Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Clinical Samples
2.3. Preparation of Assay Buffer
2.4. Magnetic Bead Preparation
2.5. Assay Buffer Sample Preparation
2.6. Mock Sample Preparation
2.7. Clinical Sample Preparation
2.8. Hb Sample Preparation and Assay
2.9. General Protease Assay
2.10. Protease Comparison Assay
2.11. Pepstatin Protease Assay
2.12. Raman Spectroscopy
2.13. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.14. Data Analysis
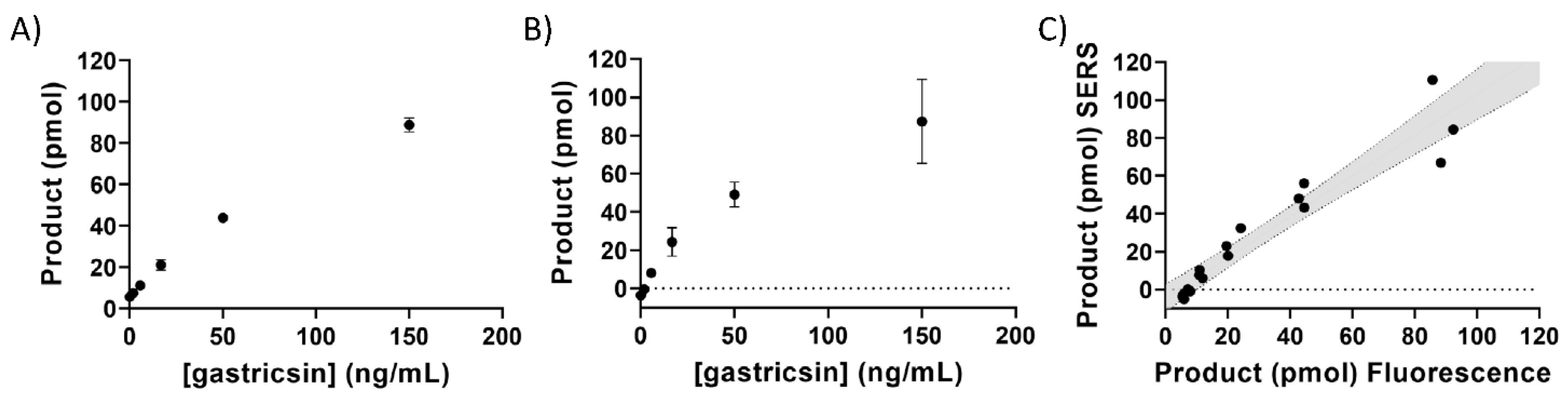
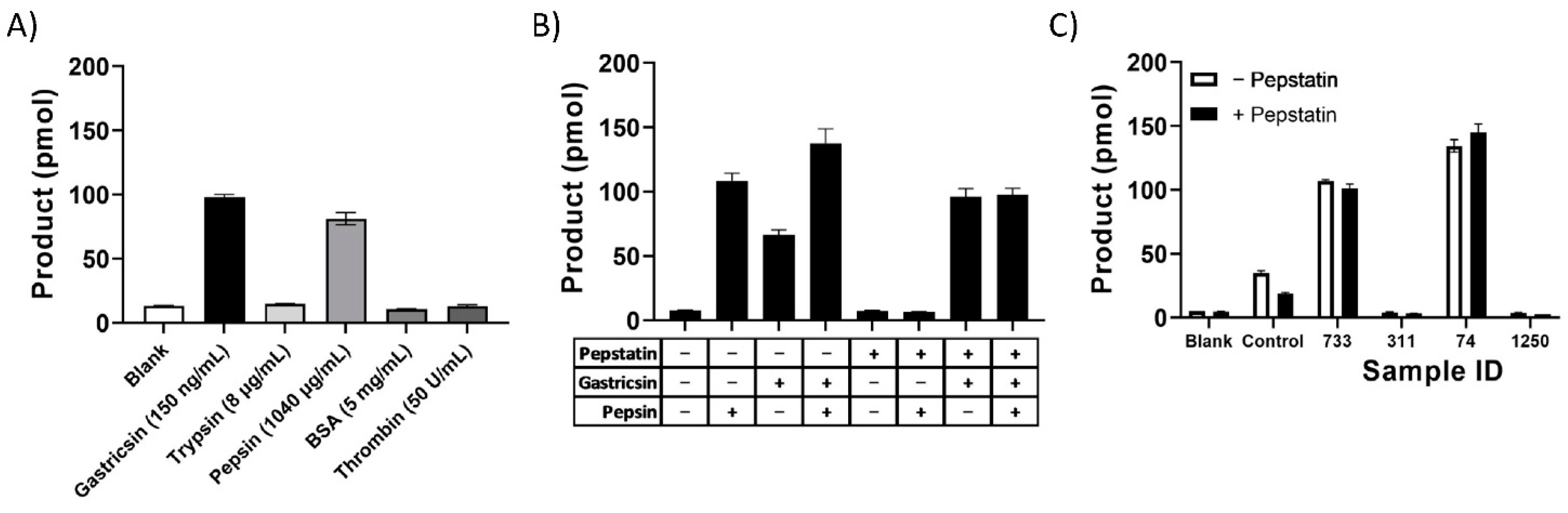
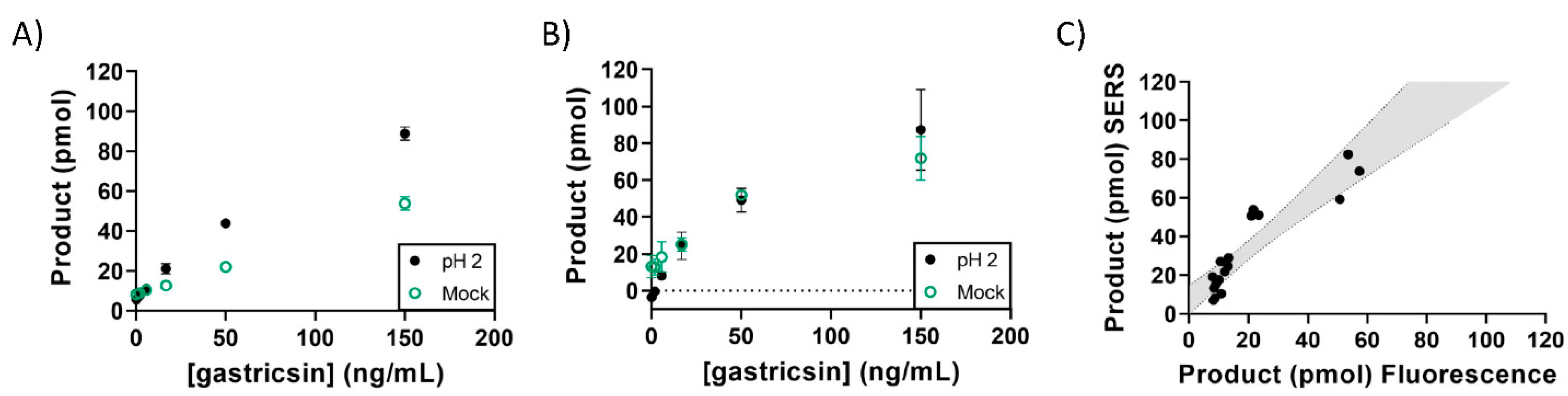
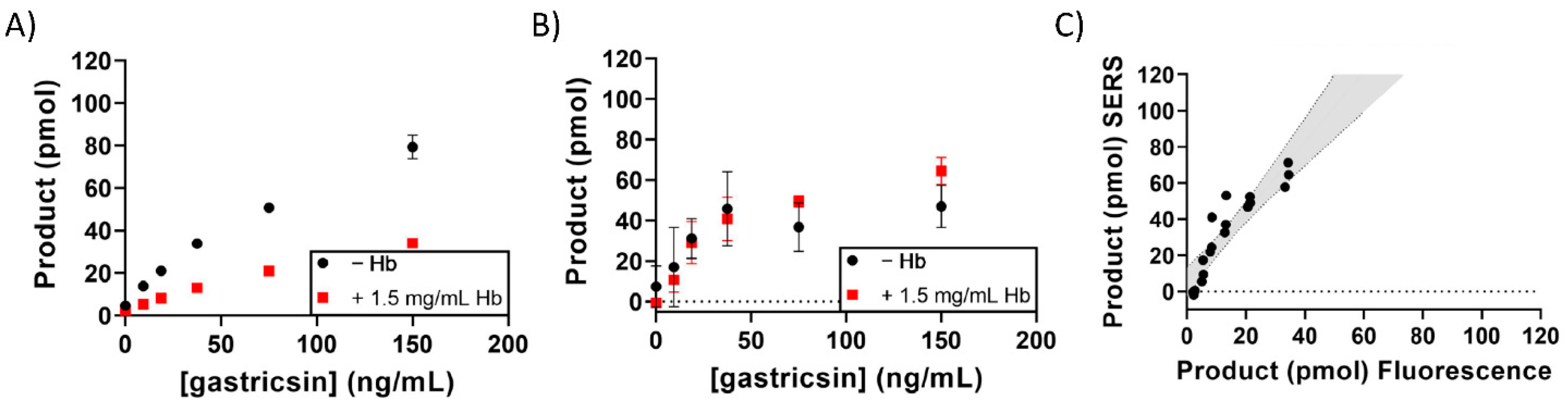
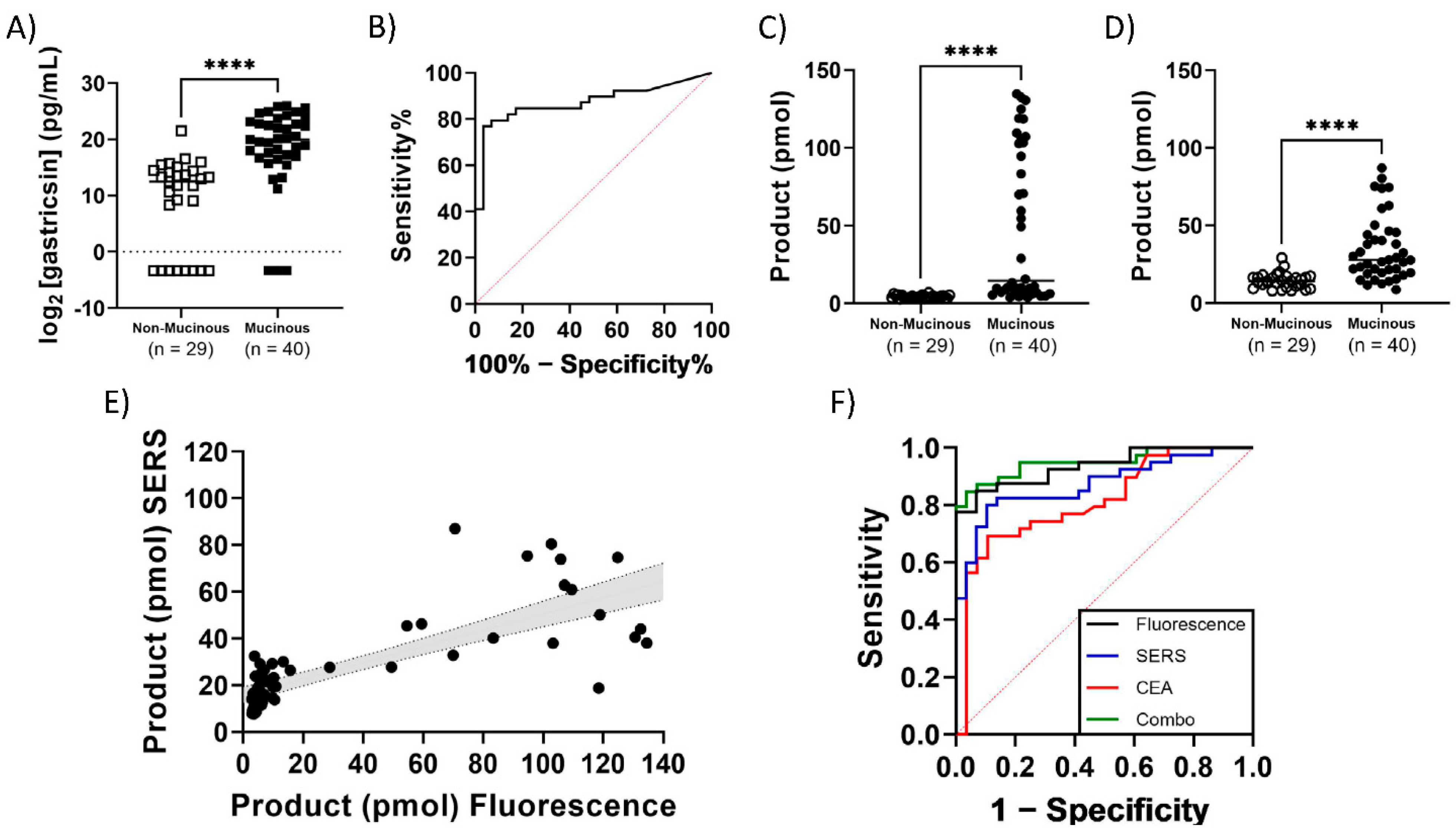
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting Cancer Incidence and Deaths to 2030: The Unexpected Burden of Thyroid, Liver, and Pancreas Cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2022 American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2022.html (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Kenner, B.J.; Go, V.L.W.; Chari, S.T.; Goldberg, A.E.; Rothschild, L.J. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, D.A.; Koay, J.E.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chari, S.T.; Kelly, K.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Thayer, S.P.; Ahlquist, D.A.; Andersen, D.K.; Batra, S.K.; Brentnall, T.A.; Canto, M.; Cleeter, D.F.; et al. Early Detection of Sporadic Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniaux, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Yalniz, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Shostrom, V.K.; Standop, J.; Lele, S.M.; Ouellette, M.; Pour, P.M.; Sasson, A.R.; et al. Early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusateri, A.J.; Krishna, S.G. Pancreatic Cystic Lesions: Pathogenesis and Malignant Potential. Diseases 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, M.; Bridges, M.D.; Pooley, R.A.; Raimondo, M.; Woodward, T.A.; Stauffer, J.A.; Asbun, H.J.; Wallace, M.B. Association Between Advances in High-Resolution Cross-Section Imaging Technologies and Increase in Prevalence of Pancreatic Cysts from 2005 to 2014. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 585–593.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffan, T.A.; Horton, K.M.; Klein, A.P.; Berlanstein, B.; Siegelman, S.S.; Kawamoto, S.; Johnson, P.T.; Fishman, E.K.; Hruban, R.H. Prevalence of Unsuspected Pancreatic Cysts on MDCT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancreatic Cysts: A New Way to Detect Malignant Potential. Medscape. Available online: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/757476 (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Tanaka, M. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas as the Main Focus for Early Detection of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2018, 47, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postlewait, L.M.; Ethun, C.G.; McInnis, M.R.; Merchant, N.; Parikh, A.; Idrees, K.; Isom, C.A.; Hawkins, W.; Fields, R.C.; Strand, M.; et al. Association of Preoperative Risk Factors with Malignancy in Pancreatic Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsangkar, N.P.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Wargo, J.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C. 851 resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: A 33-year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Surgery 2012, 152, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, J.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Moayyedi, P. American Gastroenterological Association Technical Review on the Diagnosis and Management of Asymptomatic Neoplastic Pancreatic Cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 824–848.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, D.; Takahashi, H.; Asukai, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Wada, H.; Matsuda, C.; Yasui, M.; Omori, T.; Miyata, H.; Sakon, M. Investigation of the influence of pancreatic surgery on new-onset and persistent diabetes mellitus. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2021, 5, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.S.; Russ, A.J.; Loeffler, A.G.; Rettammel, R.J.; Oudheusden, G.; Winslow, E.R.; Weber, S.M. Preoperative classification of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: The clinical significance of diagnostic inaccuracy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3112–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.Y.; Visser, B.C.; Poultsides, G.A.; Norton, J.A.; Chen, A.M.; Banerjee, S.; Friedland, S.; Park, W.G. Predictive Factors for Surgery Among Patients with Pancreatic Cysts in the Absence of High-Risk Features for Malignancy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Herran, C.E.; Garcia, M.T.; Herrera, L.; Bejarano, P.A. Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas: Clinical and Pathologic Review of Cases in a Five Year Period. JOP. J. Pancreas 2010, 11, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- Correa-Gallego, C.; Ferrone, C.R.; Thayer, S.P.; Wargo, J.A.; Warshau, A.L.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C. Incidental Pancreatic Cysts: Do We Really Know What We Are Watching? Pancreatology 2010, 10, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Baig, M.; Bandepalle, T.; Puli, S.R. Utility of Cyst Fluid Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Differentiating Mucinous and Non-mucinous Pancreatic Cysts: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, T.R.; Paleti, S.; Rustagi, T. Molecular analysis of EUS-acquired pancreatic cyst fluid for KRAS and GNAS mutations for diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia and mucinous cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1019–1033.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivry, S.L.; Sharib, J.M.; Dominguez, D.A.; Roy, N.; Hatcher, S.E.; Yip-Schneider, M.T.; Schmidt, C.M.; Brand, R.E.; Park, W.G.; Hebrok, M.; et al. Global Protease Activity Profiling Provides Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cysts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4865–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanman, L.E.; Bogyo, M. Activity-Based Profiling of Proteases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, B.D.; Teruya, J. Use of the ADAMTS13 activity assay improved the accuracy and efficiency of the diagnosis and treatment of suspected acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Arch. Pathol Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Mottini, M.; Lämmle, B. Measurement of ADAMTS-13 activity in plasma by the FRETS-VWF73 assay: Comparison with other assay methods. J. Thromb. Haemost 2014, 4, 1146–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petryayeva, E.; Algar, W.R. Proteolytic Assays on Quantum-Dot-Modified Paper Substrates Using Simple Optical Readout Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8817–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudani, J.S.; Jain, P.K.; Kwong, G.A.; Stevens, K.R.; Bhatia, S.N. Photoactivated Spatiotemporally-Responsive Nanosensors of in Vivo Protease Activity. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11708–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljeva, O.; Menendez, E.; Nguyen, M.; Craik, C.S.; Kavanaugh, W.M. Monitoring protease activity in biological tissues using antibody prodrugs as sensing probes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, U.S.; Ornatsky, O.; Baranov, V.; Nitz, M. Development of inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry-based protease assays. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 398, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Su, K.-H.; Valentine, J.; Rosa-Bauza, Y.T.; Ellman, J.A.; Elboudwarej, O.; Mukherjee, B.; Craik, C.S.; Shuman, M.A.; Chen, F.F.; et al. Time-Resolved Single-Step Protease Activity Quantification Using Nanoplasmonic Resonator Sensors. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Shen, A.; Zhou, X.; Hu, J. A simple and universal “turn-on” detection platform for proteases based on surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, N.; Raza, A.; Wuytens, P.; Demol, H.; Van Daele, M.; Detavernier, C.; Skirtach, A.; Gevaert, K.; Baets, R.G. Waveguide-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy detection of protease activity using non-natural aromatic amino acids. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 4800–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolowits, M.D.; Xin, M.; Petrov, D.P.; Tague, T.J.; Davisson, V.J. Multimeric Rhodamine Dye-Induced Aggregation of Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.-Y.; Tang, J. On the Specificity of Human Gastricsin and Pepsin. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Han, D.; Do, M.; Woo, J.; Wang, J.I.; Han, Y.; Kwon, W.; Kim, S.-W.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, Y. Proteome characterization of human pancreatic cyst fluid from intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, M.; Han, D.; Wang, J.I.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Han, Y.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis of pancreatic cyst fluid proteins associated with malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Clin. Proteom. 2018, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamaysi, I.; Abu Ammar, A.; Vasilyev, G.; Arinstein, A.; Chowers, Y.; Zussman, E. Differentiation of Pancreatic Cyst Types by Analysis of Rheological Behavior of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep45589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, T.; Katanuma, A.; Yane, K.; Takahashi, K.; Osanai, M.; Takaki, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Gon, K.; Matsumori, T.; Tomonari, A.; et al. Diagnostic ability of EUS-FNA for pancreatic solid lesions with conventional 22-gauge needle using the slow pull technique: A prospective study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenger, A.K.; Korpi-Steiner, N. Chapter One–Advances in Cardiac Biomarkers of Acute Coronary Syndrome. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 78, pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]

| Non-Mucinous | Mucinous | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudocyst * | SCA | MCN | IPMN | ||
| Samples (n) | 15 | 14 | 13 | 27 | |
| Age (Years ± SD) | 54.2 ± 18.5 | 60.1 ± 9.6 | 53.2 ± 17.3 | 66.8 ± 11.6 | |
| Gender | Female | 7 | 8 | 10 | 13 |
| Male | 7 | 6 | 3 | 14 | |
| Institution | Pittsburgh | 4 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Indiana | 6 | 9 | 6 | 13 | |
| Stanford | 4 | 3 | 5 | 10 | |
| UCSF | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Collection Method ** | Surgery | 6 | 10 | 13 | 24 |
| EUS-FNA | 8 | 4 | 0 | 2 | |
| Cyst Size *** (mm ± SD) | 66.6 ± 33.6 | 60.2 ± 39.7 | 54.5 ± 38.1 | 47.8 ± 32.8 | |
| CEA (ng/mL ± SD) | 31 ± 43 | 7354 ± 27,413 | 10,773 ± 25,538 | 5398 ± 16,290 | |
| Gastricsin Mass (ng/mL ± SD) | 220 ± 775 | 10,231 ± 12,485 | 6972 ± 10,449 | 10,630 ± 19,431 | |
| Gastricsin Activity (pmol prod ± SD) | Fluorescence | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 56 ± 54 | 46 ± 47 |
| SERS | 16 ± 5.7 | 13 ± 3.5 | 36 ± 22 | 34 ± 21 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suresh, V.; Byers, K.; Rajesh, U.C.; Caiazza, F.; Zhu, G.; Craik, C.S.; Kirkwood, K.; Davisson, V.J.; Sheik, D.A. Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061343
Suresh V, Byers K, Rajesh UC, Caiazza F, Zhu G, Craik CS, Kirkwood K, Davisson VJ, Sheik DA. Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(6):1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061343
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuresh, Vallabh, Kaleb Byers, Ummadisetti Chinna Rajesh, Francesco Caiazza, Gina Zhu, Charles S. Craik, Kimberly Kirkwood, Vincent Jo Davisson, and Daniel A. Sheik. 2022. "Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts" Diagnostics 12, no. 6: 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061343
APA StyleSuresh, V., Byers, K., Rajesh, U. C., Caiazza, F., Zhu, G., Craik, C. S., Kirkwood, K., Davisson, V. J., & Sheik, D. A. (2022). Translation of a Protease Turnover Assay for Clinical Discrimination of Mucinous Pancreatic Cysts. Diagnostics, 12(6), 1343. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12061343









