Baseline Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease Is Associated with Disease Progression and Cognitive Decline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Clinical Test Scales, CSF Sampling, and α-Synuclein Measurement
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Information and Baseline Data in PD, PDD, and DLB
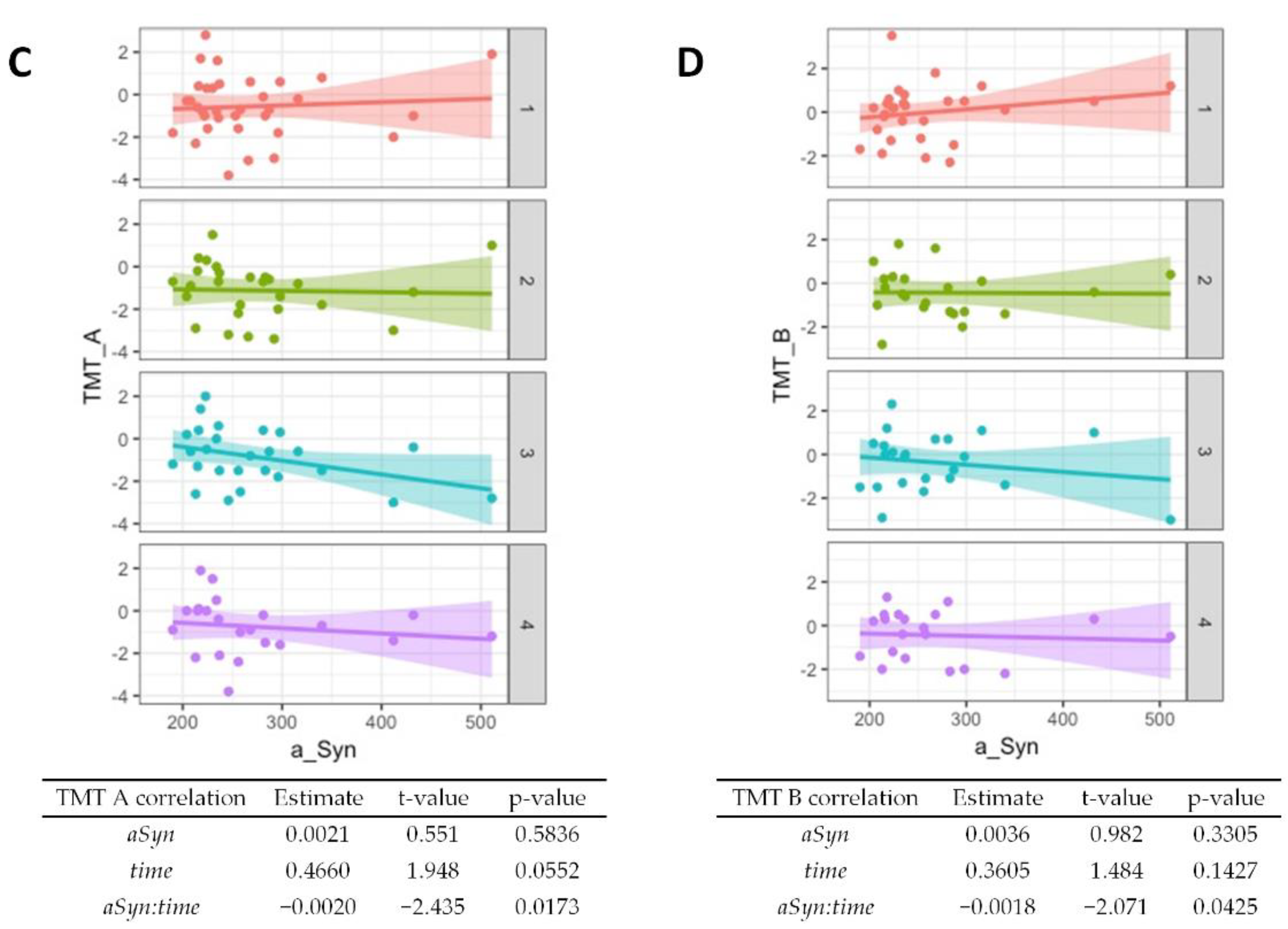
3.2. Association of CSF α-Synuclein Levels and Motor Symptom Progression in PD
3.3. Association of CSF α-Synuclein Levels and Cognitive Decline in PD
4. Discussion
4.1. CSF α-Synuclein in the Diagnostic Groups
4.2. Associations with Symptoms and Disease Progression
4.3. Study Limitations
4.4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brás, I.C.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Gerhardt, E.; Koss, D.; Lázaro, D.F.; Santos, P.I.; Vasili, E.; Xylaki, M.; Outeiro, T.F. Synucleinopathies: Where we are and where we need to go. J. Neurochem. 2020, 153, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Overk, C.R.; Oueslati, A.; Masliah, E. The many faces of α-synuclein: From structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olanow, C.W.; Brundin, P. Parkinson’s disease and alpha synuclein: Is Parkinson’s disease a prion-like disorder? Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerman, A.L.; Stöhr, J.; Aoyagi, A.; Rampersaud, R.; Krejciova, Z.; Watts, J.C.; Ohyama, T.; Patel, S.; Widjaja, K.; Oehler, A.; et al. Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4949–E4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aarsland, D.; Andersen, K.; Larsen, J.P.; Lolk, A.; Nielsen, H.; Kragh-Sørensen, P. Risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: A community-based, prospective study. Neurology 2001, 56, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Korczyn, A.D. Are dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia the same disease? BMC Med. 2018, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J.; Landwehrmeyer, B.G.; Mandelkow, E.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Burn, D.J.; Caparros-Lefebvre, D.; Frey, K.A.; de Yebenes, J.G.; Gasser, T.; et al. Reisensburg Working Group for Tauopathies with Parkinsonism. Tauopathies with parkinsonism: Clinical spectrum, neuropathologic basis, biological markers, and treatment options. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, T.; Tampiyappa, A.; Robertson, T.; Grimley, R.; Burke, C.; Ng, K.; Patrikios, P. Dual pathology of corticobasal degeneration and Parkinson’s disease in a patient with clinical features of progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurol. India 2011, 59, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alster, P.; Madetko, N.; Koziorowski, D.; Friedman, A. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy-Parkinsonism Predominant (PSP-P)—A Clinical Challenge at the Boundaries of PSP and Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, U.; Lang, A.E.; Masellis, M. Neuroimaging Advances in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 572976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Locascio, J.J.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Trenkwalder, C.; Schlossmacher, M.G. α-Synuclein and tau concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of patients presenting with parkinsonism: A cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Maes, J. Vorschlag zur Vereinfachung des Beck-Depressions-Inventars (BDI). Diagnostica 2000, 46, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.S.; Ehrensperger, M.M.; Berres, M.; Beck, I.R.; Monsch, A.U. The Extension of the German CERAD Neuropsychological Assessment Battery with Tests Assessing Subcortical, Executive and Frontal Functions Improves Accuracy in Dementia Diagnosis. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2014, 4, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahn, S.; Elton, R.L.; Members of the UPDRS Development Committee. Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale IN. In Recent Developments in Parkinson’s Disease; Fahn, S., Marsden, C.D., Goldstein, M., Stoker, T.B., Barker, R.A., Eds.; Macmillan Healthcare Information: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Counsell, C.; Giladi, N.; Holloway, R.G.; Moore, C.G.; Wenning, G.K.; et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: Status and recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; Schmitz, M.; Shafiq, M.; da Cunha, J.E.; Gotzman, N.; Zafar, S.; Thüne, K.; De Oliveira, J.R.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; et al. Quantification of CSF biomarkers using an electrochemiluminescence-based detection system in the differential diagnosis of A.D and sCJD. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; Karch, A.; Schmitz, M.; Zafar, S.; Gotzmann, N.; Sun, T.; Köchy, S.; Knipper, T.; Cramm, M.; et al. Validation of α-Synuclein as a CSF Biomarker for Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luck, T.; Riedel-Heller, S.G.; Wiese, B.; Stein, J.; Weyerer, S.; Werle, J.; Kaduszkiewicz, H.; Wagner, M.; Mosch, E. CERAD-NP-Testbatterie: Alters-, geschlechts- und bildungsspezifische Normen ausgewählter Subtests. Ergebnisse der German Study on Ageing, Cognition and Dementia in Primary Care Patients (AgeCoDe) [CERAD-NP battery: Age-, gender- and education-specific reference values for selected subtests. Results of the German Study on Ageing, Cognition and Dementia in Primary Care Patients (AgeCoDe)]. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 42, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, G.; Molenberghs, G. Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, M.; Salim, S.; Majbour, N.; Erskine, D.; Stoops, E.; Mollenhauer, B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Parkinson’s disease biomarkers based on α-synuclein. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Tang, H.; Nie, K.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Gan, R.; Huang, J.; Zhu, R.; Feng, S.; Duan, Z.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, A.H.; Kuiperij, B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Engelborghs, S.; Herukka, S.-K.; Parnetti, L.; Rektorova, I.; Vanmechelen, E.; Kapaki, E.; Verbeek, M.; et al. The utility of α-synuclein as biofluid marker in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review of the literature. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, F.; Schmitz, M.; Varges, D.; Kruse, N.; Gotzmann, N.; Gmitterová, K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Zerr, I. Cerebrospinal α-synuclein in α-synuclein aggregation disorders: Tau/α-synuclein ratio as potential biomarker for dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Caspell-Garcia, C.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Taylor, P.; Singleton, A.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Frasier, M.; Simuni, T.; Iranzo, A.; et al. Longitudinal analyses of cerebrospinal fluid α-Synuclein in prodromal and early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Öhrfelt, A.; Constantinescu, R.; Andreasson, U.; Surova, Y.; Bostrom, F.; Nilsson, C.; Widner, H.; Decraemer, H.; Nägga, K.; et al. Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.D.; Bidinosti, M.; Weiss, A.; Raijmakers, P.; Berendse, H.W.; Van De Berg, W.D. Reduced α-synuclein levels in cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson’s disease are unrelated to clinical and imaging measures of disease severity. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Öhrfelt, A.; Swedish BioFINDER Study; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Longitudinal Measurements of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Öhrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Lindqvist, D.; Hansson, O. CSF biomarkers and clinical progression of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 84, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lillig, R.; Ophey, A.; Schulz, J.B.; Reetz, K.; Wojtala, J.; Storch, A.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Becker, S.; Berg, D.; Balzer-Geldsetzer, M.; et al. A new CERAD total score with equally weighted z-scores and additional executive and non-amnestic “CERAD-Plus” tests enhances cognitive diagnosis in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Evidence from the LANDSCAPE study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 90, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compta, Y.; Valente, T.; Saura, J.; Segura, B.; Iranzo, Á.; Serradell, M.; Junque, C.; Tolosa, E.; Valldeoriola, F.; Muñoz, E.; et al. Correlates of cerebrospinal fluid levels of oligomeric- and total-α-synuclein in premotor, motor and dementia stages of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stav, A.L.; Aarsland, D.; Johansen, K.K.; Hessen, E.; Auning, E.; Fladby, T. Amyloid-β and α-synuclein cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cognition in early Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Wee, H.L.; Chan, Y.-H.; Seah, S.H.; Au, W.L.; Lau, P.N.; Pica, E.C.; Li, S.C.; Luo, N.; Tan, L.C. Progression of Parkinson’s disease as evaluated by Hoehn and Yahr stage transition times. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Kurz, M.W. The epidemiology of dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Zimmermann, J.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Focke, N.K.; Wicke, T.; Ebentheuer, J.; Schaumburg, M.; Lang, E.; Trautmann, E.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Monitoring of 30 marker candidates in early Parkinson disease as progression markers. Neurology 2016, 87, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, M.A.; Moran, N.F.; Kopelman, M.D. Subcortical dementia. Br. J. Psychiatry 2002, 180, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeders, U.; Zimmermann, J.; Wicke, T.; Schaumburg, M.; Lang, E.; Trenkwalder, C.; Mollenhauer, B. Dynamic interplay of cognitive functioning and depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychology 2022, 36, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, H.C.; Munro Cullum, C.; Hynan, L.S.; Lacritz, L.H. The CERAD Neuropsychologic Battery Total Score and the Progression of Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer. Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2010, 24, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ejma, M.; Madetko, N.; Brzecka, A.; Guranski, K.; Alster, P.; Misiuk-Hojło, M.; Somasundaram, S.G.; Kirkland, C.E.; Aliev, G. The Links between Parkinson’s Disease and Cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.; Villar-Piqué, A.; Llorens, F.; Gmitterová, K.; Hermann, P.; Varges, D.; Zafar, S.; Lingor, P.; Vanderstichele, H.; Demeyer, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Total and Phosphorylated α-Synuclein in Patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Synucleinopathy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3476–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaslan, S.; Schmitz, M.; Villar-Piqué, A.; Maass, F.; Gmitterová, K.; Varges, D.; Lingor, P.; Llorens, F.; Hermann, P.; Zerr, I. Detection of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Chain as a Marker for Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 717930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Dakna, M.; Kruse, N.; Galasko, D.; Foroud, T.; Zetterberg, H.; Schade, S.; Gera, R.G.; Wang, W.; Gao, F.; et al. Validation of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker of Parkinson’s Disease Progression. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
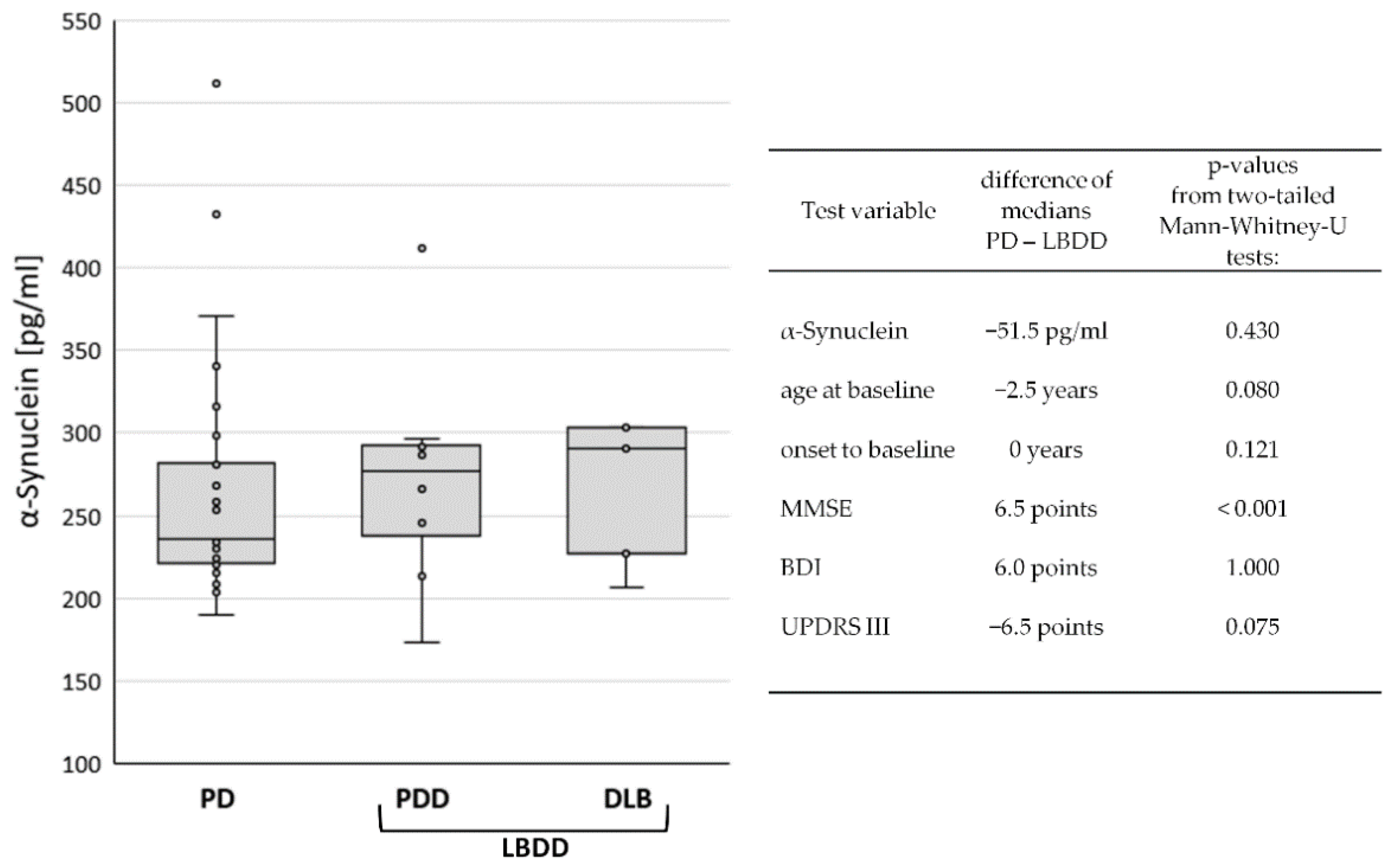


| PD | PDD | DLB | LBDD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 28 | 8 | 5 | 13 |
| CSF α-synuclein: median (IQR) (pg/mL) | 236 (61) | 277 (64) | 291 (76) | 287 (73) |
| sex: female/male | 6/22 | 1/7 | 0/5 | 1/12 |
| age at sampling: median (IQR) (years) | 69 (16) | 74 (8) | 70 (6) | 71 (7) |
| onset to baseline: median (IQR) (years) | 2 (3) | 6 (10) | 1 (2) | 2 (6) |
| MMSE: median (IQR) (score) | 29 (2) | 24 (6) | 20 (4) | 22 (6) |
| BDI: median (IQR) (score) | 28 (21) | 23 (36) | 18 (3) | 22 (18) |
| UPDRS III: median (IQR) (score) | 17 (7) | 24 (12) | 23 (7) | 24 (12) |
| PD + PDD | Hoehn + Yahr Stage | UPDRS Score | BDI Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Median (IQR) | n | Median (IQR) | n | Median (IQR) | |
| Baseline | 36 | 1.5 (1) | 36 | 18 (10) | 31 | 23 (22.25) |
| 6 months | 14 | 1.75 (1) | 4 | 17 (14) | 25 | 20 (19) |
| 12 months | 21 | 2 (0.5) | 17 | 19 (5) | 27 | 19.5 (19.5) |
| 24 months | 13 | 2 (0.5) | 19 | 20 (9) | 23 | 17 (17) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emdina, A.; Hermann, P.; Varges, D.; Nuhn, S.; Goebel, S.; Bunck, T.; Maass, F.; Schmitz, M.; Llorens, F.; Kruse, N.; et al. Baseline Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease Is Associated with Disease Progression and Cognitive Decline. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051259
Emdina A, Hermann P, Varges D, Nuhn S, Goebel S, Bunck T, Maass F, Schmitz M, Llorens F, Kruse N, et al. Baseline Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease Is Associated with Disease Progression and Cognitive Decline. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051259
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmdina, Anna, Peter Hermann, Daniela Varges, Sabine Nuhn, Stefan Goebel, Timothy Bunck, Fabian Maass, Matthias Schmitz, Franc Llorens, Niels Kruse, and et al. 2022. "Baseline Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease Is Associated with Disease Progression and Cognitive Decline" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051259
APA StyleEmdina, A., Hermann, P., Varges, D., Nuhn, S., Goebel, S., Bunck, T., Maass, F., Schmitz, M., Llorens, F., Kruse, N., Lingor, P., Mollenhauer, B., & Zerr, I. (2022). Baseline Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease Is Associated with Disease Progression and Cognitive Decline. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051259









