novel Case Report of Congenital Lobar Emphysema in a Patient with Williams Syndrome. Chest 2012, 142, 1009A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, E.S.; Pober, B.R.; Washko, G.R.; Raby, B.A.; Silverman, E.K. Pulmonary function and emphysema in Williams-Beuren syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2010, 152A, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, M.H.; Carmichael, N.; Bieber, F.R.; Wiener, D.C.; Madan, R.; Pober, B.R.; Raby, B.A. A new diagnosis of Williams-Beuren syndrome in a 49-year-old man with severe bullous emphysema. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangallo, E.; Cianci, P.; Favuzza, F.; Milani, D.; Vimercati, C.; Moretti, A.; Picchi, R.; De Paoli, A.; Agosti, M.; Selicorni, A. Pulmonary function in Williams-Beuren syndrome: Spirometric data of 22 Italian patients. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2020, 185, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifren, A.; Durmowicz, A.G.; Knutsen, R.H.; Hirano, E.; Mecham, R.P. Elastin protein levels are a vital modifier affecting normal lung development and susceptibility to emphysema. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L778–L787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozel, B.A.; Knutsen, R.H.; Ye, L.; Ciliberto, C.H.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Mecham, R.P. Genetic modifiers of cardiovascular phenotype caused by elastin haploinsufficiency act by extrinsic noncomplementation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44926–44936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, G.; Kwon, S.; Caraher, E.J.; Haider, S.H.; Lam, R.; Batra, P.; Melles, D.; Liu, M.; Nolan, A. Quantitative lung morphology: Semi-automated measurement of mean linear intercept. BMC Pulm Med. 2019, 19, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherratt, M.J. Tissue elasticity and the ageing elastic fibre. Age 2009, 31, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laboratories ATSCoPSfCPF. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.Y.; Faury, G.; Taylor, D.G.; Davis, E.C.; Boyle, W.A.; Mecham, R.P.; Stenzel, P.; Boak, B.; Keating, M.T. Novel arterial pathology in mice and humans hemizygous for elastin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Brooke, B.; Davis, E.C.; Mecham, R.P.; Sorensen, L.K.; Boak, B.B.; Eichwald, E.; Keating, M. T Elastin is an essential determinant of arterial morphogenesis. Nature 1998, 393, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, R.H.; Gober, L.M.; Sukinik, J.R.; Donahue, D.R.; Kronquist, E.K.; Levin, M.D.; McLean, S.E.; Kozel, B.A. Vascular Casting of Adult and Early Postnatal Mouse Lungs for Micro-CT Imaging. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, e61242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkel, J.; Bartling, S.H.; Kuntz, J.; Grasruck, M.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Iwasaki, M.; Dimmeler, S.; Gupta, R.; Semmler, W.; Kauczor, H.U.; et al. Intrinsic gating for small-animal computed tomography: A robust ECG-less paradigm for deriving cardiac phase information and functional imaging. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2008, 1, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kojonazarov, B.; Belenkov, A.; Shinomiya, S.; Wilchelm, J.; Kampschulte, M.; Mizuno, S.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Grimminger, F.; Weissmann, N.; Seeger, W.; et al. Evaluating Systolic and Diastolic Cardiac Function in Rodents Using Microscopic Computed Tomography. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e007653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pulmonary Function Testing Participants | Cases with WS | Controls | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number * | 22 | 22 | |
| Age (median, IQR) | 25.0, IQR: 24.3 | 28.0, IQR: 14.2 | p = 0.2 |
| Race/Ethnicity (% white) | 90.9 | 68.2 | p = 0.06 |
| Sex (% male) | 36.4 | 36.4 | p > 0.999 |
| Body surface area (median, IQR) | 1.63, IQR: 0.5 | 1.84, IQR: 0.2 | p = 0.01 |
| Body mass index (median, IQR) | 24.1, IQR: 10.4 | 25.7, IQR: 5.5 | p = 0.5 |
| Asthma | 1 | 1 | p > 0.999 |
| PFT Parameter | WS | Controls | X2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (%) | |||
| FEV1 < LLN | 10 (45.5) | 1 (4.5) | p = 0.002 |
| FVC < LLN | 8 (36.4) | 1 (4.5) | p = 0.009 |
| FEV1/FVC < LLN | 8 (36.4) | 1 (4.5) | p = 0.009 |
| TLC < LLN | 1 (4.7) | 1 (4.5) | p > 0.973 |
| RV/TLC or RV (% predicted) > 120 | 10 (47.6) | 2 (9.1) | p = 0.005 |
| At least one of the above | 16 (72.7) | 4 (18.2) | p = 0.0003 |
| Variables | N | % | p-Value | Least Square Means | Standard Error | 95% CI-L | 95% CI-U | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Old | 10 | 52.63 | 0.1107 | 103.73 | 4.5765 | 94.0276 | 113.43 |
| Young | 9 | 47.37 | 92.485 | 4.787 | 82.337 | 102.63 | ||
| Genotype | WT | 10 | 52.63 | 2.84 × 10−4 | 82.7259 | 4.5765 | 73.0242 | 92.4276 |
| Eln+/− | 9 | 47.37 | 113.49 | 4.787 | 103.34 | 123.64 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kronquist, E.K.; Kaur, M.; Gober, L.M.; Knutsen, R.H.; Fu, Y.-P.; Yu, Z.-X.; Donahue, D.R.; Chen, M.Y.; Osgood, S.; Raja, N.; et al. Airflow Obstruction in Adults with Williams Syndrome and Mice with Elastin Insufficiency. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061438
Kronquist EK, Kaur M, Gober LM, Knutsen RH, Fu Y-P, Yu Z-X, Donahue DR, Chen MY, Osgood S, Raja N, et al. Airflow Obstruction in Adults with Williams Syndrome and Mice with Elastin Insufficiency. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(6):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061438
Chicago/Turabian StyleKronquist, Elise K., Maninder Kaur, Leah M. Gober, Russell H. Knutsen, Yi-Ping Fu, Zu-Xi Yu, Danielle R. Donahue, Marcus Y. Chen, Sharon Osgood, Neelam Raja, and et al. 2022. "Airflow Obstruction in Adults with Williams Syndrome and Mice with Elastin Insufficiency" Diagnostics 12, no. 6: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061438
APA StyleKronquist, E. K., Kaur, M., Gober, L. M., Knutsen, R. H., Fu, Y.-P., Yu, Z.-X., Donahue, D. R., Chen, M. Y., Osgood, S., Raja, N., Levin, M. D., Barochia, A., & Kozel, B. A. (2022). Airflow Obstruction in Adults with Williams Syndrome and Mice with Elastin Insufficiency. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061438






